如果您的 Windows 11/10升级(Upgrade)失败并且您已记下错误代码,那么这篇文章提供了一些基本解决方案来解决和解决问题。我们已经了解了如何对Windows 安装和更新失败错误进行故障排除(troubleshoot Windows Installation & Update Failed Errors)。在这篇文章中,我将列出来自微软的(Microsoft)升级(Upgrade)错误代码及其解决过程。
如何识别错误代码代表什么:
假设错误代码是 0x80070070
假设错误代码是 0xC1900107
一些结果代码是不言自明的,而另一些是通用的,需要分析。
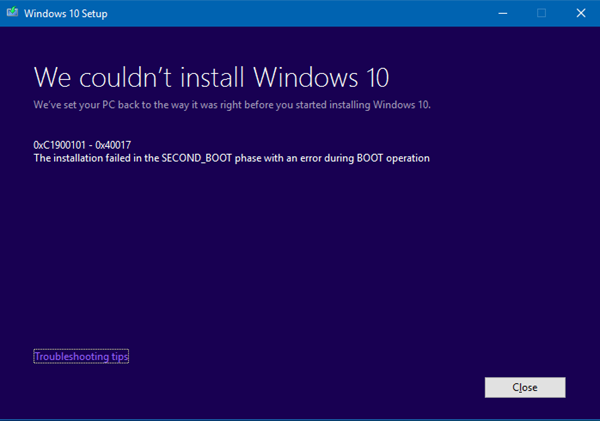
Windows 11/10 升级错误代码
0xC1900101 – 0x20004:这通常是由过时的驱动程序引起的。删除(Remove)所有未使用的设备和驱动程序,更新(Update)驱动程序,卸载您的安全,删除(Remove)所有未使用的SATA设备。
0xC1900101 – 0x2000c:这通常是由过时的驱动程序引起的。断开(Disconnect)连接到系统的所有设备,鼠标、键盘和显示器除外,联系(Contact)您的硬件供应商以获取更新的设备驱动程序,确保在升级过程开始时接受“下载并安装更新(推荐) ”。(Download and install updates (recommended))
0xC1900101 – 0x20017:这是SafeOS启动失败,通常由驱动程序或非 Microsoft 磁盘加密软件引起。Windows无法迁移驱动程序,导致操作系统回滚。确保所有这些驱动程序都已更新,打开%windir%\PantherSetuperr.log和Setupact.log文件,然后找到有问题的驱动程序,更新(Update)或卸载有问题的驱动程序。
0xC1900101 – 0x30018:设备驱动程序在升级过程中停止响应 setup.exe。断开(Disconnect)连接到系统的所有设备,鼠标、键盘和显示器除外,联系(Contact)您的硬件供应商以获取更新的设备驱动程序,确保在升级过程开始时接受下载并安装更新(推荐) 。(Download and install updates (recommended))
0xC1900101 – 0x3000D:这可能是由于显示驱动程序出现问题而发生的。断开(Disconnect)连接到系统的所有设备,鼠标、键盘和显示器除外,更新(Update)或卸载显示驱动程序(display driver)。
0xC1900101 – 0x4000D:由于驱动程序配置问题而发生回滚。尝试更换视频适配器。确保您有足够的磁盘空间,禁用BIOS内存选项,例如缓存或阴影。
0xC1900101 – 0x40017:这通常是由错误的驱动程序、防病毒过滤器驱动程序或加密驱动程序引起的。执行干净启动(Perform Clean Boot),然后尝试升级到Windows 10,确保(Make)选择下载并安装更新(推荐)(Download and install updates (recommended))选项。
0x8007025D – 0x2000C:重新下载ISO/Media并重新尝试升级。或者,使用媒体创建工具重新创建安装媒体。
0x80070490 – 0x20007:验证计算机上的设备驱动程序,并分析日志文件以确定问题驱动程序。
0xC1900101 - 0x2000c :更新电脑驱动,升级过程中选择“下载并安装更新(推荐) ”。(Download and install updates (recommended))断开(Disconnect)鼠标、键盘和显示器以外的设备。
0xC1900200 - 0x20008:请参阅 Windows 10 规格并验证计算机是否满足最低要求。
800704B8 – 0x3001A:在第一个引导阶段发生了扩展错误。禁用或卸载非 Microsoft 防病毒应用程序,断开所有不必要的设备,并执行干净启动。
8007042B – 0x4000D:由于文件系统、应用程序或驱动程序问题,可能会出现此问题。分析(Analyze)日志文件以确定无法迁移/断开、更新、删除或替换设备或对象的文件、应用程序或驱动程序。它可能是由于HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList下的注册表项损坏或用户目录中的无效文件而发生的。要修复此错误,请确保已删除的帐户不再存在于Windows注册表中,并且用户目录下的文件有效。删除导致此错误的无效文件或用户配置文件。导致错误的特定文件和配置文件将记录在Windows安装日志文件中。
8007001F – 0x4000D:这是一般故障,连接到系统的设备可能无法运行。分析(Analyze)日志文件以确定运行不正常的设备,断开连接(Disconnect)、更新或更换设备。
8007042B – 0x4001E:在第二个引导阶段尝试PRE_OOBE操作时安装失败。此错误有多个可能的原因。尝试下面提到的快速修复,如果不成功,请分析日志文件以确定问题和解决方案。
