切换到另一个操作系统(operating system)或导入数据有时意味着您在切换后无法访问您的文件和文件夹。这是因为您的用户帐户(user account)失去了这些文件和文件夹的所有权,或者不再具有所需的权限。此外,访问某些受系统保护的文件或文件夹有时会涉及修改这些资源的权限。当您无法从磁盘读取或更改文件或文件夹时,这意味着您需要获得它们的所有权或者您需要更改用户的权限。在本文中,您将学习如何更改文件或文件夹(file or folder)的所有权,以及如何管理访问和修改文件和文件夹的权限。
注意:(NOTE:)本指南适用于Windows 7和Windows 8.1。
如何查看文件或文件夹的现有用户(A File Or Folder)权限(Existing User Permissions)
在更改文件和文件夹的权限之前,您应该首先了解如何查看文件或文件夹的当前权限。
首先,选择某个文件或文件夹,然后右键单击或(click or press)按住它。当上下文菜单打开时,按Properties。
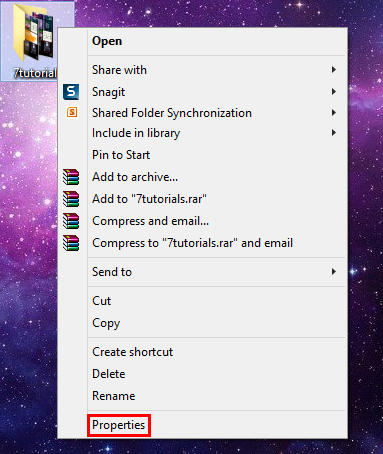
在 Windows 8.1 中,在文件资源管理器(File Explorer)中,您还可以使用功能区。首先(First),选择您感兴趣的文件夹,展开功能区上的“主页”(Home)选项卡,然后单击(ribbon and click)或点击“打开(Open)”部分中的“属性(Properties)”按钮。

将打开具有该文件或文件夹属性的窗口。转到安全(Security)选项卡,您可以查看分配给每个用户或组(user or group)的权限。例如,如果您选择用户“Madalina Blaga”,您可以查看下面的权限列表。

每个用户都分配有以下一项或多项权限:
-
完全控制(Full control)- 允许读取、写入、更改和删除选定的文件或文件夹;
-
修改(Modify)- 允许读取、写入、更改但不能删除选定的文件或文件夹;
-
读取和执行(Read & execute)- 允许查看和列出文件和子文件夹以及执行文件;
-
列出文件夹内容(List folder contents)- 允许查看和列出文件和子文件夹;
-
读取(Read)- 允许用户查看文件夹的内容并打开文件和子文件夹;
-
写入(Write)- 使您能够创建新文件和文件夹并对现有文件和子文件夹进行更改;
-
特殊权限(Special permission)- 包含一组允许配置高级权限的可配置操作。
注意:(NOTE:)要了解有关特殊权限(Special permission)的更多信息,请查看有关文件和文件夹权限(File and Folder Permissions)的文章。
如何更改文件或文件夹(A File Or Folder)的权限(Permissions)
现在,您知道如何查看文件或文件夹(file or folder)的现有权限,您就可以学习如何更改它们了。
首先,打开“属性(Properties)”窗口,如前所示,然后按“安全”选项卡中的“(Security)编辑(Edit)”按钮。

您现在将看到一个列表,其中包含您计算机上存在的所有用户组和用户帐户,以及每个用户组的权限列表。如果您在列表中找不到某个用户帐户或用户组(account or user group),请按添加(Add)。
删除(Remove)按钮允许您从权限列表中删除用户帐户或用户组。(user account)
对于本指南的这一部分,我们(guide let)假设您要授予新用户权限。按添加(Add)继续。

选择用户或组(Select Users or Groups)窗口打开。键入将添加的用户名(user name)或用户组(user group),以便对所选文件夹具有权限。例如,如果要添加管理员(Administrators)组,请在“输入要选择的对象名称”字段中键入("Enter the object names to select")“管理员”("Administrators"),然后按“检查名称”(Check Names)按钮。
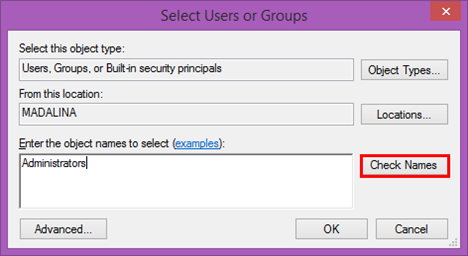
但是,我们建议使用另一种方法来选择用户或组。按高级(Advanced)按钮继续。

