域名系统(Domain Name System)( DNS ) 服务器是存储您访问过的网站的所有域名的地方。在 Web 浏览器中搜索域名时,它会由您的路由器转发到DNS服务器。如果特定站点的域名已保存,则返回相应的 IP 地址。这使得这些站点的加载过程特别快。
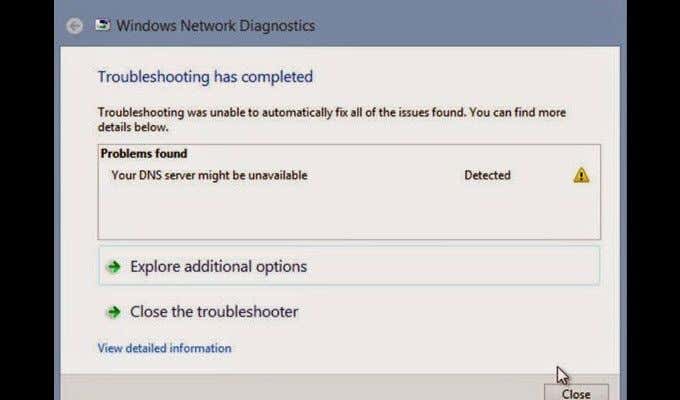
尽管这个过程很棒,但DNS服务器有时无法建立连接的情况并不少见。在这种情况下尝试对您的 Web 浏览器进行故障排除通常会导致“ DNS服务器无响应”错误。

许多因素可能会导致此特定错误出现在您的屏幕上。其中最突出的是服务器本身当前正在经历中断的可能性。幸运的是,这个问题通常伴随着一些简单的解决方案。
如何修复“DNS 服务器不可用”错误(How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error)
您是否收到过DNS服务器不可用的错误消息?为了快速解决这些问题,有时可以通过更改浏览器、弄乱一些防火墙设置或重新启动路由器等简单的方法来纠正这些问题。找出问题的原因和随后的纠正措施将由您决定。
首先为您尝试打开的网页使用不同的浏览器。这意味着,如果您当前在使用Mozilla Firefox浏览器时收到错误消息,请将其切换到Microsoft Edge或Google Chrome。如果问题仍然存在,我们可以继续测试其他设备。
尝试在同一网络上使用移动设备打开网页,以确保问题不是硬件故障造成的。尝试使用您的数据计划连接到相同的网页以确定原因实际上是否与DNS服务器有关,这也是有益的。
完成这些步骤后,重新启动路由器。如果“DNS 服务器不可用”错误仍然存在,我们将不得不采取一些更有效的方法。
刷新 DNS (Windows)(Flushing Your DNS (Windows))

解决DNS(DNS)服务器不可用问题的最有效方法是使用命令提示符(Command Prompt)刷新它。
- 同时按下Windows 键和 R 键(Windows key and R key)拉出运行(Run)对话框。
- 在字段中输入cmd并按Enter。
- 在命令提示符窗口中,键入ipconfig /flushdns并按Enter。

- ipconfig /release并按Enter进行跟进。

- 最后,输入ipconfig /renew并按Enter。

- 关闭命令提示符(Command Prompt)窗口并重新启动系统。
刷新 DNS (MacOS)(Flushing Your DNS (MacOS))

您还可以在Mac上刷新(Mac)DNS。执行此操作的方式会因计算机运行的Mac版本而略有不同。(Mac)它通常只涉及在此过程中使用的语法的更改。
- 打开一个Finder窗口,然后进入Applications,然后是Utilities,最后是Terminal。
- 输入以下与您当前使用的MacOS版本有关的语法:
- MacOS High Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; sleep 2; echo macOS DNS Cache Reset | say
- MacOS Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;说 DNS 缓存已被刷新(sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say DNS cache has been flushed)
- MacOS Mojave – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;sleep 2;
- MacOS X El Capitan/Yosemite – sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;说缓存已刷新(sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say cache flushed)
- 按回车(Return )键,输入密码,然后再次按回车(Return )键。
- 在退出终端(Terminal)之前等待指示DNS刷新成功的音频警报。
MacOS X缓存清除需要一些额外的步骤才能完全清除。您必须在之前采取的步骤之上刷新MDNS和UDNS缓存。(UDNS)
在从终端(Terminal)退出之前,请执行以下命令:
- 对于 MDNS 缓存,键入sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache
- 对于 UDNS 缓存,键入sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches
删除多个防病毒软件(Remove Multiple Antiviruses)

“你永远不能有太多的保护。” 这在现实世界中可能有些真实,但在技术世界中,在同一台计算机上安装多个防病毒程序实际上会阻碍所提供的保护。
检查您当前是否有两个或更多防病毒程序正在运行,因为这可能是DNS问题的原因。禁用所有其他程序后,重新启动系统,问题应该会自行解决。
确保继续前进,您只需要运行一个软件程序,以帮助保护自己免受不需要的恶意软件攻击。这不仅可以提高安全性,还可以帮助您避免遇到更多DNS服务器错误。
更改 DNS 服务器(Changing DNS Servers)

