您可能已经installed Ubuntu or any other Linux distro on your PC alongside Windows 11/10.但也许现在如果你不想再使用Linux。在这种情况下,您最终会在硬盘驱动器上拥有一个占用一些磁盘空间的Linux分区。(Linux)在这篇文章中,我们将向您展示如何在 Windows 双启动中安全地卸载 Linux 而不会丢失数据或应用程序。

如果您安装了 Ubuntu 或类似的 Linux 发行版(similar Linux distribution like Linux Mint),例如带有Wubi的 Linux Mint,您可以通过(Wubi)Windows 10中的(Windows 10)程序(Programs)和功能(Features)小程序轻松卸载该发行版。在已安装程序列表中找到 Ubuntu(Find Ubuntu),然后像卸载任何其他程序一样卸载它。卸载程序会自动从您的计算机中删除Ubuntu文件和引导加载程序条目。
另一方面,如果您在双引导配置中将 Linux 安装到其自己的分区,则卸载它需要从您的计算机中删除Linux分区(Linux),然后扩展您的 Windows 分区以使用现在可用的硬盘空间。
在Windows 双启动(Windows Dual Boot)设置中卸载Linux
此过程分为两部分,第一部分是删除Linux操作系统,第二部分是修复主引导记录(Master Boot Record),因为仅删除Linux分区会导致Grub救援错误。
在开始之前,您可以备份文件并确保手边有Windows 10安装介质。如果您没有现成的可用,您可以在 Windows 10 计算机或Linux 或 Mac 计算机上创建它(create it on a Windows 10 computer)。
1]从Windows 10中(Windows 10)删除Linux(Delete Linux)分区
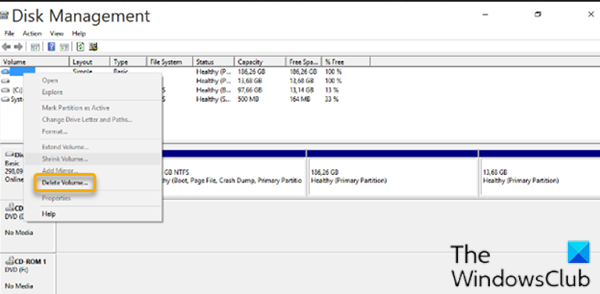
要从Windows 10(Windows 10)中删除Linux分区,请执行以下操作:
或者,您可以在提升的CMD(CMD)提示符下运行以下命令,将正确的EFI可执行文件设置为默认启动项:
bcdedit /set “{bootmgr}” path \efi\microsoft\boot\bootmgfw.efi
要查看上述命令是否有效,请重新启动计算机。如果成功,它应该直接启动到Windows。
- 在桌面上,按Windows 键(Windows key) + R调用“运行”对话框。
- 在“运行”对话框中,键入
diskmgmt.msc,按 Enter 以打开“磁盘管理”工具(open the Disk Management tool)。
Linux分区与(Linux)Windows不同,因为它们没有驱动器号和文件系统。而Windows分区可以通过驱动器标签来识别,例如 C、D 和 E。它们通常也是FAT 或 NTFS(FAT or NTFS)文件。
- 要删除Linux分区,请右键单击每个分区并选择 Delete Volume。
- 将弹出一个警告,让您知道您正在尝试删除不是由Windows创建的分区。然后,系统会询问您是否要删除它。
- 选择 是(Yes)。
- 重复该过程以删除其他Linux分区。
删除分区将释放驱动器上的空间。现在,您需要扩展 Windows 分区(extend your Windows partition)以占用可用空间。
该过程完成后,您将只看到一个卷,这意味着您已将所有磁盘空间归还给Windows。
您现在可以继续下一步。
2]修复(Repair)主引导记录(Master Boot Record)(MBR)
Linux现在已从您的计算机中删除,但它的引导加载程序仍然存在。我们需要使用Windows安装介质来修复和重建 MBR(repair and rebuild MBR),以便用Windows引导加载程序覆盖(Windows)Linux引导加载程序。
注意(Note):如果bootrec.exe /fixmbr命令不起作用,您可以从高级故障排除选项尝试(Advanced troubleshooting options)自动修复(Automatic Repair)。
完成后,您现在可以重新启动计算机。它将从其硬盘驱动器启动,正常启动Windows。Linux的所有痕迹现在都应该被删除 - 但是,如果当您启动计算机时出现双启动菜单,列出您刚刚删除的Linux发行版以及(Linux)Windows 10操作系统,您可以删除双启动-boot menu,以便在您重新启动计算机时 PC 直接启动到Windows 10,请执行以下步骤:
- 按Windows key + R调用“运行”对话框。
- 在“运行”对话框中,键入
msconfig并按 Enter。 - 转到 启动 (Boot )选项卡。
- 选择 Windows 10 条目。
- 单击设置为默认 (Set as Default )按钮。
- 您可以通过选择它然后单击删除 (Delete )按钮来删除Linux条目。(Linux)
- 单击 应用。(Apply.)
- 单击 确定。(OK.)
- 重启你的电脑。
就是这样!
How to uninstall Linux in Windows Dual Boot setup
You may have installed Ubuntu or any other Linux distro on your PC alongside Windows 11/10. But maybe now if you don’t want to use Linux anymore. In this case, you will end up having a Linux partition on your hard drive that is taking up some disk space. In this post, we will show you how to safely uninstall Linux in Windows dual boot without losing data or applications.

