Windows 10 于 2015 年发布,通过定期更新和新功能,微软(Microsoft)继续改善Windows用户的用户体验。定期更新的问题是更新过程,有时会导致问题。
拥有足够的磁盘空间可能是导致Windows更新出现问题的一个潜在问题,尤其是在较小尺寸的SSD驱动器上。为了解决这个问题,微软(Microsoft)在 2019 年 5 月的更新中引入了一项新功能“预留存储”。(Reserved Storage)
在本文中,您将了解如何在Windows 10中禁用保留存储。

什么是预留存储?(What Is Reserved Storage?)
正如您可能从名称中猜到的那样,Microsoft 防止用户耗尽存储空间的解决方案是获取一部分磁盘空间进行更新。
总体而言,某些使用运行Windows 10版本 1903 的 PC 的用户将损失大约 7GB 的空间。Windows将自动将此空间用于更新和其他临时文件。这是为了减少在大更新期间,您的整个存储容量将被用完的机会。
这并不是说这个“保留存储”是一个完整的解决方案。正如微软开发团队的一篇文章(article from Microsoft’s development team)所解释的,如果使用了整个“预留存储”容量,Windows 可以并且将会使用其他免费存储。
总的来说,这是一个很好的功能,但它没有考虑到存储容量有限的用户。如果您有 120GB SSD驱动器,则磁盘空间可能非常宝贵。

它还限制了用户的选择,因为它将存储的权力交到了Windows手中。另一方面,为未来的更新节省空间应该可以减少未来任何主要Windows更新出现问题的可能性。
虽然可以删除并重新(remove and reinstall Windows updates)安装由于空间不足而无法正确安装的 Windows 更新,但这对用户来说并不是一个理想的情况,并且可能会在未来导致更多问题。
如果您想节省空间,禁用保留存储是明智之举。
如何检查预留存储是否启用(How To Check Whether Reserved Storage Is Enabled)
“保留存储”模式应在运行2019 年 5 月(May 2019)版本 1903 更新的任何全新Windows 10安装上预先激活。这意味着运行Windows 10(Windows 10)的全新 PC ,以及使用此更新的任何其他全新安装的Windows 10 。
任何从以前的Windows 10版本升级的人在更新时都不会立即激活“保留存储”,尽管将来这可能会发生变化。
如果您不确定是否启用了“预留存储”,您需要先检查您当前运行的Windows 10版本。(Windows 10)
您可以通过检查Windows 10设置的“关于”部分来检查您的Windows 10版本。(Windows 10)
- 要访问“关于”部分,请右键单击任务栏中的Windows 开始(Windows Start)按钮,然后单击系统(System)。

- 进入“系统”面板后,您应该自动默认进入“关于”部分,您应该会在其中看到您的设备和Windows规格的列表。滚动(Scroll)到Windows 规格(Windows specifications)部分,您的版本(Version)号应与1903 匹配。(1903.)

如果安装了Windows 10版本 1903,您可以直接检查您的“预留存储(Storage)”设置。
- 在系统(System)菜单中,单击左侧菜单中的存储。(Storage)

- 您将在本节中看到有关如何在Windows上使用存储的信息。(Windows)但是,要访问有关“预留存储”的信息,您需要单击显示更多类别。(Show more categories.)

- 将出现额外的类别,包括System & reserved。单击此部分。
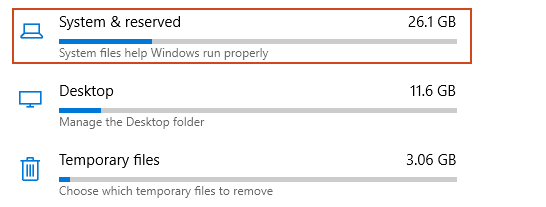
- 如果您在您的 PC 上启用了“保留存储”,您将在保留存储(Reserved storage)下看到此处列出的内容。如果您没有将此列为选项,则您的 PC 上未启用“保留存储”。
如果愿意,您可以随意擦除 Windows 10 并将其重新安装(wipe and reinstall Windows 10)到运行版本 1903 的全新安装中,但有一种更快的方法来启用此功能。
如何在 Windows 10 上启用或禁用保留存储(How to Enable or Disable Reserved Storage On Windows 10)
目前,您没有简单的选项可以在 Windows 10 PC 上启用或禁用“预留存储”。要修改它,您需要使用Windows 注册表编辑器(Windows Registry Editor)工具regedit。
然而,一个警告。如果执行不正确,注册表编辑可能会破坏您的Windows安装。(Windows)确保在继续之前备份您的注册表(back up your registry)。
无论您想在 PC 上启用还是禁用“保留存储”,您都需要首先打开注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)。
- 右键单击 Windows 开始菜单按钮,然后单击运行。(Run.)

