如果您使用 Google 服务,如Google Docs、Google Sheets、Google Analytics、Gmail等,您可以使用Google Apps Script连接和自动化这些服务。
将Google Apps 脚本视为(Google Apps Script)Google 版本的Microsoft VBA 脚本(Microsoft’s VBA script)。就像您可以使用 VBA 在Microsoft Word和Excel(Excel with VBA)中自动执行操作和任务或自定义宏一样,您可以跨Google服务自动执行任务和操作。在 Sheets 和Docs等服务中,您甚至可以编写自己的自定义菜单。

在本文中,您将了解如何在各种 Google 服务中访问和启用(various Google services)Apps 脚本(Apps Script)、如何导航Apps 脚本编辑器(Apps Script Editor)以及如何连接服务。您不会学习特定的脚本功能(learn specific script functions),但Google提供了出色的文档和应用脚本教程,可用于学习如何编写应用脚本(Apps Script)。
如何访问 Google Apps 脚本编辑器(Access Google Apps Script Editor)
您可以从许多Google服务中打开Google Apps 脚本代码编辑器。(Google Apps Script)例如,您会在 Google 表格的扩展菜单中找到(Extensions)Apps 脚本。(Apps Script)

在其他服务中,您可以通过以下方式打开Google Apps 脚本编辑器:(Google Apps Script)
- Google Docs :在工具(Tools)菜单中选择脚本编辑器。(Script editor)
- Google 幻灯片(Google Slides):在工具(Tools)菜单中选择脚本编辑器。(Script editor)
- Google 表单(Google Forms):在三点菜单中选择脚本编辑器。(Script editor)
- Google Drive:右键单击任何空白区域,选择More,然后选择Google Apps Script。
使用这些方法中的任何一种,您都会看到Apps 脚本(Apps Script)代码编辑器在新选项卡中打开。这是您将编写构成整个脚本的每个函数的窗口。默认情况下,您会看到一个名为 myFunction() 的空函数,您可以开始填写代码。
注意(Note):为了避免错误,代码格式非常重要。使用如下代码所示的注释来提醒自己在代码段中尝试执行的操作。这与使用 Web 编程的HTML代码中的注释工作方式非常相似。

在浏览代码编辑器时,您可以通过在编辑器(Editor)窗口的左侧导航窗格中选择Code.gs来返回此部分。要查看其他可用窗口,请将鼠标悬停在最左侧窗格中的图标上,主导航窗格将打开。
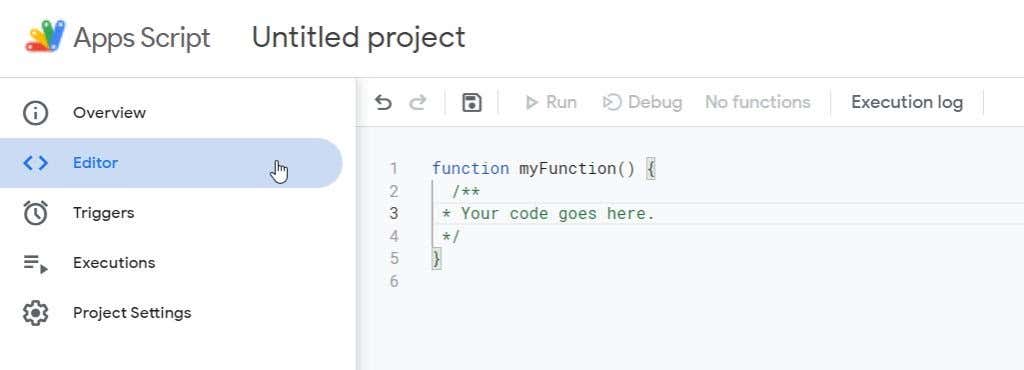
您可以在概览(Overview)部分找到有关脚本的统计信息,例如发生了多少错误、执行了多少次等等。

我们将在下面的每个部分中介绍Google Apps 脚本(Google Apps Script)编辑器的每个其他部分。
浏览Google Apps 脚本编辑器(Google Apps Script Editor)
当您在编辑器中编辑代码时,最好经常选择磁盘 ( Save ) 图标,以免丢失您的工作。