如果您已经尝试了此处编写的所有修复程序并且仍然收到相同的“ DNS服务器不可用”错误,那么更改您的(DNS)DNS服务器可能符合您的最佳利益。有很多公共DNS可供选择,谷歌的免费DNS是更受欢迎的选择之一。
此过程非常简单,只需单击几下即可完成,具体取决于您选择更改它的位置。我们将在每个示例中使用Windows操作系统。
通过路由器更改 DNS(DNS Changes via Router)

- 通过启动 Web 浏览器并在URL栏中 输入默认网关(Default Gateway)地址来访问您的路由器。
- 您可以通过打开命令(Command)提示符窗口、键入 ipconfig 并按Enter来找到(Enter)默认网关(Default Gateway)。复制位于提取信息中默认网关(Default Gateway)旁边的数字。

- 使用正确的凭据登录路由器。
- 找到您的 Internet 帐户信息,这些信息通常可以在类似名称的选项卡中找到。
- 导航到DNS服务器并选择最能反映您使用的Internet 协议(internet protocol)(IPv4 或 IPv6)的选项。
- 输入(Enter)您要使用的DNS服务器的地址来代替当前的地址。
- Google 的 DNS 服务器将是首选 DNSv4 中的 8.8.8.8 和备用(8.8.4.4)DNS服务器(8.8.8.8)中(alternate DNS server)的 8.8.4.4 。对于IPv6,您需要分别使用2001:4860:4860::8888和2001:4860:4860::8844。
- 保存修改后的信息,退出路由器界面。
通过 Windows 操作系统更改 DNS(DNS Changes via Windows OS)

- (Access)通过启动运行(Run)功能(Windows key + R)并输入ncpa.cpl来(ncpa.cpl)访问您的网络连接属性。按Enter。

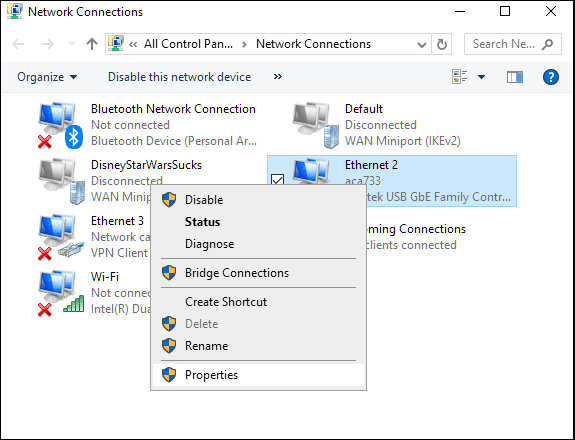
- Windows 10 用户可以右键单击桌面屏幕左下方的Windows图标,然后从菜单中选择网络连接。(Network Connections)
- 选择(Select)当前使用的网络适配器。WLAN用于WiFi连接,LAN用于直接连接,通常通过以太网电缆。
- Windows 10 将在左侧面板上提供您的选项。选择一个(Select one)并从主窗口中选择更改适配器选项。(Change)
- 右键单击您的选择并选择Properties。
- 在Networking选项卡中,从菜单中突出显示您的 IP 版本(v4 或 v6),然后单击Properties按钮。

- 单击径向用于使用以下 DNS 服务器地址:(Use the following DNS server addresses:)以启用编辑功能。

- 输入您计划使用的DNS服务器地址。(DNS)
- 如果您一直在使用以前未自动获得的DNS服务器,请记住对地址进行注释,以防您想在以后使用它们返回。
- 单击确定(OK)完成更改。
测试新的 DNS 服务器(Test New DNS Server)

更改DNS服务器后,打开浏览器并尝试启动像(DNS)www.google.com这样的知名站点。如果该站点可以立即访问,则新的DNS运行正常。如果没有,请直接在浏览器中输入Google 的 IP 地址之一172.217.16.195 并按(172.217.16.195)Enter。
等待(Wait)熟悉的Google徽标和搜索栏出现。如果这也失败了,那么问题可能出在互联网上,而不是DNS服务器本身。如果是这种情况,请联系您的互联网服务提供商以获得更多帮助。
How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error
The Domain Name System (DNS) server is where all of the domain names for the sites you’ve visited are stored. When searching a domain name in a web browser, it iѕ forwarded by уour router to a DNS server. If the pаrticular site’s domain name has been saved, it then returns the corresponding IP address. This makes the loading process for those sites particularly faster.
As great as this process is, it’s not uncommon for the DNS server to fail to establish a connection from time to time. Attempting to troubleshoot your web browser in this instance can often result in a ‘DNS server not responding’ error.

Many factors could cause this particular error to show up on your screen. The most prominent of which is the possibility that the server itself is currently experiencing an outage. Luckily, this problem is often accompanied by a few easy solutions.
How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error
Have you’ve received an error that the DNS server is unavailable? For a quick fix, these problems can sometimes be corrected by something as simple as changing browsers, messing with a few of your firewall settings, or rebooting your router. It’ll be up to you to figure out the cause and subsequent correction for the problem.

