什么是性能监视器? (What is Performance Monitor? )很多时候,我们的计算机只是停止响应、意外关闭或行为异常。这种行为可能有多种原因,指出确切原因可能会有很大帮助。Windows有一个名为Performance Monitor的工具,您可以将其用于此目的。使用此工具,您可以检查系统性能并确定不同程序如何影响系统性能。您可以分析与您的处理器、内存、网络、硬盘驱动器等相关的数据。它可以告诉您如何管理系统资源以及其他可能对您有用的配置信息。它还可以收集和记录文件中的数据,以便以后进行分析。继续阅读以了解如何使用性能监视器可修复(Performance Monitor)Windows 10中与性能相关的问题。

如何打开性能监视器(How to open Performance Monitor)
您可以使用Windows 10上的性能监视器(Performance Monitor)来分析数据并检查系统的性能,但首先,您必须知道如何打开此工具。打开Windows 性能监视器(Windows Performance Monitor)的方法有很多种,我们来看看其中的几种:
- 在任务栏上的搜索字段中键入“性能监视器(performance monitor)”。
- 单击性能监视器(Performance Monitor)快捷方式将其打开。

要使用Run打开性能监视器(Performance Monitor),
- 按 Windows 键 + R 打开运行。
- 键入perfmon并单击确定。

要使用控制面板(Control Panel)打开性能监视器(Performance Monitor),
- 使用任务栏上的搜索字段打开控制面板。(Control panel.)
- 单击“系统和安全(System and Security)”,然后单击“管理工具(Administrative tools)”。

- 在新窗口中,单击“性能监视器(Performance Monitor)”。

如何在 Windows 10 中使用性能监视器(How to Use Performance Monitor in Windows 10)
确保 创建一个还原点(create a restore point) 以防万一出现问题。
当您第一次打开性能监视器(Performance Monitor)时,您将看到概述和系统摘要。(overview and system summary.)
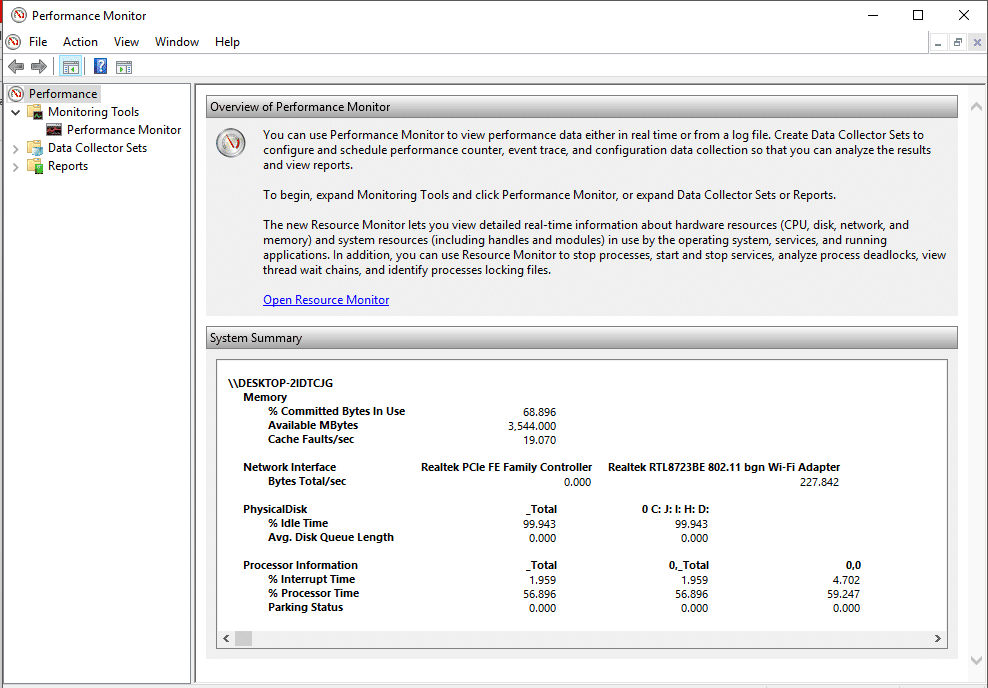
现在,从左侧窗格中,选择“监视工具(Monitoring Tools)”下的“性能监视器(Performance Monitor)”。您在此处看到的图表是过去 100 秒的处理器时间。水平轴显示时间,垂直轴显示处理器在活动程序上工作所消耗的时间百分比。