保存后,您会看到其他菜单选项亮起。

这些包括:
- 运行(Run):尝试从头到尾运行整个脚本。
- 调试(Debug):一次单步执行您的脚本。
- 函数下拉列表(Function dropdown):浏览并导航到您创建的每个函数。
- 执行日志(Execution log):查看您每次尝试运行脚本的任何状态或错误消息。
左侧导航菜单中的库(Libraries)选项是您可以访问其他人编写的库(或者您已经编写并保存在其他地方)的地方。如果您的朋友已经编写了您想在Google 表格(Google Sheets)或Google 文档(Google Docs)中使用的功能,但您想在此基础上添加其他功能,这将非常有用。
将这些库添加到项目中所需的只是Script ID。您可以在项目设置部分找到它,我们将在本文末尾向您展示如何找到它。

Google Apps 脚本服务插件
服务(Services)部分是最有用的。在这里,您可以将当前脚本与您可能使用 的其他Google服务集成在一起。(Google)
当您选择它时,您将看到“添加服务(Add a service)”窗口打开。向下滚动(Scroll)到要用作现有项目的附加组件的服务。
例如,如果您想将Google Analytics帐户中的数据提取到此脚本中,您可以选择Google Analytics API,然后选择Add。

如果您想详细了解哪些功能可用于该新附加服务以及如何使用它们,请选择API右侧的三个点,然后选择查看文档(See documentation)。

这将在新选项卡中打开Google Apps 脚本(Google Apps Script)文档,该选项卡会自动打开到该Google服务的部分。

探索可在您自己的脚本中使用的函数语法、教程和代码示例的文档。
此外,请注意,您可以导航到文档的其他部分,以根据您最初打开Apps 脚本(Apps Script)代码编辑器时使用的服务查看脚本中可用的常规功能。
例如,如果您在Google Sheets中打开了编辑器,请查看文档菜单中的Sheets部分,了解您可以在脚本中使用的Google Sheets功能。(Google Sheets)
设置和使用 Apps 脚本触发器(Using Apps Script Triggers)
Google Apps 脚本(Google Apps Script)中的另一个有用功能是能够根据许多事件或时间表设置触发器。
要为脚本配置新触发器,请从最左侧的导航菜单中选择触发器。(Triggers)在打开的新触发器(Triggers)窗口中,选择添加触发器(Add Trigger)按钮。
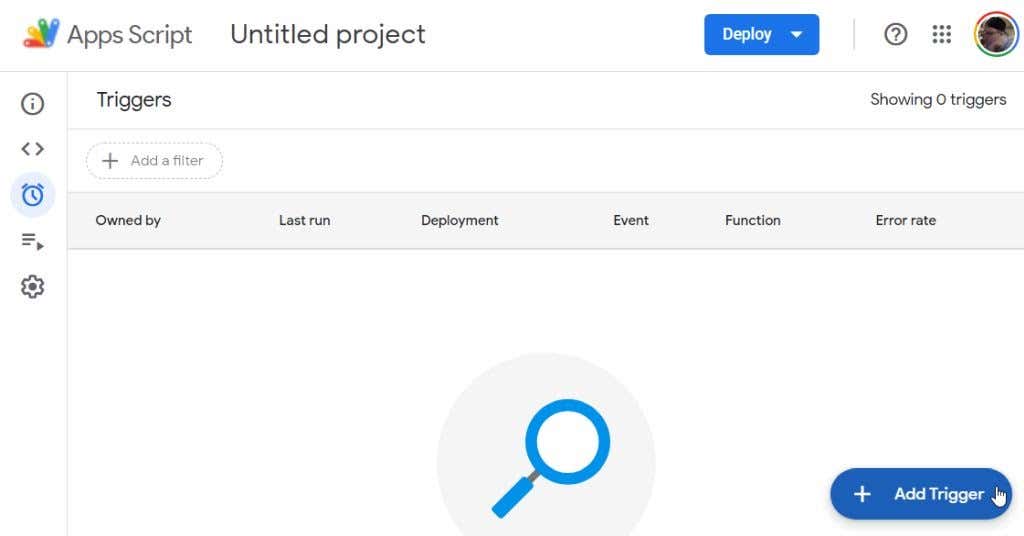
“添加触发器(Add Trigger)”窗口包含一长串选项,可帮助您准确自定义脚本运行的方式和时间。
注意(Note):其中许多选项取决于您为其编写脚本的服务或您添加的 API(the APIs that you’ve added)。

