如果您希望从远程位置连接到您的 Windows PC,有多种方法可以实现。例如,您可以通过 SSH 建立 VNC 隧道(tunnel VNC over SSH),允许您通过加密的SSH连接使用开源VNC协议。(VNC)但是,最好的方法是使用Windows 远程桌面(Windows Remote Desktop)工具。
在准备好远程连接到Windows PC之前,您需要执行一些步骤。您需要通过路由器配置远程桌面(Remote Desktop),确保打开必要的端口并且端口转发处于活动状态。要执行此操作并远程使用远程桌面(use Remote Desktop),您需要按照以下步骤操作。

配置 Windows 防火墙以允许远程桌面访问(Configuring Windows Firewall to Allow Remote Desktop Access)
在您可以通过路由器配置远程桌面(Remote Desktop)连接之前,您需要确保Windows将允许与您的 PC 的传入和传出连接。
- 为此,请右键单击“开始(Start)”菜单并选择“设置”(Settings)。

- 在“设置”(Settings)菜单中,选择“更新和安全”(Update & Security ) > “ Windows 安全(Windows Security )” > “防火墙和网络保护”(Firewall & network protection)。

- 在防火墙和网络保护(Firewall & network protection)菜单中,选择允许应用程序通过防火墙(Allow an app through firewall )选项。

- 在允许的应用程序(Allowed apps)窗口中选择更改设置(Change settings)按钮以解锁菜单。

- 解锁此菜单后,在提供的列表中找到远程桌面(Remote Desktop)和远程桌面 (WebSocket)(Remote Desktop (WebSocket) )选项。选中这些选项旁边的复选框以允许RDP连接通过防火墙。选择确定(OK)按钮以保存您的选择。

更改 Windows 10 上的默认 RDP 端口(Changing the Default RDP Port on Windows 10)
您已将Windows 防火墙(Windows Firewall)设置为允许RDP(远程桌面协议(Remote Desktop Protocol))连接。现在,您应该将Windows(Windows)用于RDP连接的默认RDP端口从端口 3389(port 3389)更改为备用端口号。
这是因为远程桌面协议攻击的风险(risk of Remote Desktop Protocol attacks)非常高。虽然更改端口并不是保护RDP连接的唯一方法,但它有助于减慢和限制随机端口扫描机器人在路由器上搜索开放RDP端口的风险。(RDP)
- 要更改RDP端口,请右键单击“开始(Start)”菜单并选择“运行”(Run)选项。或者,选择键盘上的Windows key + R
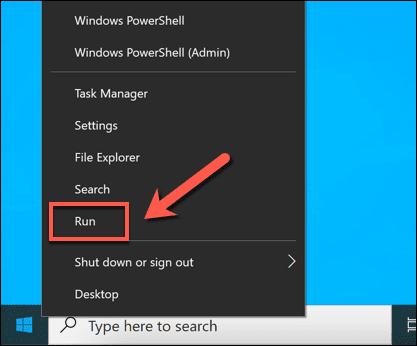
- 在“运行”(Run)对话框中,键入regedit,然后选择“确定(OK)” 。这将打开Windows 注册表编辑器(Windows Registry Editor)。

- 使用新注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)窗口左侧的树形菜单,找到HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber键。右键单击右侧的PortNumber键,然后选择Modify选项。

- 在Edit DWORD (32-bit) Value框中,从Base类别中选择Decimal ,然后在(Decimal)Value data框中设置一个新的端口值,确保您使用的值不被任何其他已知端口常用。选择确定(OK)以保存您的选择。

更改默认RDP端口号后,您需要重新启动 PC。您使用RDP与 PC 建立的任何连接都需要使用您选择的端口号进行配置(例如10.0.0.10:1337而不是10.0.0.10:3389)。
在网络路由器上启用端口转发(Enabling Port Forwarding on Your Network Router)
您现在可以开始配置路由器以允许从 Internet 连接到本地网络上的 PC。此过程的第一步是在您的路由器上启用端口转发,而不会让黑客进入(without letting hackers in)。
- 首先,使用网络浏览器(通常为192.168.1.1、192.168.1.254或类似变体)访问路由器的网络管理页面并登录。您需要确保您用于访问网络的设备门户连接到同一网络。如果您不确定,请查阅网络路由器的用户手册以获取更多信息。

