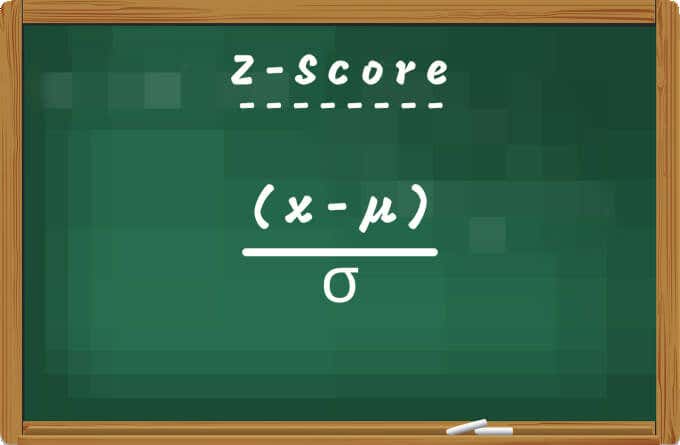如您所知,您可以使用Microsoft Excel执行许多数学计算。在本教程中,我们将引导您完成在Excel中计算(Excel)Z 分数(Z-Score)所涉及的步骤。
如果这是您第一次使用Excel,我们建议您花五分钟时间仔细阅读此Microsoft Excel 初学者教程(Microsoft Excel beginner’s tutorial)。您将了解基本功能的工作原理、导航快捷方式、创建工作簿、格式化数据以及作为初学者使用电子表格程序的所有知识。

完成后,继续下一节学习如何在Excel中计算 Z 分数。但首先,让我们简要解释一下Z-Score、它的用途、您可能需要计算的原因以及如何完成它。
什么是 Z 分数?
Z 分数(也称为“标准分数”)是一种衡量分布中值之间关系的指标。更准确地说,它描述了数据集中值相对于它们的均值和标准差的位置。Z-Score 允许准确测量和比较数据集中的值。
计算Z-Score的数学公式为(x-µ) / σ;其中x = Cell Value、µ = Mean和σ = Standard Deviation。
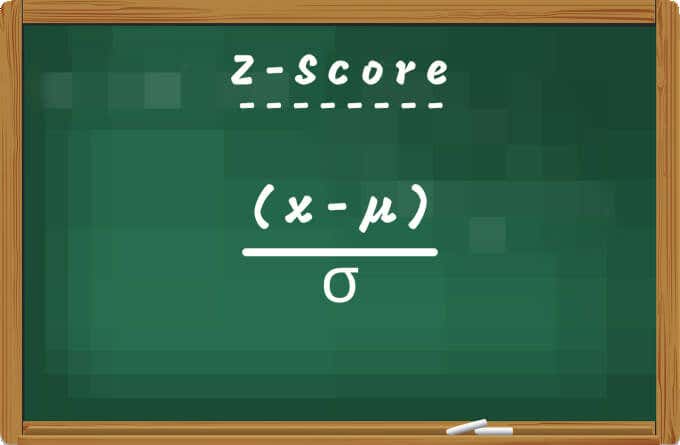
公司有时会使用Z-Score来预测和估计即将破产的情况。此外,它是确定机构财务状况的重要指标。研究人员(Researchers)还利用Z-Score来比较从不同样本或人群中获得的观察结果。
如何在 Excel 中计算 Z 分数
由于Z 分数(Z-Score)是平均值和标准差的函数,因此您需要首先计算数据集的平均值和标准差。尽管您可以在任何单元格中提取平均值和标准偏差,但我们在工作表中为“平均值”和“标准偏差”创建了专用列。我们还为“ Z-Score ”创建了一个列。
我们的示例文档包含一家造纸公司 10 名员工的绩效评级。现在让我们计算员工评分的Z-Score。
计算平均数(Calculate Mean Average)
要计算数据集的平均平均值,请键入=AVERAGE(,选择数据集中的第一个值(first value),按列键(column key),选择数据集范围内的最后一个值,按右(last value)括号(closing parenthesis)键,然后按Enter。公式应如下所示像下面的一个:
=AVERAGE(B2:B11)

