您是否与他人共享您的工作或家庭计算机?来宾帐户中的应用程序和文件是否会消耗大量磁盘空间?Windows有一个配额系统,可授予管理员对存储管理的更多控制权。您可以使用该工具为内部和外部存储设备设置磁盘使用配额。
我们将引导您完成通过设置磁盘配额限制来控制用户可以在您的 PC 上存储的数据的步骤。在跳转到这些步骤之前,请注意Windows 配额管理工具仅适用于使用(Windows Quota Management)NTFS 文件系统(NTFS file system)格式化的驱动器。

通过文件资源管理器(File Explorer)配置磁盘配额(Disk Quota)
有几种方法可以在Windows 11中启用配额管理系统。您可以通过文件资源管理器(File Explorer)、注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)或组策略编辑器(Group Policy Editor)执行此操作。但是,文件资源管理器(File Explorer)路线是最简单的。
- 打开文件资源管理器并在侧边栏上选择这台电脑(This PC)。

- 滚动到“设备(Devices)和驱动器”部分,右键单击要限制的磁盘,然后选择属性(Properties)。

- 前往配额选项卡并选择显示配额设置(Show Quota Settings)。

- 选中启用配额管理(Enable quota management)框。

- 接下来,选中拒绝超过配额限制的用户的磁盘空间(Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit)框。这将强制执行限制并确保达到配额限制的任何用户都不能再将数据写入磁盘。

- 选择将磁盘空间限制为(Limit disk space to)。

- 下一步是设置磁盘限制。假设(Say)您要设置 30GB 的磁盘配额,请在第一个对话框中输入数字 (30),然后在相邻的下拉框中选择存储单元 (GB)。
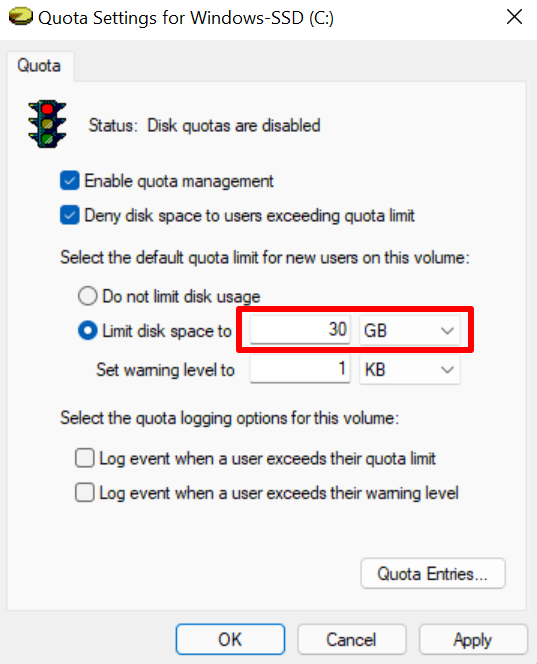
您还应该设置一个略低于磁盘限制的警告级别。对于 30GB 的磁盘限制,最好设置 25GB 的警告级别。当用户达到或超过警告限制时,Windows会发出提醒,提醒他们即将耗尽分配给他们的磁盘空间。
- 如果您希望 Windows在用户超出其磁盘配额或达到存储限制时记录事件日志(在Windows 事件查看器中),请检查(Windows Event Viewer)用户超出其配额限制(Log event when a user exceeds their quota limit)时的日志事件和用户超出其警告级别时的日志事件(Log event when a user exceeds their warning level)。

- 选择应用(Apply)以继续。
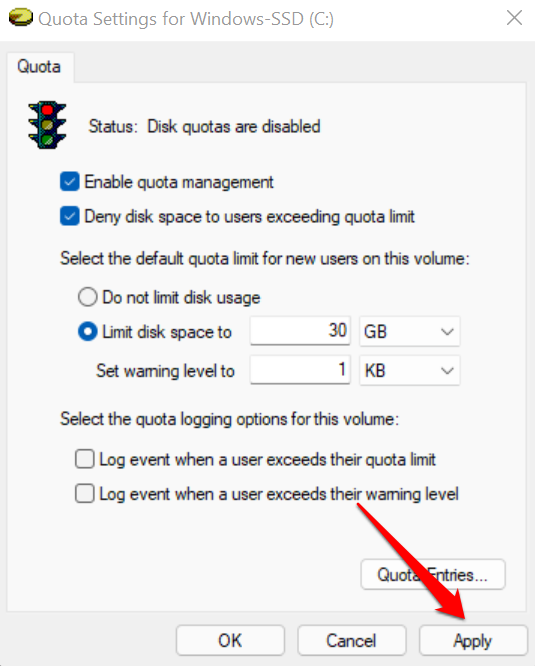
- 在警告提示上选择确定(OK)以启用您配置的配额系统。

