无论您是经验丰富的Linux 用户还是刚开始使用PopOS或Ubuntu等发行版,您仍然需要知道如何管理您的文件和文件夹(how to manage your files and folders)。这意味着您知道在Linux(Linux)中有许多方法可以重命名目录或文件。在Linux世界中,文件夹也称为目录。它们是可以互换的。

重命名文件和文件夹时有两种情况。您正在重命名单个文件或文件夹,或者您想要一次重命名多个文件或文件夹。就像(Just)Windows或Mac一样,Linux也有多种方法可供您选择。
使用文件管理器在 Linux 中重命名单个文件或目录(Rename a Single File or Directory in Linux Using File Manager)
大多数Linux发行版或发行版都有一个图形文件管理器,类似于 Windows 中的文件资源管理器(file manager similar to File Explorer in Windows)或MacOS 中的 Finder(Finder in MacOS)。它们中的大多数将以相同的方式运行,但可能存在差异。
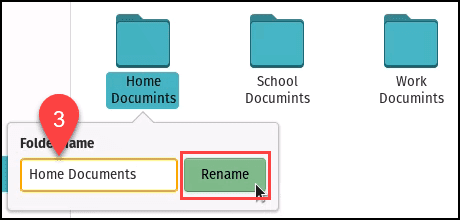
使用重命名重命名(Rename Using Rename)
- 右键单击文件或文件夹。
- 选择重命名(Rename )或按F2。

- 文件或文件夹的名称字段变为可编辑。进行所需的更改并选择“重命名(Rename )”按钮或按Enter 键(Enter)。
使用文件属性重命名(Rename Using File Properties)
这种方法很奇怪,你不太可能使用它,但它仍然是可能的。
- 右键单击文件或文件夹。
- 选择属性(Properties)或按Ctrl + I I。

- 选择名称字段并进行编辑。然后关闭属性(Properties )窗口,文件或文件夹被重命名。

使用文件管理器在 Linux 中重命名许多文件或文件夹(Rename Many Files or Folders in Linux Using File Manager)
此功能可能不适用于不同 Linux 发行版中的所有文件管理器(Linux)。这是在PopOS中。
- 选择多个文件或文件夹,然后右键单击并选择重命名(Rename )或按F2。

- 您可以使用模板重命名(Rename using a template )或查找和替换文本(Find and replace text)。

- 使用模板重命名(Rename using a template)允许您执行诸如对文件和文件夹按顺序编号或将文本添加到原始文件名的正面、背面或两侧的操作。

它可以根据原始名称或修改日期将模板应用于文件。

- 查找和替换文本(Find and replace text)允许搜索特定的文本序列并将其替换为其他内容。这对于纠正拼写错误非常有用。

在 Linux 中获得帮助(Get Help in Linux)
有很多方法可以使用下面的命令和实用程序。如果您不确定需要做什么,请输入命令man(用于手册)和您需要帮助的实用程序的命令或名称。例如,man mv将显示使用mv命令的手册。
在Linux中重命名文件或目录后,始终通过查看文件资源管理器(File Explorer)或使用ls命令列出它们来检查它们。
使用 MV 命令重命名单个文件或文件夹(Rename a Single File or Folder with the MV Command)
MV 命令用于移动文件和文件夹,但它也适用于重命名。MV 命令的语法是:mv [OPTIONS] source destination
- 导航到要重命名的文件或文件夹所在的文件夹。

- 使用mv命令重命名文件夹或文件。如果名称中有空格,请用引号将名称引起来。让我们把名称中的01- 去掉(01-)。
输入mv “01-Work Documents” “Work Documents”然后回车。

列出文件显示它已重命名。

使用 Bash 脚本重命名多个文件或文件夹(Rename Multiple Files or Folders Using Bash Script)
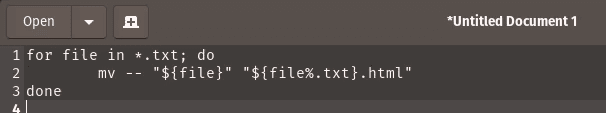
要创建 bash 脚本(create a bash script),您需要在纯文本编辑器中工作。假设我们有几个HTML文件,我们不小心将它们保存为纯文本文件。我们需要将文件扩展名从 .txt 更改为 .html。我们可以使用这个 bash 脚本来重命名它们:
- 在文本编辑器中输入它,并将其另存为 rename-txt.sh,保存在与要更改的文件相同的文件夹中。

