启动计算机系统涉及在计算机开机时从各种启动设备(如驱动程序、网络和USB(USB)驱动器)加载操作系统 。一旦启动序列完成加载操作系统,系统硬件将准备好执行复杂的操作。引导日志(Boot log)是一个记录,在引导过程中维护各种Windows系统的成功或失败列表。(Windows)
在Windows 11中启用或禁用启动日志(Boot Log)
引导(Boot)日志记录在引导过程中从计算机存储系统加载到内存时发生的所有事情。它适用于各种设备,如网络、硬件设备和操作系统,有助于识别引导过程中的问题以及与故障排除有关的其他问题。在引导(Boot)日志的帮助下,用户可以在引导过程中找出从系统启动时卸载和加载的驱动程序。在Windows中,用户可以启用或禁用启动(Boot)日志功能。
日志文件命名为ntbtlog.txt,其中列出了所有成功加载的进程以及启动过程中不成功的进程。日志保存到驱动器 C:\Windows\ntbtlog.txt。用户可以通过两种方式启用或禁用引导(Boot)日志。一种是使用System Configuration (msconfig),另一种是使用Command Prompt。在本文中,我们将解释如何在Windows 11/10启动(Boot)日志。
在系统配置(System Configuration)中启用引导日志(Boot Log)
按Win + R键打开运行。(Run)要打开System Configuration,请键入msconfig并单击 OK。
在系统配置(System Configuration)窗口中,转到引导选项卡(Boot tab)并检查引导选项下的引导日志(Boot Log)选项(Boot options)以启用引导日志功能。
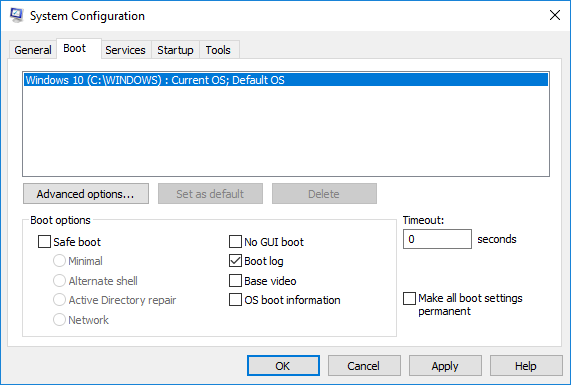
单击确定(OK)以保存更改。
单击提示窗口中的重新启动(Restart)按钮以启动引导(Boot)日志过程。
重新启动完成后,导航到C:\Windows\ntbtlog.txt以访问启动日志。
日志文件包含所有成功加载的驱动程序列表以及在启动序列期间未能加载的驱动程序列表。每次用户重新启动系统时,日志文件都会不断更新并最终增加列表条目。轻松找到驱动程序并使您的故障排除更容易 建议在故障排除后禁用引导日志。
在系统配置(System Configuration)中禁用引导日志(Boot Log)
按Win + R键打开运行。(Run)要打开System Configuration,请输入msconfig并单击 Ok。
在系统配置(System Configuration)窗口中,转到引导选项卡(Boot tab)并取消选中(uncheck)引导选项 下的引导日志(Boot Log)选项(Boot options)以禁用引导日志功能。
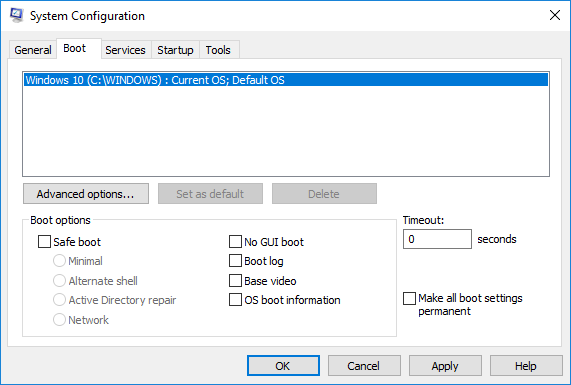
单击确定(OK)以保存更改。
使用命令提示符(Command Prompt)启用引导日志(Boot Log)
在开始菜单中,在搜索栏中键入命令提示符(Command Prompt)。右键(Right)单击命令提示符(Command Prompt)选项并以管理员身份运行(Run as administrator)。
在命令提示符下键入bcdedit并单击(bcdedit)Enter。