- 在配额设置窗口中选择确定。(OK)

请注意,您可能必须重新启动计算机才能使这些更改生效。我们还应该提到磁盘配额配置是特定于驱动器的。如果您的PC 有多个磁盘分区(PC has multiple disk partitions)(与 C: 驱动器分开),则本地磁盘的配额限制不适用于其他分区。
查看和调整磁盘配额限制
当您为磁盘设置存储配额限制时,Windows会将限制应用于您计算机上的所有用户。“配额设置”(Quota Settings)窗口中有一个“配额条目”工具,可让您调整或禁用特定用户的磁盘配额限制。您还可以使用该工具根据设置的配额检查所有用户帐户的当前磁盘空间使用情况。
- 打开驱动器的配额设置(Quota Settings)窗口,然后点击配额条目(Quota Entries)按钮。
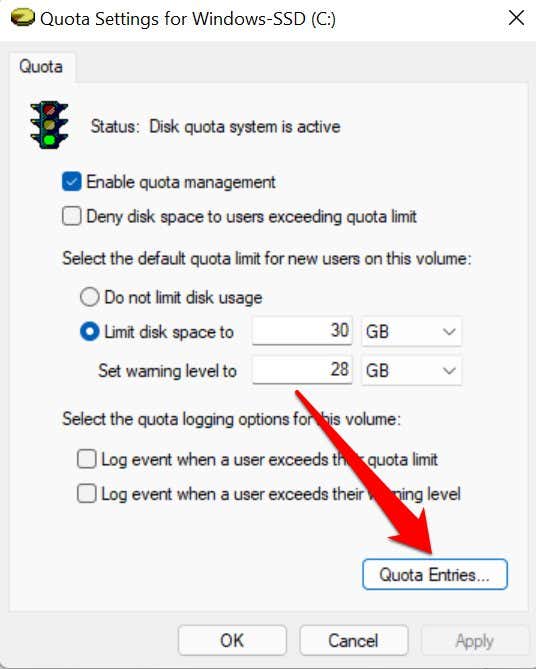
- “使用量(Amount)”和“配额限制”列显示用户在分配的配额限制下消耗了多少磁盘空间。

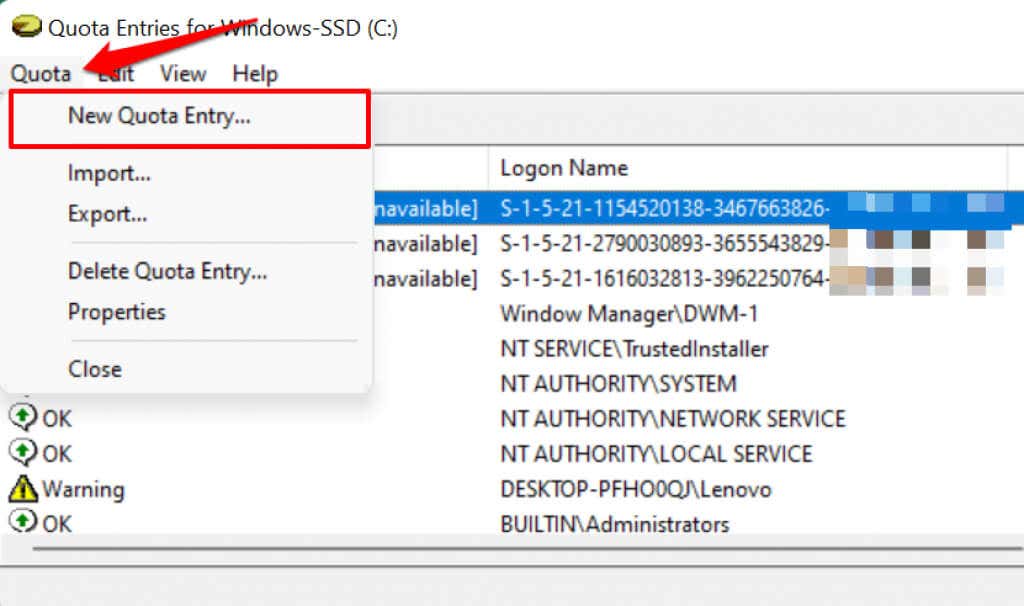
如果您在“名称”或“登录名称”列中没有找到帐户,请继续手动将用户添加到列表中。点击菜单栏上的配额,然后选择(Quota)新建配额条目(New Quota Entry)。
- 选择左下角的高级。(Advanced)

