如果您是网络工程师或普通用户,您可能需要查找、打开或阻止虚拟端口,例如应用程序的TCP或UDP端口。(UDP)虚拟端口可帮助您管理与信息流量相关的网络硬件和软件。通俗地说,虚拟端口充当特定流量的专用通道,例如网站流量、接收电子邮件、文件传输等。
基本上有两种类型的虚拟端口,即TCP和UDP。TCP代表传输控制协议(Transmission Control Protocol);而 UDP 代表用户数据报协议(User Datagram Protocol)。TCP和UDP端口在处理信息流量时使用不同的网络协议。网络协议只不过是一组关于如何发送和接收某些信息的规则和规定。但是,TCP或UDP端口的基础是IP,即Internet 协议(Internet Protocol)。
让我们看看这两个端口的特性和功能有何不同。
TPC 端口如何工作?
TCP端口要求用户在发送方机器和接收方机器之间建立连接。这与拨打电话非常相似。一旦发送者和接收者之间建立连接,信息就可以来回传输,直到外部断开连接。
虽然TCP是最复杂的传输层协议,但在接收无差错信息方面,它也是最可靠的协议。该协议确保目标机器确认收到数据报。只有这样,它才会传输信息。因此(Hence),TCP比(TCP)UDP更常用。
UDP 端口如何工作?
另一方面,UDP端口不需要用户在发送方和接收方之间建立连接来发送信息。但是,与TCP端口不同的是,通过(TCP)UDP端口发送的信息可能无法到达接收方。它类似于发送一封信。用户不必收到该信件。因此(Hence),需要广播的信息通过UDP端口发送。调谐或监听指定UDP端口的用户可以接收信息。
UDP具有低延迟并提供恒定的信息流。因此,UDP是流式广播、在线视频游戏和 IP 语音 ( VoIP ) 流式传输的完美选择。因此,仅当对发送信息有特定需求时才使用UDP端口。(UDP)
识别正确的端口
任何 PC 都有许多虚拟端口可用;范围从 0 到 65535。但是,这些端口中的每一个都有特定的标准,并且专用于特定的应用程序。其中,以下某些端口使用TCP和UDP。
- 20(TCP):FTP(文件传输协议(File Transfer Protocol))
- 22 (TCP):安全外壳 (SSH)
- 25(TCP):简单邮件传输协议(Mail Transfer Protocol)(SMTP)
- 53(TCP和UDP):域名系统(System)(DNS)
- 80(TCP):超文本传输协议(Transfer Protocol)(HTTP)
- 110(TCP):邮局协议(Post Office Protocol)(POP3)
- 143(TCP):互联网消息访问协议(Message Access Protocol)(IMAP)
- 443 (TCP):HTTP 安全 (HTTPS)。
可以检查 Windows PC 上的哪些端口打开或关闭。如果您希望阻止或打开某个TCP或UDP端口,那么这里是过程。
查找打开的 TCP 或 UDP 端口
打开开始菜单(Start Menu)。(对于Windows 10,请按Windows按钮)并键入CMD。现在单击以管理员身份运行(Run as Administrator)选项。
当命令提示符(Command Prompt)窗口打开时,键入Netstat -ab并按Enter。TCP和UDP端口列表以及 IP 地址和其他详细信息开始出现。
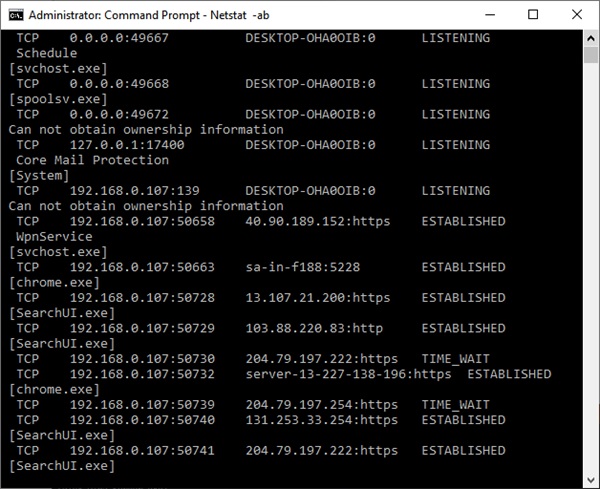
您等待的时间越长,打开的端口列表就越大。等到(Wait)完整列表出现在窗口中。列表完全出现后,按(Press) CTRL+C和CTRL+V将信息复制并粘贴到记事本(Notepad)或任何其他文本编辑器中。
如上图所示,括号中的信息是指使用开放TCP或UDP端口的程序的名称。在协议名称旁边,您可以看到冒号后面的 IP 地址和端口号。例如,在192.168.0.107:50741 中(192.168.0.107: 50741),数字192.168.0.107是IP 地址( IP address),而数字50741是端口号。
阅读(Read): 如何检查哪些端口是打开的(How to check what Ports are open)?
查找阻塞的 TCP 或 UDP 端口
要了解Windows 防火墙(Windows Firewall)阻止了哪些端口,请按照以下步骤操作。
第一步与查找打开的TCP或UDP端口相同。按Windows按钮打开开始菜单(Start Menu)并键入CMD。现在单击以管理员身份运行(Run as Administrator)选项。
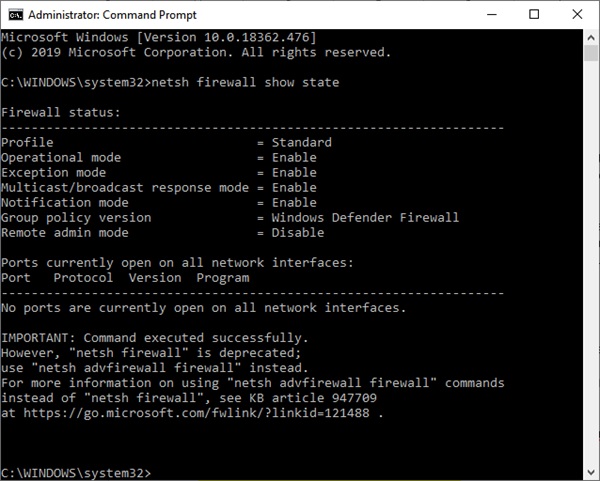
当命令提示符(Command Prompt)窗口打开时,键入以下命令:netsh firewall show state
某些端口可能被路由器或ISP阻止,这些端口可能未在上述列表中列出。要查找这些端口,请键入以下命令:netstat -ano | findstr -i SYN_SENT
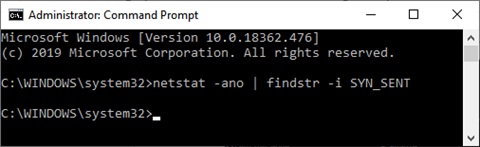
如果此命令没有返回任何列表,则表示路由器或ISP没有阻止任何端口。
如何打开或阻止TCP或UDP端口
现在,既然您已经确定了Windows PC 上的(Windows)TCP和UDP端口,那么最重要的部分就来了。
