Windows计算机(Windows)每 24 小时(every 24 hours)刷新一次DNS服务器托管的域区域中的DNS记录。当Windows计算机从域中删除或无法更新其DNS服务器(DNS Server)中的DNS记录时,该Windows计算机的 DNS 记录仍保留在DNS数据库中,并被视为过时的DNS记录。除非手动删除,否则旧的DNS记录会保留在DNS数据库中。(DNS)DNS 老化(DNS Aging)和清除(Scavenging)有助于快速识别过时的 DNS 记录并手动删除它们(quickly identify the stale DNS records and remove them manually)。在这篇文章中,我们将描述什么是DNS 老化(DNS Aging)和清除,并概述在(Scavenging)Windows服务器上配置/启用此功能所需的步骤。
什么是 DNS 老化?
老化(Aging)是一项允许识别过时DNS记录的功能。它实际上使用了两个时间间隔,并且一旦两个时间间隔都过去了, DNS记录就会被认为是陈旧的。
这些间隔是:
- Non-Refresh Interval : 这是一个资源记录不能被刷新的时间段 (*)。在这段时间内拒绝刷新会减少复制流量,因为不需要再次复制相同的信息。
- 刷新间隔(Refresh Interval):可以刷新资源记录的时间段 (*)。
(*) 资源记录刷新是主机名和 IP 不变的DNS动态更新。(DNS)更改资源记录的注册 IP的DNS动态更新不被视为刷新,并且不受非刷新间隔(Interval)的影响。
什么是 DNS 清除?
清理是一项允许清理和删除DNS区域中陈旧资源记录的功能。
只有在以下情况下启用清理时,才会删除陈旧的资源记录:
- 资源记录
- 资源记录所在的DNS区域(DNS)
- 至少一个DNS托管资源记录所在的DNS区域的主要副本
在DNS(DNS)服务器上启用时,会定期进行清理。然后,陈旧的资源记录仍然存在,直到下一个DNS清理周期。
如果不启用DNS Aging and scavenging,可能会遇到以下情况:
- 域(Domain)区域将保存不需要的DNS记录。(DNS)
- 随着时间的推移,DNS数据库的大小将会增加。
- DNS服务器服务在内存中枚举和加载DNS数据库需要更多时间。
- DNS服务器响应DNS查询需要更多时间。这是因为DNS服务器需要枚举所有DNS记录,然后才能找到所需的DNS记录,然后发送响应。
- DNS服务器可能会以网络上不再存在的无效DNS记录进行响应,从而导致网络上出现命名解析问题。(DNS)
- 如果过时的DNS(DNS)记录使用相同的 IP 地址,另一台Windows客户端计算机可能无法注册自己的DNS记录。
启用(Enable)和配置 DNS 老化(Configure DNS Aging)和清理
要在Windows(Windows)服务器上成功配置/启用DNS 老化(DNS Aging)和清除,您需要按此顺序执行 3 个步骤;
- 检查服务器 DNS 记录(Check Server DNS Records)(非常重要的第一步)
- 在DNS(DNS)区域上启用DNS老化和清理
- 在至少一台托管DNS区域主副本的DNS服务器上启用DNS清理(DNS)
让我们来看看详细的步骤。
1]检查服务器DNS记录(Check Server DNS Records)(非常重要的第一步)
此步骤至关重要,因为如果您不先执行此步骤,您最终可能会删除服务器DNS记录。作为预防措施,您可能还需要备份DNS服务器和/或记录。
清除工作在时间戳上,因此任何带有时间戳的DNS记录都将被处理并可能被删除。(DNS)因此,建议您检查您的服务器DNS记录并确保它们是静态的。
要检查您的记录,请打开DNS控制台并检查时间戳(Timestamp)列,您的服务器应设置为静态。如果没有,只需打开记录,然后取消选中删除此记录时它变得陈旧(Delete this record when it becomes stale )框。
完成此操作后,刷新DNS控制台,时间戳现在将显示该记录的静态(static)。
检查所有服务器记录并将其更改为静态,然后再进行下一步。
2]在DNS区域上启用 DNS(Enable DNS)老化和清理
请执行下列操作:
- 使用 DNS 管理工具 (dnsmgmt.msc),转到DNS 区域(zones)的属性,然后单击 Aging…
- 启用Scavenge stale resource records 复选框,指定非刷新(Refresh)间隔和刷新(Refresh)间隔周期。
- 单击确定。(OK.)
要使DNS服务器上的所有(DNS)DNS区域默认启用 DNS 老化和清除,(DNS)您需要执行以下操作:
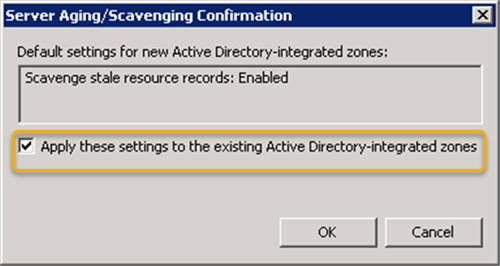
- 右键单击(Right-click)服务器名称,然后单击Set Aging/Scavenging for All Zones…
- 启用Scavenge stale resource records 复选框,指定非刷新(Refresh)间隔和刷新(Refresh)间隔周期。
- 单击确定。(OK.)