If you installed Ubuntu or a similar Linux distribution like Linux Mint with Wubi, you can easily uninstall the distro via the Programs and Features applet in Windows 10. Find Ubuntu in the list of installed programs, and then uninstall it like you would any other program. The uninstaller automatically removes the Ubuntu files and boot loader entry from your computer.
On the other hand, if you installed Linux to its own partition in a dual-boot configuration, uninstalling it requires removing the Linux partitions from your computer and then expanding your Windows partitions to use the now-free hard disk space.
Uninstall Linux in Windows Dual Boot setup
This procedure is broken down into two parts, of which the first part is to remove the Linux operating system and the second part is to repair the Master Boot Record, as just deleting the Linux partition will result in a Grub rescue error.
Before you begin, you can back up your files and make sure you have a Windows 10 installation media handy. If you don’t have one readily available, you can create it on a Windows 10 computer or on a Linux or Mac computer.
1] Delete Linux partition from Windows 10

To delete the Linux partition from Windows 10, do the following:
Alternatively, you can run the command below in an elevated CMD prompt to set the correct EFI executable as the default boot entry:
bcdedit /set “{bootmgr}” path \efi\microsoft\boot\bootmgfw.efi
To see if the above command worked, reboot your computer. If successful, it should boot directly to Windows.
- At the desktop, press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
diskmgmt.msc, hit Enter to open the Disk Management tool.
Linux partitions are differentiated from Windows because they don’t have a drive number and file system. While, Windows partitions can be identified by the drive label such as C, D, and E. They are also usually FAT or NTFS files.
- To delete the Linux partitions, right-click on each one and choose Delete Volume.
- A warning will pop-up letting you know that you are trying to delete a partition that wasn’t created by Windows. Then, you will be asked if you want to delete it.
- Select Yes.
- Repeat the process to delete other Linux partitions.
Deleting the partitions will free up space on your drive. Now, you’ll need to extend your Windows partition to occupy the free space.
After the process is complete, you will see only one volume meaning you have claimed all your disk space back to Windows.
You can now proceed with the next step.
2] Repair the Master Boot Record (MBR)
Linux has now been removed from your computer, but its boot loader persists. We’ll need to use a Windows installation media to repair and rebuild MBR so as to overwrite the Linux boot loader with the Windows boot loader.
Note: If the bootrec.exe /fixmbr command didn’t work, you can try Automatic Repair from the Advanced troubleshooting options.
Once done, you can now restart your computer. It will boot from its hard drive, starting Windows normally. All traces of Linux should now be erased – but, if when you boot the computer and you’re presented with the dual-boot menu, listing the Linux distro you’ve just removed along with the Windows 10 OS, you can remove the dual-boot menu, so that the PC boots directly into Windows 10 when you restart your computer, by following these steps:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
msconfig and hit Enter. - Go to Boot tab.
- Select the Windows 10 entry.
- Click Set as Default button.
- You can delete the Linux entry by selecting it and then clicking the Delete button.
- Click Apply.
- Click OK.
- Restart your computer.
That’s it!


