(Fast Logon Optimization)Windows 操作系统(Windows OS)中的快速登录优化类似于执行后台刷新的操作。它有助于减少登录对话框出现在屏幕上的时间。
Windows 11/10中默认启用,但有一个缺点。在将某些组策略(Group Policy)设置应用于客户端计算机之前,它可能会导致您多次登录或重新启动计算机。因此,根据您的偏好,您可以禁用快速登录优化(Fast Logon Optimization)。
什么是Windows 11/10快速登录优化(Fast Logon Optimization)功能?
可能禁用快速登录优化(Fast Logon Optimization)的情况包括:
- 当用户登录到计算机时。
- 当用户具有用于登录目的的漫游用户配置文件或主目录时。
- 当用户有同步登录脚本时。
在Windows 11/10中启用或禁用快速登录优化(Fast Logon Optimization)
管理员可以使用组策略编辑器更改默认策略配置。
使用快速登录优化(Fast Logon Optimization),启用的组策略(Group Policy)前台处理异步运行。异步处理是指不依赖于其他进程的结果的进程。因此,它们可以同时出现在不同的线程上。
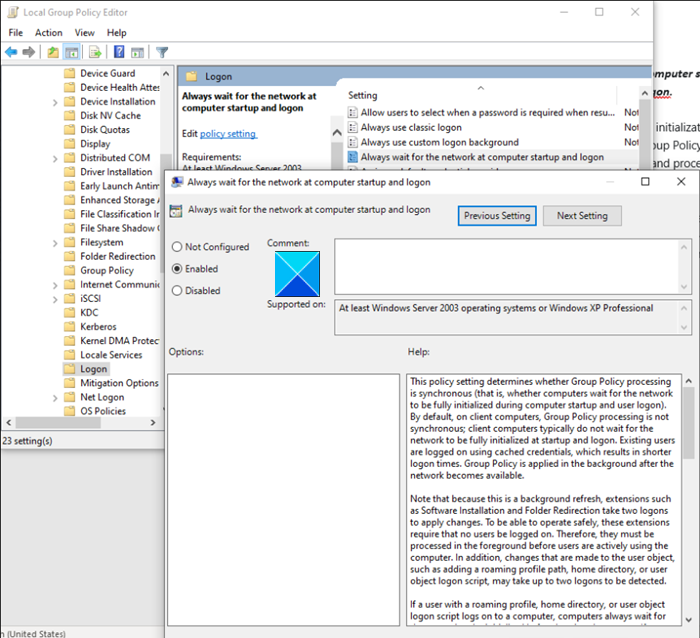
在计算机启动和登录时始终等待网络
打开“运行”对话框,在框的空白字段中键入gpedit.msc ,然后(gpedit.msc)按 Enter(Enter)。
当组策略编辑器(Group Policy Editor)打开时,导航到以下路径地址 -
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Logon > Always在计算机启动和登录时始终等待网络。
在这里,将计算机启动和登录时始终等待网络(Always wait for the network at computer startup and logon)设置为禁用(Disabled)并重新启动您的 PC。要启用它,请将其设置为Enabled。
此策略设置确定组策略(Group Policy)处理是否同步(即计算机是否在计算机启动和用户登录期间等待网络完全初始化)。默认情况下,在客户端计算机上,组策略(Group Policy)处理不是同步的;客户端计算机通常不会等待网络在启动和登录时完全初始化。现有用户使用缓存的凭据登录,从而缩短了登录时间。网络可用后在后台应用组策略。(Group Policy)
因为这是后台刷新,所以软件安装(Software Installation)和文件夹重定向(Folder Redirection)等扩展需要两次登录才能应用更改。为了能够安全操作,这些扩展要求没有用户登录。因此,在用户主动使用计算机之前,必须在前台对其进行处理。此外,对用户对象所做的更改(例如添加漫游配置文件路径、主目录或用户对象登录脚本)可能需要最多两次登录才能被检测到。
如果具有漫游配置文件、主目录或用户对象登录脚本的用户登录到计算机,则计算机总是在用户登录之前等待网络初始化。如果用户以前从未登录到这台计算机,计算机总是等待网络初始化。
如果启用此策略设置,计算机会在用户登录之前等待网络完全初始化。组策略(Group Policy)在前台同步应用。
如果您禁用或未配置此策略设置,并且用户登录到客户端计算机或运行Windows Server 2008或更高版本且配置如前所述的服务器,则计算机通常不会等待网络完全初始化。在这种情况下,用户使用缓存的凭据登录。组策略(Group Policy)在后台异步应用。
这是您可以在Windows 11/10快速登录优化(Fast Logon Optimization)功能的方法。
Hope it helps!
How to Enable or Disable Fast Logon Optimization in Windows 11/10
Fast Logon Optimization in Windows OS is something like the action of performing a background refresh. It helps in reducing the time it takes for the logon dialog box to appear on your screen.
This feature is enabled by default in Windows 11/10 but there’s one drawback. It may cause you to sign in or restart the computer multiple times before certain Group Policy settings are applied to the client computer. So, depending on your preferences, you can disable Fast Logon Optimization.
What is Fast Logon Optimization feature in Windows 11/10?
Conditions during which Fast Logon Optimization may be disabled include instances like,
- When a user logs on to a computer.
- When a user has a roaming user profile or a home directory for logon purposes.
- When a user has synchronous login scripts.
Enable or Disable Fast Logon Optimization in Windows 11/10

Administrators can change the default policy configuration by using the Group Policy Editor.
With Fast Logon Optimization, enabled Group Policy foreground processing runs asynchronously. Asynchronous processing refers to processes that do not depend on the outcome of other processes. Therefore, they can occur on different threads simultaneously.
Always wait for the network at computer startup and logon
Open the Run dialog box, type gpedit.msc in the empty field of the box, and hit Enter.
When the Group Policy Editor opens, navigate to the following path address –
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Logon > Always wait for the network at computer startup and logon.
Here, set the Always wait for the network at computer startup and logon setting to Disabled and restart your PC. To enable it, set it to Enabled.
This policy setting determines whether Group Policy processing is synchronous (that is, whether computers wait for the network to be fully initialized during computer startup and user logon). By default, on client computers, Group Policy processing is not synchronous; client computers typically do not wait for the network to be fully initialized at startup and logon. Existing users are logged on using cached credentials, which results in shorter logon times. Group Policy is applied in the background after the network becomes available.
Because this is a background refresh, extensions such as Software Installation and Folder Redirection take two logons to apply changes. To be able to operate safely, these extensions require that no users be logged on. Therefore, they must be processed in the foreground before users are actively using the computer. In addition, changes that are made to the user object, such as adding a roaming profile path, home directory, or user object logon script, may take up to two logons to be detected.
If a user with a roaming profile, home directory, or user object logon script logs on to a computer, computers always wait for the network to be initialized before logging the user on. If a user has never logged on to this computer before, computers always wait for the network to be initialized.
If you enable this policy setting, computers wait for the network to be fully initialized before users are logged on. Group Policy is applied in the foreground, synchronously.
If you disable or do not configure this policy setting and users log on to a client computer or a server running Windows Server 2008 or later and that is configured as described earlier, the computer typically does not wait for the network to be fully initialized. In this case, users are logged on with cached credentials. Group Policy is applied asynchronously in the background.
This is how you can enable or disable the Fast Logon Optimization feature in Windows 11/10.
Hope it helps!