- 选择“立即查找”(Find Now)按钮并双击要包含在存储配额限制中的帐户。

- 选择确定(OK)继续。

- 为用户设置(Set)配额限制和警告级别,然后选择OK。

- 要调整或禁用用户的磁盘配额,请右键单击该帐户并选择Properties。

- 在“将磁盘空间限制为”(Limit disk space to)和“将警告级别设置为”(Set warning level to)对话框中调整用户的磁盘配额。选择应用(Apply),然后选择确定(OK)。

- 如果要删除或移除配额限制,请选择不限制磁盘使用单选按钮。(Do not limit disk usage)选择应用(Apply)和确定(OK)继续。

禁用配额限制的另一种方法是右键单击“配额条目”窗口中的帐户名称,然后选择删除(Delete)。

在下一页上选择Take Ownership以将文件保存在您分配给用户帐户的磁盘空间中。(Take Ownership)如果您不需要这些文件,请选择删除。(Delete)

使用组策略编辑器设置磁盘配额(Set Disk Quotas Using Group Policy Editor)
在某些情况下,Windows无法强制执行通过文件资源管理器(File Explorer)配置的存储配额限制。如果发生这种情况,请在组策略编辑器(Group Policy Editor)中修改或重新启用磁盘配额。
请注意,组策略编辑器(Group Policy Editor)仅在Windows 11 专业版(Pro)、教育(Education)版和企业(Enterprise)版中可用。如果您使用Windows 11 家庭版,请尝试在(Home)注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)中重新启用存储配额。
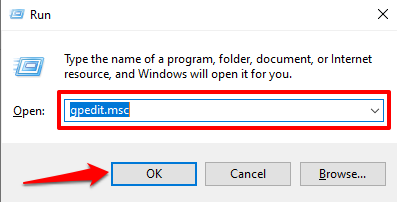
- 使用Window 键(Window key)+ R键盘快捷键打开Windows 运行(Windows Run)框。在对话框中键入gpedit并按(gpedit)Enter。
- 在边栏上,转到计算机配置(Computer Configuration)>管理模板(Administrative Templates)>系统(System),然后选择磁盘配额(Disk Quotas)文件夹。