除了“处理器时间(Processor Time)”计数器,您还可以分析许多其他计数器。
如何在性能监视器下添加新计数器(How to add new counters under Performance Monitor)
1.单击图表顶部的绿色加号图标。(green plus shaped icon)
2.添加计数器窗口将打开。(Add Counters window will open.)
3.现在,在“从计算机中选择计数器(Select counters from computer)”下拉菜单中选择您的计算机名称(select the name of your computer)(通常是本地计算机) 。

4.现在,扩展您想要的计数器类别,例如处理器。(Processor.)
5.从列表中选择一个或多个计数器。( one or more counters)要添加多个计数器,请选择第一个计数器(select the first counter),然后在选择计数器时按下Ctrl 键(Ctrl key)。

6.如果可能,选择所选对象的实例。(instances of the selected object(s))
7.单击添加按钮(Add button)添加计数器。添加的计数器将显示在右侧。

8.点击确定确认。
9.您将看到新的计数器开始( new counters start)以不同的颜色出现在图表中。(graph with different colors.)

10.每个计数器的详细信息将显示在底部,例如与其对应的颜色、其比例、实例、对象等。(like which colors correspond to it, its scale, instance, object, etc.)
11.使用每个复选框(checkbox)来对抗以在图表中显示或隐藏(show or hide)它。
12.您可以按照上面给出的相同步骤添加更多计数器。(add more counters)
添加所有所需的计数器后,就可以自定义它们了。
如何在性能监视器中自定义计数器视图(How to Customize the Counter View in Performance Monitor)
1.双击图表下方的任何计数器。
2.若要选择多个计数器,请在选择计数器的同时按住Ctrl 键(Ctrl key)。然后右键单击(right-click)并从列表中选择属性。(Properties)
3.性能监视器(Monitor) 属性(Properties)窗口将打开,从那里切换到“数据(Data)”选项卡。
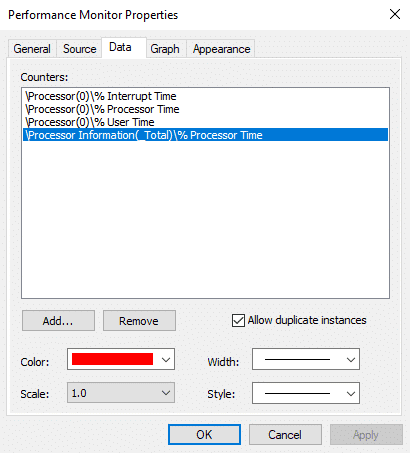
4.在这里您可以选择计数器的颜色、比例、宽度和样式。(select the color, scale, width, and style of the counter.)
5.单击应用,然后单击确定。
这里需要注意的重要一点是,当您重新启动性能监视器时,所有这些设置的计数器和配置都将默认丢失(all these set counters and configurations will be lost by default)。要保存这些配置,请右键单击(right-click)图表并(graph)从菜单中选择“将设置另存为”。(Save settings as)

键入所需的文件名,然后单击Save。该文件将保存为.htm 文件(.htm file)。保存后,有两种方法可以加载保存的文件以供以后使用,
- 右键单击(Right-click)保存的文件并选择Internet Explorer作为“打开方式”程序。
- 您将能够在 Internet Explorer 窗口中看到性能监控图。(see the performance monitor graph)
- 如果您还没有看到图表,请单击弹出窗口中的“允许阻止的内容(Allow blocked content)”。

