查看计算机信息的最简单方法是使用Windows图形工具,例如任务管理器或系统信息(Task Manager or System Information)。但是,有些人更喜欢将命令提示符或 PowerShell(Command Prompt or PowerShell)用于几乎任何事情。如果您想知道如何在CMD(命令提示符)中获取(Command Prompt)系统信息(system info),或者如果您想了解如何从命令行(command line)管理正在运行的进程,请继续阅读。我们将展示如何做所有这些事情:
注意:(NOTE:)本教程中的信息适用于Windows 10、Windows 8.1 和 Windows 7,并且这些命令可在命令提示符(Command Prompt)和PowerShell中使用。
1.使用systeminfo命令(systeminfo command)获取系统信息(system information)
Windows有一个内置命令来检查系统配置(system configuration)。它被称为systeminfo,当您运行它时,它会向您显示有关您计算机的一长串信息。打开Command Prompt 或 PowerShell(Command Prompt or PowerShell),输入 systeminfo 并按 Enter(type systeminfo and press Enter)。
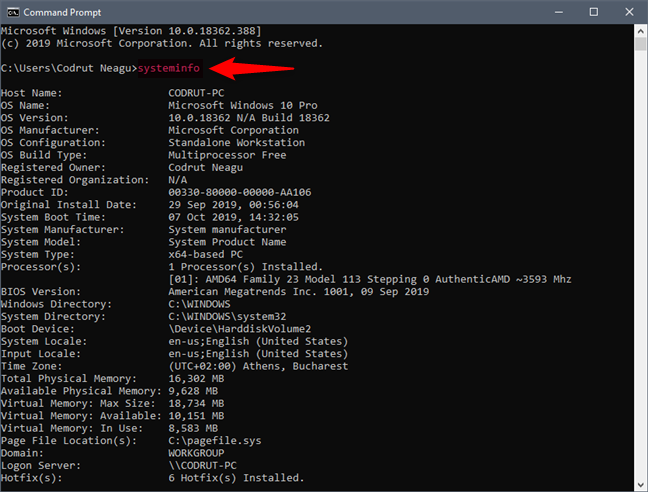
你看到发生了什么吗?systeminfo 命令(systeminfo command)显示有关您的操作系统(operating system)、计算机硬件和软件组件(computer hardware and software components)的详细信息列表。您会看到详细信息,例如计算机上安装的操作系统版本、 (operating system)RAM的状态或您拥有的处理器。还有一些网络信息(network information),例如网卡的 IP 和MAC地址。
2.使用tasklist命令查看(tasklist command)Windows中正在运行的进程列表
要查看当前正在运行的进程列表,您可以在命令提示符和 PowerShell中使用(Command Prompt and PowerShell)tasklist 命令(tasklist command)。键入任务列表(tasklist)并按 Enter。

该命令应输出与上述类似的列表,其中包含有关正在运行的进程的名称、它们的PID(进程标识符)(PID (Process identifier))和它们使用的内存的详细信息。
3.使用taskkill命令(taskkill command)停止一个进程
要从命令提示符或 PowerShell(Command Prompt or PowerShell)中终止或停止正在运行的进程,可以使用taskkill 命令(taskkill command)。假设您要停止OneDrive。它的进程称为OneDrive.exe。要杀死它,您应该运行命令taskkill /f /im OneDrive.exe。/f 参数告诉 Windows 强制终止进程,而/im parameter用于通过键入进程名称来识别和停止进程。

有时您需要打开一个程序两次(program twice)甚至多次。每个新窗口,有时甚至是特定程序(例如Firefox)的选项卡都会创建一个名为 instance 的单独进程,并附加一个唯一的PID(进程标识符) 。(PID (Process identifier))
要停止进程的单个实例,您需要指定其PID(进程标识符)(PID (Process identifier))。假设您的计算机上打开了几个Firefox实例。(Firefox)该进程的名称是 firefox.exe,但您只想关闭其中一个正在运行的实例(选项卡、窗口)。
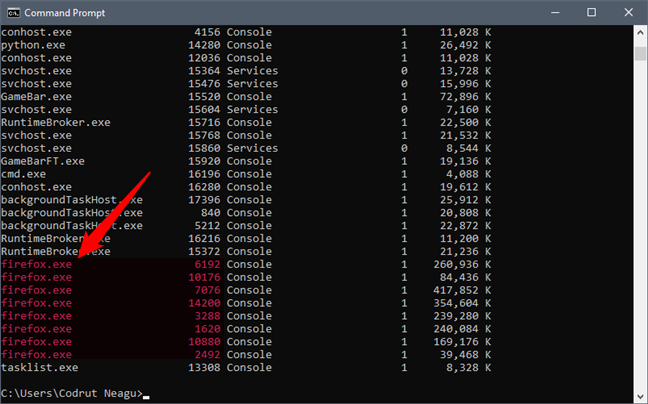
如果要终止PID为 2492 的进程,则应键入 taskkill / PID 2492 然后按Enter。

