您是否曾经需要无限期地离开计算机但又不想将其关闭?这可能有多种原因;也许您有一些工作希望在午休后或您的 PC 像蜗牛一样启动后立即回到工作中。Windows 操作系统(Windows OS)中的睡眠模式可以让你做到这一点,但如果我告诉你有比通常的睡眠模式更好的省电功能呢?
休眠(Hibernation)模式是一种电源选项,可让 Windows 用户利用完全系统关闭和睡眠模式的功能。就像(Just)Sleep一样,用户可以配置他们希望他们的系统何时进入休眠(Hibernation)状态,如果他们愿意,也可以完全禁用该功能(尽管保持它处于活动状态确实可以获得更好的整体体验)。
在本文中,我们将解释睡眠和休眠模式之间的区别,并向您展示如何在Windows 10上启用或禁用休眠。
什么是冬眠?(What is Hibernation?)
休眠是一种主要用于笔记本电脑的省电状态,尽管它也适用于某些计算机。它在电源使用情况和您当前打开的位置(在您离开系统之前)方面与睡眠不同;(Sleep)文件被保存。
当您离开计算机而不关闭计算机时,默认情况下会激活睡眠模式。在睡眠状态下,屏幕关闭,所有前台进程(文件和应用程序)都保存在内存(RAM)中。这允许系统处于低功耗状态但仍在运行。您可以通过单击键盘或移动鼠标重新开始工作。屏幕将在几秒钟内启动,您的所有文件和应用程序将处于与您离开时相同的状态。
