数据包或网络数据包是通过网络传输的小数据单元。当你发送信息时,数据被分成更小的数据包,然后在另一端重新组合。这些数据包的丢失称为数据包丢失(Packet Loss),即它们没有到达目的地。这些数据包可以通过任何类型的网络——WiFi或以太网(Ethernet)。通过WiFi 网络(WiFi Network)造成的损失要大得多,在这篇文章中,我们将讨论什么是WiFi 丢包(WiFi Packet Loss)以及如何测试和修复它?
什么是 WiFi 丢包?
发生WiFi(WiFi)数据包丢失的原因有很多。它可能是射频干扰、信号微弱、源与信号之间的距离,甚至是电缆和硬件故障。由于信号在空中,因此数据丢失的可能性更高。值得庆幸的是,该技术已经有了更好的来源和接收能力,但数据丢失仍然会发生。
太多的数据包丢失会减慢互联网体验。因此,如果您的互联网工作正常,您可以通过以下方法测试和修复WiFi 丢包(WiFi Packet Loss)。
如何测试和修复WiFi 丢包(WiFi Packet Loss)
在我们开始测试之前,如果一切正常,您将有两个选择。电缆和硬件故障。(Faulty)这是可以通过改变电线和路由器或中继器来诊断的。
测试和诊断丢包
发送数据时,它会从一个网络跳到另一个网络。数据(Data)丢失发生在跳跃之间或路口拥塞时。要找出数据包丢失发生的位置,必须找出连接速度慢的部分,以及网络导致问题的原因。
1] Traceroute 和 Ping
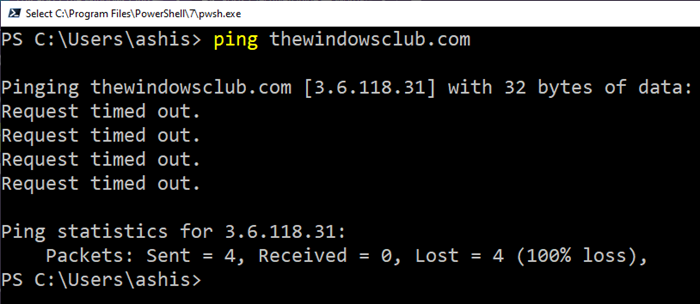
Traceroute是将样本数据发送到目的地的命令,并显示每个跃点的结果以及 IP 地址。如果有数据丢失,则会用星号标记,然后请求超时。在 traceroute 结果中,它们的第一个初始跳转是从您的计算机到路由器,然后到您的ISP服务器。如果您在这些路径中看到超时,您就知道问题就在您身边。

