UEFI是Unified Extensible Firmware Interface的首字母缩写。它基本上是 BIOS 的替代品,BIOS用于在当今的(replacement for BIOS)Windows 10/8 PC中设置硬件以及加载和启动操作系统。

什么是统一可扩展固件接口(Firmware Interface)或UEFI?
UEFI的祖先是英特尔(Intel)为其基于 Itanium 的服务器开发的。BIOS的主要限制是它是 16 位的,只有 1 MB 的可寻址空间并使用主引导记录(Master Boot Record)( MBR ) 分区方案。因此BIOS可以使用的RAM数量受到限制,它无法支持容量超过 2.2TB的HDD 。为了克服这些限制,英特尔(Intel)推出了后来更名为EFI的(EFI)Intel Boot Initiative。然后由统一 EFI 论坛(Unified EFI Forum)接管,它演变成UEFI。
原始EFI接口用于Mac(Macs),仅支持Intel处理器。但另一方面,UEFI同时支持(UEFI)Intel和AMD处理器。
阅读(Read):UEFI 与 BIOS
UEFI 的优势
UEFI支持 32 位和 64 位架构。因此,它可以利用更多的RAM来执行比BIOS更复杂的过程。UEFI还支持独立于CPU的架构和驱动程序。
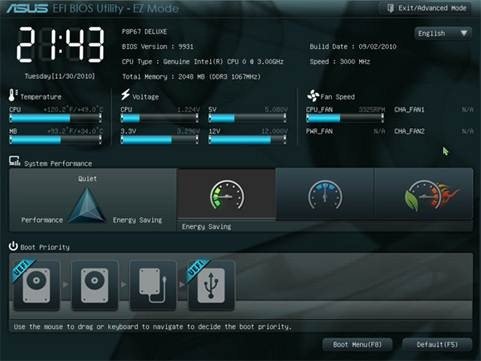
与BIOS不同,UEFI可以有一个更美观的支持鼠标的界面。请参阅下面的华硕 UEFI(Asus UEFI)界面。
除了标准的MBR分区方案,UEFI还支持GUID 分区表(GUID Partition Table)或GPT。GPT允许最大磁盘和分区大小为 9.4 ZB(与MBR的 2.2TB 相比)和(MBR)Windows上的 128 个分区(与MBR的 4 个相比)。
UEFI带有一个引导管理器,无需单独的引导加载程序。UEFI还支持非 16 位的ACPI等扩展。此外,UEFI还为您提供更快的启动和更好的网络支持。
随着硬件行业的进步,BIOS越来越不足以处理当今机器的功率和容量,而UEFI有能力至少在未来二十年内满足我们对更多计算能力日益增长的需求。
阅读(Read):在启动到 Windows Setup 或 Windows PE 时选择 UEFI 或 Legacy BIOS。
一般来说,与基于 BIOS 的机器相比,启用UEFI的机器具有更快的启动和关闭时间。(UEFI)以下是需要UEFI的(UEFI)Windows 10功能列表:
- 安全启动可保护 Windows 10 预启动过程免受 bootkit 和其他恶意软件攻击。
- 早期启动反恶意软件(Early Launch Anti-malware)( ELAM ) 驱动程序首先由安全启动(Secure Boot)加载,并在加载之前检查所有非 Microsoft 驱动程序。
- Windows 可信启动(Boot)在启动期间保护内核和系统驱动程序。
- Measured Boot将测量从固件到引导启动驱动程序的组件,并将这些测量结果存储在TPM芯片中。
- Device Guard使用CPU虚拟化和TPM支持来支持带有AppLocker的Device (Device Guard)Guard(Device Guard)和带有Credential Guard 的 Device Guard(Credential Guard)。
- Credential Guard与Device Guard一起使用,并使用CPU虚拟化和TPM支持来保护NTLM哈希等安全信息。
- (BitLocker Network Unlock)当连接到公司网络时,BitLocker 网络解锁将在重新启动时自动解锁Windows 10 。
- 启用大型引导磁盘需要GUID 分区表或GPT磁盘分区。(GPT)
希望更多的制造商会从 BIOS 切换到 UEFI。(Hopefully, more manufacturers will switch to UEFI from BIOS.)
相关阅读:(Related reads:)
- 检查您的电脑是否支持 UEFI 或 BIOS
- 恢复或设置 Windows 计算机的 BIOS 或 UEFI 密码
- 如何在 VirtualBox 虚拟机中启用 EFI
- 如何访问 UEFI 固件设置
- 使用 EasyUEFI 管理 EFI/UEFI 引导选项。
What is UEFI or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface?
UEFI is the acronym for Unified Extensible Firmware Interface. It is basically a replacement for BIOS which is used to set up the hardware and load and start an operating system in today’s Windows 10/8 PCs.

