希望启用以禁用 Windows 10 上的保留存储但不知道如何操作?别担心,在本指南中,我们将看到在 Windows 10 上启用禁用此功能的确切步骤。(Looking to Enable to Disable Reserved Storage on Windows 10 but don’t know how? Don’t worry, in this guide, we will see exact steps to enable to disable this feature on Windows 10.)
存储问题是科技界的普遍问题。几年前,512 GB 的内存被认为是多余的,但现在,相同的数量被认为是基本变体甚至低于标准的存储选项。每千兆字节的存储空间都被认为是最重要的,当谈到入门级笔记本电脑和个人电脑时,这一说法更为重要。

在(Amid)这样的存储困难中,如果某个特定功能或软件占用了不必要的空间,那么最好放手。Reserved Storage提出了类似的情况,这是去年推出的一项Windows功能,它占用一定数量的内存(以GB(gigabytes)为单位)用于软件更新和其他可选功能。禁用该功能有助于腾出一些空间并获得一些宝贵的存储空间。
在本文中,我们将了解禁用保留存储(Reserved Storage)功能是否安全以及如何进行。
什么是预留存储?(What is Reserved Storage? )
从Windows 1903 版本(2019 年 5 月更新)(Windows 1903 version (May 2019 update))开始,Windows开始在系统上为软件更新、某些内置应用程序、缓存等临时数据和其他可选文件保留大约 7GB 的可用磁盘空间。在许多用户抱怨无法下载新的Windows更新、存储空间不足、更新体验缓慢等类似问题后,更新和保留存储功能推出。(Reserved Storage)所有这些问题都是由于缺少可用于更新的剩余存储或磁盘空间而引起的。通过保留一定数量的内存的功能有助于解决所有这些问题。
早些时候,如果您的个人计算机上没有足够的可用磁盘空间,Windows将无法下载和安装任何新更新。然后,该修复程序将要求用户通过从他或她的系统中删除或卸载一些有价值的货物来清理空间。
现在,在较新的系统中启用保留存储(Reserved Storage)后,所有更新将首先利用该功能保留的空间;最终,当需要更新软件时,所有临时和不必要的文件将从保留存储(Reserved Storage)中删除,更新文件将占用整个保留空间。这可确保系统能够下载和安装软件更新,即使在磁盘空间非常少且无需清除额外内存的情况下也是如此。
