Windows Media Player 12旨在复制您在物理家庭立体声或影院系统(home stereo or theater system)上看到的许多功能,并配有混音器、均衡器和其他音频调整(audio tweaking)设备。与您在高端立体声设备(end stereo equipment)上看到的无数旋钮和滑块(myriad knobs and sliders)等效(software equivalent)的软件称为Windows Media Player 12上的播放增强功能(playback enhancements),它们甚至比物理对应物更易于使用。使用Windows Media Player 12的内置播放增强功能(playback enhancements),您可以动态调整和优化音频和视频(audio and video),以最适合您的情况,扬声器系统和口味(speaker system and tastes)。在本教程中,我们将介绍如何使用Windows Media Player 12中的所有播放增强功能(playback enhancements),并解释一下它们的工作原理。
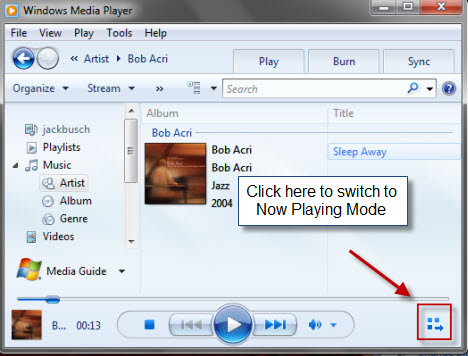
要访问播放增强功能(playback enhancements),您必须处于“正在播放模式”('Now Playing Mode')。单击播放器库(Player Library)右下角的图标以切换到“正在播放模式”('Now Playing Mode')。
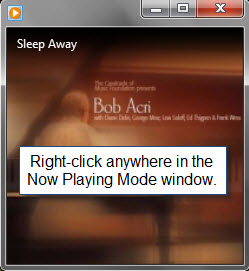
接下来,右键单击“正在播放”(Now Playing)窗口中的任意位置并选择“增强”(Enhancements)以查看可用的播放增强列表。
通过单击右侧下拉菜单中的任何选项打开“增强”窗口。(Enhancements)

音量增强以及如何(Volume Enhancements & How)使用它们(Them)
Windows Media Player 12具有内置功能,可帮助减少歌曲之间和歌曲本身之间的响亮和柔和声音之间的差异(即标准化)。这有助于避免一首非常安静的歌曲之后是一首刺耳的响亮歌曲(loud song)的烦恼,这在收听由从各种专辑中提取并使用不同参数编码的曲目组成的播放列表时很常见。例如,尝试将Neil Young 1972 年的Harvest中的歌曲与石器时代(Stone Age)皇后(Queens)乐队的聋人(Deaf)之歌(Songs)中的任何歌曲背靠背播放从 2002 年开始,您会听到我们在谈论什么。有关为什么录音越来越响亮的解释,请查看 NPR 中的这篇文章:响度战争(The Loudness War)。
根据您的硬件和其他因素,您的播放量肯定会因这些播放增强而有所不同,但这是朝着(相对)公平的竞争环境(音量方面)获得所有音乐迈出的不错的一步。有两个窗格包含这些功能:“交叉淡化和自动音量调节”('Crossfading and auto volume leveling')和安静模式(Quiet mode)。下面,我们将介绍Windows Media Player 12的所有不同音量调整增强功能。
Crossfading - in the Crossfading and auto volume leveling window, click 'Turn on Crossfading' to have Windows Media Player 12 gradually fade out the song at the end and then have the next song on the playlist gradually fade in. Move the slider to the left to shorten the overlap between songs. Move the slider to the right to lengthen the overlap. (On a personal note: I don't particularly like this feature since it will fade songs out before their natural end, meaning you might miss something. So, if you want to hear the songs as the producers intended, skip this feature.)
自动音量(Auto volume leveling)调节- 在“交叉淡化和自动音量调节”('Crossfading and auto volume leveling')窗口中,单击“打开自动音量调节”('Turn on Auto volume leveling')以让Windows Media Player 12自动调整歌曲之间的音量(volume level)以使它们更加相似。Windows Media Player 12通过在播放过程中分析歌曲,然后在歌曲播放完后添加自动音量(volume level)调节信息来实现这一点(这样您在下次播放歌曲时才会听到效果)。

