如果您的大多数员工都在家工作,那么将他们升级到Windows 10 功能更新(Feature Update)将是一项具有挑战性的任务。这些计算机不会在 IT 人员身边解决问题。在这种独特的情况下,您需要一种可以帮助您顺利部署Windows 10更新的策略。(Windows 10)
微软(Microsoft)提供了一项战略,公司可以遵循推出Windows 10 v2004 2004 年 5 月更新(Windows 10 v2004 May 2004 Update)。事实上,如果时间需要,任何功能更新都可以遵循它。让我们看一下微软建议的远程Windows 10功能更新部署(Feature Update Deployment Remotely)计划(Plan)。
远程规划 Windows 10 功能更新部署(Update Deployment)
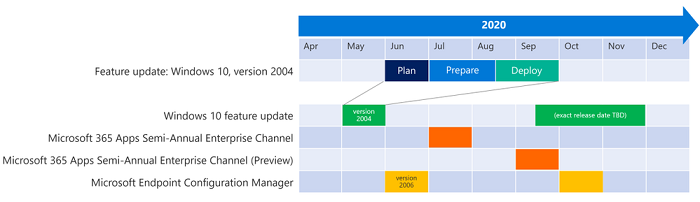
分三个阶段 -计划、准备和部署(Plan, Prepare, and Deploy)- 业务 IT 部门可以通过 Internet 安全地部署Windows 更新(Windows Update)。很明显,必须使用Configuration Manager或Windows Update for Business才能完成此操作。下面的日历显示了在整个组织中推出Windows 10版本 2004 的潜在时间表。(Windows 10)请注意,它与Microsoft 365 应用(Apps)和Configuration Manager发布周期保持一致。
第一阶段:计划(六月)
规划有四个部分——现代化、兼容性、部署和能力。(Modernizing, Compatibility, Deployment, and Capability.)
现代化应确保 Windows 可以安全部署,VPN 配置(VPN configuration)更改、桌面分析(Desktop Analytics)、共同管理(Co-management)将需要与适用于企业的(Business)Windows 更新(Windows Update)一起使用。其次是兼容性(Compatibility)规划,IT 必须列出远程工作人员使用的应用程序,并确定哪些应用程序对功能更新测试至关重要,哪些可以正常工作。
接下来是部署计划(Deployment Planning),团队必须准备好部署的所有最低要求。这包括最新版本的Configuration Manager、InTune和Windows Update for Business。您还需要更新管理模板、安全基线等。
这一阶段的最后一部分是 能力规划(Capability Planning),每个人都应该了解随最新更新发布的一组新功能,并且应该能够找到如何使用组策略(Group Policy)、注册表(Registry)甚至PowerShell 命令(PowerShell Commands)来更改它。
第 2 阶段:准备(7 月/8 月)
它分为三个准备部分——兼容性、部署和能力(Compatibility, Deployment, and Capability)。所有这些都是对第一阶段(Phase)计划的扩展。
从兼容性(Compatibility)准备开始,建议测试所有列出的应用程序,尤其是那些对工作至关重要的应用程序。主要想法是弄清楚如何测试,以及如何将测试扩展到试点组。这就是桌面(Desktop) 分析(Analytics)将为您提供见解并为修复做准备并执行更多测试的地方。可以有多种测试方法,包括使用桌面分析来创建一个试验组设备来验证应用程序和驱动程序。
部署准备(Deployment Preparation)的重点是基础架构升级(如有必要)和配置以支持新的Windows 10 功能(Feature)更新和远程工作人员。强烈建议进行试点测试,以清楚地了解最终部署开始时流程将如何形成。要遵循的步骤是更新配置管理器(Configuration Manager)、将新配置应用到试验设备、延迟创建Windows 10基础映像,然后准备适用于企业的(Business)Windows 更新(Windows Update)。
这一阶段的最后一部分是关于能力(Cabapility)准备。在这里,您可以将新功能映射到工作角色,并向试点用户提供通信以展示已知的新功能。
第 3 阶段:部署(8 月/9 月)
这里只有两个阶段——试点和广泛部署(Pilot and Broad Deployment)。这里有趣的是部署方法。它不使用任何红色(Red)按钮将更新推送到所有设备——相反,它是一种防止更新自动进入下一个环的拉式方法。
建议在 8 月开始试点阶段,基于(August)准备(Pilot)阶段准备好的配置和基础设施(Preparation Phase)。使用适用于企业的(Business)Windows 更新(Windows Update),以最小的更新包大小和最低的延迟发送更新。这就是为什么VPN配置是必要的,并且建议采用更基于云的方法,而不是将这些计算机锁定到公司网络。
试点阶段(Pilot Phase)至关重要,建议通过从分析工具获取反馈和数据来密切监控试点设备。如果事情不顺利,可以立即使用Windows 10 Rollback 。
最后一部分是您进行广泛部署(Broad Deployment)的地方,具体取决于试点部署的成功程度。你可以使用部署环,适用于企业的(Business)Windows 更新(Windows Update)将继续推送更新。为了加快部署,微软(Microsoft)建议扩展配置和策略,强制更新的合规期限,制定广泛的部署计划,密切关注支持请求,创建基线映像,自动驾驶以将新设备部署到远程工作,并记录体验。
推出Windows 10 功能更新对(Feature)企业(Businesses)来说是一场不同的比赛。有很多因素需要照顾和仔细计划,以确保不会出现大规模故障。IT 管理员必须记录所有内容,以便下次必须再次执行此操作时有所帮助。
请务必通过官方网站(official website)了解有关此过程的更多详细信息。
How to plan Windows 10 Feature Update Deployment Remotely
If most of your employеes are working from home, then upgrаding them to the Windows 10 Feature Update iѕ going to be a challenging task. Those computers won’t be arоund the IT ѕtaff physically to fix the problems. In this unique situation, you neеd a strategy that cаn help you deploy Windows 10 Uрdates smoothly.