首先(First),您可能需要打开一个端口才能使应用程序顺利运行。另一方面,您可能需要阻止某些端口,因为它们不再被使用并且可能构成威胁的网关。因此(Hence),此类端口被防火墙阻止。
按照以下步骤打开或阻止TCP或UDP端口。
按Windows 键(Windows-key)打开开始菜单(Start Menu)。键入Windows Defender Firewall,然后从结果中选择具有高级安全性(Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security)的 Windows Defender 防火墙。
将打开以下窗口。
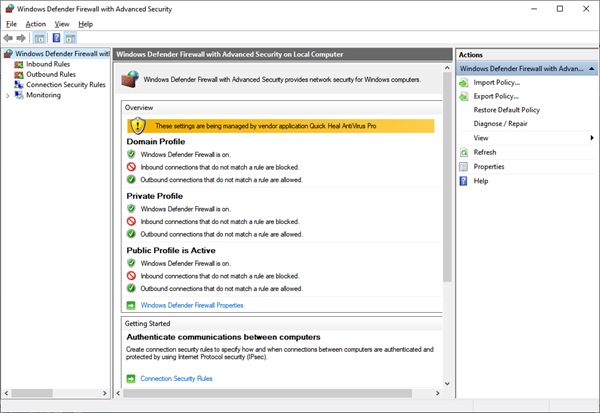
单击左侧菜单中的入站规则选项卡。(Inbound Rules)
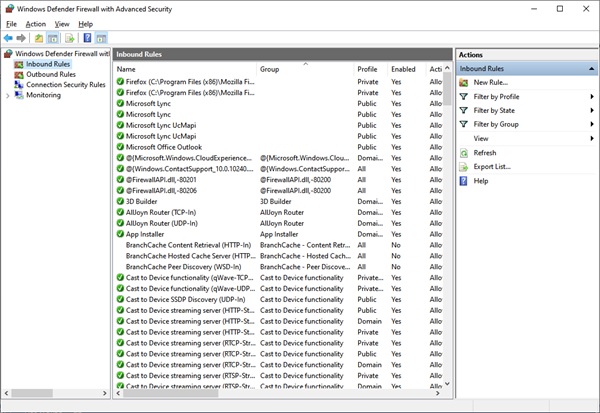
从右侧菜单的“操作(Actions)”窗格中单击“新规则...”(New Rule…)选项卡。当此窗口打开时,选择端口(Port)单选按钮并单击下一步(Next)。
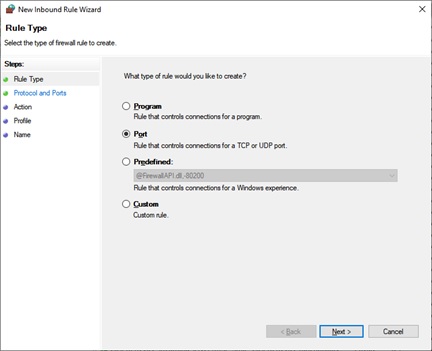
当按下Next选项卡时,将打开(Next )New Inbound Rule Wizard的以下窗口。在此窗口中,您可以选择要打开或阻止的端口类型。您还可以选择是否要打开或阻止所选类型的所有端口或特定的本地端口。指定要打开或阻止的本地端口的数量或范围。然后单击下一步(Next)。
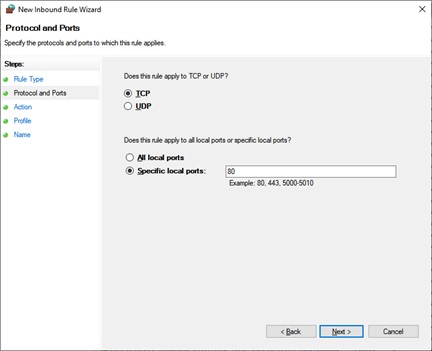
单击下一步时将打开以下窗口。在这里,您可以通过选择允许连接(Allow the connection)或允许连接(如果它是安全(Allow the connection if it is secure)单选按钮)来打开端口。选择第三个单选按钮阻止连接(Block the connection)以阻止指定端口。
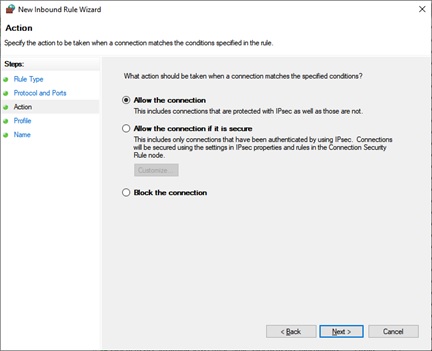
现在选择规则是否适用于Domain、Private或Public或所有这些。单击下一步(Next)。
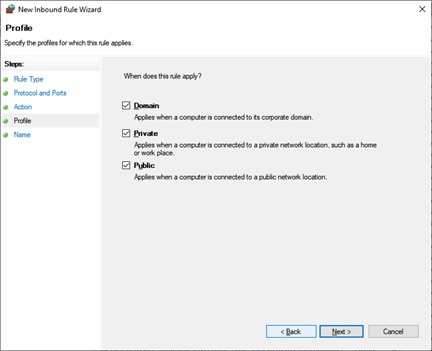
单击Next(Next)时会打开以下窗口。在此窗口中,为这个新的入站规则指定一个(Inbound Rule)名称(Name)。您还可以在“描述(Description)”部分指定哪些端口已被阻止或打开。
单击完成(Finish)以创建这个新的入站规则。
请(Please)注意,有时在阻止某个端口后,应用程序可能无法正常运行。在连接到某些资源时,您也可能会遇到问题。这意味着您阻止的端口可能需要打开。您可以在同一过程之后随时撤消对端口的阻塞。
阅读下一篇(Read next):如何使用 PortExpert监控 Windows 中的 TCP、UDP 通信。
What is TCP and UDP Port? How to block or open them in Windows?
If you are a network еngineer оr a normal user, you may neеd to find, open or block a virtual роrt, such as a TCP or a UDP port for an application. Virtual ports help you manage your network hardware and software with respect to the information traffic. In a layman’s language, virtual ports serve as the dedicated lanes for particular traffic such as website traffic, receiving emails, transfer of files and so on.
There are basically two types of virtual ports, namely TCP and UDP. TCP stands for Transmission Control Protocol; while UDP stands for User Datagram Protocol. TCP and UDP ports use different network protocols when handling information traffic. Network protocols are nothing but the set of rules and regulations of how certain information should be sent and received. However, the basis of a TCP or UDP port is IP, i.e. Internet Protocol.
Let’s see how these two ports defer in their features and functions.
How does a TPC port work?
