什么是计算机网络?这不是您经常听到的问题,但它仍然很重要。没有计算机网络,互联网就不会像今天这样高效,因此考虑到这一点,我们决定向初学者解释什么是网络,以及不同类型的网络。不仅如此,本文还将讨论网络的优势。没有真正的缺点,因此,我们甚至不会去那里。
什么是计算机网络
嗯,网络是一组连接起来共享资源和通信的计算机系统。此外,网络也是通过传输媒体和通信设备链接在一起的设备和计算机的集合。
我们将在另一篇文章中详细讨论传输媒体,因此请尽快关注。
网络的效用
- 加快沟通
- 共享连接的硬件
- 分发数据和信息
1] 加快沟通
由于网络,人们可以通过电子邮件、信使工具、聊天室、社交媒体、诸如此类的网站、在线视频通话等等轻松地相互交流。如果网络出现故障,则连接到它的所有工具将不再运行。
2]共享连接的硬件
如果有某些硬件设备连接到网络,那么这些设备很容易与所有有权访问网络的人共享。例如,数据库文件或打印机在网络上很常见,它们被称为网络资源。
3] 分发数据和信息
事情是这样的;如果您是授权用户,那么您应该可以毫无问题地访问存储在网络上的数据和信息。像微软(Microsoft)这样的公司将拥有一个庞大的客户信息数据库,所有这些都对拥有适当权限的员工开放。
计算机网络的类型
- 局域网 (LAN)
- 无线局域网 (WLAN)
- 广域网 (WAN)
- 城域网 (MAN)
- 个域网 (PAN)
- 校园区域网络 (CAN)
- 存储区域网络 (SAN)
1]局域网(LAN)
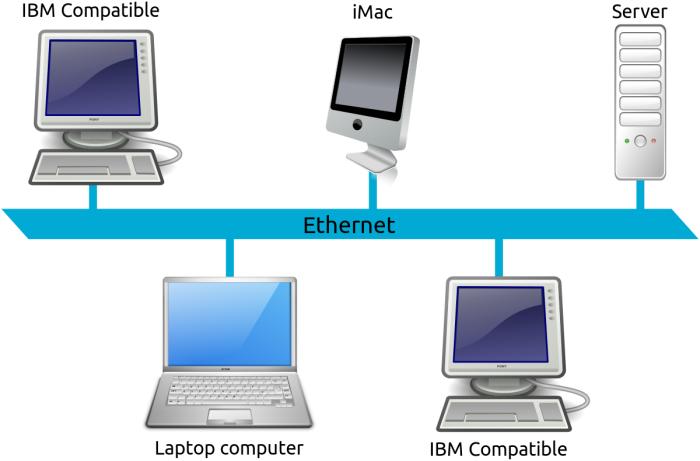
我们在这里拥有的是一个连接小地理区域内的计算机和设备的网络。例如,LAN通常位于建筑物中。事实上,一个建筑物可以有多个相互连接的局域网。(Local Area Networks)
2]无线局域网(WLAN)
顾名思义,这种类型的网络是 100% 无线的。它依赖于连接到互联网的路由器,而后者又为任何受支持的设备提供无线连接。该网络目前在您的家中。
3]城域网(MAN)
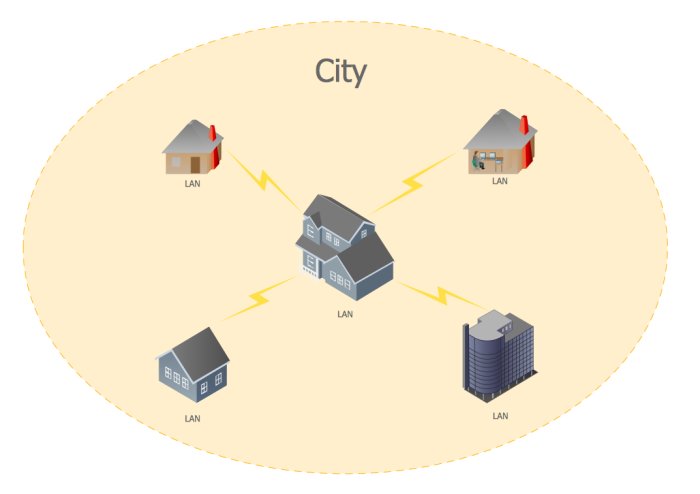
好的,所以一个MAN就是连接大都市地区的局域网(Area Networks)。由于(Due)距离的原因,连接这些网络以创建城域网(MAN)是通过传输技术完成的,其中有几种。由于成本原因,同轴电缆和光纤可能是最常用的。
4]广域网(WAN)