- 登录路由器后,您需要找到端口转发设置(例如, TP-Link路由器上的转发(Forwarding)>虚拟服务器)。( Virtual Servers)找到这些设置后,您需要添加一个条目,将RDP端口(默认为 3389,或您设置的自定义端口)映射到您 PC 的本地网络 IP 地址(不是您的公共 IP 地址)。

映射RDP(RDP)端口后,端口转发应该处于活动状态并准备好允许通过 Internet进行远程桌面连接。(Remote Desktop)您应该能够使用您的公共 IP 地址和RDP端口号远程连接到您的 PC,您的网络路由器将请求转发到您的 PC。
使用动态 DNS 服务映射您的 IP 地址 (Mapping Your IP Address Using a Dynamic DNS Service )
一旦端口转发处于活动状态,只要端口转发规则处于活动状态、您的 PC 已打开并连接到路由器、您的互联网连接处于活动状态以及您的公共 IP 地址(public IP address),您就应该能够通过 Internet 建立远程桌面(Remote Desktop)连接保持原样。
但是,如果您的ISP使用动态 IP 地址(定期更改的 IP 地址),那么当您的公共 IP 地址发生更改时,您将无法连接。为了解决这个问题,您可以使用动态 DNS 服务(using a Dynamic DNS service)映射您的 IP 地址,这样,当您的 IP 地址更改时,您仍然可以进行远程连接。
但是,在您可以使用动态 DNS服务之前,您需要使用适当的提供商(如(Dynamic DNS)No-IP)设置一个帐户。
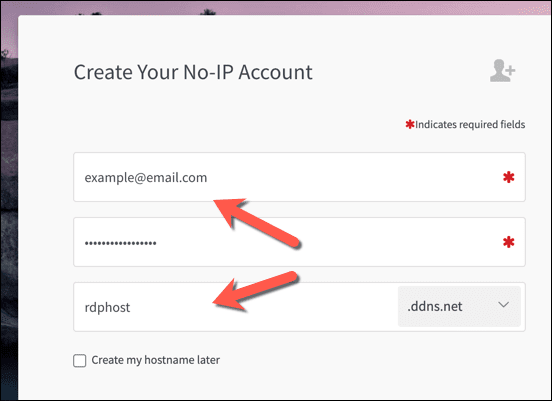
- 如果您想对动态 DNS使用(Dynamic DNS)无 IP(No-IP),请通过提供您的电子邮件地址和合适的密码来创建您的帐户。(create your account)您还需要提供一个主机名(例如 example.ddns.net),您可以使用它来建立RDP连接,而无需使用您的 IP 地址。
- 创建帐户后,您需要激活它。检查您的电子邮件收件箱,并在收到确认电子邮件后选择确认帐户按钮。(Confirm account )

- 激活您的帐户后,您接下来需要在您的 PC 上安装动态更新客户端。(Dynamic Update Client)这可确保您的无 IP 帐户始终拥有正确的公共 IP 地址,从而允许您建立连接。将动态更新客户端下载(Download the Dynamic Update Client)到您的 PC 并安装它以继续。

- 在您的 PC 上安装动态更新客户端后,该应用程序应该会自动打开。(Dynamic Update Client)此时使用您的无 IP 用户名和密码登录(Sign)。

- 登录后,您需要选择将哪些主机名链接到您的公共 IP 地址。从列表中选择适当的主机名,然后选择保存(Save)以确认。

- 此时,您应该能够使用您的动态 DNS(Dynamic DNS)主机名和正在使用的RDP端口(例如example.ddns.net:3389)远程连接到您的 PC。动态更新客户端(Dynamic Update Client)将每五分钟检查一次公共 IP 地址的更改,但如果您想自己刷新,请在 DUC 设置窗口中选择立即刷新按钮。(Refresh Now)