作为快速侧边栏,请注意自动音量调节(Auto volume leveling)仅适用于包含音量调节值的Windows Media Audio ( WMA ) 或MP3文件。(MP3)此值是在编码期间添加的,但您也可以在将歌曲添加到播放器库(Player Library)时添加它。为此,导航到播放器库(Player Library)并单击工具(Tools)并选择选项(Options)。在“库(Library)”选项卡中,选中“媒体库设置”('Media Library Settings')下的“为新文件添加音量调节信息值('Add volume leveling information values for new files')” ,然后单击“应用(Apply)”并选择“确定(OK)” 。所有后续的WMA 和 MP3(WMA and MP3)添加到您的库(Library)中的文件现在将自动添加音量调节值,如果它们还没有的话。

安静模式- 与(Quiet Mode)“自动音量调节”('Auto volume-leveling')类似的功能是安静模式(Quiet mode),它有自己的窗口。安静模式(Quiet mode)使音轨内(而不是两个音轨之间)的急剧音量变化变得柔和。如果您不太习惯 The Pixies和Nirvana开创的响亮/柔和/响亮的动态,这可能会很方便(但说真的,伙计,接受这个程序。这是 90 年代!)。
安静模式(quiet mode)的功能非常简单。您可以通过单击左上角的文本来打开或关闭它,并使用下面的单选按钮在“中等差异”('medium difference')和“小差异”之间进行切换。('little difference')很不(Pretty)言自明。

但是,有一个警告:您的歌曲必须使用Windows Media Audio 9或Windows Media Audio 10 无损或专业编解码器(Lossless or Professional codec)进行编码,以便安静模式(Quiet mode)工作。无损 Windows Media 音频(Lossless Windows Media Audio)文件将在 Windows 资源管理器中显示为“.WMA”文件。('.WMA')
低音增强(Bass Boost)、均衡器(Equalizer)和其他声音整形(Sound Shaping)增强
Windows Media Player 12还具有一系列功能,可以模拟工作室中制作人的旋钮旋转或(knob twiddling)立体声系统(stereo system)上的各种滑块和效果。这些可以极大地改变您正在播放的歌曲的动态,以便根据流派、扬声器大小(speaker size)和其他变量优化播放。在本节中,我们将逐个介绍这些功能。
图形均衡器(Graphic Equalizer)- 到目前为止,我们都熟悉图形均衡器 (EQ) 的作用。Windows Media Player 12的图形均衡器(graphic equalizer)按您的预期工作,允许您调整各种声音频率以及选择一些预设。
如果您不知道自己在做什么,最好的办法是根据您正在听的音乐类型选择一个预设。单击右上角的文本及其旁边的箭头(一开始可能会读取默认值(Default))以查看您的预设列表。这些预设将尽最大努力根据流派优化频率(例如,Rock会提升高低音以适应人声、鼓、贝司和吉他驱动的音乐,而Speech则专注于中频,同时缓和高音结束,那些嘶嘶声的地方)。如您所见,当您选择预设时,滑块会自动移动到位。

