有许多Windows和Mac用户大部分时间都在盯着 Web 浏览器中打开的选项卡。它是活动的中心点,可让您回复电子邮件、玩游戏、查看社交媒体、观看视频等。可能性是无穷无尽的,但不幸的是,您的系统资源并非如此。
像Mozilla Firefox之类的浏览器可以而且会随着您使用的次数越多而耗尽可用的系统内存。这可能会导致您的计算机变慢并停止响应,尤其是在您无法找出原因的情况下。如果Firefox在一般使用期间使用过多内存,您将需要尝试这些修复以查看它们是否能解决问题。

重启火狐(Restart Firefox)
所有网络浏览器都存在内存泄漏问题,包括Firefox和Chrome。当具有多个运行选项卡的浏览器长时间运行时,通常会导致内存泄漏。一段时间后,打开的选项卡开始消耗并占用大部分可用系统资源,使您的 PC 难以响应。
如果发生这种情况,并且您认为Firefox是原因,那么简单的解决方案就是重新启动Firefox。但是,关闭 Firefox(Closing Firefox)可能不会完全结束任何正在运行的Firefox进程。如果您运行的是Windows,您需要检查所有正在运行的Firefox进程是否已在(Firefox)Windows 任务管理器(Windows Task Manager)中关闭。
- 为此,请右键单击任务栏并选择任务管理器(Task Manager)选项。

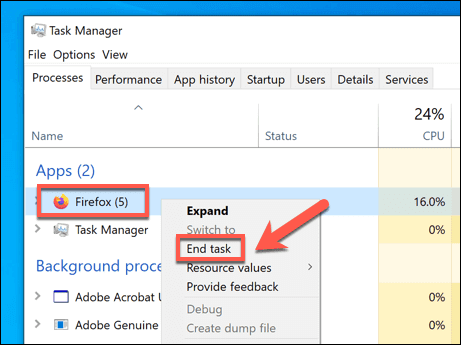
- 在任务管理器(Task Manager )窗口中,找到所有正在运行的Firefox进程。要结束它们,请右键单击该条目并选择“结束任务”(End Task)选项。这将强制Firefox关闭。
- 如果您使用的是Mac ,您可以通过右键单击Dock 上的Firefox 图标并选择(Firefox icon)Quit来强制退出正在运行的Firefox窗口。如果Firefox没有关闭并完全停止响应,请重复该过程,改为选择强制退出(Force Quit)。

禁用 Firefox 扩展、插件和主题(Disable Firefox Extensions, Plugins, and Themes)
Firefox是一个可定制的浏览器,带有各种可以扩展其功能的插件(add-ons),从主题到扩展(类似于Chrome 扩展(Chrome extensions)的工作方式)。不幸的是,添加太多附加组件有时会对您的浏览器性能产生不利影响,尤其是当您在低功率 PC 上运行时。
如果您想知道Firefox主题、插件或扩展是否导致Firefox使用过多内存,您需要禁用它们。就是这样。
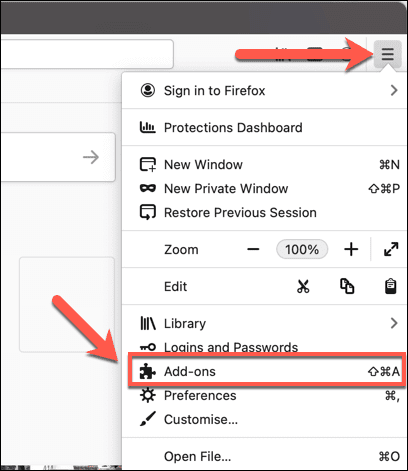
- 要禁用Firefox附加组件,请打开Firefox并选择右上角的汉堡菜单图标。(hamburger menu icon)从菜单中,选择附加组件(Add-ons )选项。
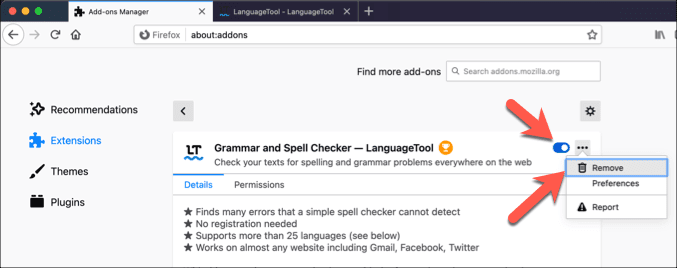
- 在Add-ons菜单中,您会在左侧看到Extensions、Themes和Plugins的选项。(Plugins)在Extensions中,选择启用的扩展程序旁边的滑块以禁用它。要删除它,请选择它旁边的三点菜单图标,然后从菜单中选择(three-dots menu icon )删除(Remove)。
- 如果您使用的是自定义Firefox主题,请通过选择Add-ons > Themes菜单中的启用(Enable)按钮切换回默认主题。(Default )作为默认的Firefox主题,它提供了导致不必要的内存使用的最小可能性。

