每当我们的计算机遇到一些性能问题时,我们要做的第一件事就是打开任务管理器(Task Manager),然后寻找使用最多资源的应用程序或组件。如果您熟悉任务管理器(Task Manager),那么您一定也注意到有时,“ Windows 任务的主机进程(Host Process for Windows Tasks)”或“服务主机(Service Host)”进程会消耗资源。如果您的主机(Host)进程停止工作或消耗高CPU、磁盘(Disk)或内存(Memory)使用率,这些进程以及您可以做什么。
(Host Process)Windows 任务(Windows Tasks)或服务主机(Service Host)的主机进程
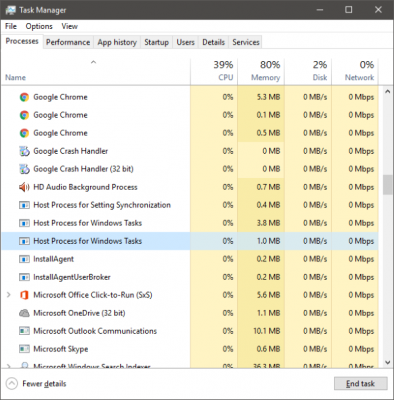
Windows基本上是因为它的服务(Services)而工作。后台运行的大量服务方便您的日常任务和操作。其中一些服务被编译成EXE文件,它们本身就是完整的。这些服务显示在任务管理器(Task Manager)中。但是有些服务是写在DLL文件中的,不能直接执行。Microsoft转向DLL文件,因为从编程的角度来看,它们易于维护和更新。DLL服务需要一个宿主进程,一个可执行它们的EXE ,这就是(EXE)Windows中的“taskhost”。
Windows 11/10中的Taskhost是位于System32文件夹中的核心文件,已从Windows 7中的“ (Windows 7)taskhost.exe ”重命名为“ taskhostw.exe ” 。如果您在任何其他位置找到具有此名称的文件,则很可能是病毒,您可能需要使用安全软件对其进行检查。
每个“ Windows 任务的主机进程(Host Process)”都是在后台运行某些服务的“taskhost”实例。尽管Windows 任务管理(Windows Task Manager)器不能完全让您查看它正在运行的服务,但其他工具可以。
(Host Process)Windows 服务的(Services)主机进程已停止工作或消耗大量资源
如果您看到“停止工作”消息框,您可以尝试以下故障排除建议:
- 打开任务计划程序(Task Scheduler)。在左窗格中,单击任务计划程序(Task Scheduler)库 > Microsoft > Windows> RAC。接下来(Next),单击查看菜单(View Menu)并选择显示隐藏的任务(Show Hidden Tasks)。在中间窗格中,右键单击RAC 任务(RAC Task)并单击禁用(Disable)。看看这是否有帮助。如果不是,请撤消所做的更改。
- 打开事件查看器(Event Viewer)并在左侧窗格中选择最新的应用程序事件日志,其中有一个红色标记。双击(Double-click)某个事件可查看该事件的详细信息。看看你是否在这里找到任何有用的信息。如果它显示Windows的(Windows)主机(Host)进程已停止工作消息,它可能会有所帮助。
- 执行干净启动(Perform Clean Boot)并手动解决问题。
有时您可能会发现此过程正在使用大量资源。您现在可以理解这是由于底层服务而不是流程本身引起的。此外,您可能会注意到Windows(Windows)启动时资源的大量消耗。那只是因为任务主机正在加载所有DLL文件并计划运行它们。完成后,使用量将稳定在较低的值,并且在其余时间保持相当低的水平。
我之前提到过,任务管理器(Task Manager)不允许您查看底层服务。但是您可以使用Microsoft的(Microsoft)Process Explorer查看任务主机下的服务。它是一个便携式实用程序,下载后可以直接运行。您可以使用此工具查看与任务主机关联的所有详细信息。
在左窗格中找到“(Find ‘) taskhostw.exe”,您可以在下窗格中阅读所有详细信息。查看 taskhost 加载的DLL(DLL)文件列表的另一种方法是在 cmd 窗口中键入以下命令:
tasklist /M /FI "IMAGENAME eq taskhostw.exe
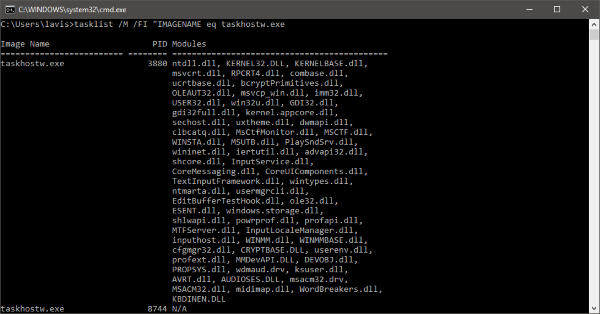
此命令将列出此进程在Windows 启动时加载的所有(Windows Startup)DLL文件。如果您浏览该列表,您会发现一些为Windows提供核心功能的基本文件。
因此,简而言之,Taskhost是一个核心 Windows 进程(core Windows process),提供加载和执行动态链接库的功能。由于它托管各种DLL文件,因此有时它会以高于正常的速度消耗资源。如果您遇到进程停止响应或使用大量资源的任何此类问题。使用Process Explorer、Performance Monitor和Resource Monitor,并尝试手动解决问题。
想了解这些进程、文件或文件类型吗?(Want to know about these processes, files or file types?)
