如果您使用的是来自其他设备或单独购买的平板电脑或智能手机充电器,则电池充电速度可能会更慢。(tablet or smartphone charger)此外,即使您使用设备的原装充电器和 USB 数据线(charger and USB cable)为其充电,它也可能随着时间的推移而出现故障。当您过多地扭曲或缠绕电缆时,它们会断裂。当您将它们插入和拔出时,连接器的接头会变得更松,并且没有充电器(power charger)可以永远使用。当你知道有问题但你不知道具体是什么时,你能做什么?如果您有Android 智能手机或平板电脑(Android smartphone or tablet),以下是如何确定您的充电器是否有缺陷或您用于将其连接到充电器的电缆不再正常工作:
安培是什么以及在哪里获得
Ampere是一款Android 应用程序(Android app),可用于测量设备电池的充电和放电电流。它适用于几乎所有运行Android 4.0.3或更高版本的智能手机或平板电脑。(smartphone or tablet)例如,我们在运行Android 7.0的(Android 7.0)Motorola Nexus 6和运行Android 7.1.1的(Android 7.1.1)Nexus 6P上对其进行了测试。
在您的Android 智能手机或平板电脑(Android smartphone or tablet)上,打开Play 商店(Play Store)并搜索“安培”,或点击此直接链接:安培(Ampere)。
安装Ampere后,在(Ampere)主屏幕(home screen)或应用程序抽屉(app drawer and tap)中找到它,然后点击其快捷方式以启动它。

安培显示电池的健康状况、温度、电压、充电速率等
Ampere 将立即开始测量设备电池的当前充电或放电速率。在获得值之前不应该超过 10 秒,在此期间应用程序将在屏幕顶部区域显示“测量”消息。("measuring")

只要您保持打开状态,Ampere就会不断测量设备电池的当前充电或放电速率。当前读数以大字体显示在屏幕顶部,同时在左侧和右侧显示记录的最低和最高值。
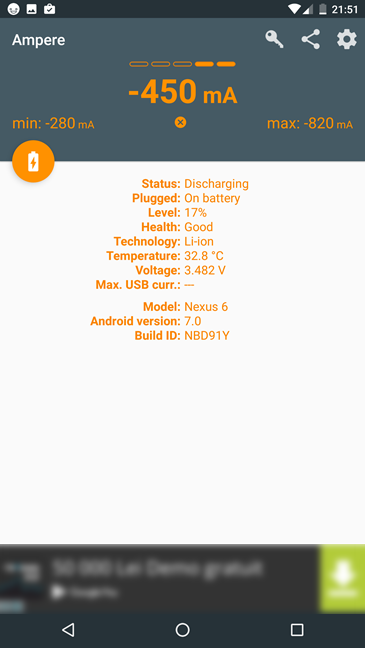
在当前读数下,安培(Ampere)显示附加信息:
-
状态(Status)- 应该是Charging或Discharging。当您的Android 智能手机或平板电脑(Android smartphone or tablet)连接到充电器(power charger)时,状态(Status)应为正在充电(Charging)。如果您的设备使用电池运行,则状态(Status)应为Discharging。
-
已插入(Plugged)- 可以是“电池供电”("On battery")或“交流充电器”,("AC charger,")具体取决于您的Android 设备(Android device)是否连接到电源充电器(power charger)。它告诉您或多或少与“状态”(Status)字段相同的内容。
-
级别- 向您显示(Level)电池电量(battery charge)的百分比。
-
健康(Health)状况 - 告诉您设备的电池状况是否良好,或者其健康状况是否较弱并且应该更换。

-
技术(Technology)- 向您展示您的Android 智能手机或平板电脑(Android smartphone or tablet)的电池类型。最常见的是锂离子电池(Lithium-ion)。
-
温度(Temperature)- 显示设备电池的温度。如果您仍然拥有三星 Galaxy Note 7(Samsung Galaxy Note 7) ,此信息尤其重要。🙂开玩笑(Kidding),电池的高温可能意味着问题,所以这是一个相当有用的信息。
-
电压(Voltage)- 显示电池的当前电压。
-
最大限度。USB 电流 (Max. USB curr.)- 告诉您设备电池接收到的最高电流强度。如果您的智能手机或平板电脑(smartphone or tablet)使用电池运行,您将不会看到此处显示的任何值。如果您的设备已插入电源充电器(power charger),您应该会看到充电器提供的最大电流强度,以 mAh 或毫安时表示。
-
型号、Android 版本(Model, Android version )和Build ID - 这些都是有关您的Android 设备型号名称和软件(Android device model name and software)的详细信息。
Ampere 应用程序(Ampere app)可以以几种不同的视觉风格显示上述信息,您可以通过向左或向右滑动屏幕来切换。这是他们的样子:

如何使用安培(Ampere)识别损坏的充电器和USB数据线
您应该做的第一件事是打开Ampere并让它测量您的Android 设备(Android device)的放电电流。换句话说,使用未(NOT)连接充电器的(power charger)智能手机或平板电脑运行(smartphone or tablet)Ampere,仅使用电池。写下(Write)你得到的读数。例如,我们的测试智能手机(test smartphone)-摩托罗拉 Nexus 6(Motorola Nexus 6) - 的放电电流速率约为 500 mAh。

然后,拿起您要检查的电源充电器(power charger)和USB 数据线。(USB cable)查看充电器的所有侧面并找到其规格。许多充电器(power charger)上都印有标准输出(standard output)等相关规格。您应该看到如下内容:

您需要的信息是输出电流。在我们的摩托罗拉 Nexus 6(Motorola Nexus 6)原装充电器上,标准输出功率(standard output power)为 1.6 安培或 1600 毫安时(请记住,1 安培表示 1000 毫安时)。
一旦您知道您正在检查的充电器的标准输出电流,请将其插入墙上插座(wall socket),然后将其连接到您的Android 智能手机或平板电脑(Android smartphone or tablet)。在您的Android 设备(Android device)上,打开Ampere 应用程序并等待(Ampere app and wait)大约一分钟。记(Write)下应用程序测量的充电电流。例如,在我们的摩托罗拉 Nexus 6(Motorola Nexus 6)上,它约为 1100 mAh。

将您刚刚测量的充电电流添加到您在本节开头写下的放电电流。我们的摩托罗拉 Nexus 6(Motorola Nexus 6)的放电率为 500 mAh,当连接到我们的充电器时,它以 1080 mAh 充电。这使得总电量为 1580 mAh,非常接近其标准输出功率(standard output power)1.6 安培或 1600mAh。使用您要测试的充电器对您的Android 智能手机或平板电脑进行相同的计算。(Android smartphone or tablet)

如果你得到的结果接近你的充电提供的(power charge)标准输出(standard output)电流,那么这意味着充电器和USB线(USB cable)都是健康的。如果结果与充电器的输出电流不同,则充电器或USB 电缆(USB cable)有故障。
在这种情况下,您将不得不使用不同的电源充电器和不同的USB电缆进行交替测量,直到您遗漏了损坏的那些。
重要提示:在具有快速充电功能的智能手机和平板电脑上,以不同的方式测量事物!
一些现代设备的原装电源充电器,比如我们的摩托罗拉 Nexus 6(Motorola Nexus 6),可能会有不止一个输出。那是因为它们支持快速充电技术,让您可以比平时更快地为电池充电。在Nexus 6上,turbo 充电模式一直工作到电池电量达到(battery reaches) 78% capacity。如果您有快充的设备,并且您要检查的充电器也支持该技术,我们建议您在通过快充等级(charge level)后进行测量。例如,如果您有像我们这样的Nexus 6,请使用至少 78% 电量的电池进行测量。
结论
Ampere for Android是一个很棒的小工具,可用于找出哪些电源充电器和USB电缆不再正常工作。尽管许多人在怀疑有问题时会使用此应用程序,但我们的建议是立即使用并检查所有电源充电器和USB数据线。一些“春季大扫除(spring cleaning)”总是一个好主意。您如何看待适用于 Android 的Ampere应用(Android)程序(Ampere app)?它帮助识别了多少损坏的 USB 数据线和(How)充电器?(USB)
How to identify broken chargers and USB cables on your Android smartphone or tablet
If you're using a tablet оr smartphone charger from another device or that was bought separаtely, it's possible that the battery will charge mоre slowly. Also, even if you use your device's original charger and USB cable to charge it, it may have become defective with time. When you're twisting or winding cables too much, they break. When you plug them in and out, the joints of the connectors become looser, and no power charger lives forever. What can you do when you know that something is wrоng, but you don't know exactly what? If you'vе got аn Android smartphone or tablet, here's how to identify whether your charger is defective or the cable that you are using to connect іt to the charger is no longer working well:
What Ampere is and where to get it
Ampere is an Android app which can be used to measure both the charging and the discharging electrical current of your device's battery. It works with almost any smartphone or tablet running Android 4.0.3 or newer. For instance, we've tested it on a Motorola Nexus 6 running on Android 7.0 and a Nexus 6P running on Android 7.1.1.
On your Android smartphone or tablet, open the Play Store and search for "ampere," or follow this direct link: Ampere.