- 在终端中,导航到该文件夹并输入命令bash rename-txt.sh并按Enter 键(Enter)。

- 使用ls检查或查看文件管理器(File Manager )以查看它是否有效。

那是如何工作的?第一行是寻找任何以.txt结尾的文件。星号 (*) 是通配符,因此文件名中 .txt 之前的任何内容都将匹配。do告诉它只要有匹配的文件就执行命令。这是一个循环(loop)。第二行有mv命令。
双破折号 ( — ) 告诉它命令没有选项,准备好一些正则表达式或正则表达式。$file 是一个变量,告诉它处理第一行选取的任何文件。如果.txt(.txt)位于名称的尾部,则% 告诉它用大括号外的值替换.html。
如何使用 Linux 实用程序安全地重命名文件和文件夹(How to Safely Rename Files and Folders with Linux Utilities)
本文的其余部分是关于Linux shell 中使用的实用程序。很容易犯错误并重命名可能会阻止程序或Linux运行的关键文件。始终使用-n选项。它告诉命令不要覆盖现有文件。
在实用命令中使用它可能类似于:mmv -n “*” “#l1”。请参阅下面它如何显示命令将执行的操作的预览。然而,如果您列出 ( ls ) 文件,您将看到它们都没有改变。如果这不是您所期望的,请调整您的命令并重试。

使用重命名重命名多个文件和文件夹(Rename Multiple Files and Folders with Rename)
重命名(Rename)是一个Linux实用程序。将(Think)其视为没有图形用户界面的小程序。您的Linux发行版可能没有它,但它很容易安装。
在终端中,输入命令sudo apt-get install rename并按Enter。它可能会要求您输入密码,输入密码,然后按Enter 键(Enter)。它将开始安装。
安装后,您可以开始使用Rename。
- 导航到要更改文件或文件夹名称的位置。

- 就像在 bash 脚本中一样,您需要使用正则表达式来选择文件并定义要对它们执行的操作。这是一个示例:rename ‘s/.html/.txt/’ *.html

如果您猜到这会将我们文件的文件扩展名从 .html 改回 .txt,那么您猜对了!

使用 MMV 重命名文件和文件夹(Rename Files and Folders Using MMV)
MMV是另一个Linux实用程序,类似于Rename。可以使用命令安装它sudo apt install mmv。安装后,您可以创建自己的命令。
- 我们将使用的示例MMV命令会将目录中的所有文件名从小写更改为大写(UPPER CASE):mmv -r “*” “#u1”

- -r告诉它重命名。星号告诉它更改目录中的任何文件。#u1 很特别。这是 降价代码。(Markdown code.)这告诉它将文本更改为大写。

这就是在 Linux 中重命名目录和文件的所有方法吗?(Is That All the Ways to Rename Directories and Files in Linux?)
如果此处的其中一种方法对您不起作用,您可以使用具有图形用户界面的批量重命名(bulk renaming)工具。

有几种可供选择。Thunar和KRename只是一对夫妇。
How to Rename Files and Folders in Linux
Whether you’re а veteran Linux user оr just picked up a distro like PopOS or Ubuntu, you still need to know how to manage your files and folders. That means knowing that there are many ways you can rename directories or files in Linux. In the Linux world, folders are called directories, too. They’re interchangeable.

There are two scenarios when renaming files and folders. Either you’re renaming a single file or folder, or you want to rename many files or folders at once. Just like Windows or Mac, Linux has several ways you can do either.
Rename a Single File or Directory in Linux Using File Manager
Most distributions, or distros, of Linux have a graphical file manager similar to File Explorer in Windows or Finder in MacOS. Most of them will function in the same way, but there may be differences.
Rename Using Rename
- Right-click on the file or folder.
- Select Rename or press F2.

- The name field of the file or folder becomes editable. Make the change you want and select the Rename button or press Enter.

Rename Using File Properties
This method is odd and you’re unlikely to use it, but it’s still possible.
- Right-click on the file or folder.
- Select Properties or press Ctrl + I.