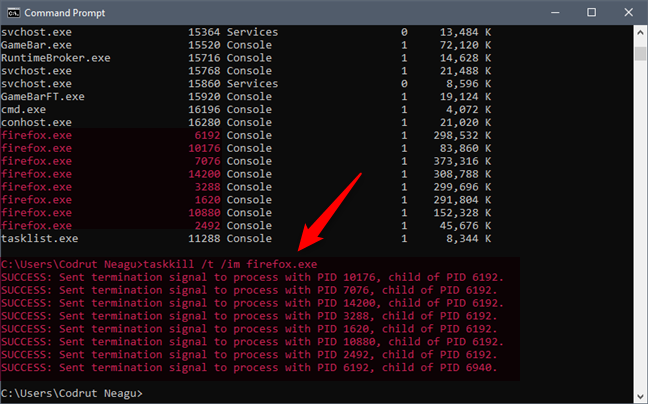
可用于命令 taskkill(command taskkill)的另一个参数是 /t。此参数允许您终止指定进程和由它启动的任何子进程。再举一个例子:Firefox 进程(Firefox process)。假设您有八个进程,并且您想使用parameter /t杀死所有进程。您应该键入命令“taskkill /t /im firefox.exe ”,然后按Enter。检查下面的屏幕截图以查看您刚刚键入的命令的确认。
请注意,如果您滥用本文中列出的命令,您可能会丢失在运行进程中打开的数据。必须小心并为您的数据准备好备份。因此(Therefore)请谨慎行事,不要说我们没有警告您。🙂
注意:(NOTE:)为了能够杀死任何正在运行的进程,您需要以管理员身份运行命令提示符或 PowerShell 。(Command Prompt or PowerShell)如果您不知道如何操作,请阅读:在Windows中以管理员身份运行程序的 9 种方法。
您喜欢使用命令行(command line)来检查系统信息(system info)和管理正在运行的进程吗?
您知道如何使用命令提示符或 PowerShell中的一些文本命令来显示 PC 的(Command Prompt or PowerShell)系统信息(system information),以及如何停止进程。你现在不觉得怪怪的吗?如果您这样做,请在下方发表评论,并告诉我们您有多喜欢使用CMD 或 PowerShell(CMD or PowerShell)。🙂
View system information and manage processes from CMD or PowerShell
The easiest waу to view information about your computеr is to υse Windows graphicаl tools such as Task Manager or System Information. However, some people prеfer to use the Command Prompt or PowerShell for, well, almost anything. If уou're wondering how to get system info in CMD (Command Prompt), or if you want to learn how to manage running processeѕ from the command line, read on. We're going to show how you can do all of these things:
NOTE: The information in this tutorial applies to Windows 10, Windows 8.1, and Windows 7, and the commands work both in Command Prompt and PowerShell.
1. Use the systeminfo command to get system information
Windows has a built-in command to check the system configuration. It's called systeminfo and, when you run it, it shows you a long list of information about your computer. Open Command Prompt or PowerShell, type systeminfo and press Enter.

Do you see what's happening? The systeminfo command displays a list of details about your operating system, computer hardware and software components. You see details such as the version of the operating system installed on your computer, the status of your RAM or the processor that you have. There's also some network information, like the IP and the MAC addresses of your network cards.
2. Use the tasklist command to see the list of running processes in Windows
To view the list of the processes that are currently running, you can use the tasklist command, both in Command Prompt and PowerShell. Type tasklist and press Enter.

The command should output a list similar to the one above, with details about the names of running processes, their PID (Process identifier) and the memory they use.
3. Use the taskkill command to stop a process
To kill or stop a running process from Command Prompt or PowerShell, you can use the taskkill command. Let's assume that you want to stop OneDrive. Its process is called OneDrive.exe. To kill it, you should run the command taskkill /f /im OneDrive.exe. The /f parameter tells Windows to forcefully terminate the process, and the /im parameter is used to identify and stop a process by typing its name.

There are times when you need to open a program twice or even several times. Every new window and sometimes the tabs of a specific program (for example, Firefox) creates a separate process called instance with a unique PID (Process identifier) attached to it.
To stop a single instance of a process, you need to specify its PID (Process identifier). Let's assume that there are a couple of instances of Firefox open on your computer. The process's name is firefox.exe, but you want to close only one of its running instances (tabs, windows).

If you want to kill the process that has a PID of 2492, you should type taskkill /PID 2492 and then press Enter.

Another parameter that you can use for the command taskkill is /t. This parameter allows you to terminate a specified process and any child processes which were started by it. Take the same example: the Firefox process. Let's assume that you have eight processes, and you want to kill all of them using the parameter /t. You should type the command "taskkill /t /im firefox.exe" and then press Enter. Check the screenshot below to see the confirmation of the command you just typed.

Note that if you misuse the commands listed in this article, you risk losing the data opened in the running processes. It is essential to be careful and have a backup available for your data. Therefore proceed carefully and do not say that we didn't warn you. 🙂
NOTE: To be able to kill any running process, you need to run the Command Prompt or PowerShell as administrator. If you do not know how, read: 9 ways to run programs as administrator in Windows.
Do you like using the command line to check for system info and manage your running processes?
You know how to display the system information of your PC, and how to stop processes, using a few text commands in the Command Prompt or PowerShell. Don't you feel geeky right now? If you do, comment below, and tells us how much you enjoy using CMD or PowerShell. 🙂