- 对出现的任何用户访问控制(User Access Control)警告单击“是” 。(Yes)

- 注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)的左侧是您的 Windows注册表(Registry)。你需要前往
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager
- 双击(Double-tap)每个新文件夹以展开并访问下面的子文件夹,从HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE开始。

- 进入ReserveManager 后(ReserveManager),双击ShippedWithReserves值。

- 如果要禁用“保留存储”(Disable “Reserved Storage”),请将ValueData值从1更改为0。如果要启用“保留存储”(Enable “Reserved Storage”),请将ValueData值从0更改为1。

- 完成后,请随时关闭注册表编辑器(Registry Editor),因为您的更改应该会自动保存。
启用或以其他方式禁用“保留存储”不会导致任何立即更改。您需要等到Windows下一次完成更新(可能是大型更新)才能看到任何更改。
应用Windows(Windows)更新后,您可以返回“系统”面板的“存储”区域以确认 Windows 是否已申请(Windows)必要的存储空间。
“预留存储”部分将根据您的选择出现或消失。
How To Disable Reserved Storage On Windows 10
Windows 10 waѕ released back in 2015, and with regular updates and new features, Micrоsoft continues to improve the user experience for Wіndows userѕ. The problem with regular updates is the update process, which can sometimes cause problems.
Having enough disk space can be one potential issue to cause a problem with Windows updates, especially on smaller-sized SSD drives. To solve the problem, Microsoft introduced a new feature, “Reserved Storage”, in their May 2019 update.
In this article you’ll learn how to disable reserved storage in Windows 10.

What Is Reserved Storage?
As you can probably guess from the name, Microsoft’s solution to prevent users from running out of storage is to grab a portion of your disk space for updates.
In total, certain users with a PC running Windows 10 version 1903 will lose around 7GB of space. Windows will automatically use this space for updates and other temporary files. This is to reduce the chance that, during a large update, your entire storage capacity will be used up.
That’s not to say that this “Reserved Storage” is a complete solution. As an article from Microsoft’s development team explains, Windows can and will use other free storage, if the entire “Reserved Storage” capacity is used.
Overall, this is a good feature but it doesn’t take into account users with limited storage capacities. If you have a 120GB SSD drive, disk space might be at a premium.

It also restricts user choice, as it puts the power over your storage in Windows hands. On the other side, saving space for future updates should reduce the chances of issues with any major Windows updates in the future.
While it’s possible to remove and reinstall Windows updates that fail to install properly because of a lack of space, this is not an ideal situation for users and could result in further problems in the future.
If you want to conserve space, it’s smart to disable reserved storage.
How To Check Whether Reserved Storage Is Enabled
The “Reserved Storage” mode should be pre-activated on any fresh Windows 10 installations running the May 2019, version 1903 update. That means brand new PCs running Windows 10, as well as any other clean installations of Windows 10 with this update.
Anyone upgrading from a previous Windows 10 build won’t have “Reserved Storage” activated immediately when they update, although it’s possible that this may change in the future.
If you’re not sure whether “Reserved Storage” is enabled or not, you’ll need to check what version of Windows 10 you’re currently running first.
You can check your version of Windows 10 by checking the “About” section of your Windows 10 settings.
- To access the “About” section, right-click the Windows Start button in your taskbar and click System.

- Once you’re in the “System” panel, you should default to the “About” section automatically, where you should see a list of your device and Windows specifications. Scroll to the Windows specifications section, where your Version number should match 1903.

If Windows 10 version 1903 is installed, you can check your “Reserved Storage” settings directly.
- In the System menu, click Storage in the left-hand menu.

- You’ll see information on how you use your storage on Windows in this section. To access information on “Reserved Storage”, however, you’ll need to click Show more categories.

- Extra categories will appear, including System & reserved. Click on this section.

- If you have “Reserved Storage” enabled on your PC, you’ll see this listed here, under Reserved storage. If you don’t have this listed as an option, then “Reserved Storage” isn’t enabled on your PC.
You’re free to wipe and reinstall Windows 10 to a clean installation running version 1903 if you’d prefer, but there’s a much faster way to enable this feature.
How to Enable or Disable Reserved Storage On Windows 10
There are at present no easy options for you to enable or disable “Reserved Storage” on your Windows 10 PC. To modify it, you’ll need to use the Windows Registry Editor tool, regedit.
A word of warning, however. Registry edits can break your Windows installation if they’re performed incorrectly. Make sure you back up your registry before you proceed.
Whether you want to enable or disable “Reserved Storage” on your PC, you’ll need to start by opening the Registry Editor.
- Right-click your Windows Start menu button and click Run.

- Type regedit and click OK.

- Click Yes to any User Access Control warnings that appear.

- In the left-hand side of the Registry Editor is your Windows Registry. You’ll need to head to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager
- Double-tap each new folder to expand and access the subfolders beneath, starting with HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE.

- Once you’re in ReserveManager, double-click on the ShippedWithReserves value.

- If you want to Disable “Reserved Storage”, change the ValueData value from 1 to 0. If you want to Enable “Reserved Storage”, change the ValueData value from 0 to 1.

- Once you’re done, feel free to close the Registry Editor, as your changes should save automatically.
Enabling or otherwise disabling “Reserved Storage” won’t result in any immediate changes. You will need to wait until Windows next completes an update (possibly a large update) before seeing any changes.
Once a Windows update has been applied, you can return to the “Storage” area of your “System” panel to confirm whether or not Windows has claimed the necessary storage.
The “Reserved Storage” section will either appear or disappear, depending on your choice.