- Select the name field and make edits. Then close the Properties window and the file or folder is renamed.

Rename Many Files or Folders in Linux Using File Manager
This feature may not be available in all the file managers available in the different distros of Linux. This is in PopOS.
- Select multiple files or folders and then either right-click and select Rename or press F2.

- You can Rename using a template or Find and replace text.

- Rename using a template allows you to do things like sequentially number files and folders or add text to the front, back, or both sides of the original filename.

It can apply the template to the files based on the original name or modified date.

- Find and replace text allows searching out a specific sequence of text and replacing it with something else. This is great for correcting spelling mistakes.

Get Help in Linux
There are a lot of ways to use the commands and utilities below. If you’re not sure what you need to do, ender the command man (for manual) and the command or name of the utility you need help with. For example, man mv will show the manual for using the mv command.
After renaming files or directories in Linux, always check them by either looking in the File Explorer or using the ls command to list them.
Rename a Single File or Folder with the MV Command
The MV command is for moving files and folders, yet it works well for renaming too. The syntax for the MV command is: mv [OPTIONS] source destination
- Navigate to the folder where files or folders you want to rename are located.

- Use the mv command to rename the folder or file. If the name has spaces in it, surround the name with quotes. Let’s take the 01- off the name.
Type in mv “01-Work Documents” “Work Documents” and press enter.

Listing the files shows it’s renamed.

Rename Multiple Files or Folders Using Bash Script
To create a bash script, you need to work in a plain text editor. Let’s say we had several HTML files that we accidentally saved as plain text files. We need to change the file extension from .txt to .html. We can use this bash script to rename them:
for file in *.txt; do
mv — “$file” “${file%.txt}.html”
done
- Enter that in the text editor and save it as rename-txt.sh in the same folder as the files to change.


- In the terminal, navigate to that folder and enter the command bash rename-txt.sh and press Enter.

- Check using ls or look in the File Manager to see if it worked.

How did that work? The first line is looking for any file that ends in .txt. The asterisk (*) is a wildcard, so anything before .txt in a filename will match. The do tells it to do the command as long as there are matching files. This is a loop. The second line has the mv command.
The double-dash (—) tells it there are no options for the command, get ready for some regular expression or regex. The $file is a variable that tells it to work with any file picked up by the first line. The % tells it to replace the .txt if it’s at the tail of the name with the value outside the curly bracket, which is .html.
How to Safely Rename Files and Folders with Linux Utilities
The rest of the article is about utilities used in the Linux shell. It can be easy to make a mistake and rename critical files that may stop programs or Linux from working. Always use the -n option. It tells the command to not overwrite an existing file.
Using it in a utility command may look like: mmv -n “*” “#l1”. See below how it shows a preview of what the command will do. Yet if you list (ls) the files you’ll see none of them have changed. If it’s not what you were expecting, adjust your command and try again.

Rename Multiple Files and Folders with Rename
Rename is a Linux utility. Think of it as a small program that doesn’t have a graphical user interface. Your Linux distro might not have it, but it’s easy to install.
In the terminal, enter the command sudo apt-get install rename and press Enter. It may ask for your password, enter it, and press Enter. It will start installing.
Once installed, you can start using Rename.
- Navigate to the location where you want to change file or folder names.

- Just like in the bash script, you’ll need to use regex to select files and define what’s going to be done to them. Here’s an example: rename ‘s/.html/.txt/’ *.html

If you guessed that will change the file extensions on our files back to .txt from .html, you’re right!

Rename Files and Folders Using MMV
MMV is another Linux utility, similar to Rename. It can be installed with the command sudo apt install mmv. Once it’s installed, you can create your own commands.
- The example MMV command we’ll use will change all the filenames in the directory from lower case to UPPER CASE: mmv -r “*” “#u1”

- The -r tells it to rename. The asterisk tells it to change any file in the directory. The #u1 is something special. It’s Markdown code. This tells it to change the text to uppercase.

Is That All the Ways to Rename Directories and Files in Linux?
If one of the methods here doesn’t work for you, you could use a bulk renaming tool that has a graphical user interface.

There are several to choose from. Thunar and KRename are just a couple to start with.
