另一种加载方法是粘贴计数器列表。但是,此方法可能不适用于某些用户。
- 使用记事本打开保存的文件并复制其内容。(copy its contents.)
- 现在使用前面给出的步骤打开性能监视器(Performance Monitor),然后单击图表顶部的“粘贴计数器列表(Paste Counter list)”图标。
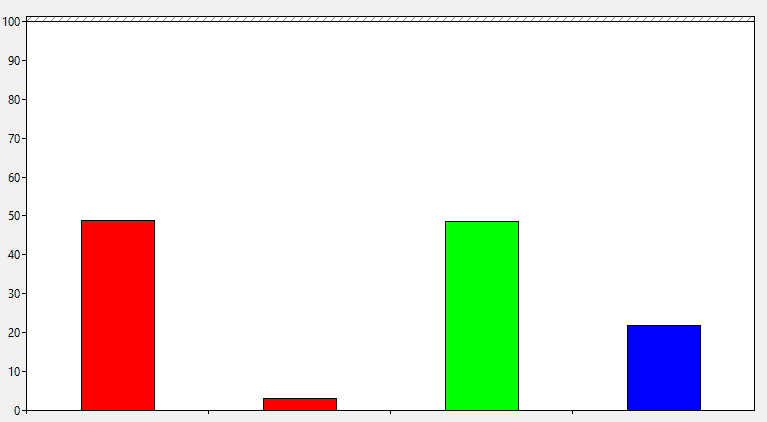
图表上方的第三个图标用于更改图表类型。单击(Click)其旁边的向下箭头以选择图形类型。您可以从线条、直方图条或报告中进行选择。( line, histogram bar or report.)您也可以按Ctrl + G在图表类型之间切换。上面显示的屏幕截图对应于折线图。直方图条如下所示:
报告将如下所示:

如果您想分析它,工具栏上的暂停按钮(pause button)将允许您在任何情况下冻结不断变化的图形。(freeze the constantly changing graph)您可以通过单击播放按钮恢复。( play button.)
一些常见的性能计数器(Some Common Performance Counters)
处理器:(Processor:)
- % Processor Time:这是处理器执行非空闲线程所花费的时间百分比。如果这个百分比一直保持在 80% 以上,这意味着你的处理器很难处理所有的进程。
- % 中断时间:这是您的处理器接收和服务硬件请求或中断所需的时间。如果此时间超过 30%,则可能存在一些与硬件相关的风险。
记忆:(Memory:)
- % Committed Bytes In Use:此计数器显示您的RAM当前正在使用或已提交的百分比。这个计数器应该随着不同程序的打开和关闭而波动。但如果它继续增加,则可能存在内存泄漏。
- 可用字节(Bytes):此计数器描述可用于立即将其分配给进程或系统的物理内存量(以字节为单位)。(Bytes)少于 5% 的可用字节意味着您的可用内存非常少,可能需要添加更多内存。
- 缓存(Cache)字节:此计数器跟踪当前在物理内存中处于活动状态的系统缓存部分。
分页文件:(Paging File:)
- % Usage:这个计数器告诉当前页面文件正在使用的百分比。它不应高于 10%。
物理磁盘:(PhysicalDisk:)
- % Disk Time:此计数器监控驱动器处理读取和写入请求所花费的时间。这不应该太高。
- Disk Read Bytes/sec:此计数器映射在读取操作期间从磁盘传输字节的速率。
- Disk Write Bytes/sec:此计数器映射在写入操作期间将字节传输到磁盘的速率。
网络接口:(Network Interface:)
- Bytes Received/sec:它表示通过每个网络适配器接收的字节速率。
- Bytes Sent/sec:它表示通过每个网络适配器发送的字节速率。
- Bytes Total/sec:它包括Bytes Received和Bytes Sent。
如果此百分比介于 40%-65% 之间,则应谨慎。对于超过 65% 的情况,性能将受到不利影响。
线:(Thread:)
- % Processor Time:它跟踪单个线程使用的处理器工作量。
有关详细信息,您可以访问Microsoft 网站(Microsoft website)。
如何创建数据收集器集(How to Create a Data Collector Sets)
数据收集器集是一个或多个性能计数器的组合,(combination of one or more performance counters)可以保存这些计数器以在一段时间内或按需收集数据。当您想要在指定时间段内(例如,每个月)监控系统组件时,这些功能特别有用。有两个可用的预定义集,
系统诊断:(System Diagnostics:)此数据收集器集可用于解决与驱动程序故障、硬件故障等相关的问题。它包括从系统性能(System Performance)收集的数据以及其他详细的系统信息。
系统性能:(System Performance:)此数据收集器集可用于处理与性能相关的问题,例如计算机速度慢。它收集与内存、处理器、磁盘、网络性能等相关的数据。
要访问这些,请在性能监视器(Performance Monitor)窗口的左窗格中展开“数据收集器集(Data Collector Sets)”,然后单击系统。(System.)