要启用Boot log,首先需要找到当前操作系统的 Identifier 。(find the Identifier)您可以在名为“描述”的字段中的(Description)Windows 引导加载程序(Windows Boot Loader)部分下找到操作系统。在我们的例子中,它是 Windows 10。
您可以在字段名称标识符旁边的Windows 引导加载程序(Windows Bootloader)部分下找到操作系统标识符。通常,标识符将是{current}。要了解启动日志条目是启用还是禁用,请检查Windows Boot Loader下的“Bootlog”字段。如果启用了“引导日志”条目,则该条目将为“是”。如果引导日志被禁用,则该条目将为“否”。
要启用引导日志,请键入以下带有操作系统标识符的命令。
bcdedit /set {identifier} bootlog Yes
确保(Make)在上面的 {identifier} 字段中替换您的操作系统标识符
在这种情况下,我们将 {identifier} 替换为实际的操作系统标识符,如下所示
bcdedit /set {current} bootlog Yes
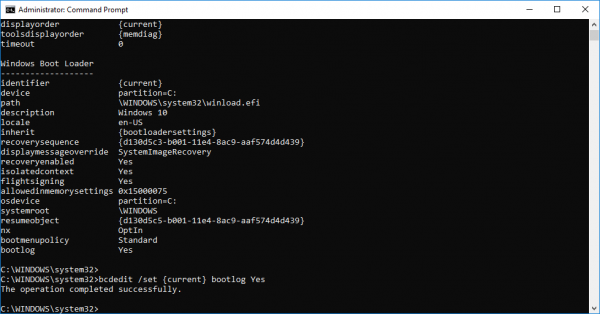
重新启动系统以启动引导(Boot)日志进程。
重新启动完成后,导航到C:\Windows\ntbtlog.txt以访问启动日志。
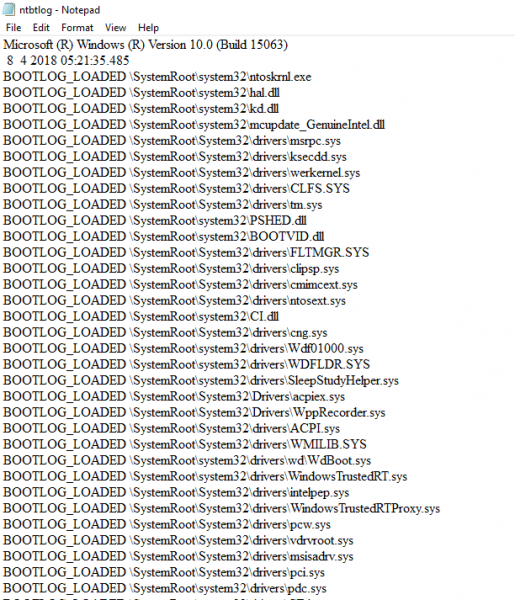
每次用户重新启动系统时,日志文件都会不断更新,最终会增加日志的大小。轻松找到驱动程序并使您的故障排除更容易 建议在故障排除后禁用引导日志。按照以下步骤使用命令提示符禁用引导日志
使用命令提示符(Command Prompt)禁用引导日志(Boot Log)
在开始菜单中,在搜索栏中键入命令提示符(Command Prompt)。右键(Right)单击命令提示符(Command Prompt)选项并以管理员身份运行。(Run as administrator.)
键入以下命令以禁用启动日志-
bcdedit/ set {identifier} bootlog No
确保(Make)在上面的 {identifier} 字段中替换您的操作系统标识符
在这种情况下,我们将 {identifier} 替换为实际的操作系统标识符,如下所示
bcdedit /set {current} bootlog No
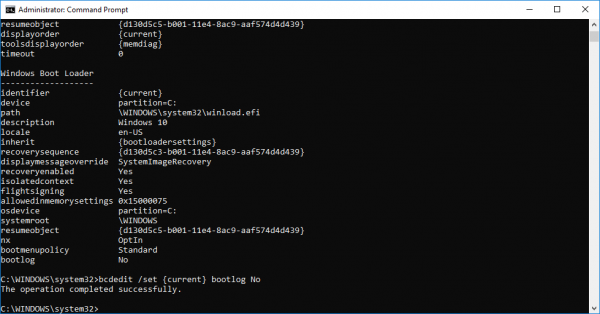
完成后,关闭命令提示符。
就这样。(That’s all.)
How to Enable or Disable Boot Log in Windows 11/10
Booting the computer system invоlves loadіng an operating systеm frоm the various boot deνices like drivers, network, and USB drives when the comрuter is switched on. Once the startup sequence finishes loading the operating system, thе system hardware will be rеady to perform complex operations. The Boot log is a record that maintains the list of success or failure of various pieces of Windows system during the booting process.
Enable or Disable Boot Log in Windows 11
The Boot log keeps a record of everything that has happened while loading from the computer storage system to the memory during the boot process. It is available for various devices like network, hardware devices, and operating system which assists in identifying problems during the boot process and other issues pertaining to the troubleshooting. With the help of the Boot log, users can find out the drivers unloaded and loaded from the start of the system during the boot process. In Windows, users can either enable or disable the Boot log feature.
The log file is named as ntbtlog.txt which lists all the successfully loaded processes as well as an unsuccessful process during the boot process. The log is saved to drive C:\Windows\ntbtlog.txt. Users can enable or disable the Boot log in two ways. One is by using System Configuration (msconfig), and the other way is to use a Command Prompt. In this article, we explain how to enable or disable Boot log in Windows 11/10.
Enable Boot Log in System Configuration
Open Run by pressing Win + R key. To open System Configuration, type msconfig and click on OK.
In the System Configuration window, Go to Boot tab and check the with option Boot Log under Boot options to enable the Boot log feature.