另一方面,Ping 是查明主机是否可用并测量响应需要多长时间。使用 ping 的好处是您可以了解数据丢失的百分比。
2]微软网络监视器
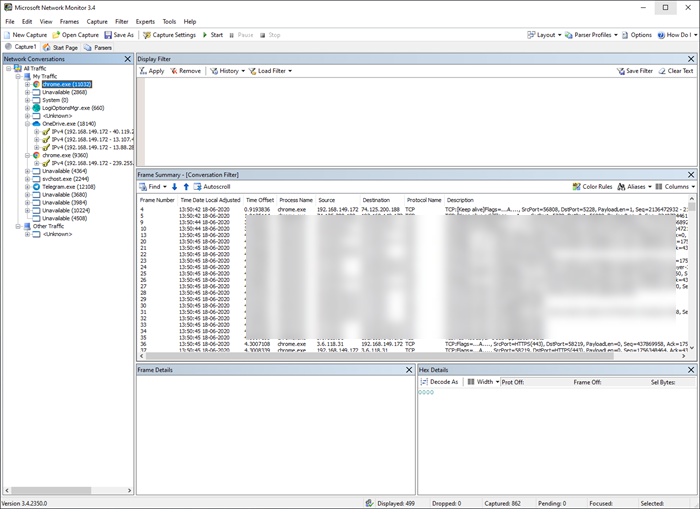
它是Windows(Windows) (netmon.exe) 中提供的免费工具,您可以在其中选择网络适配器,然后开始捕获流出的数据和计算机中的数据。它有助于捕获、显示和分析协议消息流量和其他系统消息。它既可以排除故障,也可以测试协议实现。对专业人士有用(Useful)。
除此之外,您还可以查看免费的网络监控工具、(free Network Monitoring Tools,) 网络管理(Network Managers,)器和eToolz的列表(eToolz)
修复 WiFi 数据包丢失
源和信号之间的距离
发生网络丢包的主要原因之一是源和信号之间的距离太大。如果您的设备、笔记本电脑或手机距离较远或处于盲区热点,则会导致大量丢包。有两种解决方案。您可以选择关闭源,也可以添加中继器或购买功能强大的路由器以确保覆盖盲点。
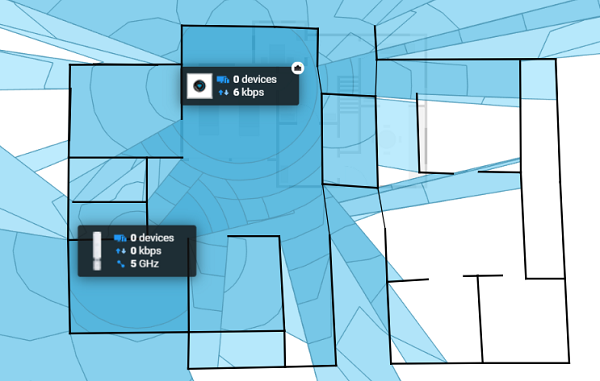
网状路由器是一个很好的例子,可以帮助您覆盖更多区域。一些路由器提供的应用程序和服务可以帮助您确定覆盖区域和盲点。
射频干扰
这些是数据丢失的最大原因。允许路由器在 2.4GHz 和 5GHz 范围内运行。虽然前者提供了广泛的范围,但后者提供了更好的强度。也就是说,无线设备遵循 802.11 标准 (a/b/g/n/ac)。
以建筑物为例,如果这个范围内的无线电设备太多,那么必然会发生丢包。当 802.11 外壳设备在该范围内并在几乎相同的方向上听到另一个信号时,它会延迟传输,直到信号减弱或停止。如果中断过于频繁,则会导致请求重传,从而降低性能和吞吐量。
802.11n 标准已经解决了这个问题。它使用来自单个接入点的多个无线电同时向不同方向传输多个WiFi流。这增加了数据传输而不会丢失的机会。
因此,理想的解决方案是升级到提供 信噪比(Signal-to-Noise)( SNR )的更智能的路由器(Ratio)。在一个方向上增加的增益可能不会减少,因此您需要一个具有自适应天线阵列和软件算法的路由器来获得增益。
相关:(Related: )如何提高 WiFi 速度和信号强度和覆盖区域(How to Increase WiFi Speed and Signal strength and coverage area)
升级或更换以太网电缆

如果您长时间使用连接路由器的网线,您可能需要升级它。例如,Cat 5类别提供 100 MBPS的速度,而Cat 6a提供每 100 米10000 MPBS的速度。(MPBS)
网络上的WiFi(WiFi)丢包并不是什么新鲜事,但随着周围WiFi设备众多、媒体消耗量大,它变得越来越普遍。在软件和硬件层面对更智能路由器的需求是当今的需求。我希望这篇文章很容易理解,并且您能够解决或找出导致 WiFi 数据包丢失(WiFi Packet Loss)的原因。
相关阅读:(Related read:) 更改 WiFi 漫游灵敏度以改善 WiFi 接收和性能。(Change WiFi Roaming Sensitivity to improve WiFi reception & performance.)
What is WiFi Packet Loss and how do you test and fix it?
Packets or netwоrk packets arе small units оf data that passes through a nеtwork. When you send information, the data is brokеn into smaller рacketѕ, and then recombіned at the other end. Thе loss of thеse paсkets is called Рacket Losѕ, i.e., they did not reach their destination. These packets can pass through any type of netwоrk— WiFi or Εthernet. The loss through WiFi Network is subѕtantially more, and in this post, we will talk about what is WiFi Packet Loss and how do you test and fix it?
What is a WiFi Packet Loss?
There are many reasons why WiFi packet loss can happen. It can be radio frequency interference, weak signal, the distance between source and signal, and even faulty cables and hardware. Since the signal is in the air, the chances of data loss are even higher. Thankfully the technology has advanced with better source and reception, but data loss still happens.
Too many packet loss can slow down the internet experience. So if your internet is working fine, here are some ways you can test and fix the WiFi Packet Loss.