要设置触发器,您需要选择:
- 最初启动哪个功能
- 事件源,例如特定时间、日期或服务中的事件,例如Google电子表格单元格更改或文档最初打开时
- 事件类型,例如打开或编辑Google电子表格或文档中的某些内容,或者日期或时间的特定设置
- 您希望在脚本失败时获得更新的频率
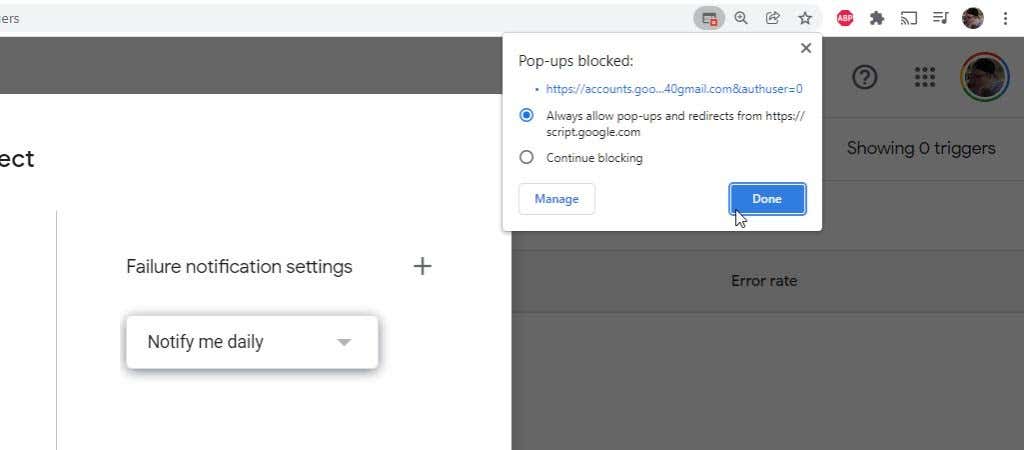
选择Save后,如果这是您第一次保存新触发器,您可能会看到“脚本授权失败”消息。(Script)

如果您在浏览器中启用了弹出窗口阻止程序,这通常会触发。如果您使用的是Google Chrome,只需选择上面带有红色“X”的小窗口图标。将设置更改为始终允许弹出窗口(Always allow pop-ups),然后选择完成(Done)。
当您再次选择保存(Save)时,您需要逐步完成该过程以授权您编写的脚本在您的Google帐户或Google Workspace下运行。
首先,选择您希望允许脚本在其下运行的Google帐户。(Google)

您会看到一条警告,说明您编写的自定义函数或脚本未经过Google的“验证” 。如果您是编写脚本的人,那么这无关紧要,在您自己的Google 帐户(Google Account)或Google Workspace下运行是安全的。
要绕过此警告,只需选择Advanced,然后选择底部的Go to <project> (unsafe)