Windows.edb 文件(Windows.edb files) | csrss.exe | svchost.exe | StorDiag.exe | 妈妈.exe | ApplicationFrameHost.exe | ShellExperienceHost.exe | winlogon.exe | atieclxx.exe | 主机.exe(Conhost.exe) | mDNSResponder.exe。
What is Host Process for Windows Tasks or Service Host in Windows PC
Whеnever wе face some pеrformance issues with our computer, the first thіng we do is open υp the Τask Manager, and then look for the applications or components which are using the most resources. If yоu are familiar with Task Mаnager, then yоu must have also noticed that at times, the ‘Host Process for Windows Tasks’ or ‘Service Host’ process consuming resources. What these processes and what can you do if your Host process has stopped working or consumes high CPU, Disk or Memory usage.
Host Process for Windows Tasks or Service Host

Windows is essentially working just because of its Services. A large number of services running the background facilitate your daily tasks and operations. Some of these services are compiled into EXE files, and they are complete in themselves. These services show up in the Task Manager. But some services are written in DLL files, and they cannot be executed directly. Microsoft shifted to DLL files as they were easy to maintain and update from a programming point of view. DLL services require a host process, an EXE that can execute them and this is what ‘taskhost’ in Windows is.
Taskhost in Windows 11/10 is a core file located in the System32 folder and has been renamed as ‘taskhostw.exe’, from ‘taskhost.exe’ in Windows 7. If you find a file with this name in any other location, it could well be a virus and you might want to get it checked with your security software.
Each ‘Host Process for Windows Task’ is an instance of ‘taskhost’ running some service in the background. Although Windows Task Manager does not exactly let you view what services it is running, other tools can.
Host Process for Windows Services has stopped working or consuming High resources
If you see a ‘stopped working’ message box, you can try the following troubleshooting suggestions:
- Open Task Scheduler. In the left pane, click on Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows> RAC. Next, click the View Menu and select Show Hidden Tasks. In the middle pane, right-click on RAC Task and click Disable. See if this helps. If not, reverse the change made.
- Open Event Viewer and select the latest Application event log in the left pane which has a red mark. Double-click an event to view the details of the event. See if you find any useful information here. If it displays Host process for Windows has stopped working message, it could help.
- Perform Clean Boot and troubleshoot the issue manually.
There might be times when you find that this process is using high resources. You can now understand that this is caused due to the underlying service and not the process itself. Also, you might notice high consumption of resources at Windows startup. That is just because the taskhost is loading all the DLL files and schedule to run them. Once it is completed, the usage will settle down to a lower value and will remain pretty low for the rest of the time.
I mentioned earlier that the Task Manager does not let you view the underlying services. But you can use Process Explorer from Microsoft to view the services beneath the taskhost. It is a portable utility, and you can run it directly after downloading. You can use this tool to view all the details associated with the taskhost.
Find ‘taskhostw.exe’ in the left pane, and you can read all the details in the lower pane. Another way to view the list of DLL files loaded by taskhost is by typing in the following command in a cmd window:
tasklist /M /FI "IMAGENAME eq taskhostw.exe

This command will list all the DLL files that were loaded by this process on Windows Startup. If you go through the list, you will find out some essential files that provide core functionality to Windows.
So, in a nutshell, Taskhost is a core Windows process that provides functionality to load and execute dynamic link libraries. Since it hosts various DLL files, sometimes it can consume resources at a more than normal rate. If you are facing any such issues where the process has stopped responding or is using a lot of resources. Use the Process Explorer, Performance Monitor and Resource Monitor, and try to troubleshoot the problem manually.
Want to know about these processes, files or file types?
Windows.edb files | csrss.exe | Svchost.exe | StorDiag.exe | MOM.exe | ApplicationFrameHost.exe | ShellExperienceHost.exe | winlogon.exe | atieclxx.exe | Conhost.exe | mDNSResponder.exe.