Once you've installed Ampere, find it on your home screen or in your app drawer and tap on its shortcut to launch it.

Ampere shows the health of the battery, its temperature, voltage, charging rates and more
Ampere will immediately start measuring the current charging or discharging rate of your device's battery. It shouldn't take more than 10 seconds before you get a value, during which time the app will show a "measuring" message on the top area of the screen.

As long as you keep it open, Ampere keeps measuring the current charging or discharging rate of your device's battery. The current reading is displayed in a large font at the top of the screen, together with the lowest and highest values recorded, on the left and the right side.

Under the current readings, Ampere shows additional information:
- Status - should be either Charging or Discharging. When your Android smartphone or tablet is connected to a power charger, the Status should be Charging. If your device runs on battery, the Status should be Discharging.
- Plugged - can be "On battery" or "AC charger," depending on whether your Android device is connected to a power charger or not. It tells you more or less the same thing as the Status field.
- Level - shows you the percentage of battery charge.
- Health - tells you whether your device's battery is in good shape, or if its health is weak and should be replaced.

- Technology - shows you what type of battery your Android smartphone or tablet has. The most common is Lithium-ion.
- Temperature - shows you the temperature of the device's battery. This information is of particular importance if you still own a Samsung Galaxy Note 7. 🙂 Kidding aside, a high temperature of your battery can mean problems, so this is a rather useful piece of information.
- Voltage - shows the current voltage of your battery.
- Max. USB curr. - tells you the highest current intensity received by your device's battery. If your smartphone or tablet is running on battery, you won't see any value displayed here. If your device is plugged into a power charger, you should see the maximum current intensity provided by the charger, expressed in mAh, or milliampere hour.
- Model, Android version and Build ID - these are all details regarding your Android device model name and software.
The Ampere app can display the above information in a few different visual styles, which you can switch between by swiping the screen left or right. Here's what they look like:

How to use Ampere to identify broken chargers and USB cables
The first thing you should do is open Ampere and let it do a measurement of your Android device's discharging current. In other words, run Ampere with your smartphone or tablet NOT connected to a power charger, just on battery. Write down the reading you get. For instance, our test smartphone - a Motorola Nexus 6 - has a discharging current rate of approximately 500 mAh.

Then, take the power charger and the USB cable(s) that you want to check. Look on all the charger's sides and find its specifications. Many power chargers have printed on them relevant specs like the standard output. You should see something like this:

The information that you'll need is the output current. On the original charger of our Motorola Nexus 6, the standard output power is of 1.6 Amperes or 1600mAh (remember that 1 Ampere means 1000 mAh).
Once you know the standard output current of the charger you're checking, plug it into a wall socket and then connect it to your Android smartphone or tablet. On your Android device, open the Ampere app and wait for about a minute. Write down the charging current measured by the app. For instance, on our Motorola Nexus 6, it's around 1100 mAh.

Add the charging current that you just measured to the discharging current you've written down at the beginning of this section. Our Motorola Nexus 6 has a discharging rate of 500 mAh, and when connected to our charger, it is charged at 1080 mAh. That makes a total of 1580 mAh, which is very close to its standard output power is of 1.6 Amperes or 1600mAh. Do the same math for your Android smartphone or tablet, using the charger that you want to test.

If the result you get is close to the standard output current provided by your power charge, then it means that both the charger and the USB cable are healthy. If the result is different from the charger's output current, then either the charger or the USB cable is faulty.
In this case, you will have to do alternate measurements, with different power chargers and different USB cables, until you've left out the ones that are broken.
IMPORTANT: On smartphones and tablets with quick charging, measure things differently!
The original power chargers of some modern devices, like our Motorola Nexus 6, will probably have more than one output. That's because they support quick charging technologies, which let you charge the battery faster than normal. On the Nexus 6, turbo charging mode works until the battery reaches 78% capacity. If you have a device with quick charging, and the charger you want to check also supports this technology, we recommend you do the measurements after you pass its quick charge level. For instance, if you have a Nexus 6 like us, do your measurements with a battery that's at least 78% full.
Conclusion
Ampere for Android is a great little tool for finding out which power chargers and USB cables are no longer functioning properly. Although many will use this app when they suspect something's faulty, our recommendation is to do it right now and check all your power chargers and USB cables. Some "spring cleaning" is always a good idea. What do you think about the Ampere app for Android? How many broken USB cables and chargers did it help identify?