Hibernation与(Hibernation)Sleep非常相似,它还保存文件和应用程序的状态,并在您的系统长时间处于睡眠(Sleep)状态后激活。与将文件存储在RAM中并因此需要恒定电源的Sleep不同, (Sleep)Hibernation不需要任何电源(例如当您的系统关闭时)。这可以通过将文件的当前状态存储在硬盘驱动器(hard drive)而不是临时存储器中来实现。
当处于长时间睡眠状态时,您的计算机会自动将文件状态传输到硬盘驱动器并切换到休眠(Hibernation)状态。由于文件已被移动到硬盘驱动器,系统(System)将需要比Sleep所需的额外时间来启动。虽然,按时启动仍然比完全关机后启动计算机要快。
(Hibernation)当用户不想丢失他/她的文件状态但又没有机会为笔记本电脑充电一段时间时,休眠特别有用。
很明显,保存文件的状态需要保留一些内存,而这个内存被系统文件 (hiberfil.sys) 占用。预留量大致等于75% of the System’s RAM。例如,如果您的系统(System)安装了8 GB 的RAM,则休眠系统文件将占用将近 6 GB 的硬盘存储空间。
在我们继续启用休眠(Hibernation)之前,我们需要检查计算机是否有 hiberfil.sys 文件。如果不存在,计算机将无法进入休眠状态(装有(Hibernation)InstantGo的PC没有休眠电源选项)。
要检查您的计算机是否可以休眠,请按照以下步骤操作:
1. 通过双击桌面上的图标或按键盘快捷键Windows Key + E. Click启动文件资源管理器(Launch File Explorer)。单击本地驱动器(Local Drive)(C:) 打开 C 驱动器(open C Drive)。
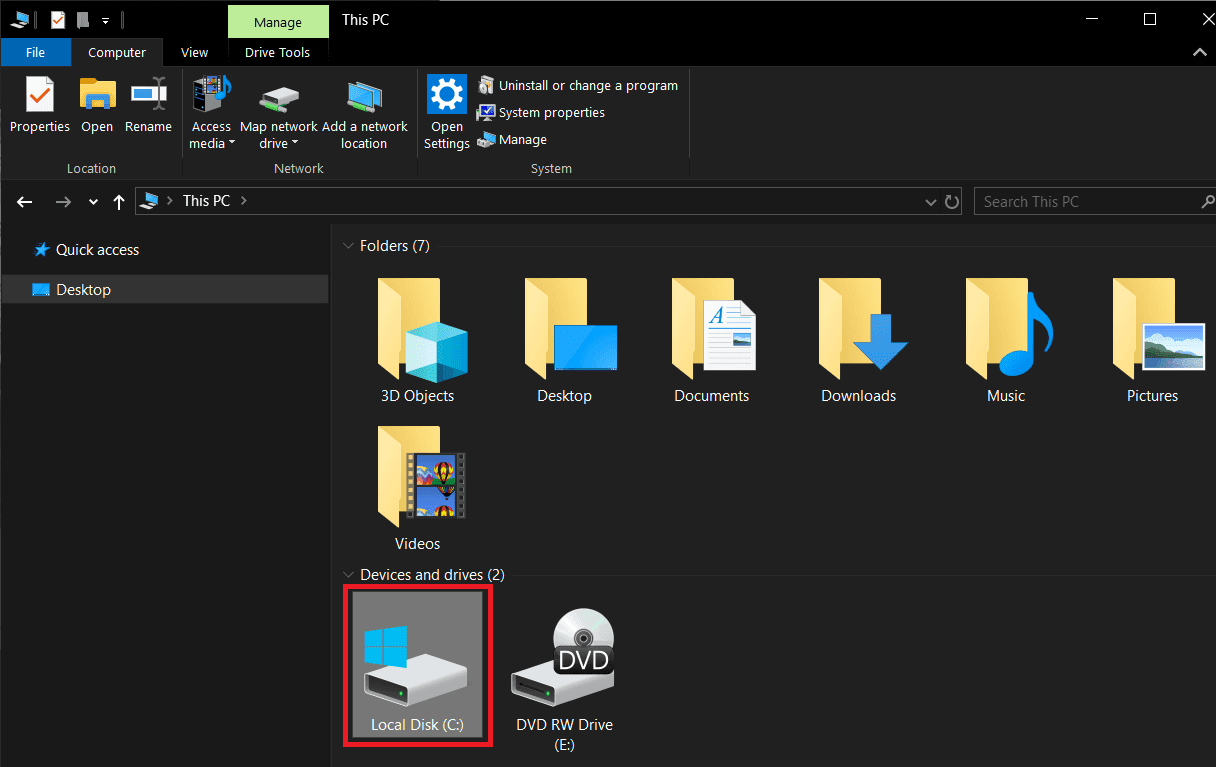
2. 切换到视图 (View )选项卡并单击 功能区末尾的选项 。(Options )选择 “更改文件夹和搜索选项”。(‘Change folder and search options’.)
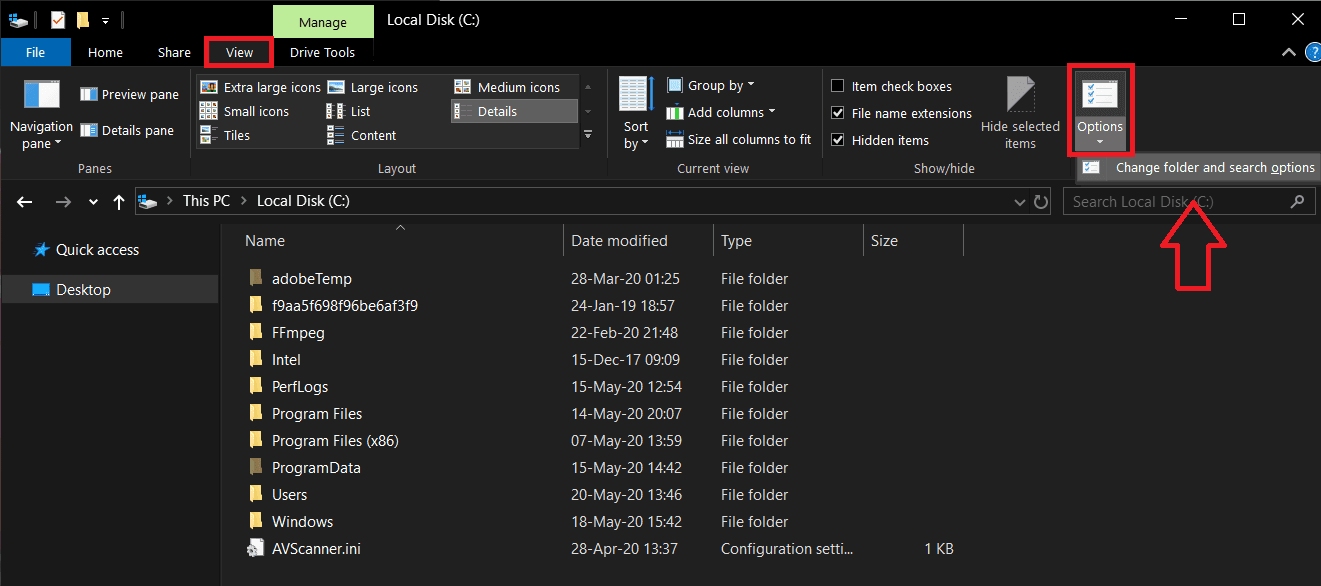
3. 再次切换到“文件夹选项”窗口的“查看” 选项卡。(View )
4. 双击 隐藏文件和文件夹( Hidden files and folders) 打开子菜单并 启用显示隐藏文件、文件夹或驱动器。(enable Show hidden files, folders, or drives.)
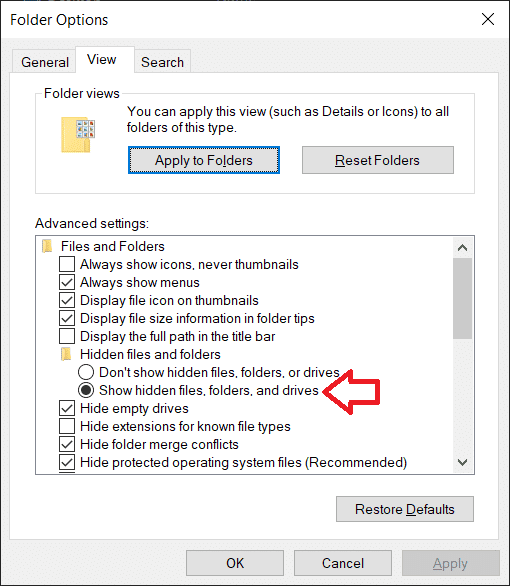
5.Uncheck/untick “隐藏受保护的操作系统文件(推荐)”( ‘Hide protected operating system files (Recommended).’)旁边的框。 当您尝试取消选中该选项时,将出现一条警告消息。单击(Click)“ 是” (Yes )以确认您的操作。