通过为软件更新和其他重要文件保留必要的磁盘空间,该功能还确保所有关键和必要的操作系统功能始终有一些内存可以使用。据说预留存储(Reserved Storage)占用的内存量会随着时间的推移而变化,并且取决于人们使用系统的方式。
该功能在预装了 Windows 1903 版的任何和所有新系统中或在执行该特定版本的全新安装的系统上启用。如果您是从以前的版本更新,那么您仍然会收到保留存储(Reserved Storage)功能,但默认情况下将禁用它。
在 Windows 10 上启用或禁用保留存储
幸运的是,在特定系统上启用和禁用保留存储非常简单,只需几分钟即可完成。
注意:(Note:)确保创建一个还原点(create a restore point) 以防万一出现问题。
如何禁用保留存储?(How to Disable Reserved Storage? )
禁用 Windows 系统上的保留存储功能涉及到弄乱Windows 注册表(Windows Registry)。但是,当使用Windows 注册表(Windows Registry)作为不正确的步骤或意外修改注册表(Registry)中的项目时,必须非常小心,否则可能会给您的系统带来严重问题。因此,在遵循指南时要格外小心。
此外,在我们开始执行该过程之前,让我们检查一下Windows是否确实为我们的系统中的更新保留了一些存储空间,并确保我们的操作不会徒劳无功。
要检查您的计算机上是否有预留存储空间:
步骤 1:(Step 1:)通过以下任一方法打开Windows 设置(Windows Settings):
- 按键盘上的Windows Key + S(或单击任务栏中的开始按钮)并搜索Settings。找到后,按回车键或单击打开。
- 按Windows Key + X或右键单击开始按钮,然后单击设置。
- 按Windows Key + I直接打开 Windows 设置。
第 2 步:(Step 2:)在“窗口设置”(Window Settings)面板中,查找“系统(System )”(列表中的第一项),然后单击以打开。
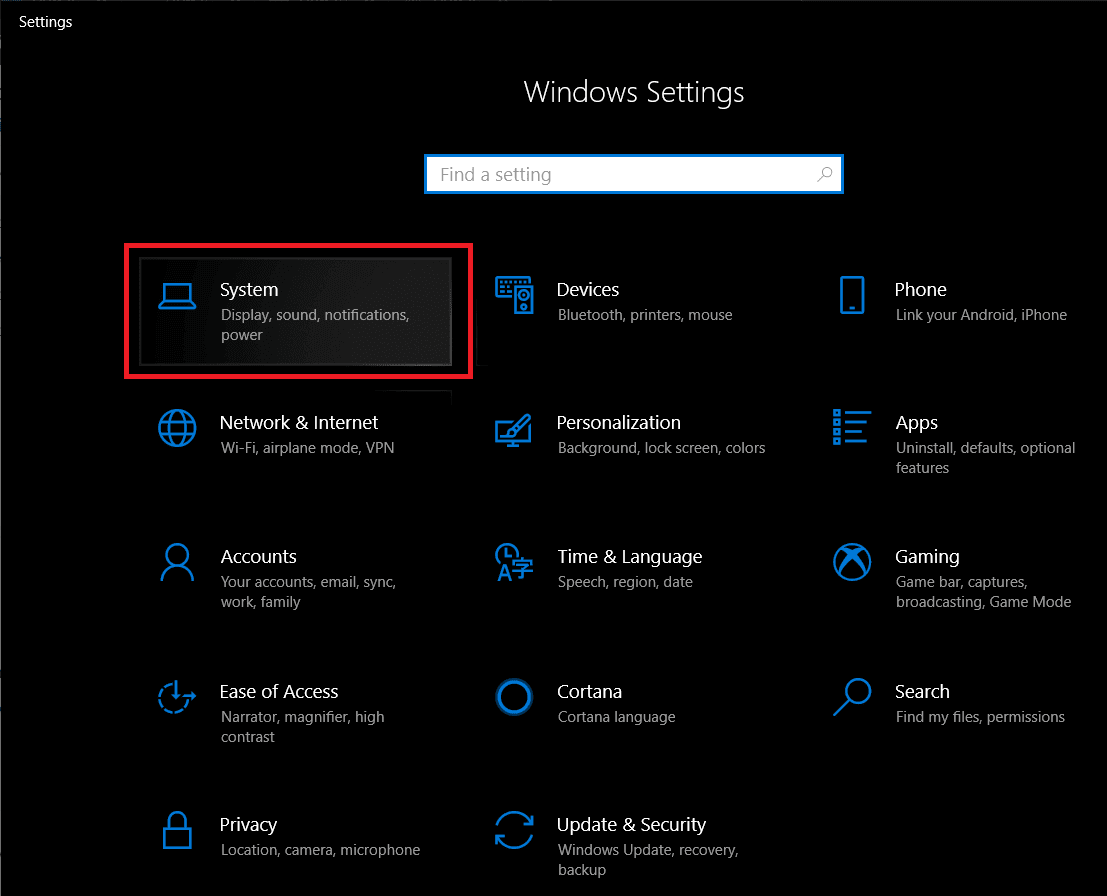
第 3 步:(Step 3:)现在,在左侧面板中找到并单击存储(Storage )以打开存储(Storage)设置和信息。
(您也可以通过按键盘上的Windows key + S存储设置(Storage Settings),搜索存储设置(Storage Settings)并按 Enter)