或者,您可以使用自定义设置(custom setting)并自己移动滑块。一旦您开始摆弄滑块,预设将自动切换到自定义。(Custom)
移动滑块的三种方式:
-
独立移动滑块(Move sliders independently)- 当您单击并向上或向下拖动时,只有一个滑块会移动。
-
在一个松散的组中一起移动(Move together in a loose group)- 移动一个滑块将导致任一侧的滑块也向上或向下移动以创建波浪形状。松散组设置使曲线更加圆弧。
-
在一个紧密的组中一起移动(Move together in a tight group)- 移动一个滑块将导致任一侧的滑块也向上或向下移动以创建更平缓的波浪。紧密的组设置创造了一个不那么引人注目的弧线。在屏幕截图中,我们使用的是紧凑模式。请注意围绕正在移动的滑块创建的波浪。
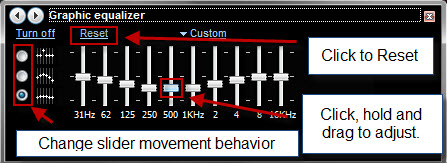
您可以实时移动滑块以找出听起来不错的东西。如果您真的把事情弄得一团糟,请单击重置(Reset)以使一切恢复正常。
注意:(Note:)尽管有大量关于EQ 设置(EQ setting)的资料(其中大部分是针对录音和制作的),但没有“最佳” EQ 设置(EQ setting),尤其是考虑到硬件和品味(hardware and taste)的差异时。对于那些真正想了解频段之间差异的人,请查看判别频率训练测试(discriminative frequency training test)和均衡的简要概述(overview of equalization)。
SRS Wow 效果(SRS Wow Effects)器 - 它们允许您增强低频(低音)和立体声性能(sound performance)(即左右声道之间的声像)。这里的选项也很简单。
将TruBass 滑块(TruBass slider)向左移动可降低低频效果(low-frequency effect),向右移动可增强低频声音。
将WOW 效果滑块(WOW Effect slider)向左移动可降低立体声效果(stereo sound performance),向右移动可提高立体声效果。这种增强创造了更多的“环绕声(surround sound)”效果。
最后,您可以通过单击左上角的文本及其旁边的箭头,让SRS Wow优化您的扬声器类型。(speaker type)从普通(Normal)扬声器、耳机(Headphones)或大扬声器中选择。
您可以通过打开SRS WOW效果来增强低频和立体声效果(sound performance)。

SRS WOW效果的唯一问题是它们不能应用于DVD 播放(DVD playback)。
杜比数字设置(Dolby Digital Settings)- 这些设置类似于SRS Wow效果中的扬声器类型设置。(speaker type setting)但是,这些设置仅影响杜比数字内容(Dolby Digital content)(例如,许多DVD(DVDs)具有杜比数字声音(Dolby Digital sound),例如星球大战(Star Wars)前传)。在此菜单中,您可以从三种不同的预设中进行选择:
-
正常(Normal)- 降低杜比数字的整个范围以实现更安静的播放。
-
夜晚(Night)- 增强对话,同时降低其他声音。适合笔记本电脑。
-
剧院(Theater)- 增加所有声音的动态范围,使柔和和响亮的声音之间的差异更加显着,并获得更完整的聆听体验。适合家庭影院系统。

