查找并连接到您所在地区的网络的最快方法是单击任务栏上的网络图标。通常,您现在会看到可用网络列表,您只需选择一个网络即可连接到它。

但是,某些用户可能会遇到单击网络图标不显示任何内容的问题。可以假设没有可用的网络,但如果您确定有可用的网络可以连接,那么您手头就有问题。这意味着您的计算机不再发现可用网络。如果您遇到此问题,请阅读这篇文章以了解如何永久解决该问题。
工具栏上的 Wi-Fi 图标未显示可用网络列表。
多种因素可能导致您的计算机停止发现可用网络。加入本节,我们将解决这个令人沮丧的问题。以下是我们将采用的修复:
- 重新启用无线适配器驱动程序。
- 打开网络发现。
- (Delete)从Windows注册表中删除过时的VPN条目。(VPN)
- 配置网络位置感知(Network Location Awareness)和网络列表(Network List) 服务(Services)。
- (Unblock)使用Netsh命令取消阻止被阻止的SSID 。(SSIDs)
在制定了这些解决方案之后,让我们深入研究执行它们的深入指南。
1]重新启用无线适配器驱动程序
Windows key + R组合 打开运行对话框 并运行devmgmt.msc命令。这将打开设备管理器(Device Manager)。
在这里,展开 网络适配器(Network adapters)部分并右键单击您的无线适配器驱动程序。从上下文菜单中选择 禁用设备选项。(Disable device)
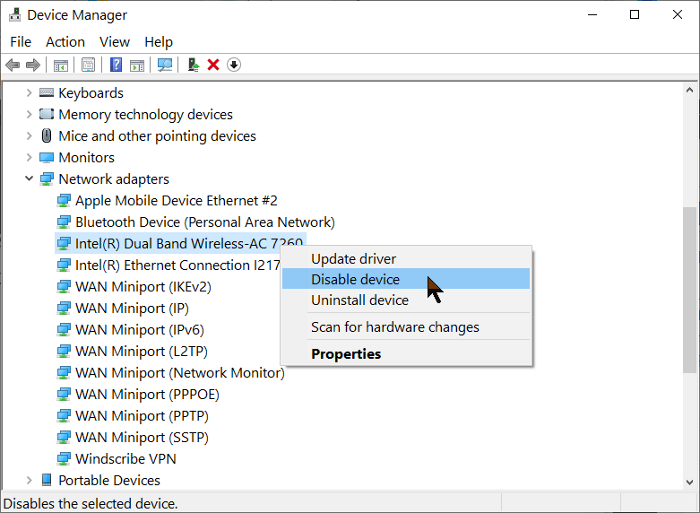
该列表现在将刷新,并且 Wi-Fi 图标可能会从您的任务栏中完全消失,但不要害怕。
再次右键单击(Right-click)无线适配器驱动程序,然后 从上下文菜单中单击启用设备 。(Enable device )在此之后,当您单击任务栏上的网络图标时,确认现在显示可用的网络。
2]打开网络发现
网络(Network)发现可让您查看网络中的其他设备并与之通信。因此,如果您点击网络(Network)图标但没有看到任何设备,您可能只需要打开网络发现。这是如何做到的:
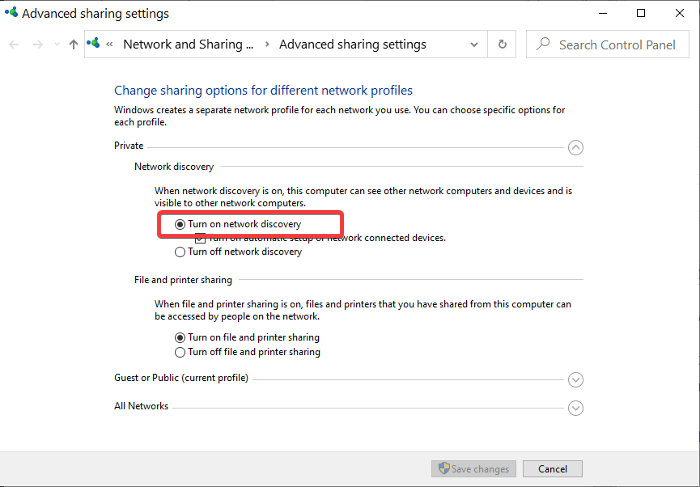
Windows key + I组合打开 Windows 设置 。在设置中,转到 Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Change Advanced Sharing Option。
展开 专用(Private)网络部分并选择 网络发现下的打开(Turn on network discovery)网络发现。
展开访客或公共(Guest or Public)网络部分并在网络发现中选择打开网络发现(Turn on network discovery)选项。
最后,点击下面的 保存更改(Save changes)按钮。
3]从Windows注册表中删除(Delete)过时的VPN条目(VPN)
如果您过去或现在通过虚拟专用网络 ( VPN ) 连接,您可能希望从系统注册表中删除其条目。这些条目可能会主动阻止对可用网络的发现。
首先,在Windows注册表上工作可能会破坏您的系统。因此,我建议您在继续进行此修复之前备份您的注册表。(back up your registry)
按 Windows 键并键入 cmd。右键单击建议中的命令提示符(Command Prompt),然后单击 以管理员身份运行(Run as administrator)。
(Input)在命令提示符窗口中(Command Prompt)输入以下命令,然后按 ENTER:
netcfg - n
您现在将看到列出的所有驱动程序、服务和网络协议。请注意此列表中的DNI_DNE,因为它属于旧的Cisco VPN客户端。如果找到 DNI_DNE,请键入以下命令并按 ENTER(ENTER)运行它。