第 4 步:(Step 4:)有关预留存储(Reserved Storage)的信息隐藏在Show more categories下。所以点击它可以看到所有的类别和它们所占用的空间。
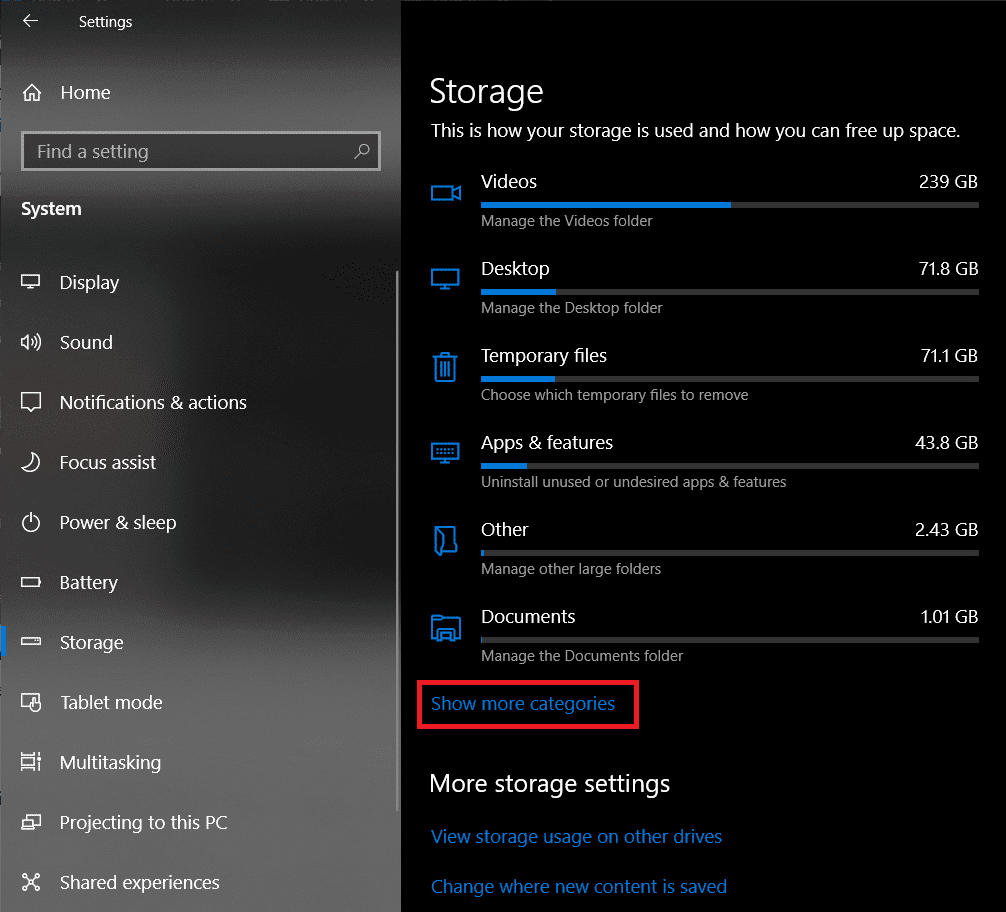
第 5 步:(Step 5:)找到System & reserved并单击以打开类别以获取更多信息。

如果您没有看到“保留存储”(“Reserved Storage”)部分,则表示该功能已被禁用或在您系统上当前安装的版本中不可用。

但是,如果确实有保留存储部分并且您希望禁用它,请仔细遵循以下指南:
第 1 步:(Step 1:)首先,通过按键盘上的Windows键 + R启动运行命令。(Run )现在,输入regedit并按 enter 或单击 OK 按钮打开注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)。
您还可以通过在搜索栏中搜索注册表编辑器,然后从右侧面板中选择以管理员身份运行来启动(Run as Administrator)注册表编辑器。(Registry Editor)
(用户帐户控制将请求允许应用程序注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)对您的设备进行更改,只需单击是(Yes )授予权限。)

第 2 步:(Step 2:)从注册表编辑器左侧面板中的项目列表中,单击(Registry Editor)HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE旁边的下拉箭头。(或直接双击名称)

