我们生活在互联网和无线连接(internet and wireless connections)的时代,大多数人家中都有无线路由器(wireless router)。Wi-Fi已经成为我们词汇中的一个常用术语,但无线网络标准并不容易理解甚至发音。那是因为它们的名称很复杂,是由网络工程师和公司发明的。你知道什么是 802.11ax 吗?那么 802.11ad 或 802.11ac 呢?您(Did)是否听说这些名称正在变成更简单的术语,例如Wi-Fi 6、Wi-Fi 5 或Wi-Fi 4?你想了解这一切意味着什么以及它为什么重要吗?阅读本文以找到您需要的信息:
Wi-Fi联盟(Alliance)负责制定无线网络标准
Wi-Fi 联盟(Wi-Fi Alliance)是一个由来自世界各地的计算制造商组成的联盟,负责开发和发布 Wi-Fi 网络标准。整个科技行业(tech industry)都在追随他们,并在 Wi-Fi 标准的帮助下开发相互兼容的无线设备。

如果没有 Wi-Fi联盟(Alliance),我们将无法在无线路由器和无线设备(例如您的笔记本电脑和智能手机(laptop and smartphone))之间实现良好的互操作性。Wi-Fi联盟(Alliance)发布了本文中涵盖的所有标准。让我们一一讨论:
什么是 802.11n,也称为 Wi-Fi 4?
802.11n,全称IEEE 802.11n-2009(name IEEE 802.11n-2009),是 2009 年发布的无线网络标准。Wi-Fi 802.11n 也称为 Wi-Fi 4(Wi-Fi 802.11n is also referred to as Wi-Fi 4)。802.11n 允许使用两个无线电(radio frequency)频段,2.4 GHz和 5 GHz,并且可以提供高达 600 Mbps的数据传输速度。Wi-Fi 802.11n 也是第一个支持MIMO(多输入多输出)的无线标准。MIMO是一种允许使用多个天线通过组合独立的数据流来传输更多数据的技术。

现代无线路由器在 2.4 (Modern wireless)GHz 频段(GHz band)上使用 Wi-Fi 4 标准。Wi-Fi 4 用于将旧设备连接到网络,或智能家居设备,如智能插头、智能灯泡、传感器等。
什么是 802.11ac,也称为 Wi-Fi 5?
802.11ac 或IEEE 802.11ac是 2013 年底发布的无线网络标准。Wi-Fi 802.11ac 也称为 Wi-Fi 5(Wi-Fi 802.11ac is also known as Wi-Fi 5)。802.11ac 是当今最常见的无线标准(standard today),因为过去几年销售的大多数路由器都与 802.11ac 兼容。该标准与之前的 802.11n 一样,支持MU-MIMO,但它可以提供高达 2.3 Gbps的最大数据传输速度。802.11ac 标准仅适用于 5 GHz(GHz frequency)频段,但大多数支持它的无线路由器也支持 2.4 GHz 频段(GHz frequency)上的 802.11n 标准。

802.11ac 设备分为两类,称为 802.11ac Wave 1和Wave 2。作为 802.11ac Wave 1的一部分销售的产品于 2013 年推出市场,而Wave 2中的产品于 2016 年推出。Wave 2(Wave 2)是该标准的改进版本。802.11ac Wave 2无线路由器具有更高的吞吐量并增加了对MU-MIMO的支持:Wave 1路由器可提供高达 1.3 Gbps的速度,而 Wave 2(Wave 2)中的路由器可提供高达 2.3 Gbps的速度。因此,如果您今天购买无线路由器(wireless router today),最好检查一下它是否支持 802.11ac Wave 2,以便从改进的无线速度和覆盖范围(wireless speed and coverage)中受益。
什么是 802.11ax?
802.11ax 或IEEE802.11ax是一种无线网络标准,仍在开发中,尚未获得批准。预计它将在 2019 年底的某个时间完成并获得批准,正如 ZDNet 所分享的:下一代 802.11ax wi-fi:密集、快速、延迟(Next-generation 802.11ax wi-fi: Dense, fast, delayed)。
802.11ax 也称为 Wi-Fi 6(802.11ax is also referred to as Wi-Fi 6)。它也被称为高效无线(High-Efficiency Wireless)( HEW ),设计用于与我们迄今为止提到的标准相同的 2.4 GHz和 5 GHz频段。(GHz frequency)似乎它还可以使用 1 到 7 GHz之间的其他频段,当它们可用时。802.11ax 无线网络标准旨在将平均数据传输速度提高多达 802.11ac 标准的四倍。它应该提供显着提高的速度,尤其是在机场、火车站、餐馆或咖啡店等拥挤的地方。