6. 单击应用 (Apply ),然后 单击确定 (OK )以保存更改。

7. 休眠文件 ( hiberfil.sys ),如果存在,可以在C 驱动器(C drive)的根目录中找到。这意味着您的计算机可以休眠。(This means your computer is eligible for hibernation.)

如何在 Windows 10 上启用或禁用休眠?(How to Enable or Disable Hibernation on Windows 10?)
启用或禁用休眠(Hibernation)非常简单,任何一个操作都可以在几分钟内完成。还有多种方法可以启用或禁用休眠(Hibernation)。最简单的方法是在提升的命令提示符下执行单个命令,而其他方法包括编辑Windows 注册表编辑器(Windows Registry Editor)或访问高级电源选项。
方法 1:使用命令提示符(Command Prompt)启用或禁用休眠(Hibernation)
如前所述,这是在Windows 10上启用或禁用休眠的最简单方法,因此应该是您尝试的第一种方法。
1.使用任何列出的方法(any of the listed methods)以管理员身份打开命令提示符(Open Command Prompt as an administrator)。
2. 要启用休眠,请键入powercfg.exe /hibernate on,然后按 Enter。
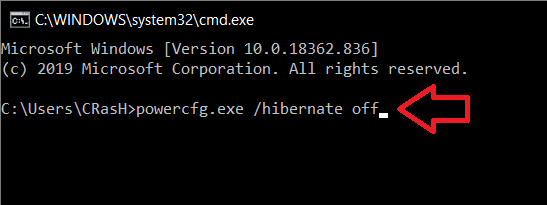
要禁用休眠,请键入 powercfg.exe /hibernate off 并按 Enter。
这两个命令都不返回任何输出,因此要检查您输入的命令是否正确执行,您需要返回 C 盘并查找 hiberfil.sys 文件(look for the hiberfil.sys file)(步骤在前面提到过)。如果您找到 hiberfil.sys,则表明您已成功启用Hibernation。另一方面,如果该文件不存在,则休眠(Hibernation)已被禁用。
方法 2:通过注册表编辑器(Hibernation Via Registry Editor)启用或禁用休眠
第二种方法让用户在注册表编辑器中编辑 HibernateEnabled 条目。(HibernateEnabled entry in the Registry Editor.)遵循此方法时要小心,因为注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)是一个非常强大的工具,任何意外事故都可能导致其他一系列问题。
1.使用以下任一方法打开Windows 注册表编辑器(Windows Registry Editor)
一种。按Windows Key + R打开运行命令(Run Command),键入regedit并按 Enter。
湾。按 Windows 键 + S,键入regedit 或注册表编辑器,然后在(regedit or registry edito)搜索返回时(Open when the search returns)单击打开。
2. 在注册表编辑器窗口的左侧面板中,双击HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE 或单击其左侧的箭头来展开它。
3. 在HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE下,双击SYSTEM 展开。
4. 现在,展开CurrentControlSet。
遵循相同的模式并导航到 Control/Power。
地址栏中指示的最终位置应为:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power

5. 在右侧面板中,双击HibernateEnabled 或右键单击它并选择 Modify。

6. 要启用休眠,请在数值数据下的文本框中输入 1(type 1 in the text box under Value Data)。
要禁用休眠,请在 Value Data 下的文本框中(text box under Value Data)键入 0(type 0 in the) 。
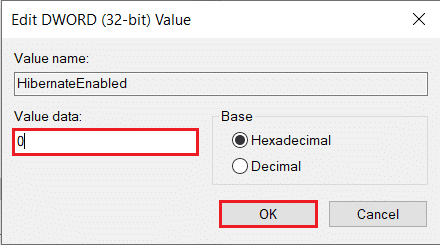
7. 单击确定 (OK )按钮,退出注册表编辑器,然后重新启动计算机。
再次,返回C 驱动器(C drive)并查找 hiberfil.sys 以确保您是否成功启用或禁用了Hibernation。
另请阅读:(Also Read:) 禁用 Windows 页面文件和休眠以释放空间(Disable Windows Pagefile and Hibernation To Free Up Space)
方法 3:通过高级电源(Hibernation Via Advanced Power)选项启用或禁用休眠
最后一种方法是让用户通过“高级电源选项(Advanced Power Options)”窗口启用或禁用休眠。(Hibernation)在这里,用户还可以设置他们希望系统进入休眠(Hibernation)状态的时间范围。和前面的方法一样,这个也很简单。
1. 通过两种方法中的任何一种打开高级电源选项(Open Advanced Power Options)
一种。打开运行命令,输入powercfg.cpl,然后按回车。

湾。打开Windows 设置(Windows Settings)(Windows Key + I)并单击系统(System)。在电源和睡眠设置下,单击其他电源设置(Power & Sleep settings, click on Additional power settings)。
2. 在电源选项(Power Options)窗口中,单击选定(Selected)计划部分下的更改计划设置(Change plan settings) (以蓝色突出显示) 。

3. 单击以下编辑计划设置(Edit Plan Settings)窗口中的更改高级电源设置。(Change advanced power settings)

4. 单击左侧的加号或双击标签展开睡眠。(Expand Sleep)
5. 双击Hibernate after 并将设置(Settings)(分钟(Minutes))设置为您希望系统(System)在进入休眠(Hibernation)状态之前空闲多少分钟。