What is Unified Extensible Firmware Interface or UEFI?
The ancestor of UEFI was developed by Intel for its Itanium-based servers. The main limitation of BIOS was that it was a 16-bit with just 1 MB of addressable space and utilized the Master Boot Record (MBR) partition scheme. Thus there were constraints on the amount of RAM that could be used by BIOS, and it couldn’t support an HDD with a capacity of above 2.2TB. In order to overcome these limitations, Intel introduced the Intel Boot Initiative which was later renamed as EFI. It was then taken over by the Unified EFI Forum, which evolved it into UEFI.
The original EFI interface is used in Macs and only supports Intel processors. But UEFI, on the other hand, supports both Intel and AMD processors.
Read: UEFI vs BIOS
Advantages of UEFI
UEFI supports both 32-bit and 64-bit architecture. Thus it can utilize more RAM to do more complex processes than BIOS. UEFI also supports CPU independent architecture and drivers.
Unlike BIOS, UEFI can have a more visually pleasing interface that supports a mouse. See the Asus UEFI interface below.

Apart from the standard MBR partition scheme, UEFI also supports GUID Partition Table or GPT. GPT allows for a maximum disk and partition size of 9.4 ZB (compared to 2.2TB of MBR) and 128 partitions on Windows (compared to 4 of MBR).
UEFI comes with a boot manager which removes the needs for a separate boot loader. UEFI also supports extensions such as ACPI that are not 16-bit. Besides, UEFI also gives you faster start-ups and better networking support.
With the advancement in the hardware industry, BIOS is becoming more and more insufficient to handle the power and capacities of today’s machines and UEFI has the capability to handle our ever-growing thirst for more computing power at least for the next two decades.
Read: Choose UEFI or Legacy BIOS when booting into Windows Setup or Windows PE.
In general, UEFI-enabled machines have faster startup and shutdown times as compared to BIOS-based machines. Here is a list of Windows 10 features that requires UEFI:
- Secure Boot protects Windows 10 pre-boot process against bootkit and other malware attacks.
- Early Launch Anti-malware (ELAM) driver gets loaded by Secure Boot first and checks all non-Microsoft drivers before they are loaded.
- Windows Trusted Boot protects the kernel and system drivers during launch.
- Measured Boot will measure components from firmware till the boot-start drivers & stores these measurements in the TPM chip.
- Device Guard uses CPU virtualization and TPM support to support Device Guard with AppLocker, and Device Guard with Credential Guard.
- Credential Guard works with Device Guard and uses CPU virtualization and TPM support to protect security information like NTLM hashes, etc.
- BitLocker Network Unlock will automatically unlock Windows 10 at reboot when connected to a corporate network.
- GUID Partition Table or GPT disk partitioning is required to enable large boot disks.
Hopefully, more manufacturers will switch to UEFI from BIOS.
Related reads:
- Check if your PC supports UEFI or BIOS
- Recover or set a BIOS or UEFI Password for Windows computers
- How to enable EFI in VirtualBox virtual machine
- How to access UEFI Firmware settings
- Manage EFI/UEFI boot options with EasyUEFI.