第 3 步:(Step 3:)从下拉项目中,单击旁边的箭头打开软件。(SOFTWARE )

第 4 步:(Step 4:)按照相同的模式,前往以下路径
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager

第 5 步:(Step 5:)现在,在右侧面板中双击条目ShippedWithReserves。这将打开一个对话框来更改ShippedWithReserves的(ShippedWithReserves)DWORD值。

第 6 步:(Step 6:)默认情况下,该值设置为 1(表示已启用预留存储(Reserved Storage))。将该值更改为0 以禁用保留存储( 0 to disable reserved storage)。(反之亦然,如果您想启用保留存储(Reserved Storage)功能)
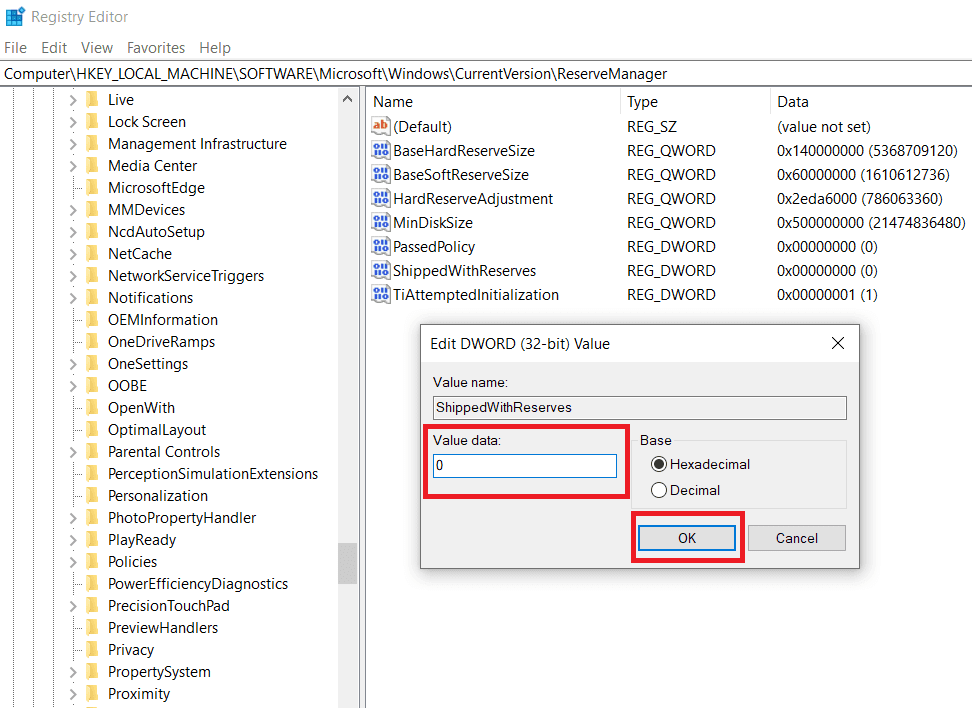
第 7 步:(Step 7:)单击OK按钮或按 Enter 保存更改。关闭注册表编辑器(Close Registry Editor)并重新启动计算机以应用我们所做的更改。
但是,重新启动/重新启动不会立即禁用保留存储(Reserved Storage)功能。该功能将在您收到并执行的下一次Windows升级中被禁用。(Windows)
当您收到并执行升级时,请按照前面的指南检查保留的存储是否已被禁用或仍处于启用状态。
另请阅读:(Also Read:) 启用或禁用 Windows 10 沙盒功能(Enable or Disable Windows 10 Sandbox Feature)
如何减少 Windows 10 中的预留存储空间?(How to reduce Reserved Storage in Windows 10? )
除了在您的个人计算机上完全禁用保留存储之外,您还可以选择减少Windows为更新和其他内容保留的空间/内存量。
这是通过卸载预装在Windows上的可选功能来实现的,这些功能是操作系统按需自动安装或由您手动安装的。每次安装可选功能时,Windows都会自动增加保留存储(Reserved Storage)的大小,以确保这些功能有足够的空间并在安装更新时保留在您的系统上。
许多这些可选功能很少被用户使用,可以卸载/删除以减少预留存储(Reserved Storage)量。
要减少预留存储(Reserved Storage)功能占用的内存,请执行以下步骤:
第 1 步:(Step 1:)通过前面讨论的三种方法中的任何一种再次打开 Windows设置(Settings )(Windows键 + I),然后单击应用程序(Apps)。