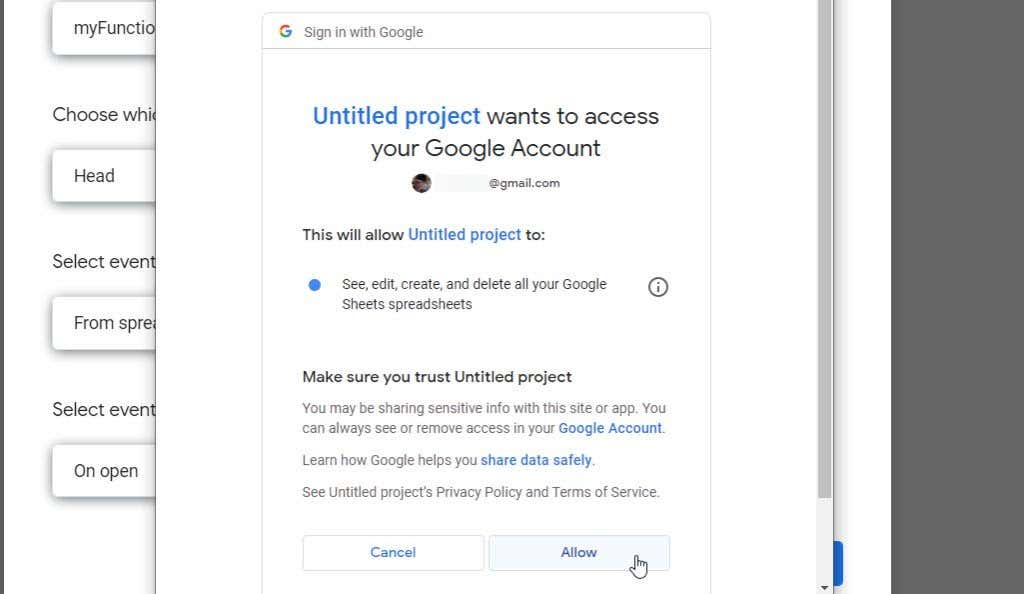
最后,在权限窗口中,选择允许(Allow)以允许您的自定义函数和脚本在您的Google帐户或Google Workspace下运行。
您无需再次重复此过程,只需在第一次保存或运行自定义Google Apps脚本项目时即可。
访问您的 Google 脚本 ID
最后一点 - 您可能希望将您的脚本提供给朋友或同事,以便他们可以使用您的脚本或将其作为库添加到他们自己的脚本中。
您可以在最左侧导航窗格的设置(Settings)图标下找到您的脚本 ID 。(Script ID)

脚本 ID(Script ID)可以在IDs部分下找到,在Script ID的右侧。
如您所见,如果您知道如何导航到要使用的每个功能, Google Apps 脚本编辑器就相当简单。(Google Apps Script)只要(Just)确保好好学习 Google 的Apps 脚本(Apps Script)文档,您就可以开始学习如何编写脚本和所有可用的函数。
Google Apps Script Editor: Everything You Need to Know to Get Started
If you use Google services like Gоogle Docs, Google Sheets, Google Analytics, Gmail, and others, you could connect and automate those services usіng Googlе Apps Script.
Think of Google Apps Script like Google’s version of Microsoft’s VBA script. Just like you can automate actions and tasks or customize macros in Microsoft Word and Excel with VBA, you can automate tasks and actions across Google services. In services like Sheets and Docs, you can even write your own custom menus.

In this article you will learn how to access and enable Apps Script in your various Google services, how to navigate the Apps Script Editor, and how to connect services. You won’t learn specific script functions, but Google has excellent documentation and apps script tutorials available to learn how to write Apps Script.
How to Access Google Apps Script Editor
You can open the Google Apps Script code editor from within a number of Google services. For example, you’ll find Apps Script in the Extensions menu inside Google Sheets.

In other services, you can open the Google Apps Script editor in the following ways:
- Google Docs: Select Script editor in the Tools menu.
- Google Slides: Select Script editor in the Tools menu.
- Google Forms: Select Script editor in the three-dot menu.
- Google Drive: Right-click any blank space, select More, and select Google Apps Script.
Using any of these methods, you’ll see the Apps Script code editor open in a new tab. This is the window where you’ll write each of the functions that make up your entire script. By default, you’ll see an empty function named myFunction() that’s ready for you to start filling in your code.
Note: Code formatting is very important in order to avoid errors. Use commenting as shown in the following code to remind yourself what you were trying to do inside sections of code. This is very similar to how commenting works in HTML code with web programming.

As you navigate the code editor, you can return to this section by selecting Code.gs in the left navigation pane in the Editor window. To see other available windows, hover over the icons in the far left pane and the main navigation pane will open.