A TCP port requires users to establish a connection between the sender’s machine and the receiver’s machine. It is quite similar to making a phone call. Once the connection is established between the sender and the receiver, the information can be transmitted back and forth, until the connection is broken externally.
Though TCP is the most complex transport layer protocol, it is also the most reliable protocol when it comes to receiving error-free information. The protocol makes sure that the destination machine acknowledges the receipt of the datagram. Only then it transmits the information. Hence, TCP is more commonly used than UDP.
How does a UDP port work?
A UDP port, on the other hand, doesn’t need users to establish a connection between the sender and the receiver to send the information. However, unlike a TCP port, the information sent over the UDP port may not reach the receiver. It is similar to sending a letter. It is not necessary that the user has received the letter. Hence, the information that needs to be broadcasted is sent over a UDP port. The user tuned over or listening to the specified UDP port can receive information.
UDP has low latency and offers a constant stream of information. Thus, a UDP is the perfect choice for streaming broadcasts, online video games, and a voice-over-IP (VoIP) streaming. As a result, a UDP port is used only when there is a specific need regarding information being sent.
Identifying the right ports
There are many virtual ports available for any PC; which range from 0 to 65535. However, each of these ports has a certain standard and is dedicated to a certain application. Out of these, some of the following ports use TCP and UDP.
- 20 (TCP): FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- 22 (TCP): Secure Shell (SSH)
- 25 (TCP): Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- 53 (TCP and UDP): Domain Name System (DNS)
- 80 (TCP): Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- 110 (TCP): Post Office Protocol (POP3)
- 143 (TCP): Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
- 443 (TCP): HTTP Secure (HTTPS).
It is possible to check which of the ports on your Windows PC are open or close. If you wish to block or open a certain TCP or UDP port, then here is the process.
Finding an open TCP or UDP port
Open the Start Menu. (For Windows 10, press the Windows button) and type CMD. Now click on Run as Administrator option.