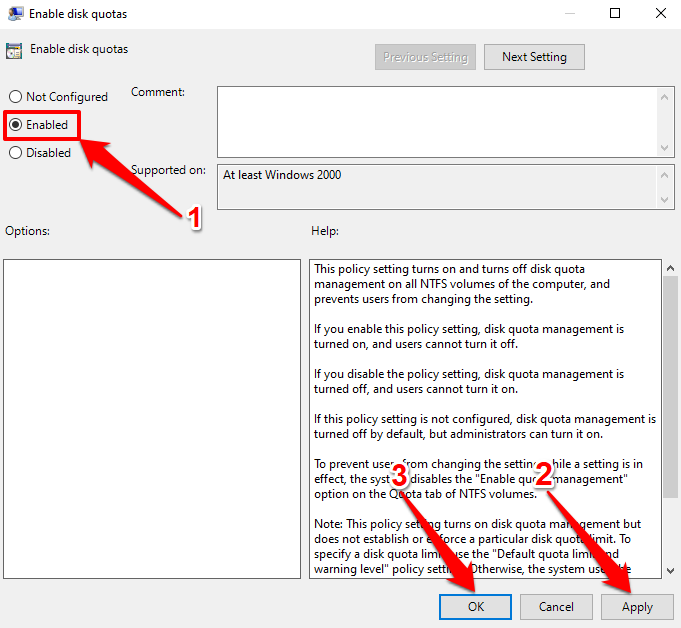
- 双击启用磁盘配额(Enable disk quotas)。

- 选择Enabled单选按钮,选择Apply,然后选择OK继续。
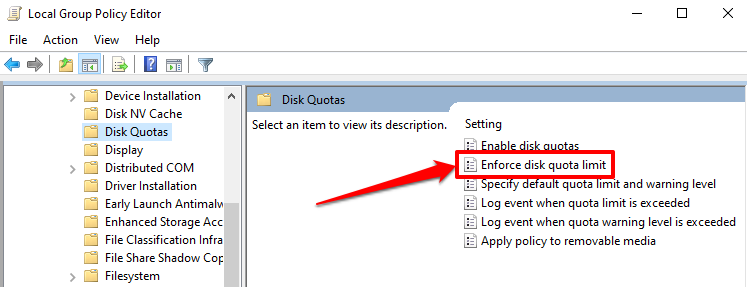
- 还有一件事:配置 Windows 以强制执行磁盘配额设置。双击强制磁盘配额限制(Enforce disk quota limit)。
- 选择启用(Enabled)并选择应用(Apply)以保存更改。然后(Afterward),选择确定(OK)关闭窗口。

- 下一步也是最关键的一步是指定您的配额限制。双击指定默认配额限制和警告级别(Specify default quota limit and warning level)。

- 选择Enabled,输入配额限制和警告级别值和单位,选择Apply,然后选择OK。

- 如果要将磁盘配额配置应用于可移动或外部驱动器,请双击将策略应用于可移动媒体(Apply policy to removable media)并将其设置为已启用(Enabled)。

通过注册表编辑器设置磁盘配额
您还可以通过注册表编辑器在(Registry Editor)Windows 11设备上强制启用磁盘配额限制。确保在继续之前备份 PC 的注册表文件(make a backup of your PC’s registry files),以免损坏任何可能损坏Windows或损坏 PC 的关键文件。
- 按Windows 键(Windows key)+ R打开 Windows 运行框。在对话框中输入regedit并选择(regedit)OK。

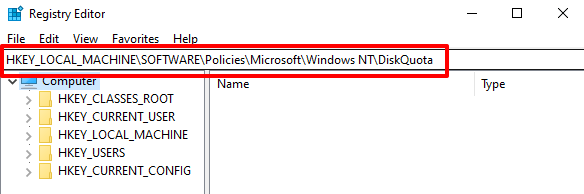
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\DiskQuota粘贴到地址栏中,然后按Enter。
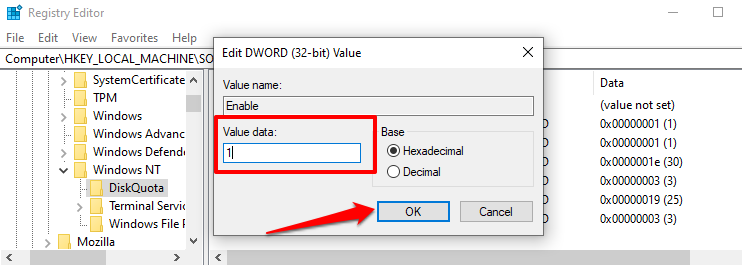
确保Enable和Enforce注册表项及其值设置为 1(即启用)。它们都启用并强制执行Windows(Windows)中的磁盘配额限制。

- 双击(Double-click)“启用”或“强制”注册表项,在“数值数据”对话框中输入1并选择“(1)确定(OK)” 。
自动化存储管理
通过本教程中的步骤,您可以在Windows 11(Windows 11)中设置磁盘配额管理系统。这些方法向后兼容旧版本的Windows操作系统。也就是说,您可以通过这些步骤在 Windows 10、Windows 8 和 Windows 7 中设置磁盘配额。
How to Set Disk Quotas for Users in Windows 11
Do you shаre уour work or home computer with others? Do apps and files from gueѕt aссounts consume an insane amоunt of disk space? Wіndows has a quota sуstem that grants administrators more control over storage management. You can use the tool to sеt dіsk usage quota for bоth internal and external storage devices.
We’ll walk you through the steps to control data users can store on your PC by setting disk quota limits. Before jumping to the steps, note that the Windows Quota Management tool only works on drives formatted using the NTFS file system.

Configure Disk Quota via File Explorer
There are several ways to enable the quota management system in Windows 11. You can do so via File Explorer, Registry Editor, or the Group Policy Editor. However, the File Explorer route is the easiest.
- Open File Explorer and select This PC on the sidebar.

- Scroll to the “Devices and drives” section, right-click the disk you want to limit, and select Properties.

- Head to the Quota tab and select Show Quota Settings.

- Check the Enable quota management box.

