从 1990 年代到 2000 年代初,人们必须携带十几根不同形状和尺寸的电缆才能充分利用他们已经笨重的小工具。如今,这种连接过程已经被简化,在充分利用它的同时,遵守行业标准的制造商已经消除了一个令人头疼的问题。大约十年前,技术巨头定义了连接端口的外观以及它们的用途。
顾名思义,通用串行总线 (USB) 现在是连接设备的普遍接受的标准。(Universal Serial Bus (USB))大多数外部设备(如有线鼠标和键盘、硬盘驱动器、打印机和扫描仪、扬声器等)都通过这些端口连接。
USB端口有几种不同的类型,根据它们的物理形状和大小以及它们的传输速度和功率承载能力来区分。今天,几乎每台笔记本电脑和 PC 上最常见的端口类型是USB type-A 和USB type-C。
本文将帮助您了解设备上发现的不同类型的USB端口以及识别它们的方法。这将通过将正确的设备连接到正确的USB端口来帮助您提高设备的整体性能。
基于形状的 USB 连接器类型(Types of USB Connectors based on the shape)
“ USB ”中的“U ”可能有点误导,因为有各种类型的USB连接器可用。但幸运的是,有几种不同的常见连接器类型。下面列出的是笔记本电脑和计算机系统中最受欢迎的。
● USB A

USB Type-A 连接器(USB Type-A connectors)是世界上最知名和最常用的连接器。它们是扁平的和矩形的。它们在几乎所有笔记本电脑或计算机型号中都大量存在。许多电视(TVs)、其他媒体播放器、游戏系统、家庭音频/视频接收器、汽车音响和其他设备也更喜欢这种类型的端口。这些连接器提供“下游”连接,这意味着它们仅用于主机控制器和集线器。
● USB C 型

USB C 型是用于传输数据和充电的最新标准之一。它现在包含在最新的智能手机、笔记本电脑、平板电脑等中。它们受到普遍的喜爱,因为它们是对称的椭圆形,是最不令人沮丧的插件,因此不可能错误地连接它们。另一个原因是它们足够强大,能够以 10 Gbps 的速度传输数据,(transmit data at 10 Gbps)并使用 20 伏特/5 安培/100 瓦特的功率为设备充电,同时保持纤薄小巧但极其耐用。
新的MacBook(MacBooks)抛弃了所有其他类型的端口,转而使用USB C 型(USB)。USB A 型连接器、HDMI、VGA、DisplayPort等的混乱在这里被简化为单一类型的端口。尽管物理USB-C连接器不向后兼容,但底层USB标准是。您只需要一个物理适配器即可通过此端口连接到外围设备。
● USB B 型

也称为USB 标准 B(USB Standard B)连接器,这种样式通常保留用于连接打印机和扫描仪等外围设备。有时,它们也存在于软盘驱动器(floppy drives)、硬盘驱动器(hard drive)外壳和光驱等外部设备中。
它以其方形的形状和略微斜角的角而闻名。使用单独端口的主要原因是将外围连接与通常的连接区分开来。这也消除了将一台主机意外连接到另一台主机的风险。
● USB 微型 B

这种类型的连接出现在较新的智能手机以及GPS装置、数码相机和智能手表上。它的 5 针设计很容易识别,矩形形状和一侧有斜边。该连接器受到许多人的青睐(在 C 型之后),因为它支持高速数据传输(速度为 480 Mbps),并且具有On-The-Go (OTG)的特性,尽管尺寸仍然较小。它足够强大,可以让智能手机与计算机通常能够连接的外围设备建立连接。
● USB 迷你 B

这些类似于USB B 型(USB B type)连接器,但尺寸要小得多。它们还用于连接外围设备。这款迷你插头有 5 个引脚,包括一个额外的 ID 引脚,支持OTG功能,允许设备充当USB主机。
您会在早期的智能手机型号中找到它们,偶尔会在数码相机中找到它们,在计算机中很少见。现在,大多数USB Mini B端口已被更时尚的 micro USB取代。
● USB Mini-B(4 针)