When the Command Prompt window opens, type Netstat -ab and press Enter. A list of TCP and UDP ports starts appearing along with the IP address and other details.

The longer you wait, the bigger the list of open ports becomes. Wait until the complete list has appeared in the window. Once the list fully appeared, Press CTRL+C and CTRL+V to copy and paste the information into Notepad or any other text editor.
As you can see in the above image, the information in the brackets refers to the name of the program that is using an open TCP or UDP port. Next to the protocol name, you can see the IP address and the port number after the colon. For example, in 192.168.0.107: 50741, the numbers 192.168.0.107 are the IP address, while the number 50741 is the port number.
Read: How to check what Ports are open?
Finding a blocked TCP or UDP port
To know which of the ports are blocked by Windows Firewall, follow the next steps.
The first step is the same as finding an open TCP or UDP port. Open Start Menu by pressing the Windows button and type CMD. Now click on Run as Administrator option.
When the Command Prompt window opens, type following command: netsh firewall show state

Some ports may be blocked by the router or ISP and those may not be listed in the above list. To find those ports, type the following command: netstat -ano | findstr -i SYN_SENT

If this command doesn’t return any list, it means none of the ports are blocked by the router or ISP.
How to open or block a TCP or UDP port
Now since you have identified the TCP and UDP ports on your Windows PC, here comes the most important part.
First of all, you may need to open a port for an application to run smoothly. On the other hand, you may need to block certain ports as they are no longer being used and may pose as a gateway for threats. Hence, such ports are blocked by the firewall.
Follow the next steps to open or block a TCP or UDP port.
Open the Start Menu by pressing the Windows-key. Type Windows Defender Firewall, and select Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security from the results.

The following window opens.

Click on the Inbound Rules tab on the left side menu.

Click on the New Rule… tab from the Actions pane on the right side menu. When this window opens, select the Port radio button and click Next.

When pressed Next tab, the following window of New Inbound Rule Wizard opens. In this window, you can select the type of port you want to open or block. You can also select whether you want to open or block all the ports of the selected type or a specific local port. Specify the number or a range of the local ports that you wish to open or block. And click Next.

The following window opens when you click Next. Here you can open the ports by selecting Allow the connection or Allow the connection if it is secure radio buttons. Select the third radio button Block the connection to block the specified ports.

Now select whether the rule applies to Domain, Private or Public or all of these. Click Next.

The following window opens when you click Next. In this window, specify a Name for this new Inbound Rule. You can also specify which ports have been blocked or opened in the Description section.

Click Finish to create this new Inbound Rule.
Please note that sometimes after blocking a certain port, apps may not work properly. You may also face issues while connecting to certain resources. This means the port you blocked may be required to be open. You can undo the blocking of ports at any time following the same process.
Read next: How to monitor TCP, UDP Communication in Windows with PortExpert.