要禁用休眠(Hibernation),请将设置(Settings)(分钟(Minute))设置为从不(Never),然后在允许混合睡眠下,将设置更改为关闭(Allow hybrid sleep, change the setting to Off)。
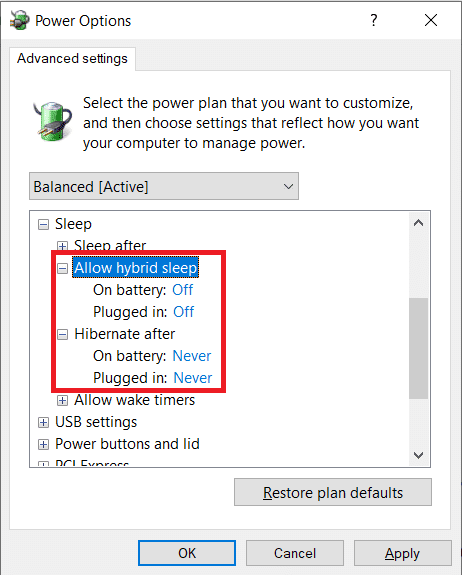
6. 单击应用, (Apply, )然后 单击确定 (OK )以保存您所做的更改。

受到推崇的:(Recommended:)
我们希望您在 Windows 10 上成功启用或禁用休眠(enabling or disabling Hibernation on Windows 10)。另外,让我们知道上述三种方法中的哪一种对您有用。
3 Ways to Enable or Disable Hibernation on Windows 10
Haνe you ever needed to step away from your сomputer for an indefinite period but dіdn’t want to shut it down? This could be fоr various reasons; maybe you have some work that you wish to get right back into post your lunch break or your PC boots on like а snail. The sleep mode in Windows OS lets you do just that, but whаt if I told you there’s a better power-saving feature than the usual slеep mode?
Hibernation mode is a power option that lets Windows users exploit the features of both a complete system shut down and the sleep mode. Just like Sleep, users can configure when they want their systems to go under Hibernation, and if they wish, the feature can be entirely disabled, too (although keeping it active does make for a better overall experience).
In this article, we will be explaining the difference between sleep and hibernation modes, and also show you how to enable or disable hibernation on Windows 10.
What is Hibernation?
Hibernation is a power-saving state primarily made for laptops, although it is available on certain computers as well. It differs from Sleep in terms of power usage and where your currently open (before you left your System); files are saved.
The sleep mode is activated by default when you leave your computer without shutting it down. In the sleep state, the screen is turned off, and all the foreground processes (files and applications) are saved in the memory (RAM). This allows the System to be in a low-power state but still be running. You can get back to work by a single click of the keyboard or by simply moving your mouse. The screen boots on within a few seconds, and all your files & applications will be in the same state as they were when you left.
Hibernation, pretty much like Sleep, also saves the state of your files & applications and is activated after your System has been under Sleep for a prolonged period. Unlike Sleep, which stores files in the RAM and therefore requires a constant power supply, Hibernation doesn’t require any power (like when your System is shut down). This is made possible by storing the current state of the files in the hard drive instead of the temporary memory.
When in an extended sleep, your computer automatically transfers the state of your files to the hard disk drive and switches to Hibernation. As the files have been moved to the hard drive, the System will take a little extra time to boot on than required by Sleep. Although, the boot on time is still faster than booting your computer after a complete shutdown.
Hibernation is particularly useful when the user doesn’t want to lose the state of his/her files but also won’t have the opportunity to charge the laptop for some time.
As obvious, saving the state of your files requires reserving some amount of memory and this amount is occupied by a system file (hiberfil.sys). The reserved amount is roughly equal to 75% of the System’s RAM. For example, if your System has 8 GB of RAM installed, the hibernation system file will take up almost 6 GB of your hard disk storage.
Before we move on to enabling Hibernation, we will need to check if the computer has the hiberfil.sys file. If absent, the computer can not go under Hibernation (PCs with InstantGo do not have the hibernation power option).
To check if your computer can hibernate, follow the below steps:
1. Launch File Explorer by double-clicking on its icon on the desktop or pressing the keyboard shortcut Windows Key + E. Click on Local Drive (C:) to open C Drive.