选择您的选项以激活它。单击重置(Reset)可将设置恢复正常。
音频和视频(Audio & Video)的其他播放增强(Playback Enhancements)
此外,Windows Media Player 12允许您更改音频和视频文件的(audio and video files)播放速度(playback speed)以及调整视频的颜色和缩放级别(zoom level)。在本节中,我们将向您展示如何使用这两个功能。
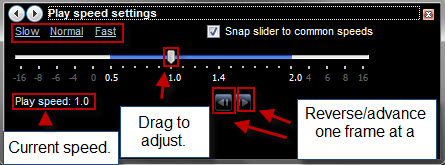
播放速度设置(Play Speed Settings)- 调整播放速度可以让您找到(Play speed)歌曲或视频(song or video)中的某个部分,或者只是减慢文件的速度以进行更好的分析或加快(analysis or speed)文件的速度以获得漫画效果(为什么要这样做?)。有几种不同的方法可以做到这一点。
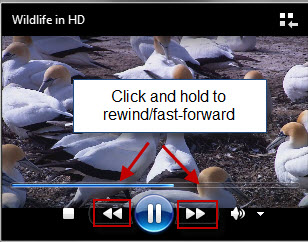
您可以通过单击并按住“下一步”(Next)按钮来快进文件,直到歌曲开始快进。松开按钮恢复正常播放。
通过单击并按住上一个(Previous)按钮直到歌曲开始倒带来倒带文件。释放以恢复正常播放。(注意:(Note:)倒带仅适用于视频文件)。
您也可以从“增强”(Enhancements)菜单更改播放速度。(Play speed)滑块从 1.0 开始,这是正常播放。将滑块移动到 0.5 以半速播放。移动到负数会反向播放文件。将滑块移动到大于 1.0 的数字会加快播放速度。选中Snap slider to common(Snap slider to common speeds) speed 按钮可以快速选择半速、双速等速度。您也可以通过单击左上角的“慢”、“正常(Slow, Normal)”或“快”来选择常用速度。(Fast)
此外,您可以通过单击底部的箭头一次前进或后退一帧。这仅适用于支持的视频文件。
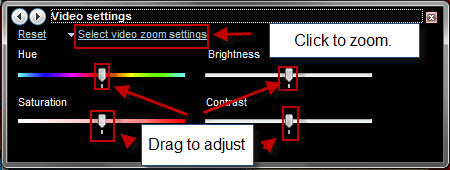
视频设置(Video Settings)- 最后,Windows Media Player 12还允许您在视频播放期间调整色调、亮度、对比度和饱和度以及缩放设置。(contrast and saturation)左右(left and right)拖动滑块以调整设置。对于这些功能,一张图片胜过千言万语 - 因此请查看Microsoft在 Microsoft.com 上对这些(Microsoft)视频设置(video settings)的演示。
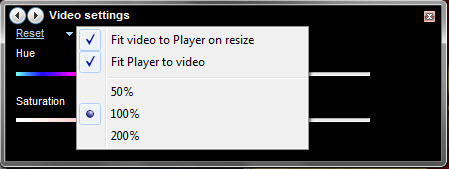
还有一些不言自明的视频缩放设置(video zoom settings),可以通过单击左上角的文本进行访问。您还可以通过按 ALT-1 快速缩放到 50%,通过(ALT-1)按ALT-2和 200% 通过按ALT-3快速缩放。
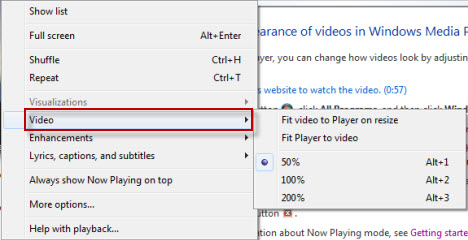
或者,您可以在播放期间右键单击“正在播放”(Now Playing)窗口,然后选择“视频(Video)”以选择缩放设置。
结论
如您所见,Windows Media Player 12不仅是一款适用于所有类型音频和视频文件的(audio and video files)多功能播放器(versatile player),它还是一款功能齐全的播放增强器(playback enhancer)。我们鼓励您摆弄各种设置,并通过您的设置发现最适合您的耳朵。请记住:您始终可以单击重置(Reset)以恢复正常,因此没有什么可丢失的。
How to Use Playback Enhancements in Windows Media Player 12
Windows Mеdia Player 12 is designed to replicate mаny of the features you'd see on a physical home stereo or theater ѕyѕtem, cоmplete with a mixer, EQ and other audio tweaking devices. The software equivalent of the myriad knobs and sliders yоu'd see on high end stereo еquipment are called playback enhancements on Windows Media Player 12 and they are even easier to use than their physical counterparts. Using the built-in playback enhancements for Windows Media Player 12, you can adjust and optimize audio and video on the fly to best suit your situation, speaker system and tastes. In this tutorial, we'll cover how to use all of the playback enhancements in Windows Media Player 12 as well as explain a bit about how they work.
To access playback enhancements, you must be in 'Now Playing Mode'. Click the icon in the bottom-right of the Player Library to switch to 'Now Playing Mode'.

Next, right-click anywhere in the Now Playing window and choose Enhancements to see the list of available playback enhancements.

Open the Enhancements window by clicking any of the options on the drop-down menu to the right.