这是数码相机中发现的一种非官方连接器,主要由柯达(Kodak)制造。由于它的斜角,它类似于标准的B 型连接器,但它的尺寸要小得多,形状是方形的。(B-style)
基于版本的 USB 连接器类型(Types of USB Connectors based on their versions)
(USB)自 1995 年推出以来,USB已经有多个版本。每个版本都进行了重大改进,以赋予这些英寸宽的端口巨大的功率和潜力。每个之间的主要区别在于它的传输速度和它可以允许流过的电流量。
1996 年发布的第一个版本USB 1.0几乎不能传输 12 Mbps,USB 1.1几乎没有改进。但这一切在 2000 年USB 2.0发布时发生了变化。USB 2.0以指数方式将传输速度提高到 480 Mbps,并提供高达 500mA 的功率。迄今为止,它是现代计算机中最常见的USB端口类型。(USB)它成为行业标准,直到2008 年推出USB 3.0。这个SuperSpeed端口允许高达 5 Gbps的传输速度(Gbps)并提供高达 900mA 的电流。制造商争相利用它并采用了这项技术,因为它的速度呈指数级增长,至少是纸上USB 2.0速度的 5 倍。(USB 2.0)但最近,USB 3.1和 3.2 发布,分别允许高达 10 和 20 Gbps的传输速度。这些被称为“ SuperSpeed + ”端口。
另请阅读:(Also Read:) 修复 USB 复合设备无法与 USB 3.0 一起正常工作(Fix USB Composite Device can’t work properly with USB 3.0)
如何识别笔记本电脑或计算机上的 USB 端口?(How to identify USB ports on your Laptop or Computer?)
一旦您通过形状直观地识别出您拥有的端口类型,就必须了解它的功能以充分利用它。例如,您可能已经注意到,您的手机从两个外观相同的USB A 型端口之一充电速度更快。当您的系统上有不同版本的端口时,就会发生这种情况。将正确的设备连接到正确的端口将提高整体性能。因此(Hence),必须在您的设备上物理识别哪个是哪个。
方法一:检查标签

很少有制造商在设备主体上直接按其类型标记端口,端口通常标记为1.0、11、2.0、3.0 或 3.1。(1.0, 11, 2.0, 3.0, or 3.1. )它们也可以用符号来标记。
大多数 USB 3.0 端口都以SuperSpeed USB的形式销售,他们的制造商会这样标记(见上图)。它通常标有前缀“ SS ”。
如果USB端口旁边有一个雷电图标,则表示“始终在线(Always on)”端口。这意味着即使笔记本电脑/计算机关闭,您也可以将设备挂在此端口上充电。这种类型的端口通常提供比任何其他端口更多的功率,从而使设备能够更快地充电。
方法二:检查端口颜色
有时,端口用颜色标记以便于视觉识别。USB 3.0 端口通常为蓝色。USB 2.0 端口的区别在于黑色内部。白色(White)保留用于较旧的USB 1.0或 1.1 端口。如果您有带有USB 3.1端口的较新设备,它们是红色的,而“始终开启”端口由黄色内部表示。
| USB Version |
Color Allocated |
| USB 1.0/ 1.1 |
White |
| USB 2.0 |
Black |
| USB 3.0 |
Blue |
| USB 3.1 |
Red |
| Always On ports |
Yellow |
方法 3:检查技术规格(Check Technical Specifications)
如果通过颜色或徽标进行识别对您来说很棘手,您可以先了解设备内置的端口类型,然后开始定位它们。这将使您大致了解您正在寻找什么。
在 Windows 系统上(On a Windows system)
此过程对于所有Windows系统都很常见,无论其制造商、型号或版本如何。
步骤 1:(Step 1:)首先,通过按 ‘Windows key + R’ 运行”(Run)对话框,或者您只需在搜索栏中输入“运行”即可。
第 2 步:(Step 2:)输入 “devmgmt.msc” 并回车。这将打开 “设备管理器(Device Manager)”。
第 3 步:(Step 3:)设备管理器(Device Manager)列出所有系统组件。找到(Locate)并双击 “通用串行总线控制器”( ‘Universal Serial Bus controllers’)以展开下拉菜单。

第 4 步:(Step 4:)大多数情况下,直接提及端口的版本,否则组件的名称会提示您其属性。
如果您在端口描述中发现“增强(Enhanced)”,则它是 USB 2.0 端口。
USB 3.0 可以通过“xHCI”或“可扩展主机控制器(Extensible Host Controller)”等术语来识别。