0xC1800118:遵循 KB3194588。
0xC1900200:确保您尝试升级的系统满足最低系统要求。有关信息,请参阅 Windows 10 规格。
0x80090011:联系您的硬件供应商并更新所有设备驱动程序。建议在升级过程中保持有效的 Internet 连接。确保在升级过程开始时接受“下载并安装更新(推荐)”。
0xC7700112:此问题已在最新版本的升级助手中得到解决。确保在升级过程开始时接受“下载并安装更新(推荐)”。
0x80190001:要解决此问题,请下载并运行媒体创建工具。请参阅下载(Download)Windows 10。
0x80246007:尝试其他升级操作系统的方法。下载并运行媒体创建工具。请参阅下载(Download)Windows 10。
0xC1900201:系统未通过安装更新的最低要求。联系硬件供应商以获取最新更新。
0x80240017:此版本的Windows无法升级。您的组织实施的管理策略可能会阻止升级。请联系您的 IT 管理员。
0x80070020:使用MSCONFIG工具在计算机上执行干净启动,然后尝试再次执行更新。有关详细信息,请参阅如何在Windows中执行干净启动。
0x80070522:确保您已以本地管理员身份登录或具有本地管理员权限。
0xC1900107:重新启动设备并再次运行设置。如果重新启动设备不能解决问题,请使用磁盘清理(Disk Cleanup)实用程序并清理临时文件和系统(System)文件。有关详细信息,请参阅Windows 10中的磁盘清理(Disk Cleanup)。
0xC1900209:不兼容的软件阻止了升级过程。卸载应用程序并再次尝试升级。有关详细信息,请参阅使用SETUP.EXE进行(SETUP.EXE)Windows 10升级前验证(Validation)。您还可以下载适用于Windows 10的(Windows 10)Windows 评估(Windows Assessment)和部署工具包(Deployment Kit)( ADK )并安装应用程序兼容性工具(Application Compatibility Tools)。
0x8007002:要解决此问题,请在与Configuration Manager服务器位于同一VLAN的客户端上尝试(VLAN)操作系统部署测试。(OS Deployment)检查远程VLAN上发生的随机客户端-服务器连接问题的网络配置。另外,分析SMSTS.log。
0x80073BC3 – 0x20009, 0x8007002 – 0x20009, 0x80073B92 – 0x20009:这些错误发生在分区分析和验证期间,并且可能是由多个系统分区的存在引起的。要解决错误,请断开或暂时禁用包含未使用系统分区的驱动器。升级完成后,您可以重新连接驱动器。或者,您可以删除未使用的系统分区。
0x80070004 – 0x3000D、0x80070005 – 0x4000D、0x80070004 – 0x50012、80040005 – 0x20007:分析日志文件以确定问题。
0xC190020e、0x80070070 – 0x50011、0x80070070 – 0x50012、0x80070070 – 0x60000:这些错误表明计算机没有足够的可用空间来安装升级。
如需详细阅读,您可以访问Microsoft。
修复Windows 升级(Windows Upgrade)错误的标准解决过程包括:
- 验证(Verify)至少有 16 GB 的可用空间
- 断开所有外部硬件
- 运行Windows 更新疑难解答
- 运行 Windows 更新(Run Windows Update)
- 卸载非 Microsoft 防病毒软件
- 卸载非必要软件
- 释放磁盘空间(Free up disk space)
- 更新固件和驱动程序(Update firmware and drivers)
- 运行SFC和DISM
- 最后,运行Windows 升级(Windows Upgrade)过程。
您必须查看其中哪些可能适用于您的情况。如果您需要更具体的帮助,请在 TheWindowsClub 上搜索错误代码或消息。这篇文章还将向您展示 IT 管理员如何解决 Windows 升级错误。
List of Windows Upgrade error codes and solutions
If your Windows 11/10 Upgrade has failed and if you have noted down the error code, then this post offers sоme basic solυtions to troubleshоot & resolve the problem. We have seen how tо troubleshoot Windows Installation & Update Failed Errors. In this post, I will list down the Upgrade error codes and their resolution process, which has been sourced from Microsoft.