您应该在输入公式的单元格中看到数据集的平均值或平均值。
计算标准偏差(Calculate Standard Deviation)
Excel 还可以轻松计算数据集的标准偏差,(calculate the standard deviation of your dataset)只需单击几下即可。
在“标准偏差”列中选择一个单元格,键入=STDEV.P(,然后选择范围中的第一个值(first value),按列键(column key),选择最后一个值,输入右括号(closing parenthesis),然后按Enter。如果您是有疑问,得到的公式应该类似于以下公式:
=STDEV.P(B2:B11)

在 Excel 中计算 Z 分数:方法 1(Calculate Z-Score in Excel: Method 1)
Excel具有STANDARDIZE函数,可提供分布中数据集的Z 分数(Z-Score)。选择Z 分数(Z-Score)列中的第一个单元格,然后按照以下步骤操作。
- 转到公式(Formulas)选项卡并选择更多公式(More Formulas)。

- 将鼠标悬停在Statistical选项上并选择STANDARDIZE。

这将启动一个新的函数参数(Function Arguments)窗口,您可以在其中计算分布的Z 分数(Z-Score)。
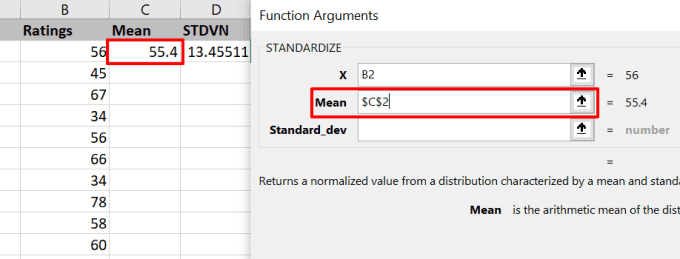
- 在“X”字段中输入(Enter)第一个值的单元格引用。

- (Enter)在“平均值”字段中输入算术平均值的单元格引用,然后按键盘上的F4锁定单元格引用。
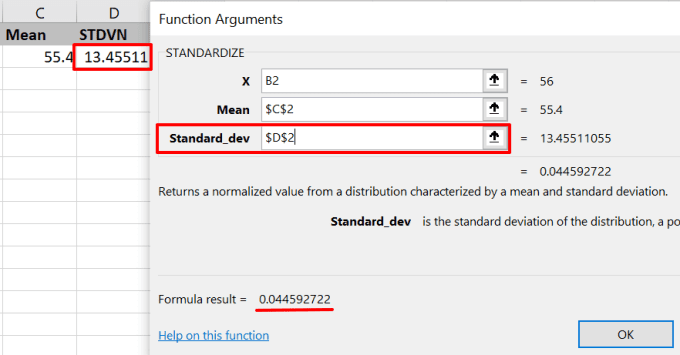
- 最后,在“Standard_dev”字段中输入标准差的单元格引用,然后按F4锁定单元格引用。该工具将显示Z 值(Z-value)的预览。按OK继续。
要获取其他值的Z 分数(Z-Score),请将光标悬停在单元格的右下角,然后将plus (+) icon拖到列下方。

Excel会将公式复制到该列并自动为相应行中的其他值生成Z 分数(Z-Score)。

在 Excel 中计算 Z 分数:方法 2(Calculate Z-Score In Excel: Method 2)
如前所述,您可以通过从数据点中减去数据集的平均值并将结果除以标准偏差来获得数据点的 Z 分数。使用 (x-µ) / σ,您可以通过手动输入这些值 来计算Excel中的 z 分数。(Excel)
- 选择Z-Score列中的第一个单元格,键入等号 ( = ),后跟左括号(open parenthesis),然后选择包含要计算其Z-Score的数据集的列中的第一个值。然后(Afterward),键入连字符(hyphen),选择算术平均值,按F4使平均值成为绝对/固定,然后按右括号(close parenthesis)图标。最后,按正斜杠(forward-slash)( / ) 键,选择标准差,然后按F4锁定单元格引用。
最终公式应类似于:=(B2-$C$2)/$D$2。按Enter 键(Enter)执行公式。