- 某些(Certain)网络路由器(例如TP-Link)支持动态 DNS(Dynamic DNS)并允许您自动刷新您的公共 IP 地址,而无需在您的 PC 上安装动态更新客户端。(Dynamic Update Client)不过,建议您仍然将其作为备份选项。例如,拥有TP-Link路由器的用户可以通过在 Web 管理页面上选择动态 DNS(Dynamic DNS)菜单选项来访问这些设置。对于其他型号,请查阅您的网络路由器的用户手册以获取有关如何继续操作的更多信息。

- 使用这些步骤配置路由器后,您应该能够使用RDP进行远程连接。确保在(Make)远程桌面连接(Remote Desktop Connection)工具中键入正确的动态 DNS(Dynamic DNS)主机名和端口号(例如example.ddns.net:3387)以正确进行身份验证。如果您的路由器配置正确并且没有其他连接问题,您应该能够建立连接并成功建立远程桌面(Remote Desktop)连接。

远程桌面的替代品(Alternatives to Remote Desktop)
上述步骤应允许您通过路由器配置远程桌面(Remote Desktop)连接。但是,如果您的远程桌面(Remote Desktop)连接不起作用,或者您对质量不满意,则可以使用 RDP 的替代方法(alternatives to RDP)。例如,TeamViewer等应用程序可让您轻松连接到 PC。
您还可以使用各种远程桌面管理工具来维护您的连接,或者您可以考虑设置 VPN(setting up a VPN)来建立与远程 PC 的连接。如果遇到问题,您可能还需要考虑如何远程关闭或重新启动您的 PC以重置您的 PC。(how to remotely shutdown or restart your PC)
How to Configure Remote Desktop Through Router
If you’re looking to connect to your Windowѕ PC from a remote location, therе are several wayѕ to do it. For instance, you could tunnel VNC over SSH, allowing you to use the open-source VNC protocol over an encrypted SSH connection. The best method, however, is to use the Windows Remote Desktop tool.
There are some steps you’ll need to take before you’re ready to connect to a Windows PC remotely. You’ll need to configure Remote Desktop through your router, ensuring that the necessary ports are open and that port forwarding is active. To do this and use Remote Desktop remotely, you’ll need to follow these steps.

Configuring Windows Firewall to Allow Remote Desktop Access
Before you can configure Remote Desktop connections through your router, you’ll need to make sure that Windows will allow ingoing and outgoing connections to your PC.
- To do this, right-click the Start menu and select Settings.

- In the Settings menu, select Update & Security > Windows Security > Firewall & network protection.

- In the Firewall & network protection menu, select the Allow an app through firewall option.

- Select the Change settings button in the Allowed apps window to unlock the menu.

- Once you’ve unlocked this menu, find the Remote Desktop and Remote Desktop (WebSocket) options in the list provided. Select the checkboxes next to these options to allow RDP connections through the firewall. Select the OK button to save your choices.

Changing the Default RDP Port on Windows 10
You have set up Windows Firewall to allow RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) connections. Now, you should change the default RDP port used by Windows for RDP connections from port 3389 to an alternative port number.
This is because the risk of Remote Desktop Protocol attacks is extremely high. While changing ports isn’t the only way to secure your RDP connections, it will help to slow down and limit the risks from random, port scanning bots that search for open RDP ports on your router.
- To change the RDP port, right-click the Start menu and select the Run option. Alternatively, select the Windows key + R on your keyboard.

- In the Run dialog box, type regedit before selecting OK. This will open the Windows Registry Editor.

- Using the tree menu on the left in the new Registry Editor window, locate the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber key. Right-click the PortNumber key on the right then select the Modify option.

- In the Edit DWORD (32-bit) Value box, select Decimal from the Base category, then set a new port value in the Value data box, making sure that the value you use isn’t commonly used by any other known ports. Select OK to save your choice.