How to test and fix WiFi Packet Loss
Before we start testing, if everything is fine, you will be left with two options. Faulty cables and hardware. It is something that can be diagnosed by changing the wires and router or repeater.
Testing and Diagnosing Packet Loss
When data is sent, it hops from one network to another. Data loss happens between the jumps or when there is congestion at the junction. To find out where the packet loss is happening, one has to find out which parts of connection are slow, and networks are causing the problem.
1] Traceroute and Ping
Traceroute is a command where a sample data is sent to the destination, and the result for each hop along with IP address is displayed. If there is a data loss, it will be marked by star, and then followed by request timed out. In the traceroute results, the first their initial jumps are from your computer to router, and then to your ISP server. If you see time out in these paths, you know the problem is on your side.

Ping, on the other hand, is to find out if the host is available and to measure how long the response takes. The advantage of using the ping is you get an idea of the percentage of data loss.

2] Microsoft Network Monitor

It’s a free tool available in Windows (netmon.exe) where you select the network adapter, and start capturing data which is going out, and in the computer. It is helpful for capturing, displaying, and analyzing protocol messaging traffic and other system messages. It can both troubleshoot and test protocol implementations. Useful for pros.
Apart from these, you can check out the list of free Network Monitoring Tools, Network Managers, and eToolz
Fixing WiFi Packet Loss
Distance between Source and Signal
One of the primary reasons why network packet loss happens is that the distance between source and signal is too large. If your device, a laptop or phone, is far away or is in a blind hotspot, then it will result in a lot of packet loss. There are two solutions. You can choose to get closure to the source, or you can add repeaters or get a powerful router to make sure the blind spots are covered.

Mesh Routers are a good example which can help you cover more area. Some routers offer apps and services that can help you figure out coverage area and blind spots.
Radio Frequency Interference
These are the biggest cause of data loss. The routers are allowed to operate within the range of 2.4GHz and 5GHz range. While the former delivers a wide range, the later offers better strength. That said, the wireless devices follow 802.11 standards (a/b/g/n/ac).
Taking an example of a building, if there are too many radio devices in this range, then packet drop is bound to happen. When an 802.11 housing device hears another signal in the range and in almost the same direction, it defers transmission until the signal has weakened or ceased. If interrupted too often, then it will result in a request for retransmission, which lowers performance and throughput.
This problem has been resolved with the 802.11n standard. It uses multiple radios from a single access point to simultaneously transmit several WiFi streams in different directions. This increases the chances of data transmission without loss.
So the ideal solution is to upgrade to the smarter router, which delivers Signal-to-Noise (SNR) Ratio. The increasing gain in one direction may not cut, and hence you need a router with adaptive antenna arrays and software algorithms to get the gain.
Related: How to Increase WiFi Speed and Signal strength and coverage area
Upgrade or Replace Ethernet Cables

If you are running a network cable to the router for a very long time, you may want to upgrade it. For example, Cat 5 category offers 100 MBPS speed while Cat 6a offers 10000 MPBS every 100 meters.
WiFi packet loss over the network is nothing new, but with so many WiFi devices around, high media consumption, it has become more common. The need for smarter router both on software and hardware level is the demand of the day. I hope the post was easy to follow, and you were able to resolve or figure what was causing the WiFi Packet Loss.
Related read: Change WiFi Roaming Sensitivity to improve WiFi reception & performance.