请注意,该公式将仅计算所选单元格中第一个值的Z 分数(Z-Score)。
- 将鼠标悬停在第一个(Hover)Z-Score单元格的右下角,然后将plus (+) icon向下拖动到列中。

解释 Z 分数
您的数据集很可能包含负数和正数Z-Score的混合。正Z 分数(Z-Score)表示值/分数高于数据集的平均平均值。当然,负Z-Score表明相反:该值低于平均平均值。如果数据点的Z 分数(Z-Score)为零 (0),那是因为它的值等于算术平均值。
数据点越大,其Z-Score越高。浏览您的工作表,您会发现较小的值具有较低的 Z-Score(Z-Score)。同样(Likewise),小于算术平均值的值将具有负Z-Score。

例如,在我们的示例工作表中,您会发现“Michael”的评分最高 (78) 和最高的 Z 分数(Z-Score)(1.679659)。另一方面,“Dwight”和“Kevin”的评分最低(34)和最低的 Z 分数(Z-Score)(-1.59047)。
成为(Become)Excel专家:教程库
您现在知道如何计算数据集的Z 分数了。(Z-Score)如果您对在Excel中计算(Excel)Z 分数(Z-Score)有任何疑问或其他有用的提示,请在下方发表评论。
我们建议阅读有关计算方差(calculating variance)、删除数据集中重复行(removing duplicate rows)以及如何使用 Excel 中的汇总函数汇总数据的(use summary functions in Excel)Excel 相关教程。
How to Calculate Z-Score in Excel
As you know, there are many mathematical calculations you can perfоrm with Microsoft Excel. In this tutorial, we’ll walk you through the steps involved in calculating Z-Score in Excеl.
If this is your first time using Excel, we recommend you take five minutes to peruse this Microsoft Excel beginner’s tutorial. You’ll learn how essential functions work, navigation shortcuts, creating workbooks, formatting data, and everything there is to know about using the spreadsheet program as a beginner.

When you’re done with that, proceed to the next section to learn how to calculate Z score in Excel. But first, let’s briefly explain Z-Score, its uses, why you might need to calculate one, and how to get it done.
What Is a Z-Score?
Z-Score (also known as a “Standard Score”) is a metric that highlights the relationship between values in a distribution. More precisely, it describes the position of values in a dataset with respect to their mean and standard deviation. Z-Score allows for accurate measurement and comparison of values in a dataset.
The mathematical formula for calculating Z-Score is (x-µ) / σ; where x = Cell Value, µ = Mean, and σ = Standard Deviation.
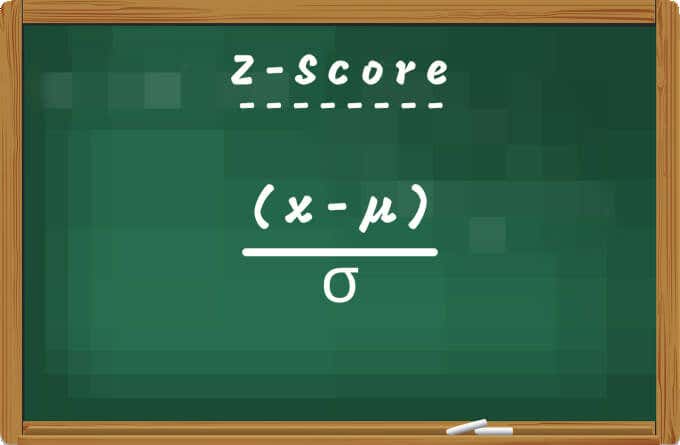
Companies sometimes use Z-Score to forecast and estimate impending bankruptcy. Additionally, it’s a great metric for ascertaining the financial position of an institution. Researchers also utilize Z-Score to compare observations obtained from different samples or populations.
How to Calculate Z-Score in Excel
Since Z-Score is a function of mean and standard deviation, you’ll need to first calculate the average and standard deviation of your dataset. Although you can extract the mean and standard deviation in any cell, we created dedicated columns for “Mean” and “Standard Deviation” in our worksheet. We also created a column for “Z-Score.”
Our sample document contains the performance ratings of 10 employees in a paper company. Now let’s calculate the Z-Score of the employees’ rating.
Calculate Mean Average
To calculate the mean average of your dataset, type =AVERAGE(, select the first value in the dataset, press the column key, select the last value within the dataset range, press the closing parenthesis key, and press Enter. The formula should look like the one below:
=AVERAGE(B2:B11)