- 如果您担心Firefox插件(例如媒体播放插件)会导致问题,请在Add-ons > Plugins 菜单中选择插件旁边的三点菜单(three-dots menu )图标。从菜单中,选择从不激活(Never Activate )选项以禁用它。

检查 Firefox 更新(Check For Firefox Updates)
每个新的Firefox版本都带来了新功能和错误修复,有助于减少已知问题的影响,包括不必要的内存使用。如果Firefox已过时,您可能会错过重要的错误修复。
- 要检查新的Firefox更新,请选择右上角的汉堡菜单图标。(hamburger menu icon )从菜单中,选择首选项(Preferences)选项。

- 在Preferences菜单中,向下滚动到Firefox Updates部分。要检查新更新,请选择检查更新(Check for updates)选项。Firefox将检查更新,如果有可用更新,它将自动更新或提示您安装,具体取决于您的设置。

使用 about:memory 菜单最小化内存使用(Use The about:memory Menu to Minimize Memory Usage)
像Firefox(Firefox)这样的现代浏览器旨在尽量减少它们的内存占用,即使它并不总是有效。如果Firefox使用过多内存,您可以利用名为about:memory的隐藏设置菜单来强制它快速减少活动内存使用量。
- 为此,请在地址栏中键入about:memory并按 Enter。

- 从about:memory设置菜单中的可用选项列表中,选择最小化内存使用(Minimize memory usage)选项。如果成功,选项下方将显示内存最小化完成消息。(Memory minimization completed )您可以随时重复此过程。

切换到 Firefox 安全模式(Switch to Firefox Safe Mode)
Firefox 安全模式(Firefox Safe Mode)是一种特殊的浏览器模式,可帮助您识别和修复浏览器问题。如果您怀疑Firefox插件或设置的问题导致不必要的内存使用,切换到安全模式(Safe Mode)可以帮助诊断问题。
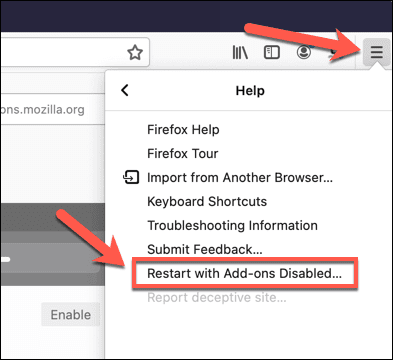
- 要切换到Firefox 安全模式(Firefox Safe Mode),请选择右上角的汉堡菜单图标。(hamburger menu icon )从菜单中,选择Help > Restart with add-ons disabled。
- (Confirm)通过在弹出窗口中选择重新启动选项,(Restart)确认您要以安全模式重新启动(Safe Mode)Firefox 。
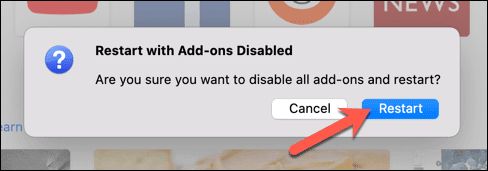
- Firefox将重新启动,您可以选择打开安全模式(Safe Mode)或完全重置Firefox。选择以安全模式(Start in Safe Mode)启动以启动安全模式。
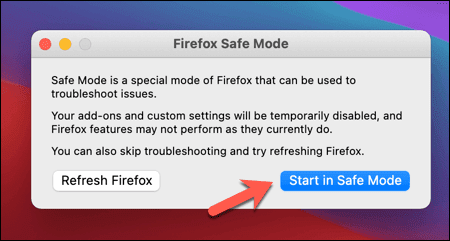
Firefox窗口将正常启动,但禁用所有扩展、主题和插件。在监控系统资源使用情况时正常使用浏览器。如果它没有使用大量内存,这表明Firefox在正常使用期间存在问题,您必须进一步调查。
更改硬件加速设置(Change Hardware Acceleration Settings)
为了最大限度地利用系统资源,Firefox使用硬件加速来平衡各种正在运行的选项卡和服务的需求。这可能会导致对系统资源的需求增加,从而导致其他正在运行的应用程序变慢或崩溃。
如果是这种情况,您需要更改 Firefox 的硬件加速设置,并在必要时完全禁用它。
- 首先,通过选择hamburger menu icon > PreferencesFirefox设置菜单。