Microsoft has offered a strategy that companies can follow to roll out the Windows 10 v2004 May 2004 Update. In fact, it can be followed for any feature update if the time demands. Let’s take a look at the Microsoft’s suggested Plan for Windows 10 Feature Update Deployment Remotely.
Plan Windows 10 Feature Update Deployment Remotely
Laid out in three phases—Plan, Prepare, and Deploy—Business IT department can follow to deploy Windows Update securely through the internet. It is rather obvious that one will have to use Configuration Manager or Windows Update for Business to complete this. The calendar below shows a potential timeline for rolling out Windows 10, version 2004, across the organization. Note that it is aligned with Microsoft 365 Apps and Configuration Manager release cycles.

Phase 1: Plan (June)
There are four parts of planning—Modernizing, Compatibility, Deployment, and Capability.
Modernizing should make sure Windows can be deployed securely, VPN configuration changes, Desktop Analytics, Co-management will be needed along with Windows Update for Business. Followed by this is Compatibility planning where IT will have to make a list of applications used by remote workers, and figure out which of them are critical to be tested with feature update, and which will work just fine.
Next comes Deployment Planning, where the team has to be ready with all minimum requirements for deployment. That includes the latest version of Configuration Manager, InTune, and Windows Update for Business. You will also need to update Administrative templates, security baselines, and so on.
The last part of this phase is Capability Planning, where everyone should know about the set of new features released with the latest update and should be able to find how to change it using Group Policy, Registry, and even PowerShell Commands.
Phase 2: Prepare (July/August)
It is divided into three preparation parts—Compatibility, Deployment, and Capability. All these are extensions to what was planned in the first Phase.
Starting with Compatibility preparation, it is advised to test all listed applications, especially those which are critical to work. The primary idea is to figure out how to test, and how to expand testing to a pilot group. That’s where the Desktop Analytics will give you insights and prepare for fixes and perform even more testing. There can be multiple approaches to testing, including the use of Desktop Analytics to create a pilot group of devices to validate apps and drivers.
Deployment Preparation is next to where the focus is need of infrastructure upgrade (if necessary), and configuration to support new Windows 10 Feature update and remote workers. It is highly recommended to pilot test to clearly understand how the process will take its shape when finally deployment starts. The steps to be followed are updating Configuration Manager, applying a new configuration to pilot devices, delay creation of Windows 10 base image, and then prepare for Windows Update for Business.
The last section in this phase is about Cabapility preparation. Here you can map new features to worker roles, and provide communications to pilot users to showcase known new features.
Phase 3: Deploy (August/September)
There are only two phases here—Pilot and Broad Deployment. What is interesting here is the approach to deployment. It does not use any Red button to push updates down to all devices—instead, its a pull approach to preventing the update from automatically going to the next ring.
The Pilot phase is recommended to start in August, where based on the prepared configuration and infrastructure from the Preparation Phase. Using Windows Update for Business, updates are sent out in the smallest update package size, and lowest latency. That is why the VPN configuration was necessary, and a more cloud-based approach was suggested instead of locking those computers to the corporate network.
Pilot Phase is critical, and it is recommended to monitor the pilot devices closely by taking feedback, data from the analytics tool. If things go south, Windows 10 Rollback can be used immediately.
The last part is where you go ahead for Broad Deployment, depending on how successful the pilot deployment. You can use deployment rings, and Windows Update for Business will continue to push updates. To accelerate deployment, Microsoft recommends to expand configuration and policies, enforce compliance deadline for the update, create broad deployment plans, keep a tab on support requests, creation of baseline image, autopilot to deploy new devices to remote works, and document the experience.
Rollout out Windows 10 Feature update is a different ballgame for Businesses. There are a lot of factors that need to be taken care of and carefully planned to make sure there is no massive breakdown. It is essential that IT admins document everything, so it helps the next time one has to do it again.
Make sure to go through the official website for more details on this process.