reg delete HKCR\CLSID\{988248f3-a1ad-49bf-9170-676cbbc36ba3} /va /f
接下来,运行以下命令:
netcfg -v -u dni_dne
最后,关闭命令提示符(Command Prompt)窗口。在这一点上,如果过时的VPN是网络问题的原因,它会得到修复。
4]配置网络位置感知(Configure Network Location Awareness)和网络列表(Network List) 服务(Services)
网络列表服务 ( netprofm ) 是负责发现您之前连接的网络的服务。该服务还检索这些网络的属性,并使用有关这些网络的信息更新适用的程序。
与网络位置感知(Network Location Awareness)服务一起,网络列表服务(Network List Service)可让您的计算机系统在任务栏中向您显示连接状态。要正常运行,您必须启用这两个系统服务并设置它们的启动类型。
打开运行(Run)对话框并搜索 services.msc。
找到网络列表服务(Network List Service)并右键单击它,然后选择属性(Properties)选项。
单击 启动类型 (Startup type )下拉菜单并选择手动(Manual)。确保 服务状态(Service status)显示(Running)为Running 。如果没有,请单击 开始(Start)按钮。
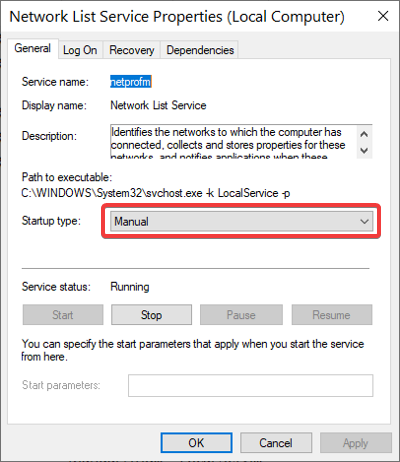
点击 应用(Apply)和 确定(OK)按钮以保存您的设置。
找到 Network Location Awareness 服务,右键单击它,然后单击 Properties。在启动类型下拉菜单中,将其更改为 Automatic。如果服务没有运行,请点击 开始(Start)按钮。
单击 应用(Apply)和 确定(OK)。
5]使用Netsh命令取消阻止(Unblock)被阻止的SSID(SSIDs)
SSID代表服务集标识符(Service Set Identifier)。SSID基本上是网络的名称。我们写了一篇关于如何阻止您的计算机连接到 SSID的详细文章。如果您阻止网络,则单击 Wi-Fi 图标时不会显示该网络。
在此修复中,我们将解锁所有被阻止的网络,以确保这不是问题的根源。当您单击网络图标时仅显示某些网络而其他网络不显示时,此解决方案最有用。
首先,敲击Windows键并搜索 cmd。右键单击命令提示符(Command Prompt)并选择 以管理员身份运行(Run as administrator)。在命令提示符(Command Prompt)中,键入以下命令并按 ENTER:
netsh wlan delete filter permission=denyall networktype=infrastructure
在此之后,关闭命令提示符(Command Prompt)并通过单击 Wi-Fi 图标查看是否仍然找不到网络。
这有帮助吗?
Wi-Fi icon on the toolbar not showing the list of available networks
The fastest way to find and connect to networks in your аrea is by clicking on the network icon on the taskbar. Normally, you’ll now see a liѕt of available networks, and you only have to sеlect a network to connect to it.