在这里,您有两个可以更改选择的字段。但是,这不是必需的,因为默认值很好并且包括所有可能的选项。
选择此对象类型(Select this object type)字段显示将搜索的对象类型。如果单击对象类型(Object Types),您将能够在用户、组或内置安全主体之间进行选择。默认情况下,全部选中,因此无需修改任何内容。
From this location字段显示将搜索对象的位置。默认情况下,将在您的计算机上搜索它们。这就是为什么您也不需要在此处更改任何内容的原因。如果您是网络域(network domain)的一部分,如果您单击或点击位置(Locations),您将能够选择其他位置。
由于您无需进行任何更改,请按“立即查找”(Find Now)按钮以显示所有用户和组的列表。这将搜索并返回您计算机上定义的所有用户和组。
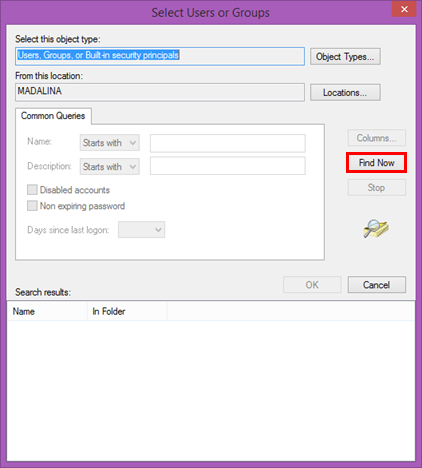
从列表中选择所需的用户帐户或用户组(user account or user group),然后单击或点击(click or tap) 确定(OK)。

再次按OK完成操作。(OK)

新用户已添加到列表中。选择它,然后在“权限(Permission)”部分中,检查您要授予的权限。单击(Click)或点击确定(OK)以完成操作。

如何在Windows 8.1中获取(Windows 8.1)文件或文件夹(A File Or Folder)的所有权(Ownership)
如果要更改文件或文件夹(file or folder)的所有者,请再次打开“属性(Properties)”窗口,然后按“安全”选项卡中的“(Security)高级(Advanced)”按钮。

高级安全设置(Advanced Security Settings)窗口将打开,您可以在其中查看所选文件或文件夹(file or folder)的当前所有者。
在Windows 8.1中,所有者显示在窗口顶部。按更改(Change)以更改设置为所有者的用户帐户。(user account)

现在,将打开“选择组用户”(Select User of Group)窗口。如上一节所示选择一个用户,然后按(section and press) OK完成操作。

现在,主人变了。最后,选中“替换子容器和对象的所有者”("Replace owner on subcontainers and objects")选项,然后按OK完成操作。

如何在Windows 7中获取(Windows 7)文件或文件夹(A File Or Folder)的所有权(Ownership)
首先,打开“属性(Properties)”窗口,然后按“安全”选项卡中的“(Security)高级(Advanced)”按钮。
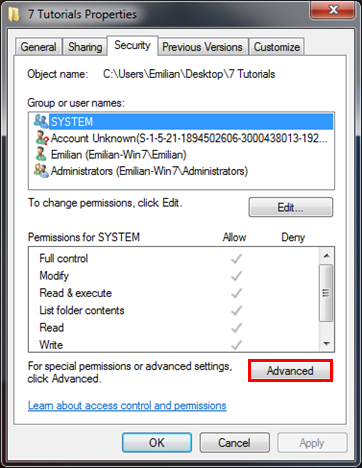
高级安全设置(Advanced Security Settings)窗口打开后,转到所有者(Owner)选项卡,您将看到所选文件夹的当前所有者。单击编辑(Edit)按钮更改所有者。

接下来,按其他用户或组(Other users or groups)。

现在,您需要选择将拥有所选文件或文件夹所有权的(file or folder)用户名(user name)或用户组(user group)。添加所需的用户或组(user or group),如前面部分所示。

然后,所有者(Owner)窗口将打开。选择添加的用户,选中“替换子容器和对象的所有者”("Replace owner on subcontainers and objects")选项,然后按( option and press )OK。

将显示一条确认消息(confirmation message)。单击确定(OK),您就完成了。
返回“高级安全设置”(Advanced Security Settings)窗口,您会注意到所有者已更改。在我们的示例中,文件夹的新所有者是来宾(Guest)用户。再单击一次确定(OK)。

结论
正如您从本指南中看到的那样,更改文件的权限和所有权(permission and ownership)并不难。本文中分享的过程在无法访问您的文件的情况下非常有用。如果按照我们的指南遇到问题或者您有其他问题,请随时在下面的评论中与我们分享。
How To Take Ownership And Change Permissions Of Files And Folders
Switching to another operating system or importing data sometimeѕ means you can't accesѕ your files and folders after the switch. This is result of the fact that your uѕer aсcount has lost ownership of those files and folders or it no lоngеr has the required permissiоns. Also, accesѕing certain system protected files or folders involves sometimes modifying the permissions fоr those resources. When you cannot read or change files or folders from your disk, it means that either you nеed to tаke ownership of them or you need to change your user's permissions. In this article yоu will learn how to change ownership of a file or foldеr and how to manage permissions for accessing and modifying files and folders.
NOTE:This guide applies to both Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
How To View The Existing User Permissions For A File Or Folder
Before changing permission of files and folder, you should first learn how to view the current permission for a file or a folder.
First, choose a certain file or a folder and right click or press and hold on it. When the contextual menu will open, press Properties.