第 5 步:(Step 5:)您也可以右键单击端口名称并打开其 属性(properties)。在这里,您将找到有关该端口的更多详细信息。

在 Mac 上(On Mac)
1. 单击屏幕左上角的Apple图标。(Apple)在出现的菜单中,选择“关于本机”(‘About This Mac’)。
2. 随后的窗口将列出您的所有系统规格。单击(Click) 底部的“系统报告...”按钮。(‘System Report…’) 如果您使用的是OS X 10.9 ( Mavericks ) 或更低版本,请单击(Click)“ 更多信息” 。(‘More info’)
3. 在系统信息(System Information) 选项卡中,单击 “硬件”(‘Hardware’)。这将列出所有可用的硬件组件。最后,单击以展开USB选项卡。
4. 您将找到所有可用USB端口的列表,根据它们的类型列出。您可以通过查看其标题来确认端口的类型。
一旦您知道类型,您就可以开始在您的设备上实际定位它们。
方法 4:通过主板技术(Technical)规格识别 USB端口(Identify USB)
这是通过查看笔记本电脑或主板的规格来确定可用USB端口的漫长方法。这将有助于找到设备的确切型号,您可以梳理其规格以查找有关端口的信息。
在 Windows 上(On Windows)
1.参考上述步骤打开运行对话框,输入(Run)“msinfo32” 并回车。

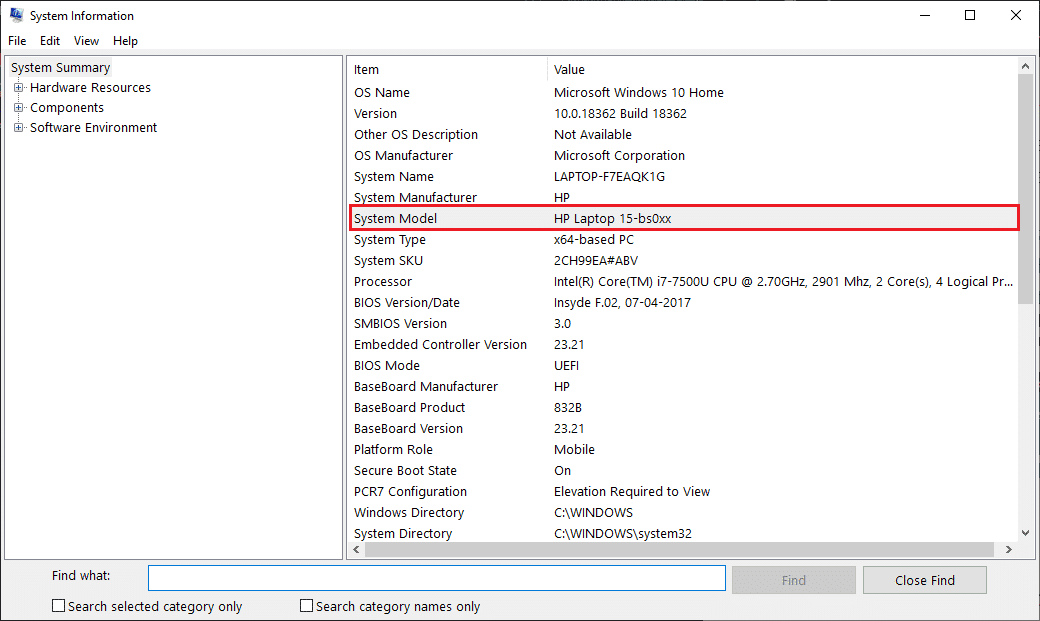
2. 在出现的系统信息(System Information) 窗口中,找到 “系统模型”(‘System Model’) 详细信息。单击(Click)该行并按“Ctrl + C”复制该值。
3. 现在,打开您喜欢的搜索引擎,将模型详细信息粘贴到搜索栏中,然后点击搜索。浏览搜索结果并找到可靠的网站(最好是您制造商的网站)。
梳理(Comb)网站并查看其规格以找到USB等字词,您只需按“ Ctrl + F ”并在栏中输入“ USB ”即可。(USB)您将找到列出的确切端口规格。

在 Mac 上(On Mac)
与Windows类似,您只需搜索特定MacBook型号的规格即可找到可用端口。
如果您还不知道,只需单击左上角的Apple标志,即可轻松确定您使用的型号。在下拉菜单中,单击 “关于 Mac”(‘About the Mac’) 选项。包括型号名称/编号、操作系统版本和序列号在内的系统信息将显示在结果窗口中。(System)
找到正在使用的模型后,您只需在线搜索其技术规格即可。请访问 Apple 的官方支持网站以获取最准确的信息。
受到推崇的:(Recommended:)
我希望本指南对您能够识别计算机上的 USB 端口(Identify USB Ports on your computer)有所帮助。但是,如果您对本文仍有疑问,请随时在评论部分提出。
How to Identify different USB Ports on your Computer
From the 1990s to the early 2000s, one would have to carry a dozen cаbles of different shapes and sizes to make the most of their already bulky gadget. Today, this connectіon process has been simplified, and a headache has been eliminated bу manufacturers whо abide by the industry standards while making the most of it. About a decade ago, the technology giants defined what сonnection ports should look like and what purpose they would serve.
The Universal Serial Bus (USB), as the name would suggest, is now the universally accepted standard for connecting devices. Most external devices like wired mouse and keyboards, hard drives, printers and scanners, speakers, and more are connected through these ports.
USB ports are found in a few different types, differentiated on the basis of their physical shape and size as well as their transfer speed and power carrying capacities. Today, the most common type of ports found on almost every laptop and PC is the USB type- A and USB type- C.
This article will help you understand different types of USB ports found on your device and methods to identify them. This will help you boost your device’s overall performance by connecting the right device in the right USB port.
Types of USB Connectors based on the shape
The ‘U’ in ‘USB’ can be a little misleading as there are various types of USB connectors available. But luckily, there are a few different common types of connectors. Listed below are the most popular ones found in laptops and computer systems.
● USB A