第 2 步:(Step 2:)默认情况下,您应该打开“应用程序和功能(Apps & Features)”部分。如果您不是这种情况,请单击左侧面板中的应用程序(Apps)和功能(Features)来执行此操作。
第 3 步:(Step 3:)单击可选功能(Optional Features)(以蓝色突出显示)。这将打开您个人计算机上安装的所有可选功能和程序(软件)的列表。

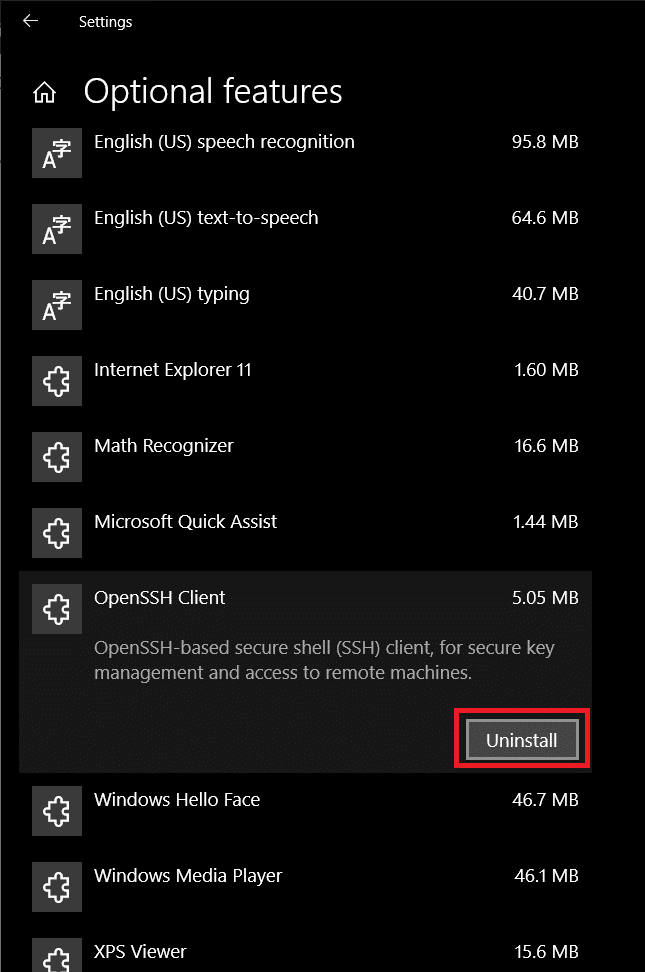
第 4 步:(Step 4:)浏览可选功能(Optional Features)列表并卸载您发现自己从未使用过的所有功能。
这可以通过简单地单击功能/应用程序名称将其展开并单击随后出现的卸载按钮来完成。(Uninstall )
除了卸载可选功能外,您还可以通过卸载安装在您的个人计算机上但您没有使用的任何语言包来进一步减少预留存储空间。(Reserved Storage)尽管大多数用户只使用一种语言,但许多用户在两种或三种语言之间切换,并且每次安装新语言时,就像可选功能一样,Windows会自动增加保留存储(Reserved Storage)的大小,以确保在您更新系统时对其进行维护。
要通过删除语言来减少保留存储(Reserved Storage)量,请执行以下步骤:
第 1 步:(Step 1:)在窗口设置(Window Settings)窗口中,单击时间和语言(Time and Language)。