Click on OK to save the changes.
Click on Restart button in the prompt window to start the Boot log process.
Once the restart is complete, navigate to C:\Windows\ntbtlog.txt to access the boot log.
The log file consists of a list of all the successfully loaded drivers as well as the list of drivers that failed to load during the startup sequence. Every time the user restarts the system, the log file keeps updating and eventually increases the list entries. To easily locate the drivers and make your troubleshooting easier It is recommended to disable the boot log after troubleshooting.
Disable Boot Log in System Configuration
Open Run by pressing Win + R key. To open System Configuration, type msconfig and click on Ok.
In the System Configuration window, Go to Boot tab and uncheck the option with Boot Log under Boot options to disable the Boot log feature.

Click on OK to save the changes.
Enable Boot Log using Command Prompt
In the Start menu, type Command Prompt in the search bar. Right click on Command Prompt option and Run as administrator.
Type bcdedit in the command prompt and click Enter.

To enable the Boot log, you need to first find the Identifier of the current operating system. You can find the OS under the Windows Boot Loader section in the field called “Description”. In our case, it is Windows 10.
You can find the operating system identifier under the Windows Bootloader section next to the field name identifier. Generally, the identifier will be {current }. To know if the boot log entry is enabled or disabled, check the field “Bootlog” under Windows Boot Loader. If the “bootlog” entry is enabled, the entry will be ‘Yes’. If the boot log is disabled, the entry will be ‘No’.
To enable the boot log, type the following command with the operating system identifier.
bcdedit /set {identifier} bootlog Yes
Make sure that you substitute your operating system identifier in the field {identifier } above
In this case we replace {identifier} with actual operating system identifier as {current} shown below
bcdedit /set {current} bootlog Yes

Restart the system to start the Boot log process.
Once the restart is complete, navigate to C:\Windows\ntbtlog.txt to access the boot log.

Every time the user restarts the system, the log file keeps updating and eventually increases the size of the log. To easily locate the drivers and make your troubleshooting easier It is recommended to disable the boot log after troubleshooting. Follow the below steps to disable the boot log using the command prompt
Disable Boot Log using Command Prompt
In the start menu, type Command Prompt in the search bar. Right click on Command Prompt option and Run as administrator.
Type the below command to disable the boot log-
bcdedit/ set {identifier} bootlog No
Make sure that you substitute your operating system identifier in the field {identifier } above
In this case, we replace {identifier} with actual operating system identifier as {current} shown below
bcdedit /set {current} bootlog No

Once done, close the command prompt.
That’s all.






