MSConfig 或 系统配置实用程序 是(System Configuration Utility )Windows中的内置工具,可让您管理启动项、启动选项、服务和以安全模式启动(manage startup items, boot options, Services & boot in Safe Mode)等。在启动部分下,有一个高级选项(Advanced Options)按钮。本部分允许您访问配置选项,例如处理器数量、内存量、调试和全局调试(Global Debug)设置。请记住,这些选项是为高级用户诊断系统的最后选择。在这篇文章中,我们将详细介绍Windows 11/10中MSCONFIG中的这些启动高级(Boot Advanced) 选项(Options)。
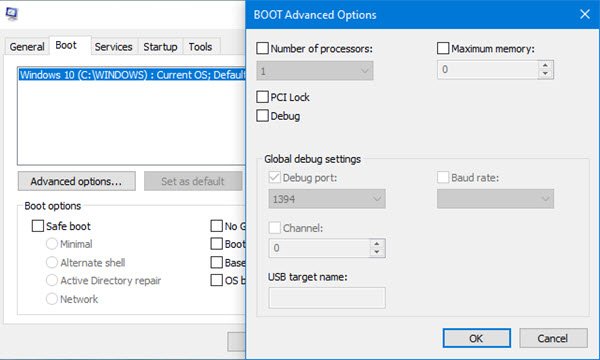
MSCONFIG 中的引导高级选项
你需要清楚地理解一件事。系统配置实用程序或 MSCONFIG(System Configuration Utility or MSCONFIG)的高级引导部分专为故障排除而构建。但是,当最终用户找到此选项时,就会出现混淆。我们强烈建议您将这些设置保留为默认值,不要更改它们。
处理器数量
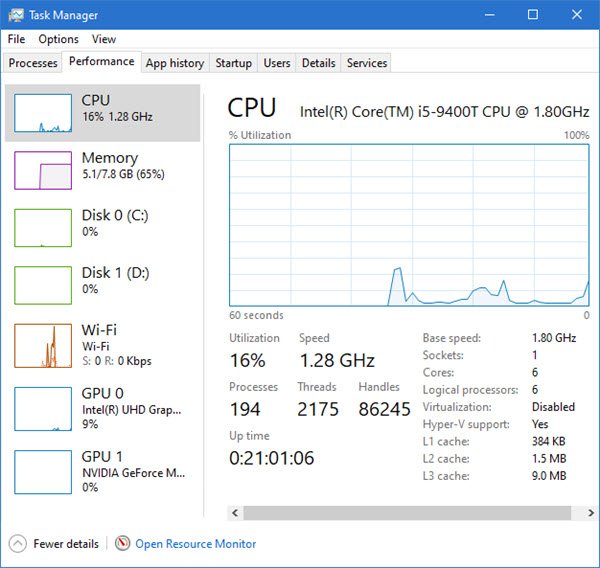
打开任务管理器(Task Manager)并切换到性能(Performance)选项卡。记下CPU内核和内存的数量。
现在,在运行提示中键入(Run)MSCONFIG,然后按Enter键。切换到启动(Boot)部分,然后单击高级选项(Advanced options)按钮
检查处理器数量框并选择任何小于下拉列表中可用最大值的选项。您看到的最大数字将与您在任务管理器(Task Manager)中看到的相同。
重新启动(Reboot),然后检查有多少处理器,以及操作系统可用的内存量。
我敢肯定,与计算机在默认配置下启动时相比,您会体验到较慢的性能。虽然我不确定为什么会有这些设置,但我猜它可以帮助开发人员在不改变实际硬件配置的情况下弄清楚他们的应用程序在低硬件配置下的性能。这同样适用于Windows。
现在让我们看看其他部分:
PCI 锁
PCI是向计算机添加组件的硬件总线。BIOS或 OS 可以确定资源需求并自动分配,因此不会发生冲突。在早期,它很有用,因为 Windows 曾经接管它。
从我在论坛中看到的情况来看,最好不要选中它,除非您在连接的硬件方面遇到问题。Windows 可以接管它,但我们还没有开始,除了检查时,它会导致BSOD。
如果您检查了PCI Lock并且遇到了BSOD,请确保启动到安全模式(boot into safe mode),然后使用 msconfig禁用PCI锁。(PCI)您可能需要一个可引导的 USB 设备才能进入高级引导配置(Advanced Boot configuration)。
调试
这是调试内核(Kernel)的开发人员选项,调试工具连接到操作系统。同样,它是一个非消费者选项,应该保持原样。当您选中Debug时,您可以配置其余选项,包括Debug端口、Channel、USB目标名称和波特率(Baud)。使用此功能时,您必须在计算机上禁用或暂停BitLocker和安全启动(Secure Boot)。
使用Windows 10中的(Windows 10)bcdedit 工具可以完成很多工作,该工具还提供 /dbgsettings作为选项之一。您可以使用它来禁用驱动程序签名(disable driver signature)、启用或禁用数据执行等。
您还将看到最大内存(Maximum memory)、全局调试设置(Global debug settings)等的其他设置。
这里有一点很清楚。这些不是消费者的选择,您无法使用它们来加速计算机(speed up computers)。这些高级(Advanced)选项是调试工具,从我记事起就一直存在。Windows中有很多这样的工具,除非你从事硬件调试,否则不要使用它。
我希望这篇文章很容易理解,并且您能够弄清楚为什么您作为消费者不应该在Windows 10的MSCONFIG中使用(MSCONFIG)Boot Advanced Options。
Boot Advanced Options in MSCONFIG in Windows 11/10 explained
MSConfig or System Configuration Utility is an inbuilt tool in Windows that allows you to manage startup items, boot options, Services & boot in Safe Mode, etc. Under the boot section, there is an Advanced Options button. This section gives you access to configure options such as the number of processors, the amount of memory, debug, and Global Debug settings. Keep in mind that these options are last-resort choices to diagnose your systems for advanced users. In this post, we will get into details about these Boot Advanced Options in MSCONFIG in Windows 11/10.

Boot Advanced Options in MSCONFIG
There is one thing you need to understand clearly. The advanced boot section of System Configuration Utility or MSCONFIG is built for troubleshooting. However, the confusion occurs when the end-user finds this option. We strongly urge you to keep these settings at their default values and not change them.