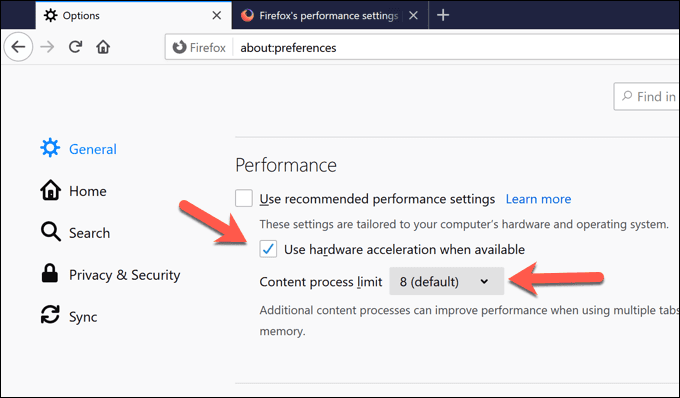
- 在“首选项”选项卡的“(Preferences)General > Performance部分下,取消选中“使用推荐的性能设置(Use recommended performance settings)”选项以查看其他设置。从那里,减少内容进程限制(Content process limit )值以限制额外运行的Firefox进程的数量并减少进程中的内存使用量。或者,通过取消选中“可用时使用硬件加速(Use hardware acceleration when available )”选项来完全禁用硬件加速。
将 Firefox 重置为默认设置(Reset Firefox to Default Settings)
当一切都失败了,并且您无法诊断Firefox的设置、附加组件或功能的问题时,您可能会发现将其重置为默认设置有助于解决Firefox使用过多内存的问题。
- 为此,请打开Firefox并选择hamburger menu icon > Help > Troubleshooting Information。

- 在故障排除信息(Troubleshooting Information )菜单中,选择右上角的刷新 Firefox选项。(Refresh Firefox)

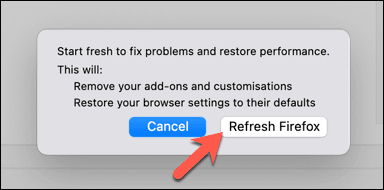
- Firefox会警告您,这将清除所有浏览器设置、附加组件和自定义设置。但是,它不会删除您的书签和浏览历史记录。要确认,请选择刷新 Firefox(Refresh Firefox)选项以开始该过程。
- 重置过程完成后,Firefox将重新启动。您将看到一条成功(Success )消息,允许您恢复以前的选项卡和窗口。确认您的选择,然后选择让我们(Let’s go )继续使用 Firefox。

有效使用 Firefox(Using Firefox Effectively)
如果Firefox使用了太多内存,在大多数情况下,上面的修复应该有助于解决问题。如果他们不这样做,您可能需要考虑替代解决方案,例如切换到另一个浏览器或升级您的硬件(upgrading your hardware)。慢速浏览器可能会指出其他可能需要诊断工具(diagnostic tools)来帮助识别和修复的问题。
一旦Firefox正常工作,您就可以利用其许多注重隐私的功能。例如,您可以通过额外的安全设置使 Firefox(make Firefox safer)使用更安全,使用Firefox Monitor提醒您任何隐私泄露(privacy breaches),或者您可以使用 Firefox Private Network(use Firefox Private Network)保持匿名在线。
Firefox Using Too Much Memory? 7 Ways to Fix
There are many Windows and Mac users who spend most оf their time staring at open tabs in their web browser. It’s the center point of activity, allowing you to respond to emails, play games, check social mediа, watch videos, and more. The pоѕsibilities are endless, but, unfortunatelу, your system resources are not.
Browsers like Mozilla Firefox can and will use up available system memory the more you use them. This can cause your computer to slow down and stop responding, especially if you can’t figure out the cause. If Firefox is using too much memory during general usage, you’ll need to try these fixes to see if they resolve the problem.

Restart Firefox
All web browsers suffer from memory leak issues, including Firefox and Chrome. Memory leaks are usually caused when a browser, with multiple running tabs, is left running for a long period of time. After a while, the open tabs begin to eat up and claim most of the available system resources, leaving your PC struggling to respond.
If that happens, and you think Firefox is the cause, an easy solution is simply to restart Firefox. Closing Firefox may not fully end any running Firefox processes, however. If you’re running Windows, you’ll need to check that all running Firefox processes have closed in Windows Task Manager.
- To do this, right-click the taskbar and select the Task Manager option.

- In the Task Manager window, find any running Firefox processes. To end them, right-click the entry and select the End Task option. This will force Firefox to close.

- If you’re on Mac, you can force quit a running Firefox window by right-clicking the Firefox icon on the Dock and selecting Quit. If Firefox doesn’t close and stops responding entirely, repeat the process, selecting Force Quit instead.

Disable Firefox Extensions, Plugins, and Themes
Firefox is a customizable browser with various add-ons that can extend its functionality, from themes to extensions (similar to how Chrome extensions work). Unfortunately, adding too many add-ons can occasionally have a detrimental impact on your browser performance, especially if you’re running on a lower-powered PC.
If you’re wondering whether a Firefox theme, plugin, or extension is causing Firefox to use too much memory, you’ll need to disable them. Here’s how.
- To disable Firefox add-ons, open Firefox and select the hamburger menu icon in the top-right. From the menu, select the Add-ons option.