要在性能监视器中创建自定义数据收集器集,(To Create a Custom Data Collector Set in Performance Monitor,)
1.在性能监视器(Performance Monitor)窗口的左窗格中展开“数据收集器集”。(Data Collector Sets)
2.右键单击“用户定义(User Defined)”,然后选择“新建”(New)并单击“数据收集器集(Data Collector Set)”。

3. 键入集合的名称并选择“手动创建(高级)(Create manually (Advanced)) ”,然后单击下一步。(Next.)

4.选择“创建数据日志(Create data logs)”选项并选中(check)“性能计数器(Performance counter)”复选框。

5. 单击下一步(Next),然后单击添加。( Add.)

6.选择您想要的一个或多个计数器(one or more counters),然后单击添加(Add),然后单击确定。(OK.)
7.设置采样间隔(Set the sample interval),以决定性能监视器(Performance Monitor)何时采样或收集数据,然后单击下一步。( Next.)

8.设置要保存的位置,(Set the location where you want it to be saved)然后单击下一步。(Next.)

9.选择您想要的特定用户(Select a specific user)或保持默认。
10.选择“保存并关闭(Save and Close)”选项并单击“完成”。(Finish.)

该集将在数据收集器集的用户定义部分中可用。( User Defined section)

右键单击该集( set)并选择“开始( Start)”以启动它。
要自定义数据收集器集的运行持续时间,(To customize the run duration for your data collector set,)
1.右键单击您的数据收集器集并选择属性。(Properties.)
2.切换到“停止条件(Stop condition)”选项卡并选中“总持续时间(Overall duration)”复选框。
3.键入(Type the time duration)您希望性能监视器(Performance Monitor)运行的持续时间。

4.设置其他配置,然后单击应用(Apply),然后单击确定。
要安排设置自动运行,(To schedule the set to run automatically,)
1.右键单击您的数据收集器集并选择属性。(Properties.)
2.切换到“计划(Schedule)”选项卡,然后单击添加。
3.设置您想要的时间表(Set the schedule),然后单击“确定”。

4.单击应用(Apply),然后单击确定。
如何使用报告分析收集的数据(How to Use Reports to Analyse Collected Data)
您可以使用报告来分析收集的数据。您可以为预定义的数据收集器集和自定义集打开报告。要打开系统报告,
- 从性能监视器(Performance Monitor)窗口的左窗格中展开“报告”。(Reports)
- 单击系统( System),然后单击系统诊断或系统性能(System Diagnostics or System Performance)以打开报告。
- 您将能够看到组织和结构化成表格的数据和结果,您可以使用这些表格快速识别问题。

要打开自定义报告,(To open a custom report,)
- 从性能监视器(Performance Monitor)窗口的左窗格中展开“报告”。(Reports)
- 单击用户定义(User Defined),然后单击您的自定义报告。(custom report.)
- 在这里,您将直接看到记录的数据,而不是结果和结构化数据。(recorded data directly instead of results and structured data.)

使用性能监视器(Performance Monitor),您可以轻松地对系统的几乎每个部分进行分析。
受到推崇的:(Recommended:)
我希望这篇文章对您有所帮助,您现在可以轻松地 在 Windows 10 上使用性能监视器( Use Performance Monitor on Windows 10),但如果您对本教程仍有任何疑问,请随时在评论部分提出。
How to Use Performance Monitor on Windows 10 (Detailed GUIDE)
What is Performance Monitor? Many times it occurs that our computer just ceases to respond, shuts down unexpectedly or behaves abnormally. There could be a number of reasons for such behavior and pointing out the exact reason could be of great help. Windows has a tool named Performance Monitor, which you can use for this purpose. With this tool, you can keep a check on the performance of your system and identify how different programs affect the system performance. You can analyze data related to your processor, memory, network, hard drive, etc. It can tell you how the system resources are managed and other configuration information that might be useful for you. It can also collect and log the data in files, which can be analyzed later. Read on to see how you can use Performance Monitor to fix performance related issues in Windows 10.