第 2 步:(Step 2:)单击左侧面板中的语言(Language )。
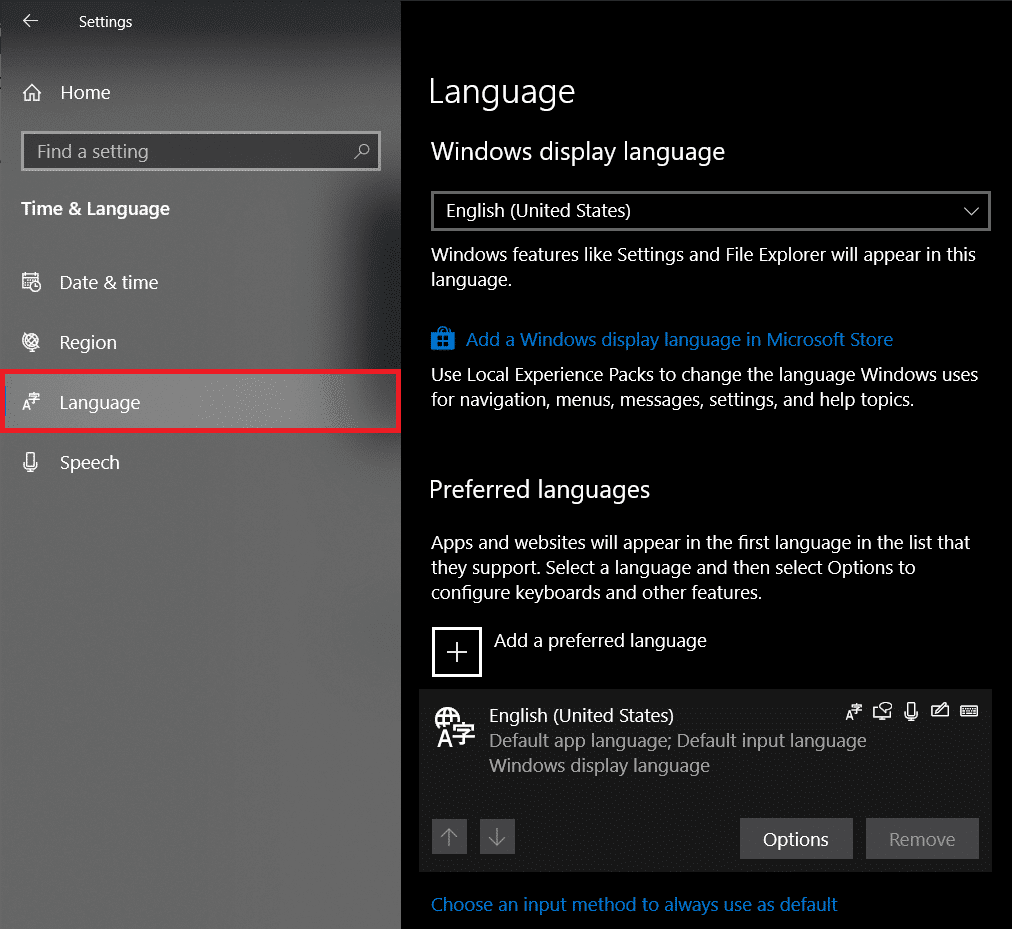
第 3 步:(Step 3:)现在,系统上安装的语言(Languages)列表将显示在右侧。通过单击展开特定语言,最后单击“删除(Remove )”按钮进行卸载。