Volume Enhancements & How to Use Them
Windows Media Player 12 has built-in features that help reduce the disparities between loud and soft sounds both between songs and within songs themselves (i.e. normalization). This helps circumvent the annoyance of having a very quiet song followed by a jarringly loud song which is a common occurrence when listening to playlists composed of tracks pulled from various albums and encoded with different parameters. For example, try playing a song off of Neil Young's Harvest from 1972 back-to-back with any song off of Queens of the Stone Age's Songs of the Deaf from 2002 and you'll hear exactly what we're talking about. For an explanation of why recordings are getting louder and louder, check out this article from NPR: The Loudness War.
Your mileage will definitely vary with these playback enhancements depending on your hardware and other factors, but it's a decent step towards getting all of your tunes on a (relatively) level playing field, volume-wise. There are two panes that contain these features: 'Crossfading and auto volume leveling' and Quiet mode. Below, we'll go over all the different volume tweaking enhancements for Windows Media Player 12.
Crossfading - in the Crossfading and auto volume leveling window, click 'Turn on Crossfading' to have Windows Media Player 12 gradually fade out the song at the end and then have the next song on the playlist gradually fade in. Move the slider to the left to shorten the overlap between songs. Move the slider to the right to lengthen the overlap. (On a personal note: I don't particularly like this feature since it will fade songs out before their natural end, meaning you might miss something. So, if you want to hear the songs as the producers intended, skip this feature.)
Auto volume leveling - in the 'Crossfading and auto volume leveling' window, click 'Turn on Auto volume leveling' to have Windows Media Player 12 automatically adjust the volume level between songs to make them more similar. Windows Media Player 12 does so by analyzing the song during playback and then adding the auto volume leveling information after the song has played all the way through (so you won't hear the effects until the next time you play the song).

As a quick sidebar, note that Auto volume leveling only works for Windows Media Audio (WMA) or MP3 files that contain a volume-leveling value. This value is added during encoding, but you can also add it while adding songs to your Player Library. To do so, navigate to the Player Library and click Tools and choose Options. From the Library tab, check 'Add volume leveling information values for new files' under 'Media Library Settings' and click Apply and choose OK. All subsequent WMA and MP3 files added to your Library will now automatically have a volume leveling value added to them, if they don't already have one.

Quiet Mode - a similar feature to 'Auto volume-leveling' is Quiet mode, which has its own window. Quiet mode mellows out the sharp volume changes within a track (rather than between two tracks). This might be handy if you're not quite accustomed to the loud/soft/loud dynamic pioneered by The Pixies and Nirvana (But seriously, man, get with the program. This is the 90s!).
The functionality of quiet mode is pretty straightforward. You can turn it on or turn it off by clicking the text in the upper-left and change between 'medium difference' and 'little difference' with the radio buttons below. Pretty self-explanatory.

There is one caveat, however: your songs must be encoded using the Windows Media Audio 9 or Windows Media Audio 10 Lossless or Professional codec in order for Quiet mode to work. Lossless Windows Media Audio files will appear as '.WMA' files in Windows Explorer.
Bass Boost, Equalizer and Other Sound Shaping Enhancements
Windows Media Player 12 also has a fleet of features that simulate the knob twiddling of a producer in a studio or the various sliders and effects on a stereo system. These can drastically change the dynamics of the songs you are playing in order to optimize the playback according to genre, speaker size and other variables. In this section, we'll cover each of these features one-by-bone.
Graphic Equalizer - by now, we're all familiar with what a graphic equalizer (EQ) does. Windows Media Player 12's graphic equalizer works as you'd expect, allowing you to tweak various sound frequencies as well as choose some presets.
If you don't know what you're doing, your best bet is to choose a preset according to the type of music you're listening to. Click the text in the top-right with the arrow next to it (will likely read Default at first) to see your list of presets. These presets will do their best to optimize the frequencies according to the genre (for example, Rock boosts the highs and lows to accommodate the vocal, drum, bass and guitar-driven music while Speech focuses on the mid-range while easing off the high end, where those hissy s-sounds live). As you'll see, the sliders automatically shift into place when you choose a preset.

Alternately, you can use the custom setting and move the sliders yourself. The preset will automatically kick over to Custom once you start fiddling with the sliders.
There are three ways to move the slider:
-
Move sliders independently - only one slider will move when you click and drag it up or down.
-
Move together in a loose group - moving one slider will cause the sliders on either side to also move up or down to create a wave shape. The loose group setting makes a more arcing curve.
-
Move together in a tight group - moving one slider will cause the sliders on either side to also move up or down to create a more gradual wave. The tight group setting creates a less dramatic arc. In the screenshot, we're using tight mode. Notice the wave created around the slider being moved.