However, some users can experience an issue where clicking on the network icon shows nothing. One could assume that there’s no available network, but if you’re sure that there are available networks to connect to, then you have a problem on your hands. This means that your computer is no longer discovering available networks. If you’re experiencing this issue, read this post to the end to learn ways to resolve it for good.
Wi-Fi icon on toolbar not showing list of available networks.
A variety of factors can cause your computer to stop discovering available networks. Join me in this section as we troubleshoot this frustrating problem. Here are the fixes we’ll employ:
- Re-enable the wireless adapter driver.
- Turn on network discovery.
- Delete outdated VPN entries from the Windows registry.
- Configure the Network Location Awareness and Network List Services.
- Unblock blocked SSIDs with the Netsh command.
Having laid down these solutions, let’s delve into the in-depth guides for performing them.
1] Re-enable the wireless adapter driver
Open the Run dialog box using the Windows key + R combination and run the devmgmt.msc command. This opens up Device Manager.
Here, expand the Network adapters section and right-click on your wireless adapter driver. Select the Disable device option from the context menu.

The list will now refresh, and the Wi-Fi icon may go missing from your taskbar completely, but don’t be scared.
Right-click on the wireless adapter driver again and hit Enable device from the context menu. After this, confirm that the available networks now show up when you click the network icon on the taskbar.
2] Turn on network discovery

Network discovery lets you see and communicate with other devices in your network. So, if you hit the Network icon and don’t see any devices, you may just need to turn on network discovery. Here’s how to do it:
Open Windows Settings using the Windows key + I combination. In Settings, go to Network & Internet > Wi-Fi > Change Advanced Sharing Option.
Expand the Private network section and select Turn on network discovery under Network discovery.
Expand the Guest or Public network section and choose the Turn on network discovery option in Network discovery.
Finally, hit the Save changes button below.
3] Delete outdated VPN entries from the Windows registry
If you’ve connected through a virtual private network (VPN) in the past or currently, you may want to remove its entries from your system registry. These entries may actively block the discovery of available networks.
Firstly, working on the Windows registry can break your system. Therefore, I recommend that you back up your registry before proceeding with this fix.
Press the Windows key and type cmd. Right-click on Command Prompt from the suggestions and click on Run as administrator.
Input the following command in the Command Prompt window and press ENTER:
netcfg - n
You will now see all your drivers, services, and networking protocols listed. Look out for DNI_DNE on this list, as it belongs to an old Cisco VPN client. If you find DNI_DNE, type the below command and hit ENTER to run it.
reg delete HKCR\CLSID\{988248f3-a1ad-49bf-9170-676cbbc36ba3} /va /f
Next, run the following command:
netcfg -v -u dni_dne
Finally, close the Command Prompt window. At this point, if an outdated VPN were the cause of the network issue, it’d be fixed.
4] Configure Network Location Awareness and Network List Services
The Network List Service (netprofm) is the service responsible for discovering networks that you have connected to previously. This service also retrieves the properties of these networks and updates applicable programs with info about these networks.
Together with the Network Location Awareness service, the Network List Service lets your computer system show you the status of connections in the taskbar. To function properly, you have to enable both system services and set their startup types.
Open the Run dialog box and search for services.msc.
Find the Network List Service and right-click on it, and choose the Properties option.
Click on the Startup type dropdown menu and select Manual. Ensure that the Service status says Running. If not, click on the Start button.

Hit the Apply and OK buttons to save your settings.
Find the Network Location Awareness service, right-click on it, and click on Properties. In the startup type dropdown menu, change it to Automatic. If the service isn’t running, hit the Start button.
Click on Apply and OK.
5] Unblock blocked SSIDs with the Netsh command
SSID stands for Service Set Identifier. An SSID is basically a network’s name. We wrote a detailed article on how to block your computer from connecting to SSIDs. If you block a network, it won’t show up when you click the Wi-Fi icon.
In this fix, we’ll unlock all the blocked networks to make sure that this isn’t the root of the issue. This solution is most useful when only some networks appear when you click the network icon, and others don’t.
First, strike the Windows key and search for cmd. Right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator. In Command Prompt, type the following command and press ENTER:
netsh wlan delete filter permission=denyall networktype=infrastructure
Following this, close the Command Prompt and look if you still don’t find networks by clicking on the Wi-Fi icon.
Did this help?