带有 Wi-Fi 6 的无线路由器和网状 Wi-Fi 系统已经出现在市场上。然而,它们往往有溢价,大多数人买不起。一旦标准获得批准并最终确定,预计将推出更实惠的 Wi-Fi 设备。
什么是 802.11ad?
IEEE 802.11ad是一种无线网络标准,也称为WiGig 或 60 GHz Wi-Fi(WiGig or 60 GHz Wi-Fi)。它是一种Wi-Fi形式,它不使用2.4 GHz或 5 GHz等传统无线频段,而是使用(wireless frequency)无线电频谱(radio spectrum)的微波部分,运行频率约为 60 GHz。它允许高达 7 Gbps的令人难以置信的快速数据传输速度。但是,因为它适用于微波范围频率(microwave range frequency),它的显着缺点是不能穿过墙壁,射程只有 3 到 32 英尺(1 到 10 米)。它“快如闪电”,但它的设计目的是在没有墙壁或障碍物阻挡的情况下只覆盖一个房间。
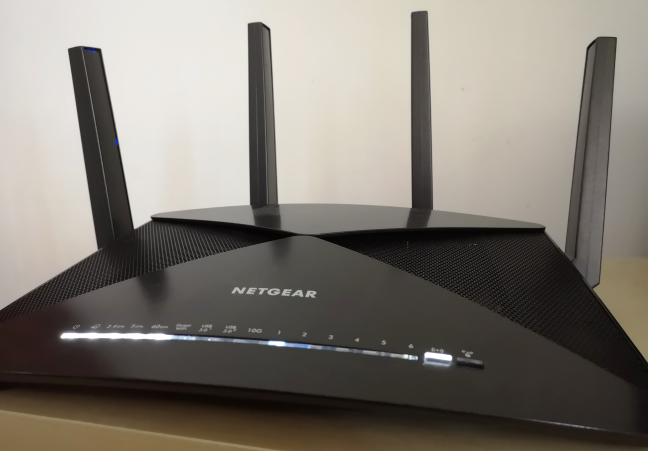

市场上支持 802.11ad 的无线路由器很少,支持 802.11ad 的网络设备也很少。我们使用 802.11ad 测试的路由器之一是Netgear Nighthawk X10。
什么是 Wi-Fi 6、Wi-Fi 5、Wi-Fi 4 等?
2018年10 月 3日,Wi-Fi(October 3)联盟(Alliance)宣布为无线网络标准增加了一个(wireless networking)新的命名(new naming),以便人们更容易识别它们。毕竟,802.11ax、802.11ad、802.11ac、802.11n 和其他所有类似的名称都不容易记住,大多数人都不知道它们的含义。他们的想法是Wi-Fi后跟一个数字,很容易记住。规则是数字越大,标准越新越好。您现在已经知道Wi-Fi 6、Wi-Fi 5 和Wi-Fi 4 的含义。但是,总而言之,它们是:
- Wi-Fi 6可识别支持802.11ax无线网络标准的设备
- Wi-Fi 5识别支持802.11ac无线网络标准的设备,包括 802.11ac Wave 2
- Wi-Fi 4识别支持802.11n无线网络标准的设备
为了帮助您了解每种现代Wi-Fi 网络(Wi-Fi networking)标准提供的功能,我们制作了一张表格,比较了它们的频段和最大理论速度:

Wi-Fi 1、Wi-Fi 2 和 Wi-Fi 3 没有品牌。这可能是因为 Wi-Fi联盟(Alliance)没有考虑过多使用旧的 Wi-Fi 标准。但是,为了完整起见,我们认为正确的品牌应该是:
- Wi-Fi 1 应该是 802.11b。该标准于 1999 年发布,使用 2.4 GHz 频段(GHz band),数据速率(data rate)高达 11 Mbps。
- Wi-Fi 2 应该是 802.11a。它于 1999 年发布,使用 5 GHz 频段(GHz band),数据速率(data rate)高达 54 Mbps。
- Wi-Fi 3 应该是 802.11g。该标准于 2003 年发布,使用 2.4 GHz 频段(GHz band),数据速率(data rate)高达 54 Mbps。
802.11ax 与 802.11ac与 802.11n(vs 802.11n)或 Wi-Fi 6 与 Wi-Fi 5 与 Wi-Fi 5,以及实际速度
如果您阅读每个Wi-Fi 标准(Wi-Fi standard)的规格,以及每个标准可以达到的最大理论速度,您会印象深刻。但是,在现实生活中,您获得的速度要低得多。您可以在本文中找到有关此主题的更多信息:AC1200、AC1750、AC1900或更多是什么意思,有什么区别?
为了让您从不同的可用标准中获得真实的速度,我们采用了最强大的无线路由器之一 - ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AX11000 - 并在笔记本电脑上使用SpeedTest进行了一些测量英特尔Wi-Fi 6 (Intel Wi-Fi 6) AX200(AX200 network)网卡。我们的互联网连接提供1 Gbps的(Gbps)下载速度(download speed)和 500 Mbps的上传速度。
我们首先使用 802.11n ( Wi-Fi 4 ) 标准连接到路由器发出的 2.4 GHz 频段的(GHz band)Wi(Wi-Fi) -Fi ,我们测得的最大下载速度(download speed)为 221.28 Mbps。
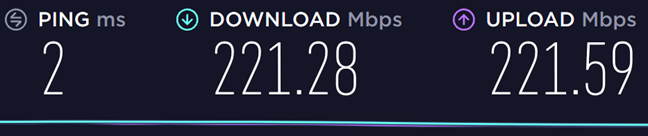
然后,我们使用 802.11ac ( Wi-Fi 5(Wi-Fi 5) ) 标准切换到路由器发射的两个频段中的第一个 5 GHz 频段。(GHz band)我们达到的最大下载速度为 630.10 (download speed)Mbps。使用这款无线路由器时, (wireless router)Wi-Fi 5标准比 Wi-Fi 4 标准快 2.8 倍。
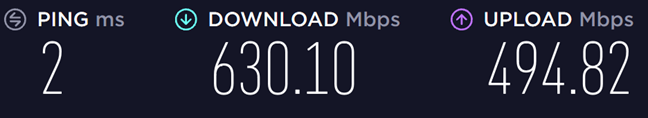
最后,我们切换到使用 802.11ax ( Wi-Fi 6 ) 标准的第二个 5 GHz 频段。(GHz band)这次我们达到了762.03 Mbps的最大(Mbps)下载速度(download speed)。这比 Wi-Fi 5 快 20%,这是一个巨大的进步,但与Wi-Fi 6(Wi-Fi 6)标准所承诺的最大理论速度相去甚远。