How to identify what the error code stands for:
Let’s say the error code is 0x80070070
- “8” indicates that this is a Win32 error code
- The last four digits are 0070, so look up 0x00000070 in the Win32 error code table on MSDN.
- The error is: ERROR_DISK_FULL
Let’s say the error code is 0xC1900107
- “C” indicates that this is an NTSTATUS error code.
- The last four digits are 0107, so look up 0x00000107 in the NTSTATUS value table on MSDN.
- The error is: STATUS_SOME_NOT_MAPPED
Some result codes are self-explanatory, whereas others are generic and require analysis.

Windows 11/10 Upgrade error codes
0xC1900101 – 0x20004: This is generally caused by outdated drivers. Remove all unused devices and drivers, Update drivers, Uninstall your security, Remove all unused SATA devices.
0xC1900101 – 0x2000c: This is generally caused by outdated drivers. Disconnect all devices that are connected to the system, except for the mouse, keyboard and display, Contact your hardware vendor to obtain updated device drivers, Ensure that “Download and install updates (recommended)” is accepted at the start of the upgrade process.
0xC1900101 – 0x20017: This is a SafeOS boot failure, typically caused by drivers or non-Microsoft disk encryption software. Windows was not able to migrate the driver, resulting in a rollback of the operating system. Ensure that all those drivers are updated, Open the Setuperr.log and Setupact.log files in the %windir%\Panther directory, and then locate the problem drivers, Update or uninstall the problem drivers.
0xC1900101 – 0x30018: A device driver has stopped responding to setup.exe during the upgrade process. Disconnect all devices that are connected to the system, except for the mouse, keyboard and display, Contact your hardware vendor to obtain updated device drivers, Ensure that Download and install updates (recommended) is accepted at the start of the upgrade process.
0xC1900101 – 0x3000D: This can occur due to a problem with a display driver. Disconnect all devices that are connected to the system, except for the mouse, keyboard, and display, Update or Uninstall the display driver.
0xC1900101 – 0x4000D: A rollback occurred due to a driver configuration issue. Try changing video adapters. Make sure you have enough disk space, Disable BIOS memory options such as caching or shadowing.
0xC1900101 – 0x40017: This is usually caused by a faulty driver, antivirus filter drivers or encryption drivers. Perform Clean Boot and then attempt the upgrade to Windows 10, Make sure you select the option to Download and install updates (recommended).
0x8007025D – 0x2000C: Re-download the ISO/Media and re-attempt the upgrade. Alternatively, re-create installation media using the Media Creation Tool.
0x80070490 – 0x20007: Verify device drivers on the computer, and analyze log files to determine the problem driver.
0xC1900101 – 0x2000c: Update drivers on the computer, and select “Download and install updates (recommended)” during the upgrade process. Disconnect devices other than the mouse, keyboard, and display.
0xC1900200 – 0x20008: See Windows 10 specifications and verify the computer meets minimum requirements.
800704B8 – 0x3001A: An extended error has occurred during the first boot phase. Disable or uninstall non-Microsoft antivirus applications, disconnect all unnecessary devices, and perform a clean boot.