据我们所知,WAN类似于MAN,区别在于距离。在广域网(Wide Area Network)中,地理上独立的LAN(LANs)或WAN(WANs)或通过无线技术(大多数情况下是卫星)连接在一起。
5]个域网(PAN)
仅从名称中,您就应该了解该网络的含义。这是一个使用有线和无线技术连接单个工作空间中的计算机和设备的网络。
阅读(Read):什么是NTP 和 SNMP 网络协议(NTP and SNMP network protocols)。
6]校园区域网络(CAN)
通常在大学或任何拥有校园式总部的公司中找到。该网络是通过附近建筑物的一系列LAN实现的。(LANs)它比普通LAN大,但同时比MAN小。
7]存储区域网络(SAN)
这个超级简单。存储设备使用高速连接连接在一起。
我们希望这个基本教程可以帮助您了解。(We hope this basic tutorial helps you get an idea.)
What is a Computer Network? Different types of Computer Networks
What is a cоmputer network? That’s not a question you heаr on a regular basis, but it iѕ important, nonetheless. Without computer networks, the internet wouldn’t be as effiсient as it is today, so with that in mind, we’ve deсided to explain whаt a network is, to beginners, along with different types of networks. Not only that, but this artіcle will dіscuss the advantages of a network. There are no real disadvantages, therefore, we won’t even go there.
What is a Computer Network
Well, a network is a group of computer systems connected to share resources and communicate. Additionally, a network is also a collection of devices and computers linked together via transmission media and communication devices.
We will talk more about transmission media in another article, so keep an eye out for that very soon.
Utility of a network
- Expedite communications
- Share connected hardware
- Distribute data and information
1] Expedite communications
Because of networks, people can easily communicate with each other via email, messenger tools, chatrooms, social media, websites such as this one, online video call, and much more. If a network goes down, then all the tools connected to it will no longer operate.
2] Share connected hardware
If there are certain hardware devices connected to a network, then it becomes quite easy for those devices to be shared with all who have access to the network. For example, database files or a printer are quite common on networks, and they are known as the network’s resources.
3] Distribute data and information
Here’s the thing; if you are an authorized user, then you should have no problems gaining access to data and information stored on the network. A company such as Microsoft would have a huge database of customer information among other things, and all of this is open to employees with the right authority.
Types of computer networks
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Wireless LAN (WLAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Personal Area Network (PAN)
- Campus Area Network (CAN)
- Storage Area Network (SAN)
1] Local Area Network (LAN)

What we have here is a network that connects computers and devices in a small geographical area. For example, a LAN is usually located in a building. In fact, a building can have multiple Local Area Networks connected to each other.
2] Wireless LAN (WLAN)
As the name suggests, this type of network is 100 percent wireless. It relies on a router that is connected to the internet, which in turn, provides wireless connectivity to any supported devices. This network is currently in your home.
3] Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)

OK, so a MAN is all about connecting Local Area Networks in a metropolitan area. Due to the distance, connecting these networks to create a MAN is done via transmission technology, of which there are several. Coaxial and fiber are probably the most used over anything else due to cost.
4] Wide Area Network (WAN)

From what we can tell, a WAN is similar to a MAN, with the difference being the distance. In a Wide Area Network, geographically separate LANs or WANs or connected together via wireless technology, a satellite in most cases.
5] Personal Area Network (PAN)
From the name alone, you should get an idea of what this network entails. It’s a network that uses wires and wireless technology to connect computers and devices in an individual workspace.
Read: What are NTP and SNMP network protocols.
6] Campus Area Network (CAN)
Usually found in universities or any company with a campus-like headquarters. The network is made possible by a series of LANs from nearby buildings. It’s larger than a regular LAN, but at the same time, smaller than a MAN.
7] Storage Area Network (SAN)
This one is super simple. Storage devices are connected together using high-speed connections.
We hope this basic tutorial helps you get an idea.