The Overview section is where you can find statistics about your script like how many errors have occurred, how many times it’s executed, and more.

We’ll cover each of the other sections of the Google Apps Script editor in each section below.
Navigating the Google Apps Script Editor
As you edit your code in the editor, it’s a good idea to select the disk (Save) icon often so that you don’t lose your work.

Once saved, you’ll see the other menu options light up.

These include:
- Run: Attempt to run your entire script from beginning to end.
- Debug: Step through your script one line at a time.
- Function dropdown: Browse through and navigate to each of the functions you’ve created.
- Execution log: See any status or error messages from each attempt you’ve made to run your script.
The Libraries option in the left navigation menu is where you can access libraries that other people have written (or you’ve written and saved elsewhere). This is useful if you have a friend who already wrote a feature you’d like to use in Google Sheets or Google Docs but you’d like to add additional features on top of that.
All you need to add those libraries into your project is the Script ID. You can find this in the project settings section, which we’ll show you how to find toward the end of this article.

Google Apps Script Services Add-Ons
The Services section is the most useful. It’s where you can integrate your current script with other Google services you may use.
When you select it, you’ll see the Add a service window open. Scroll down to the service you want to use as an add-on to your existing project.
For example, if you’d like to pull data from your Google Analytics account into this script, you can select the Google Analytics API, and select Add.

If you want to find details about what functions are available to use for that new add-on service and how to use them, select the three dots to the right of the API and select See documentation.

This will open the Google Apps Script documentation in a new tab, opened automatically to the section for that Google service.

Explore the documentation for function syntax, tutorials, and code examples that you can use in your own script.
Also, note that you can navigate to other sections of the documentation to see what general functions are available in your script based on the service you were using when you originally opened the Apps Script code editor.
For example, if you opened the editor in Google Sheets, check the Sheets section in the documentation menu for Google Sheets functions you’re able to use in your script.
Setting Up and Using Apps Script Triggers
Another useful feature in Google Apps Script is the ability to set triggers based on a number of events or schedules.
To configure a new trigger for your script, select Triggers from the far left navigation menu. In the new Triggers window that opens, select the Add Trigger button.

The Add Trigger window has a long list of options that help you customize exactly how and when you want your script to run.
Note: Many of these options depend on the service you’re writing your script for or the APIs that you’ve added.

To set up your trigger, you’ll need to choose:
- Which function to initially launch
- The event source such as a specific time, date, or an event in your service like when a Google spreadsheet cell changes or a document is initially opened
- The event type such as when something in your Google spreadsheet or document is opened or edited, or the specific setting for date or time
- Notification frequency for how often you want to get updates about when your scripts have failed
Once you select Save, you may see a “Script authorization failed” message if it’s the first time you’ve saved a new trigger.

This is usually triggered if you have a pop-up blocker enabled in your browser. If you’re using Google Chrome, just select the small window icon with a red “X” over it. Change the setting to Always allow pop-ups and select Done.

When you select Save again, you’ll need to step through the process to authorize the script you’ve written to run under your Google account or Google Workspace.
First, select the Google account that you want to allow your script to run under.

You’ll see a warning that the custom function or script you wrote isn’t “verified” by Google. If you’re the person who wrote the script, then this doesn’t matter and it’s safe to run under your own Google Account or Google Workspace.
To bypass this warning, just select Advanced and then select the Go to <project> (unsafe) link at the bottom.

Finally, in the permissions window, select Allow to allow your custom functions and script to run under your Google account or Google Workspace.

You won’t have to repeat this process again, only the first time you save or run your custom Google Apps script projects.
Accessing Your Google Script ID
One final note – you may want to provide your script to friends or colleagues so they can either use your script or add it as a library to their own script.
You can find your Script ID under the Settings icon in the far left navigation pane.

The Script ID can be found under the IDs section, to the right of Script ID.
As you can see, the Google Apps Script editor is fairly straightforward if you know how to navigate to each feature you want to use. Just make sure to study Google’s Apps Script documentation well so that you can start learning how to write your scripts and all functions that are available to use.



