Number of Processors

Open Task Manager and switch to the Performance tab. Take a note of the number of CPU cores and memory.
Now, type MSCONFIG in the Run prompt, and press the Enter key. Switch to Boot section, and click on the Advanced options button
Check the number of processors box and select anything less than the maximum available in the dropdown. The maximum figure you see will be the same as what you saw in the Task Manager.
Reboot, and then check how many processors, and amount of memory is available for the OS.
I am sure you will experience a slower performance compared to what you had when computer boots under default configuration. While I am not sure why these settings are there, but I am guessing it helps developers to figure out how their application performs under low hardware configuration without changing the actual hardware configuration. The same can apply for Windows.
Now let’s take a look at the other sections:
PCI Lock
PCI is a hardware bus to add components to a computer. The BIOS or OS can determine the resource requirement and automatically assign it, so there is no conflict. In earlier days, it was useful as Windows used to take this over.
From what I have seen in forums, it is best to keep it unchecked, unless you are having issues with connected hardware. Windows can take this over, but we haven’t head about except that when checked, it results in a BSOD.
If you have checked PCI Lock, and are getting a BSOD, make sure to boot into safe mode, and then disable the PCI lock using msconfig. You may need a bootable USB device to get into the Advanced Boot configuration.
Debug
It is a developer option where to debug Kernel, debugging tools are connected to the OS. Again it is a non-consumer option and should be left as is. When you check Debug, you can configure the rest of the options, including Debug port, Channel, USB target name, and Baud rate. When using this, you will have to disable or suspend BitLocker and Secure Boot on the computer.
There is a lot that can be done using the bcdedit tool in Windows 10, which also offers /dbgsettings as one of the options. You can use it to disable driver signature, enable or disable data execution, and so on.
You will also see other settings for Maximum memory, Global debug settings, etc.
There is one thing clear here. These are not consumer options, and there is no way you can use them to speed up computers. These Advanced options are debugging tools, and they have been there as long as I can remember. There are many such tools in Windows, and unless you are into hardware debugging, do not use it.
I hope the post was easy to understand, and you were able to figure out why you, as a consumer, should not be using the Boot Advanced Options in MSCONFIG in Windows 10.