8007042B – 0x4000D: This issue can occur due to the file system, application, or driver issues. Analyze log files to determine the file, application, or driver that is not able to be migrated/Disconnect, update, remove, or replace the device or object. It can occur due to corrupt registry entries under HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList or invalid files in the \Users directory. To repair this error, ensure that deleted accounts are not still present in the Windows registry and that files under the \Users directory are valid. Delete the invalid files or user profiles that are causing this error. The specific files and profiles that are causing the error will be recorded in the Windows setup log files.
8007001F – 0x4000D: This is general failure, and a device attached to the system may not be functioning. Analyze log files to determine the device that is not functioning properly, Disconnect, update, or replace the device.
8007042B – 0x4001E: The installation failed during the second boot phase while attempting the PRE_OOBE operation. This error has more than one possible cause. Attempt the quick fixes mentioned below, and if not successful analyze log files to determine the problem and solution.
0xC1800118: Follow KB3194588.
0xC1900200: Ensure the system you are trying to upgrade meets the minimum system requirements. See Windows 10 specifications for information.
0x80090011: Contact your hardware vendor and get all the device drivers updated. It is recommended to have an active internet connection during the upgrade process. Ensure that “Download and install updates (recommended)” is accepted at the start of the upgrade process.
0xC7700112: This issue is resolved in the latest version of Upgrade Assistant. Ensure that “Download and install updates (recommended)” is accepted at the start of the upgrade process.
0x80190001: To resolve this issue, download and run the media creation tool. See Download windows 10.
0x80246007: Attempt other methods of upgrading the operating system. download and run the media creation tool. See Download windows 10.
0xC1900201: The system did not pass the minimum requirements to install the update. Contact the hardware vendor to get the latest updates.
0x80240017: The upgrade is unavailable for this edition of Windows. Administrative policies enforced by your organization might be preventing the upgrade. Contact your IT administrator.
0x80070020: Use the MSCONFIG tool to perform a clean boot on the machine and then try to perform the update again. For more information, see How to perform a clean boot in Windows.
0x80070522: Ensure that you have signed in as a local administrator or have local administrator privileges.
0xC1900107: Reboot the device and run the setup again. If restarting device does not resolve the issue, then use the Disk Cleanup utility and clean up the temporary as well as the System files. For more information, see Disk Cleanup in Windows 10.
0xC1900209: Incompatible software is blocking the upgrade process. Uninstall the application and try the upgrade again. See Windows 10 Pre-Upgrade Validation using SETUP.EXE for more information. You can also download the Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (ADK) for Windows 10 and install Application Compatibility Tools.
0x8007002: To resolve this issue, try the OS Deployment test on a client in the same VLAN as the Configuration Manager server. Check the network configuration for random client-server connection issues happening on the remote VLAN. Also, analyze the SMSTS.log.
0x80073BC3 – 0x20009, 0x8007002 – 0x20009, 0x80073B92 – 0x20009: These errors occur during partition analysis and validation, and can be caused by the presence of multiple system partitions. To resolve the errors, disconnect or temporarily disable drives that contain the unused system partition. You can reconnect the drive after the upgrade has completed. Alternatively, you can delete the unused system partition.
0x80070004 – 0x3000D, 0x80070005 – 0x4000D, 0x80070004 – 0x50012, 80040005 – 0x20007: Analyze the log files to determine the issue.
0xC190020e, 0x80070070 – 0x50011, 0x80070070 – 0x50012, 0x80070070 – 0x60000: These errors indicate the computer does not have enough free space available to install the upgrade.
For a detailed read, you may visit Microsoft.
The standard resolution process for fixing Windows Upgrade errors include:
- Verify at least 16 GB of free space is available
- Disconnect all external hardware
- Run the Windows Update Troubleshooter
- Run Windows Update
- Uninstall non-Microsoft antivirus software
- Uninstall nonessential software
- Free up disk space
- Update firmware and drivers
- Run SFC and DISM
- Finally, run the Windows Upgrade process.
You have to see which of them may apply in your case. If you need more specific help, search for the error code or message here on TheWindowsClub. This post will also show you how IT administrators can troubleshoot Windows upgrade errors.