- In the Add-ons menu, you’ll see options for Extensions, Themes, and Plugins on the left. In Extensions, select the slider next to an enabled extension to disable it. To remove it, select the three-dots menu icon next to it, then select Remove from the menu.

- If you’re using a custom Firefox theme, switch back to the Default theme by selecting the Enable button in the Add-ons > Themes menu. As the default Firefox theme, it offers the least likelihood of causing unnecessary memory usage.

- If you’re worried that a Firefox plugin (such as a media playback plugin) is causing issues, select the three-dots menu icon next to a plugin in the Add-ons > Plugins menu. From the menu, select the Never Activate option to disable it.

Check For Firefox Updates
Each new Firefox release brings new features and bug fixes that can help to reduce the impact of known issues, including unnecessary memory usage. If Firefox is out of date, you might be missing a crucial bug fix.
- To check for new Firefox updates, select the hamburger menu icon in the top-right. From the menu, select the Preferences option.

- In the Preferences menu, scroll down to the Firefox Updates section. To check for new updates, select the Check for updates option. Firefox will check for updates and, if an update is available, it will update automatically or prompt you to install it, depending on your settings.

Use The about:memory Menu to Minimize Memory Usage
Modern browsers like Firefox are designed to try and minimize their memory footprint, even if it doesn’t always work. If Firefox is using too much memory, you can take advantage of a hidden settings menu called about:memory to force it to quickly reduce active memory usage.
- To do this, type about:memory in the address bar and press enter.

- From the list of available options in the about:memory settings menu, select the Minimize memory usage option. If successful, a Memory minimization completed message will appear beneath the options. You can repeat this process at any point.

Switch to Firefox Safe Mode
Firefox Safe Mode is a special browser mode that helps you to identify and fix issues with the browser. If you suspect that a problem with a Firefox add-on or setting is causing unnecessary memory usage, switching to Safe Mode can help to diagnose the problem.
- To switch to Firefox Safe Mode, select the hamburger menu icon in the top-right. From the menu, select Help > Restart with add-ons disabled.

- Confirm you want to restart Firefox in Safe Mode by selecting the Restart option in the pop-up.

- Firefox will restart, giving you the option to open Safe Mode or reset Firefox entirely. Select Start in Safe Mode to launch Safe Mode.

The Firefox window will launch as normal, but with all extensions, themes, and plugins disabled. Use your browser as normal while monitoring system resource usage. If it isn’t using a huge amount of memory, this would indicate a problem with Firefox during normal usage, and you’ll have to investigate further.
Change Hardware Acceleration Settings
To maximise the power of your system resources, Firefox uses hardware acceleration to balance out the demands of various running tabs and services. This can cause an increased demand on your system resources which can cause other running apps to slow down or crash.
If that’s the case, you’ll need to change Firefox’s hardware acceleration settings and, if necessary, disable it entirely.
- To start, open the Firefox settings menu by selecting the hamburger menu icon > Preferences.

- Under the General > Performance section of the Preferences tab, uncheck the Use recommended performance settings option to view additional settings. From there, reduce the Content process limit value to limit the number of additional running Firefox processes and reduce memory usage in the process. Alternatively, disable hardware acceleration completely by unchecking the Use hardware acceleration when available option.

Reset Firefox to Default Settings
When all else fails, and you can’t diagnose a problem with Firefox’s settings, add-ons, or features, you may find that resetting it to default settings can help to resolve a problem where Firefox is using too much memory.
- To do this, open Firefox and select the hamburger menu icon > Help > Troubleshooting Information.

- In the Troubleshooting Information menu, select the Refresh Firefox option in the top-right corner.

- Firefox will warn you that this will erase any browser settings, add-ons, and customization. It won’t, however, remove your bookmarks and browsing history. To confirm, select the Refresh Firefox option to begin the process.

- Once the reset process is complete, Firefox will restart. You’ll see a Success message, allowing you to restore previous tabs and windows. Confirm your choice, then select Let’s go to resume using Firefox.

Using Firefox Effectively
If Firefox is using too much memory, the fixes above should help to resolve the problem in most cases. If they don’t, you may need to consider alternative solutions, such as switching to another browser or upgrading your hardware. A slow browser could point to other issues that might require diagnostic tools to help identify and fix.
Once Firefox is working properly, you can take advantage of its many privacy-focused features. For instance, you can make Firefox safer to use with extra security settings, use Firefox Monitor to alert you to any privacy breaches, or you can use Firefox Private Network to stay anonymous online.





