- Next, check the Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit box. That will enforce the limitation and ensure any user who reaches the quota limit can no longer write data to the disk.

- Select Limit disk space to.

- The next step is to set the disk limit. Say you want to set a 30GB disk quota, enter the digit (30) in the first dialog box and select the storage unit (GB) in the adjacent drop-down box.

You should also set a warning level that’s slightly lower than the disk limit. For a 30GB disk limit, setting a 25GB warning level is ideal. When users hit or exceed the warning limit, Windows sends a reminder that they’re close to exhausting the disk space allocated to them.
- If you want Windows to record an event log (in the Windows Event Viewer) when users excess their disk quotas or hit storage limit, check Log event when a user exceeds their quota limit and Log event when a user exceeds their warning level.

- Select Apply to proceed.

- Select OK on the warning prompt to enable the quota system you configured.

- Select OK in the Quota Settings window.

Note that you might have to restart your computer for these changes to take effect. We should also mention that disk quota configurations are drive-specific. If your PC has multiple disk partitions (separate from your C: drive), quota limits on the local disk don’t apply to other partitions.
View and Adjust Disk Quota Limit
When you set a storage quota limit for disk, Windows applies the limit to all users on your computer. There’s a “Quota Entries” tool in the Quota Settings window that lets you adjust or disable the disk quota limit for specific users. You can also use the tool to check the current disk space usage for all user accounts against the set quota.
- Open the Quota Settings window for the drive and tap the Quota Entries button.

- The “Amount Used” and “Quota Limit” columns show how much disk space a user has consumed against their allotted quota limit.

If you don’t find an account in the “Name” or “Logon Name” columns, proceed to add the user to the list manually. Tap Quota on the menu bar and select New Quota Entry.

- Select Advanced in the bottom-left corner.

- Select the Find Now button and double-click the account you want to include in the storage quota limitation.

- Select OK to proceed.

- Set the quota limit and warning level for the user and select OK.

- To adjust or disable disk quota for a user, right-click the account and select Properties.

- Adjust the user’s disk quota in the Limit disk space to and Set warning level to dialog boxes. Select Apply and then OK.

- Select the Do not limit disk usage radio button if you want to delete or remove the quota limit. Select Apply and OK to proceed.

Another way to disable quota limits is to right-click the account name in the “Quota Entries” window and select Delete.

Select Take Ownership on the next page to save files in the disk space you allotted to the user account. Select Delete if you don’t need the files.

Set Disk Quotas Using Group Policy Editor
There are instances when Windows fails to enforce the storage quota limit configured via File Explorer. If that happens, modify or re-enable the disk quota in the Group Policy Editor.
Note that the Group Policy Editor is only available in Windows 11 Pro, Education, and Enterprise. If you use Windows 11 Home edition, try re-enabling the storage quota in the Registry Editor instead.
- Use the Window key + R keyboard shortcut to open the Windows Run box. Type gpedit in the dialog box and press Enter.

- On the sidebar, go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System and select the Disk Quotas folder.

- Double-click Enable disk quotas.

- Select the Enabled radio button, select Apply, and select OK to proceed.

- One more thing: configure Windows to enforce the disk quota settings. Double-click Enforce disk quota limit.

- Select Enabled and select Apply to save the changes. Afterward, select OK to close the window.

- The next and most crucial step is to specify your quota limit. Double-click Specify default quota limit and warning level.

- Select Enabled, enter the quota limit and warning level values and units, select Apply, and then OK.

- If you want the disk quota configuration applied to removable or external drives, double-click Apply policy to removable media and set it to Enabled.

Set Disk Quota via Registry Editor
You can also force-enable a disk quota limit on Windows 11 devices via the Registry Editor. Ensure you make a backup of your PC’s registry files before proceeding, so you don’t damage any critical file that could corrupt Windows or break your PC.
- Press Windows key + R to open the Windows Run box. Enter regedit in the dialog box and select OK.

- Paste HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\DiskQuota in the address bar and press Enter.

Ensure the Enable and Enforce registry keys and their values are set to 1 (i.e., enabled). They both enable and enforce the disk quota limit in Windows.

- Double-click the “Enable” or “Enforce” registry keys, enter 1 in the “Value data” dialog box and select OK.

Automate Storage Management
With the steps in this tutorial, you can set up a disk quota management system in Windows 11. These methods are backward compatible with older versions of the Windows operating system. That is, you can adopt these steps to set disk quotas in Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.





