至于是否应该考虑禁用保留存储?选择真的取决于你。推出该功能是为了让更新 Windows 的体验更加流畅,而且似乎做得特别好。
推荐:(Recommended:) 在 Windows 10 上释放硬盘空间的 10 种方法(10 Ways to Free Up Hard Disk Space On Windows 10)
但是,虽然预留存储不会占用您的大部分内存,但在可怕的情况下完全禁用此功能或将其减小到可以忽略不计的大小可能会很有帮助。我们希望上述指南能帮助您在 Windows 10 上启用或禁用保留存储,(Enable or Disable Reserved Storage on Windows 10)并且您能够在个人计算机上清理几 GB 的空间。
Enable or Disable Reserved Storage on Windows 10
Looking to Enable to Disable Reserved Storage on Windows 10 but don’t know how? Don’t worry, in this guide, we will see exact steps to enable to disable this feature on Windows 10.
Storage woes are a common issue in the tech world. A couple of years ago, 512 GB of internal memory was considered as overkill but now, the same amount is considered the base variant or even below-par storage option. Every gigabyte of storage is considered of utmost importance and the statement holds even more weight when talking about entry-level laptops and personal computers.

Amid such storage hardships, if a particular feature or software hogs up unnecessary space then it is best to let it go. A similar case is presented by Reserved Storage, a Windows feature introduced last year which occupies a set amount of memory (ranging in gigabytes) for software updates and other optional features. Disabling the feature helps make some room and get a bit of precious storage space back.
In this article, we will learn if it is safe to disable the Reserved Storage feature and how to go about it.
What is Reserved Storage?
Starting from the Windows 1903 version (May 2019 update), Windows started reserving about 7GB of the available disk space on a system for software updates, certain built-in apps, temporary data like caches, and other optional files. The update and the Reserved Storage feature was rolled out after many users complained about not being able to download the new Windows updates, about low storage space, slow update experience, and similar stuff. All of these issues are caused due to a lack of residual storage or disk space available for updates. The feature by reserving a set amount of memory helps resolve all of these issues.
Earlier, if you didn’t have enough free disk space on your personal computer, Windows wouldn’t be able to download and install any new updates. The fix would then require the user to clear up space by deleting or uninstalling some valuable cargo from his or her system.
Now, with Reserved Storage enabled in newer systems, all updates will first utilize the space reserved by the feature; and eventually, when it is time to update the software, all temporary and unnecessary files will be deleted from the Reserved Storage and the update file will occupy the entire reserve space. This ensures that systems will be able to download and install software updates even when one has very little disk space left and without having to clear additional memory.
With essential disk space reserved for software updates and other important files, the feature also ensures that all critical and necessary OS functions always have some memory to operate out of. The amount of memory occupied by Reserved Storage is said to vary over time and based on how one uses their system.
The feature comes enabled in any and all new systems that have Windows version 1903 pre-installed or on systems that perform a clean install of that specific version. If you are updating from previous versions then you will still receive the Reserved Storage feature but it will be disabled by default.
Enable or Disable Reserved Storage on Windows 10
Fortunately, enabling and disabling Reserved Storage on a particular system is quite easy and can be done in a matter of a few minutes.
Note: Make sure to create a restore point just in case something goes wrong.
How to Disable Reserved Storage?
Disabling the reserved storage feature on your windows system involves messing with the Windows Registry. However, one has to be extremely careful when using the Windows Registry as an incorrect step or any accidental modification of an item in the Registry can cause serious issues to your system. So, be extremely cautious when following the guide.
Also, before we get started with the procedure let’s check if there indeed is some storage reserved by Windows for updates in our systems and make sure our actions don’t turn out futile.
To check if there is Reserved Storage on your computer:
Step 1: Open Windows Settings by any of the following methods:
- Press Windows Key + S on your keyboard (or click on the start button in the taskbar) and search for Settings. Once found, hit enter or click on open.
- Press Windows Key + X or right-click on the start button and click on Settings.
- Press Windows Key + I to directly open Windows Settings.
Step 2: In the Window Settings panel, look for System (the very first item in the list) and click on the same to open.

Step 3: Now, in the left-hand panel locate and click on Storage to open Storage settings and information.
(You could also directly open Storage Settings by pressing Windows key + S on your keyboard, searching for Storage Settings and pressing enter)

Step 4: Information regarding Reserved Storage is hidden under Show more categories. So click on it to be able to see all the categories and the space occupied by them.

Step 5: Find System & reserved and click to open the category for more information.