The USB Type-A connectors are the most recognizable and commonly used connectors in the world. They are flat and rectangular. They are found abundantly in almost every laptop or computer model. Many TVs, other media players, gaming systems, home audio/video receivers, car stereo, and other devices prefer this type of port as well. These connectors provide a ‘downstream’ connection, which means that they are intended to be used solely on host controllers and hubs.
● USB type C

USB type C is one of the newest emerging standards for transferring data and charging. It is now included in the newest smartphones, laptops, tablets, and more. They are universally adored because they are the least frustrating ones to plugin due to their symmetrical oval shape, making it impossible to connect them incorrectly. Another reason being that these are powerful enough to transmit data at 10 Gbps and use 20 volts/5 amps/100 watts of power to charge a device while remaining thin and tiny yet extremely durable.
The new MacBooks have ditched all other types of ports in favor of USB type C. The mess of USB type-A connectors, HDMI, VGA, DisplayPort, etc. is streamlined into a single type port here. Even though the physical USB-C connector isn’t backward compatible, the underlying USB standard is. You will just need a physical adapter to connect to the peripheral devices via this port.
● USB type B

Also known as USB Standard B connectors, this style is usually reserved for connection to peripheral devices like printers and scanners. Occasionally, they are also found in external devices like floppy drives, hard drive enclosures, and optical drives.
It is recognized by its squarish shape and slightly beveled corners. The primary reason for a separate port is to differentiate peripheral connections from the usual ones. This also eliminates the risk of accidentally connecting one host computer to another.
● USB Micro B

This type of connection is found on newer smartphones as well as GPS units, digital cameras, and smartwatches. It is identified easily by its 5 pin design with a rectangular shape and beveled edges on one side. This connector is favored by many (after type C) as it supports high-speed data transfer (at the speed of 480 Mbps) as well as has the feature of On-The-Go (OTG) despite remaining physically smaller in size. It is powerful enough to allow a smartphone to make a connection with peripheral devices that a computer is generally capable of.
● USB Mini B

These are similar to USB B type connectors but are way smaller in size. They are also used to connect to peripheral devices. This mini plug has 5 pins, including an extra ID pin to support OTG capabilities that allow devices to act as a USB host.
You will find them in early smartphone models, occasionally in digital cameras, and very rarely in computers. Now, most USB Mini B ports have been replaced with the sleeker micro USB.
● USB Mini-B (4 Pin)

This is a type of unofficial connector found in digital cameras, mostly manufactured by Kodak. It resembles a standard B-style connector due to its beveled corners, but it is much smaller in size and squarish in shape.
Types of USB Connectors based on their versions
USB had had multiple versions since its inception back in 1995. With each version, major improvements have been made to give these inch wide ports immense power and potential. The main difference between each lies in its transfer speed and the amount of current it can allow to flow through.
The very first version, USB 1.0 released back in 1996 could barely transfer 12Mbps and USB 1.1 was hardly an improvement on it. But this all changed in 2000 when USB 2.0 was released. USB 2.0 exponentially increased the transfer speed to 480 Mbps and delivered up to 500mA of power. To date, it is the most common type of USB port available in modern computers. It became the industry standard until USB 3.0 was launched in 2008. This SuperSpeed port allowed transfer speeds up to 5 Gbps and delivered up to 900mA. Manufacturers rushed to take advantage of it and adopted this technology as it was exponentially faster, at least 5 times the speed of USB 2.0 on paper. But more recently, USB 3.1 and 3.2 were released, which allowed transfer speed up to 10 and 20 Gbps, respectively. These are called ‘SuperSpeed +’ ports.
Also Read: Fix USB Composite Device can’t work properly with USB 3.0
How to identify USB ports on your Laptop or Computer?
Once you have visually identified the type of port you have by its shape, it is essential to understand its capabilities to make the most out of it. For example, you might have noticed that your phone charges faster from one of the two visually identical USB type-A ports. This occurs when you have different versions of ports on your system. Connecting the right device to the right port will boost the overall performance. Hence, it is essential to physically identify which one is which on your device.
Method 1: Check for labels