Once you’ve made the changes to the default RDP port number, you’ll need to restart your PC. Any connections you make to your PC using RDP moving forward will need to be configured using the port number you selected (eg. 10.0.0.10:1337 rather than 10.0.0.10:3389).
Enabling Port Forwarding on Your Network Router
You can now begin to configure your router to allow connections from the internet to your PC on your local network. The first step in this process is to enable port forwarding on your router without letting hackers in.
- To begin, access your router’s web administration page using your web browser (typically 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.254, or a similar variation) and sign in. You’ll need to make sure that the device you’re using to access the web portal is connected to the same network. If you’re unsure, consult with the user manual for your network router for additional information.

- Once you’ve signed into your router, you’ll need to locate the port forwarding settings (eg. Forwarding > Virtual Servers on a TP-Link router). Once you’ve located these settings, you’ll need to add an entry that maps the RDP port (3389 by default, or a custom port you’ve set) to the local network IP address of your PC (not your public IP address).

With the RDP port mapped, port forwarding should be active and ready to allow Remote Desktop connections over the internet. You should be able to connect to your PC remotely using your public IP address and RDP port number, with your network router forwarding the requests to your PC.
Mapping Your IP Address Using a Dynamic DNS Service
Once port forwarding is active, you should be able to make Remote Desktop connections over the internet as long as the port forwarding rule is active, your PC is switched on and connected to your router, your internet connection is active, and your public IP address remains the same.
However, if your ISP uses dynamic IP addresses (IP addresses that regularly change), you won’t be able to connect if or when your public IP address changes. To get around this problem, you can map your IP address using a Dynamic DNS service so that, when your IP address changes, you can still make connections remotely.
Before you can use a Dynamic DNS service, however, you’ll need to set up an account with an appropriate provider like No-IP.
- If you want to use No-IP for Dynamic DNS, create your account by providing your email address and a suitable password. You’ll also need to provide a hostname (eg. example.ddns.net) that you can use to establish RDP connections without using your IP address.

- Once you’ve created your account, you’ll need to activate it. Check your email inbox and select the Confirm account button included in the confirmation email once you receive it.

- With your account activated, you’ll need to install the Dynamic Update Client on your PC next. This ensures that your No IP account always has your correct public IP address, allowing you to make connections. Download the Dynamic Update Client to your PC and install it to proceed.

- Once the Dynamic Update Client is installed on your PC, the app should open automatically. Sign in using your No IP username and password at this point.

- After signing in, you’ll need to select which hostnames to link to your public IP address. Select the appropriate hostname from the list, then select Save to confirm.

- At this point, you should be able to connect to your PC remotely using your Dynamic DNS hostname and the RDP port in use (eg. example.ddns.net:3389). The Dynamic Update Client will check for changes to your public IP address every five minutes, but if you want to refresh this yourself, select the Refresh Now button in the DUC settings window.

- Certain network routers (such as TP-Link) support Dynamic DNS and allow you to automatically refresh your public IP address without installing the Dynamic Update Client on your PC. Though, it’s recommended that you still do so as a backup option. For example, users with a TP-Link router can access these settings by selecting the Dynamic DNS menu option on the web administration page. For other models, consult your network router’s user manual for more information on how to proceed.

- Once you’ve configured your router using these steps, you should be able to connect remotely using RDP. Make sure to type the correct Dynamic DNS hostname and port number (eg. example.ddns.net:3387) in the Remote Desktop Connection tool to authenticate correctly. If your router is configured properly and there are no other connection issues, you should be able to make the connection and establish the Remote Desktop connection successfully.

Alternatives to Remote Desktop
The steps above should allow you to configure Remote Desktop connections through your router. However, if your Remote Desktop connections aren’t working, or you’re unhappy with the quality, there are alternatives to RDP available. For instance, apps like TeamViewer will allow you to connect to your PC with ease.
You can also use various Remote Desktop management tools to maintain your connections, or you could think about setting up a VPN to establish connections to your remote PC instead. You may also want to consider how to remotely shutdown or restart your PC to reset your PC if you run into problems.




