If you do not see a “Reserved Storage” section, it implies the feature is already disabled or not available in the build currently installed on your system.

However, if there indeed is a Reserved Storage section and you wish to disable it then follow the below guide carefully:
Step 1: First, launch Run command by pressing Windows key + R on your keyboard. Now, type in regedit and press enter or click on the OK button to open the Registry Editor.
You could also launch the Registry Editor by searching for it in the search bar and then selecting Run as Administrator from the right panel.
(The user account control will ask for permission to allow the application Registry Editor to make changes to your device, simply click on Yes to grant permission.)

Step 2: From the list of items in the left panel of the Registry Editor, click on the drop-down arrow next to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE. (or simply double click on the name)

Step 3: From the drop-down items, open up SOFTWARE by clicking on the arrow next to it.

Step 4: Following the same pattern, make your way to the following path
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager

Step 5: Now, in the right panel double-click on the entry ShippedWithReserves. This will open up a dialog box to change the DWORD value for ShippedWithReserves.

Step 6: By default, the value is set to 1 (which indicates Reserved Storage is enabled). Change the value to 0 to disable reserved storage. (And vice versa if you want to enable the Reserved Storage feature)

Step 7: Click the OK button or press enter to save the changes. Close Registry Editor and reboot your computer to apply the changes we made.
However, restarting/rebooting won’t disable the Reserved Storage feature right away. The feature will be disabled in the next Windows upgrade you receive and perform.
When you do receive and perform an upgrade, follow the earlier guide to check if the reserved storage has been disabled or is still enabled.
Also Read: Enable or Disable Windows 10 Sandbox Feature
How to reduce Reserved Storage in Windows 10?
Apart from entirely disabling Reserved Storage on your personal computer, you could also choose to reduce the amount of space/memory that is Reserved by Windows for updates and other stuff.
This is achieved by uninstalling optional features that come pre-installed on Windows, the ones the operating system installs automatically on demand, or manually installed by you. Every time an optional feature is installed, Windows automatically increases the size of Reserved Storage to ensure the features have enough space and are maintained on your system when updates are installed.
Many of these optional features seldom get utilized by the user and can be uninstalled/removed to reduce the amount of Reserved Storage.
To reduce the memory the Reserved Storage feature occupies perform the below steps:
Step 1: Open up Windows Settings (Windows key + I) again by any of the three methods discussed earlier and click on Apps.

Step 2: By default, you should have the Apps & Features section open. If that’s not the case for you then click on Apps & Features in the left panel to do so.
Step 3: Click on Optional Features (highlighted in blue). This will open up a list of all the optional features and programs (software) installed on your personal computer.

Step 4: Go through the list of Optional Features and uninstall any and all features that you do not find yourself ever using.
This can be done by simply clicking on the feature/application name to expand it and clicking on the Uninstall button that appears afterward.

Along with uninstalling optional features, you can further reduce Reserved Storage by uninstalling any language packages installed on your personal computer that you do not have a use for. Although most users only use one language, many switch between two or three languages, and every time a new language is installed, just like optional features, Windows automatically increases the size of Reserved Storage to ensure they are maintained when you update your system.
To reduce the amount of Reserved Storage by removing languages follow the below steps:
Step 1: In the Window Settings window, click on Time and Language.

Step 2: Click on Language in the left panel.

Step 3: Now, a list of Languages installed on your system will be displayed on the right. Expand a particular language by clicking on it and finally click on the Remove button to uninstall.

As for if you should consider disabling Reserved Storage? The choice is really up to you. The feature was rolled out to make updating windows a smoother experience and seems to do that particularly well.
Recommended: 10 Ways to Free Up Hard Disk Space On Windows 10
But while Reserved Storage does not hog up a big portion of your memory, in dire situations entirely disabling this feature or reducing it to a negligible size can prove helpful. We hope the above guide helped you to Enable or Disable Reserved Storage on Windows 10 and you were able to clear up a few gigabytes on your personal computer.


