Few manufactures have the ports labeled directly by their type on the device’s body, the ports are usually marked as 1.0, 11, 2.0, 3.0, or 3.1. They can also be marked with the use of symbols.
Most USB 3.0 ports are marketed as SuperSpeed USB, and their manufacturers will mark it as such (see above image). It is generally marked with the prefix ‘SS’.
If a USB port has a thunderbolt lightning icon located next to it, it denotes an ‘Always on’ port. This means that you can hook your device to charge on this port even when the laptop/computer is turned off. This type of port usually delivers more power than any other, allowing the device to charge faster.
Method 2: Check the color of the port
Sometimes, ports are marked by color for easy visual identification. USB 3.0 ports are generally blue in color. While USB 2.0 ports are differentiated by black insides. White color is reserved for older USB 1.0 or 1.1 ports. If you have a newer device with USB 3.1 ports, they are red in color, and ‘Always On’ ports are represented by yellow insides.
| USB Version |
Color Allocated |
| USB 1.0/ 1.1 |
White |
| USB 2.0 |
Black |
| USB 3.0 |
Blue |
| USB 3.1 |
Red |
| Always On ports |
Yellow |
Method 3: Check Technical Specifications
If identification through colors or logo is tricky for you, you can first understand what kind of ports your device has built-in and then begin to locate them. This will give you a general idea of what you are looking for.
On a Windows system
This process is common for all Windows systems irrespective of their manufactures, models, or versions.
Step 1: Firstly, open the Run dialog box by pressing ‘Windows key + R’ or you can simply type ‘Run’ in the search bar.
Step 2: Type ‘devmgmt.msc’ and hit enter. This will open the ‘Device Manager’.

Step 3: The Device Manager lists all the system components. Locate and double-click on the ‘Universal Serial Bus controllers’ to expand the drop-down menu.

Step 4: Most times, the version of the ports is directly mentioned, otherwise the name of the component will hint you to its properties.
If you spot ‘Enhanced’ in the port’s description, then it is a USB 2.0 port.
USB 3.0 can be identified by terms like ‘xHCI’ or ‘Extensible Host Controller’.

Step 5: You can also right-click on the port’s name and open its properties. Here, you will find more details about the port.

On Mac
1. Click on the Apple icon located on the top-left corner of your screen. In the resulting menu, select ‘About This Mac’.
2. The subsequent window will list all your system specifications. Click on the ‘System Report…’ button located on the bottom. Click on ‘More info’ if you are using OS X 10.9 (Mavericks) or below.
3. In the System Information tab, click on ‘Hardware’. This will list all the hardware components available. Finally, click to expand the USB tab.
4. You will find a list of all the available USB ports, listed according to their type. You can confirm the type of port by checking its title.
Once you know the type you can start locating them physically on your device.
Method 4: Identify USB ports through your Motherboard’s Technical Specifications
This is a lengthy way of determining the USB ports available by looking at the laptop or motherboard’s specifications. This will help in finding the exact model of the device and you can comb through its specifications to find information about the ports.
On Windows
1. Open the Run dialog box by referring to the steps mentioned above, type in ‘msinfo32’ and hit Enter.

2. In the resulting System Information window, find the ‘System Model’ detail. Click on the line and press ‘Ctrl + C’ to copy the value.

3. Now, open your favorite search engine, paste the model details in the search bar, and hit search. Go through the search results and find a reliable website (preferably your manufacturer’s website).
Comb through the website and check its specification to locate words like USB, you can simply press ‘Ctrl + F’ and type in ‘USB’ in the bar. You will find the exact port specifications listed.

On Mac
Similar to Windows, you simply search the specifications of your particular MacBook model to find the available ports.
If you don’t know already, you can easily determine what model you are using by simply clicking on the Apple logo located on the top left. In the drop-down menu, click on ‘About the Mac’ option. System information including model name/number, operating system version, and serial number will be displayed in the resulting window.
Once you find the model being used, you can simply search its technical specification online. Visit Apple’s official support website for the most accurate information.
Recommended:
I hope this guide was helpful you were able to Identify USB Ports on your computer. But if you still have questions regarding this article then feel free to ask them in the comment section.