How to open Performance Monitor
You can use Performance Monitor on Windows 10 to analyze data and keep a check on the performance of your system, but first, you must know how to open this tool. There are many ways to open the Windows Performance Monitor, let’s see a few of them:
- Type “performance monitor” in the search field located on your taskbar.
- Click on the Performance Monitor shortcut to open it.

To open Performance Monitor using Run,
- Press Windows key + R to open Run.
- Type perfmon and click on OK.

To open Performance Monitor using Control Panel,
- Use the search field on your taskbar to open the Control panel.
- Click on ‘System and Security’ then click on ‘Administrative tools’.

- In the new window, click on ‘Performance Monitor’.

How to Use Performance Monitor in Windows 10
Make sure to create a restore point just in case something goes wrong.
When you first open Performance Monitor, you will see the overview and system summary.

Now, from the left pane, select ‘Performance Monitor’ under ‘Monitoring Tools’. The graph you see here is the processor time over last 100 seconds. The horizontal axis displays time and the vertical axis displays the percentage of time your processor consumes working on the active programs.

Apart from the ‘Processor Time’ counter, you can also analyze many other counters.
How to add new counters under Performance Monitor
1.Click on the green plus shaped icon on top of the graph.
2.The Add Counters window will open.
3.Now, select the name of your computer (usually it is a local computer) in the ‘Select counters from computer’ drop-down menu.

4.Now, expand the category of counters you want, say Processor.
5.Select one or more counters from the list. To add more than one counters, select the first counter, then press down the Ctrl key while selecting the counters.

6.Select the instances of the selected object(s) if possible.
7.Click on Add button to add the counters. The added counters will be shown on the right side.

8.Click on OK to confirm.
9.You will see that the new counters start to appear in the graph with different colors.

10.The details of each counter will be shown at the bottom, like which colors correspond to it, its scale, instance, object, etc.
11.Use the checkbox against each to counter to show or hide it from the graph.
12.You can add more counters by following the same steps as given above.
Once you have added all the desired counters, it is time to customize them.
How to Customize the Counter View in Performance Monitor
1.Double-click on any counter below the graph.
2.To select more than one counters, press down Ctrl key while selecting the counters. Then right-click and select Properties from the list.
3.Performance Monitor Properties window will open, from there switch to the ‘Data’ tab.

4.Here you can select the color, scale, width, and style of the counter.
5.Click on Apply followed by OK.
An important thing to note here is that when you restart performance monitor, all these set counters and configurations will be lost by default. To save these configurations, right-click on the graph and select ‘Save settings as’ from the menu.

Type the desired file name and click on Save. The file will be saved as a .htm file. Once saved, there are two ways of loading the saved file for later use,
- Right-click on the saved file and select Internet Explorer as the ‘Open with’ program.
- You will be able to see the performance monitor graph in the internet explorer window.
- If you don’t see the graph already, click on ‘Allow blocked content’ in the popup.

Another way to load it is by pasting counter list. However, this method may not work for some of the users.
- Open the saved file using notepad and copy its contents.
- Now open Performance Monitor by using the steps given before and click on ‘Paste Counter list’ icon on top of the graph.
The third icon above the graph is for changing graph type. Click on the downward arrow beside it to select the type of graph. You can choose from line, histogram bar or report. You can also press Ctrl + G to switch between the graph types. The screenshots shown above correspond to the line graph. The histogram bar looks like this:

The report will look like this:

The pause button on the toolbar will allow you to freeze the constantly changing graph at any instance, if you want to analyze it. You can resume by clicking on the play button.
Some Common Performance Counters
Processor:
- % Processor Time: This is the percentage of time spent by the processor in executing a non-idle thread. If this percentage stays over 80% constantly, it means it is difficult for your processor to handle all the processes.
- % Interrupt Time: This is the time required by your processor to receive and service hardware requests or interrupts. If this time exceeds 30%, there might be some hardware related risk.
Memory:
- % Committed Bytes In Use: This counter shows what percentage of your RAM is currently in use or is committed. This counter should fluctuate values as different programs are opened and closed. But if it keeps on increasing, there might be a memory leak.
- Available Bytes: This counter depicts the amount of physical memory (in Bytes) that are available for immediately allocating it to a process or system. A less than 5% of available bytes means you have very less memory free and may need to add more memory.
- Cache Bytes: This counter tracks the part of system cache which is currently active in physical memory.
Paging File:
- % Usage: This counter tells the percentage of current pagefile in use. It should not be higher than 10%.
PhysicalDisk:
- % Disk Time: This counter monitors the time taken by a drive to process read and write requests. This should not be too high.
- Disk Read Bytes/sec: This counter maps the rate at which bytes are transferred from the disk during the read operations.
- Disk Write Bytes/sec: This counter maps the rate at which bytes are transferred to the disk during write operations.
Network Interface:
- Bytes Received/sec: It represents the rate of bytes being received over each network adapter.
- Bytes Sent/sec: It represents the rate of bytes being sent over each network adapter.
- Bytes Total/sec: It includes both Bytes Received and Bytes Sent.
If this percentage lies between 40%-65%, you should be cautious. For over 65%, the performance will be adversely affected.
Thread:
- % Processor Time: It tracks the amount of processor’s effort which is used by an individual thread.
For more information, you can go to the Microsoft website.
How to Create a Data Collector Sets
A data collector set is a combination of one or more performance counters which can be saved to collect data over a period of time or on demand. These are especially useful when you want to monitor a component of your system over a specified time period, for instance, every month. There are two predefined sets available,
System Diagnostics: This data collector set can be used troubleshooting issues related to driver failures, faulty hardware, etc. It includes data collected from System Performance along with other detailed system information.
System Performance: This data collector set can be used to handle performance related issues like a slow computer. It collects data related to memory, processor, disk, network performance, etc.
To access these, expand ‘Data Collector Sets’ in the left pane on Performance Monitor window and click on System.

To Create a Custom Data Collector Set in Performance Monitor,
1.Expand ‘Data Collector Sets’ in the left pane on Performance Monitor window.
2.Right-click on ‘User Defined’ then select New and click on ‘Data Collector Set’.

3.Type a name for the set and select ‘Create manually (Advanced)’ and click on Next.

4.Select ‘Create data logs’ option and check the ‘Performance counter’ checkbox.

5.Click Next then click on Add.

6.Select one or more counters you want then click on Add and then click OK.
7.Set the sample interval, to decide when the Performance Monitor takes samples or collects data and click on Next.

8.Set the location where you want it to be saved and click on Next.

9.Select a specific user you want or keep it default.
10.Select ‘Save and Close’ option and click on Finish.

This set will available in the User Defined section of the Data Collector Sets.

Right-click on the set and select Start to start it.

To customize the run duration for your data collector set,
1.Right-click on your data collector set and select Properties.
2.Switch to ‘Stop condition’ tab and check the ‘Overall duration’ checkbox.
3.Type the time duration for which you want Performance Monitor to run.

4.Set other configurations then click on Apply followed by OK.
To schedule the set to run automatically,
1.Right-click on your data collector set and select Properties.
2.Switch to ‘Schedule’ tab then click on Add.
3.Set the schedule you want then click on OK.

4.Click on Apply and then click on OK.
How to Use Reports to Analyse Collected Data
You can use reports to analyze the data collected. You can open reports for both predefined data collector sets and your custom sets. To open system reports,
- Expand ‘Reports’ from the left pane of the Performance Monitor window.
- Click on System then click on System Diagnostics or System Performance to open the report.
- You will be able to see the data and results organized and structured into tables that you can use to quickly identify problems.

To open a custom report,
- Expand ‘Reports’ from the left pane of the Performance Monitor window.
- Click on User Defined then click on your custom report.
- Here you will see the recorded data directly instead of results and structured data.

Using Performance Monitor, you can carry out the analysis for almost every part of your system easily.
Recommended:
I hope this article was helpful and you can now easily Use Performance Monitor on Windows 10, but if you still have any questions regarding this tutorial then feel free to ask them in the comment’s section.






