2. Switch to the View tab and click on Options at the end of the ribbon. Select ‘Change folder and search options’.

3. Again, switch to the View tab of the Folder Options window.
4. Double click on Hidden files and folders to open a sub-menu and enable Show hidden files, folders, or drives.

5. Uncheck/untick the box next to ‘Hide protected operating system files (Recommended).’ A warning message will appear when you try to untick the option. Click on Yes to confirm your action.

6. Click on Apply and then OK to save changes.

7. The Hibernation file (hiberfil.sys), if present, can be found at the root of the C drive. This means your computer is eligible for hibernation.

How to Enable or Disable Hibernation on Windows 10?
Enabling or disabling Hibernation is quite easy, and either action can be achieved in a couple of minutes. There are also multiple methods via which one can enable or disable Hibernation. The easiest one is executing a single command in an elevated command prompt while other methods include editing Windows Registry Editor or accessing advanced power options.
Method 1: Enable or Disable Hibernation using Command Prompt
As mentioned, this is the easiest way to enable or disable Hibernation on Windows 10 and, therefore, should be the first method you try.
1. Open Command Prompt as an administrator using any of the listed methods.
2. To enable Hibernation, type powercfg.exe /hibernate on, and press enter.
To disable Hibernation, type powercfg.exe /hibernate off and press enter.

Both the commands do not return any output, so to check if the command you entered was executed properly, you will need to head back to the C drive and look for the hiberfil.sys file (Steps are mentioned earlier). If you find the hiberfil.sys, it implies you were successful in enabling Hibernation. On the other hand, if the file is absent, Hibernation has been disabled.
Method 2: Enable or Disable Hibernation Via Registry Editor
The second method has the user editing the HibernateEnabled entry in the Registry Editor. Be careful when following this method as Registry Editor is an extremely powerful tool, and any accidental mishap can lead to a whole other set of problems.
1. Open Windows Registry Editor using any of the following methods
a. Open Run Command by pressing Windows Key + R, type regedit and press enter.
b. Press Windows Key + S, type regedit or registry editor, and click on Open when the search returns.

2. From the left panel of the registry editor window, expand HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE by double-clicking on it or by clicking on the arrow to its left.
3. Under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, double-click on SYSTEM to expand.
4. Now, expand CurrentControlSet.
Follow the same pattern and navigate to Control/Power.
The final location indicated in the address bar should be:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Power

5. In the right-hand panel, double click on HibernateEnabled or right-click on it and select Modify.

6. To enable Hibernation, type 1 in the text box under Value Data.
To disable Hibernation, type 0 in the text box under Value Data.

7. Click on the OK button, exit registry editor, and restart your computer.
Again, head back to the C drive and look for the hiberfil.sys to ensure if you were successful in enabling or disabling Hibernation.
Also Read: Disable Windows Pagefile and Hibernation To Free Up Space
Method 3: Enable or Disable Hibernation Via Advanced Power Options
The final method will have the user enable or disable Hibernation through the Advanced Power Options window. Here, users can also set the time frame after which they want their system to go under Hibernation. Like the previous methods, this one is also quite simple.
1. Open Advanced Power Options by any of the two methods
a. Open Run command, type powercfg.cpl, and press enter.

b. Open Windows Settings (Windows Key + I) and click on System. Under Power & Sleep settings, click on Additional power settings.
2. In the Power Options window, click on Change plan settings (highlighted in blue) under the Selected plan section.

3. Click on Change advanced power settings in the following Edit Plan Settings window.

4. Expand Sleep by clicking on the plus to its left or by double-clicking on the label.
5. Double-click on Hibernate after and set the Settings (Minutes) to how many minutes you would like your System to sit idle for before going into Hibernation.

To disable Hibernation, set the Settings (Minute) to Never and under Allow hybrid sleep, change the setting to Off.

6. Click on Apply, followed by OK to save the changes you made.

Recommended:
We hope you were successful in enabling or disabling Hibernation on Windows 10. Also, let us know which one of the three above methods did the trick for you.

