- 选中将这些设置应用于现有的 Active Directory 集成区域(Apply these settings to the existing Active Directory-integrated zones )框(这将为现有的 Active Directory 集成区域启用DNS(Active Directory-integrated)老化(DNS)和清理)。
- 单击确定。(OK.)
现在,继续下一步也是最后一步。
3]在至少一台托管DNS区域主副本的DNS服务器上(DNS)启用 DNS清理(Enable DNS)
请执行下列操作:
- 转到DNS服务器的属性。
- 转到高级 (Advanced )选项卡。
- 选中启用陈旧记录的自动清理(Enable automatic scavenging of stale records )框。
- 完成后,指定清理(Scavenging)周期(即DNS服务器上清理的重复间隔)。(Scavenging)
- 单击确定。(OK.)
That’s it! That completes the setup of DNS Aging and Scavenging.
How to Enable & Configure DNS Aging & Scavenging in Windows Server
Windows computers refresh their DNS records in the domain zones hosted by the DNS servers every 24 hours. When a Windows computer is removed from the domain or is not able to update its DNS record in the DNS Server, the DNS record of that Windows computer remains in the DNS database and is considered to be a stale DNS record. The stale DNS records remain in the DNS database unless it’s manually removed. DNS Aging and Scavenging helps to quickly identify the stale DNS records and remove them manually. In this post, we will provide a description of what DNS Aging and Scavenging is, as well as outline the steps required to configure/enable this feature on the Windows server.
What is DNS Aging?
Aging is a feature that allows identifying stale DNS records. It actually uses two intervals and a DNS record is considered as stale once both are elapsed.
These intervals are:
- Non-Refresh Interval: It is a period of time during which a resource record cannot be refreshed (*). Refusing the refresh during this period of time reduces the replication traffic as there is no need to replicate the same information again.
- Refresh Interval: It is a period of time during which a resource record could be refreshed (*).
(*) A resource record refresh is a DNS dynamic update where the hostname and IP do not change. A DNS dynamic update to change the registered IP for a resource record is not considered as a refresh and is exempt from the Non-Refresh Interval.
What is DNS Scavenging?
Scavenging is a feature that allows the cleanup and removal of stale resource records in DNS zones.
A stale resource record will be removed only if scavenging is enabled on:
- The resource record
- The DNS zone where the resource record exists
- At least one DNS hosting a primary copy of the DNS zone where the resource record exists
Scavenging occurs on recurring intervals when enabled on a DNS server. A stale resource record can then still exist until the next cycle of DNS scavenging.
If you do not enable DNS Aging and scavenging, you might face the following situations:
- Domain zones will hold the DNS records that are not needed.
- Over a period of time, the DNS database size will be increased.
- It will take more time for the DNS server service to enumerate and load the DNS database in memory.
- It will take more time for the DNS server to respond to a DNS query. This is because the DNS server needs to enumerate all DNS records before it can find the required DNS record and then send a response.
- DNS servers might respond with an invalid DNS record that no longer exists on the network causing naming resolution problems on the network.
- Another Windows client computer might not be able to register its own DNS records if the same IP address is being used by a stale DNS record.
Enable & Configure DNS Aging and Scavenging

To successfully configure/enable DNS Aging and Scavenging on Windows server, you need to follow 3 steps in this order;
- Check Server DNS Records (very important first step)
- Enable DNS aging and scavenging on DNS zones
- Enable DNS scavenging on at least one DNS server hosting primary copies of your DNS zones
Let’s take a look at the steps involved in detail.
1] Check Server DNS Records (very important first step)
This step is crucial because if you don’t follow this step first you could end up deleting server DNS records. As a precaution, you may want to also backup your DNS server and or records.
Scavenging works on timestamps, so any DNS record with a timestamp will get processed and possibly deleted. So it’s recommended you check your server DNS records and make sure they are static.
To check your records open the DNS console and check the Timestamp column, your servers should be set to static. If not, simply open the record then uncheck the Delete this record when it becomes stale box.
Once you have done that, refresh the DNS console the timestamp will now show static for that record.
Check all your server records and change them to static before moving onto the next step.
2] Enable DNS aging and scavenging on DNS zones
Do the following:
- Using DNS administrative tool (dnsmgmt.msc), go to the properties of your DNS zones and then click on Aging…
- Enable Scavenge stale resource records checkbox, specify the Non-Refresh interval, and Refresh interval periods.
- Click OK.
To make DNS aging and scavenging enabled by default for all DNS zones on a DNS server, you need to proceed as follows:
- Right-click on the server name and then click on Set Aging/Scavenging for All Zones…
- Enable Scavenge stale resource records checkbox, specify the Non-Refresh interval, and Refresh interval periods.
- Click OK.
- Check the Apply these settings to the existing Active Directory-integrated zones box (This will enable DNS aging and scavenging for the existing Active Directory-integrated zones).
- Click OK.
Now, proceed with the next and final step.
3] Enable DNS scavenging on at least one DNS server hosting primary copies of your DNS zones
Do the following:
- Go to the properties of your DNS server.
- Go to Advanced tab.
- Check the Enable automatic scavenging of stale records box.
- Once done, specify the Scavenging period (That is the recurring interval for Scavenging on a DNS server).
- Click OK.
That’s it! That completes the setup of DNS Aging and Scavenging.