In Windows 8.1, in File Explorer, you can also use the ribbon. First, select the folder you are interested in, expand the Home tab on the ribbon and click or tap the Properties button found in the Open section.

A window with that file's or folder's properties will open. Go to the Security tab and you can view the permissions assigned to each user or group. For example, if you select the user "Madalina Blaga" you can view the list of permissions below.

Each user is assigned one or more of the following permissions:
-
Full control - allows reading, writing, changing and deleting of the selected file or folder;
-
Modify - allows reading, writing, changing but not deleting of the selected file or folder;
-
Read & execute - permits viewing and listing of files and subfolders as well as execution of files;
-
List folder contents - enables viewing and listing of files and subfolders;
-
Read - allows the user to see the contents of a folder and open files and subfolders;
-
Write - enables you to create new files and folders and make changes to existing files and subfolders;
-
Special permission - contains a set of configurable actions that allow for configuring advanced permissions.
NOTE:To learn more about Special permission check out this article on File and Folder Permissions.
How To Change Permissions For A File Or Folder
Now, that you know how to view the existing permissions for a file or folder, you are ready to learn how to change them.
First, open the Properties window, as shown earlier and press the Edit button found in the Security tab.

You will now see a list with all the user groups and user accounts that exist on your computer, together with a list of permissions for each. If you can't find a certain user account or user group in the list, press Add.
The Remove button allows you to delete a user account or a user group from the permissions list.
For this part of the guide let's assume that you want to give permissions to a new user. Press Add to proceed.

The Select Users or Groups window opens. Type the user name or the user group that will be added in order to have permissions for the selected folder. For example, if you want to add the Administrators group, type "Administrators" in the "Enter the object names to select" field and then press the Check Names button.

We recommend, however, another method to select users or groups. Press the Advanced button to continue.

Here you have two fields where you can change selections. However, this is not required as the defaults are just fine and include all possible options.
The Select this object type field shows what kind of objects will be searched for. If you click on Object Types you will be able to select between user, group or built-in security principals. By default, all are selected, so there is no need to modify anything.
The From this location field shows where the objects will be searched for. By default, they will be searched on your computer. That's why you won't need to change anything here either. If you are part of a network domain, if you click or tap Locations you will be able to select other locations.
Since there is no change you need to make, press the Find Now button to display a list of all the users and groups. This will search and return all users and groups defined on your computer.

Select from the list the desired user account or user group and click or tap OK.

Press OK again to complete the action.

The new user has been added to the list. Select it and, in the Permission section, check the rights that you want to grant. Click or tap OK to complete the action.

How To Take Ownership Of A File Or Folder In Windows 8.1
If you want to change the owner of a file or folder, again, open the Properties window and press the Advanced button found in the Security tab.

The Advanced Security Settings window will open, where you can view the current owner of the selected file or folder.
In Windows 8.1, the owner is shown at the top of the window. Press Change to change the user account that is set as the owner.

Now, the Select User of Group window will open. Select a user as shown in the previous section and press OK to complete the action.

Now, the owner has changed. Lastly, check "Replace owner on subcontainers and objects" option and press OK to complete the action.

How To Take Ownership Of A File Or Folder In Windows 7
First, open the Properties window and press the Advanced button found in the Security tab.

After the Advanced Security Settings window opens, go to the Owner tab and you will see the current owner of the selected folder. Click the Edit button to change the owner.

Next, press Other users or groups.

Now, you need to select the user name or the user group that will take ownership of the selected file or folder. Add the desired user or group as shown in previous sections.

Then, the Owner window will open. Select the added user, check the "Replace owner on subcontainers and objects" option and press OK.

A confirmation message is displayed. Click OK and you are done.

Go back to the Advanced Security Settings window where you will notice the owner was changed. In our example, the new owner of the folder is the Guest user. Click OK one more time.

Conclusion
As you can see from this guide, changing permission and ownership of the files is not that hard. The procedures shared in this article can be really helpful in situations when your files cannot be accessed. If encounter problems following our guide or if you have additional questions, don't hesitate to share them with us in the comments below.






