You should see the mean or average value of the dataset in the cell you entered the formula.
Calculate Standard Deviation
Excel also makes it pretty easy to calculate the standard deviation of your dataset in a few clicks.
Select a cell in the “Standard Deviation” column, type =STDEV.P(, then select the first value in the range, press the column key, select the last value, enter the closing parenthesis, and press Enter. If you’re in doubt, the resulting formula should be similar to the one below:
=STDEV.P(B2:B11)

Calculate Z-Score in Excel: Method 1
Excel has a STANDARDIZE function that provides the Z-Score of a dataset in a distribution. Select the first cell in the Z-Score column and follow the steps below.
- Go to the Formulas tab and select More Formulas.

- Hover your mouse on the Statistical option and select the STANDARDIZE.

That’ll launch a new Function Arguments window where you’ll be able to calculate the Z-Score of the distribution.
- Enter the cell reference of the first value in the “X” field.

- Enter the cell reference of the arithmetic average in the “Mean” field and press the F4 on your keyboard to lock the cell reference.

- Finally, enter the standard deviation’s cell reference in the “Standard_dev” field and press F4 to lock the cell reference. The tool will display a preview of the Z-value. Press OK to proceed.

To get the Z-Score for other values, hover the cursor to the bottom-right corner of the cell and drag the plus (+) icon down the column.

Excel will copy the formula down the column and automatically generate the Z-Score for other values in the corresponding rows.

Calculate Z-Score In Excel: Method 2
As mentioned earlier, you can obtain a datapoint’s Z-Score by subtracting the mean of the dataset from the datapoint and dividing the result by the standard deviation. Using the (x-µ) / σ, you can calculate z-score in Excel by inputting these values manually.
- Select the first cell in the Z-Score column, type an equal sign (=) followed by an open parenthesis, and select the first value in the column containing the datasets whose Z-Score you want to calculate. Afterward, type a hyphen, select the arithmetic mean, press F4 to make the mean absolute/fixed, and press the close parenthesis icon. Finally, press the forward-slash (/) key, select the standard deviation, and press F4 to lock the cell reference.
The final formula should look similar to this: =(B2-$C$2)/$D$2. Press Enter to execute the formula.

Note that the formula will only calculate the Z-Score for the first value in the selected cell.
- Hover your mouse to the bottom-right corner of the first Z-Score cell and drag the plus (+) icon down the column.

Interpreting Z-Score
Your dataset will most likely contain a mix of negative and positive Z-Scores. A positive Z-Score indicates that the value/score is higher than the dataset’s mean average. A negative Z-Score, of course, tells the opposite: the value lies below the mean average. If a datapoint’s Z-Score is zero (0), that’s because its value equals the arithmetic mean.
The bigger a data point, the higher its Z-Score. Go through your worksheet and you’ll realize that the small values have lower Z-Scores. Likewise, values smaller than the arithmetic mean will have negative Z-Scores.

In our sample worksheet, for instance, you’ll discover that “Michael” had the highest rating (78) and highest Z-Score (1.679659). “Dwight” and “Kevin” on the other hand both had the lowest ratings (34) and lowest Z-Score (-1.59047).
Become an Excel Expert: Tutorial Repository
You now know how to calculate the Z-Score of a data set. Drop a comment below if you have questions or other useful tips regarding calculating Z-Score in Excel.
We recommend reading Excel-related tutorials on calculating variance, removing duplicate rows in your dataset, and how to use summary functions in Excel to summarize data.