You can move the sliders around in real time to figure out what sounds good. If you've really made a mess of things, click Reset to put everything back to normal.
Note: though there is a voluminous amount of reading out there about EQ settings (most of which is geared towards recording and production), there is no 'best' EQ setting, especially when you factor in differences in hardware and taste. For those who really want to understand the difference between the bands, check out the discriminative frequency training test and this condensed overview of equalization.
SRS Wow Effects - they allow you to enhance the low-frequency (bass) and stereo sound performance (i.e. panning between left and right channels). The options here are pretty straightforward as well.
Move the TruBass slider to the left to reduce the low-frequency effect and move it to the right to boost the low-frequency sounds.
Move the WOW Effect slider to the left to decrease the stereo sound performance and move it to the right to increase it. This enhancement creates more of a "surround sound" effect.
Lastly, you can have SRS Wow optimize for your speaker type by clicking the text in the top-left with the arrow next to it. Choose from Normal speakers, Headphones or Large speakers.
You can enhance low-frequency and stereo sound performance by turning on SRS WOW effects.

The only issue with SRS WOW effects is that they cannot be applied to DVD playback.
Dolby Digital Settings - these settings are similar to the speaker type setting in the SRS Wow effects. However, these settings only affect Dolby Digital content (for example, many DVDs have Dolby Digital sound, such as the Star Wars prequels). In this menu, you can choose from three different presets:
-
Normal - reduces entire range of Dolby Digital for quieter playback.
-
Night - boosts dialogue while toning down other sounds. Good for laptops.
-
Theater - increases dynamic range of all sounds for more dramatic differences between soft and loud sounds and a fuller listening experience. Good for home theater systems.

Choose your option to activate it. Click Reset to return the settings to normal.
Other Playback Enhancements for Audio & Video
Additionally, Windows Media Player 12 lets you change the playback speed of audio and video files as well as tweak the colors and zoom level of videos. In this section, we'll show you how to use these two features.
Play Speed Settings - adjusting the Play speed lets you find a certain part within a song or video or simply slow down a file for greater analysis or speed it up for comic effect (why else would you do this?). There are a few different ways to do this.
You can fast-forward a file by clicking and holding the Next button until the song begins fast-forwarding. Release the button resume normal playback.
Rewind a file by clicking and holding the Previous button until the song begins rewinding. Release to resume normal playback. (Note: Rewinding only applies to video files).

You can change the Play speed from the Enhancements menu as well. The slider begins at 1.0, which is normal playback. Moving the slider to 0.5 plays at half speed. Moving to a negative number plays the file in reverse. Moving the slider to a number greater than 1.0 speeds up playback. Check the Snap slider to common speeds button to quickly select such speeds as half speed, double speed, etc. You can also choose common speeds by clicking Slow, Normal or Fast in the top-left.
Also, you can advance or reverse one frame at a time by clicking the arrows at the bottom. This only applies to supported video files.

Video Settings - lastly, Windows Media Player 12 also allows you to tweak the hue, brightness, contrast and saturation and zoom settings during video playback. Drag the sliders to the left and right to adjust the settings. For these features, a picture is worth a thousand words - so check out Microsoft's demonstration of these video settings over at Microsoft.com.

There are also some self-explanatory video zoom settings which can be accessed by clicking the text in the upper-left. You can also quickly zoom to 50% by pressing ALT-1, 100% by pressing ALT-2 and 200% by pressing ALT-3.

Alternately, you can right-click the Now Playing window during playback and select Video to choose the zoom settings.

Conclusion
As you can see, Windows Media Player 12 is not only a versatile player for all types of audio and video files, it is also a full featured playback enhancer. We encourage you to fiddle around with the various settings and discover what sounds best to your ear with your setup. Remember: You can always click Reset to return to normal, so there's nothing to lose.