Start by using a different browser for the web pages you’re trying to open. This means that if you’re currently receiving the error while using the Mozilla Firefox browser, switch it up to Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome. Should the problem persist, we can move on to testing out other devices.
Attempt to open a webpage using a mobile device, on the same network, to ensure that the problem isn’t the result of hardware failures. It would also be beneficial to attempt to connect to the same webpages using your data plan to identify if the cause is, in fact, with the DNS server.
Once you’ve exhausted these steps, reboot your router. If the “DNS server unavailable” error is still present, we’ll have to undergo a few more effective methods.
Flushing Your DNS (Windows)

The most effective method for fixing the issue with the DNS server being unavailable is to flush it using Command Prompt.
- Pull up the Run dialog by simultaneously pressing the Windows key and R key.
- Type cmd into the field and press Enter.
- In the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.

- Follow up by typing ipconfig /release and press Enter.

- Finally, type ipconfig /renew and press Enter.

- Close out of the Command Prompt window and reboot your system.
Flushing Your DNS (MacOS)

You can also flush the DNS on a Mac. The way in which you do this will vary slightly depending on the version of Mac your computer is running. It often only involves a change in the syntax used during the process.
- Open a Finder window and then head into Applications, followed by Utilities, and ending in the Terminal.
- Enter in the following syntax pertaining to the version of MacOS you’re currently using:
- MacOS High Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; sleep 2; echo macOS DNS Cache Reset | say
- MacOS Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say DNS cache has been flushed
- MacOS Mojave – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;sleep 2;
- MacOS X El Capitan/Yosemite – sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say cache flushed
- Press the Return key, enter your password, and then hit the Return key once more.
- Await the audio alert that indicates a successful DNS flush before exiting the Terminal.
The MacOS X cache clearing will need a few added steps in order to fully flush it out. You’ll have to flush both MDNS and UDNS caches on top of the steps previously taken.
Before exiting from the Terminal, perform the following commands:
- For the MDNS cache, type sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache
- For the UDNS cache, type sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches
Remove Multiple Antiviruses

“You can never have too much protection.” This may be somewhat true in the real world, but in the world of technology, having multiple antivirus programs installed on the same computer can actually hinder the protection provided.
Check to see if you have two or more antivirus programs currently running as this may be the reason for the DNS issue. Once you disable all additional programs, reboot your system and the problem should resolve itself.
Ensure that moving forward you only keep a single software program running to help defend yourself from unwanted malware attacks. This not only increases security but can help you avoid running into more DNS server errors.
Changing DNS Servers

If you’ve already attempted all fixes written here and are still receiving the same “DNS server unavailable” error, it may be in your best interest to change your DNS servers. There are plenty of public DNS from which to choose, Google’s free DNS being one of the more popular choices.
The process for this is very simple and can be done in a few clicks, depending on where you choose to change it. We’ll be using the Windows operating system in each of our examples.
DNS Changes via Router

- Access your router by launching your web browser and entering the Default Gateway address into the URL bar.
- You can find the Default Gateway by opening a Command prompt window, typing ipconfig, and pressing Enter. Copy the numbers located beside Default Gateway in the pulled up information.

- Login to the router using the proper credentials.
- Locate your internet account information which can often be found in a similarly named tab.
- Navigate to the DNS server and select the option that best mirrors your used internet protocol (IPv4 or IPv6).
- Enter the address of the DNS server you want to use in place of the current one.
- Google’s DNS server will be 8.8.8.8 in the preferred DNSv4 and 8.8.4.4 in the alternate DNS server. In the case of IPv6, you’ll want to use 2001:4860:4860::8888 and 2001:4860:4860::8844 respectively.
- Save the edited information and exit the router interface.
DNS Changes via Windows OS

- Access your network connection properties by launching the Run function (Windows key + R) and typing in ncpa.cpl. Press Enter.

- Windows 10 users can right-click the Windows icon at the lower left of the desktop screen and select Network Connections from the menu.
- Select the network adapter currently in use. WLAN for WiFi connections and LAN for direct connection, usually via ethernet cable.
- Windows 10 will have your options on the left side panel. Select one and choose Change adapter options from the main window.
- Right-click your choice and select Properties.

- In the Networking tab, highlight your IP version (v4 or v6) from the menu and click the Properties button.

- Click the radial for Use the following DNS server addresses: to enable editing capabilities.

- Enter in the DNS server addresses you plan to use.
- If you had been using a previous DNS server not obtained automatically, remember to annotate the addresses just in case you want to return using them at a later date.
- Finalize the changes by clicking OK.
Test New DNS Server

Once the DNS servers have been changed, open a browser and attempt to launch a well-known site like www.google.com. If the site is immediately accessible, then the new DNS is functioning properly. If not, enter one of Google’s IP addresses, 172.217.16.195, directly into your browser and hit Enter.
Wait for the familiar Google logo and search bar to appear. If this also fails, then the problem may lie with the internet and not the DNS server itself. Contact your internet service provider for additional help if this is the case.

