希望这种快速比较能让您更真实地了解在现实生活中使用不同 Wi-Fi 标准时可以达到的速度。
无线(Do wireless)路由器是否使用一种或多种 Wi-Fi 标准?
是的,他们中的大多数人都这样做!制造商制造的无线路由器可以同时在一个、两个甚至三个频段上工作,同时在每个频段上支持不同的无线标准。今天的大多数无线路由器都是双频或三频路由器,因为它们提供了更高的速度和(speed and compatibility)与各种设备的兼容性。今天出售的所有无线路由器都支持 802.11n 标准(通常在 2.4 GHz 频段(GHz band)上),并且还增加了对 802.11ac 标准(在 5 GHz 频段(GHz band)上)的支持。高端无线路由器可以做到这一切,但也可以包括第三个频段(5 GHz甚至 60 GHz),用于更新的标准,例如 802.11ac Wave(Wave 2) 2、802.11ax 或 802.11ad。
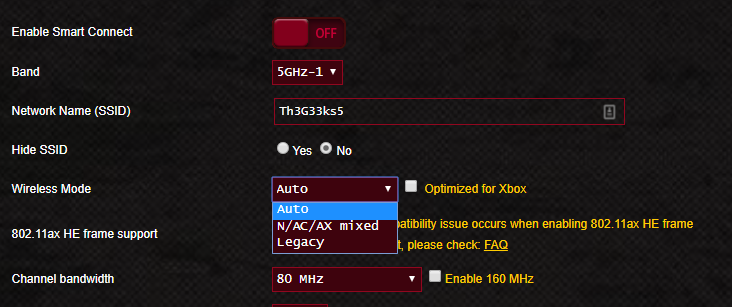
无论您有单频、双频还是三频路由器(tri-band router),好在固件应该让您选择要启用和使用的 Wi-Fi标准和频段。(Wi-Fi)您可以选择是否仅激活 2.4 GHz 频段(GHz band)及其支持的无线标准,或者您可以选择仅激活 5 GHz 频段(GHz band)及其支持的无线标准。此外,您还可以启用路由器上可用的所有频段和所有无线标准,混合所有内容以获得您的网络所需的结果。
您是否计划购买支持更新的 Wi-Fi 标准的新设备?
您(Are)使用的是 Wi-Fi 5 兼容设备吗?您认为值得升级到最新的 Wi-Fi 6 标准,还是现在投资它还为时过早?在下方发表评论(Comment) 并分享(below and share)您对所有无线网络(wireless networking)标准、它们的命名约定和功能的看法。
What is 802.11ax, 802.11ad, 802.11ac, and 802.11n? What is Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5 and so on?
We are living in the age of the internеt and wireless connеctions, and most people have a wireless router in their homes. Wi-Fi has become a common term in our vocabulary, but wirеless networking standards are not eaѕy to understand or even pronounce. Thаt is because they hаve complicated names, іnvented by network еngineers and corporations. Do you know what 802.11ax is? What about 802.11ad, or 802.11ac? Did you hear the news that theѕe names are chаnging into simpler terms like Wi-Fі 6, Wi-Fi 5, or Wi-Fi 4? Do you want to understand what all that means аnd why it matters? Read this article to find the information you need:
The Wi-Fi Alliance is in charge of developing wireless networking standards
The Wi-Fi Alliance is an alliance of computing manufacturers from all over the world that develops and publishes the Wi-Fi networking standards. The entire tech industry follows them and develops wireless devices that are compatible with each other, with the help of Wi-Fi standards.

Without the Wi-Fi Alliance, we would not have good interoperability between wireless routers and wireless devices, such as your laptop and smartphone. The Wi-Fi Alliance publishes all the standards covered in this article. Let's discuss them one by one:
What is 802.11n, also known as Wi-Fi 4?
802.11n, under its full name IEEE 802.11n-2009, is a wireless networking standard that was published in 2009. Wi-Fi 802.11n is also referred to as Wi-Fi 4. 802.11n allows the use of two radio frequency bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, and can deliver data transfer speeds of up to 600 Mbps. Wi-Fi 802.11n was also the first wireless standard that offered support for MIMO (multiple-input-multiple-output). MIMO is a technology that allows the use of multiple antennas to transmit more data by combining independent data streams.

Modern wireless routers use the Wi-Fi 4 standard on the 2.4 GHz band. Wi-Fi 4 is used to connect older devices to the network, or smart home devices like smart plugs, smart bulbs, sensors, and so on.
What is 802.11ac, also known as Wi-Fi 5?
802.11ac or IEEE 802.11ac is a wireless networking standard that was published in late 2013. Wi-Fi 802.11ac is also known as Wi-Fi 5. The 802.11ac is the most common wireless standard today, as most routers sold during the last few years are 802.11ac-compatible. This standard, just like the 802.11n before it, supports MU-MIMO, but it can offer maximum data transfer speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps. The 802.11ac standard works only on the 5 GHz frequency band but most of the wireless routers that support it also offer support for the 802.11n standard on the 2.4 GHz frequency band.

802.11ac devices are split into two categories, called 802.11ac Wave 1 and Wave 2. The products that are sold as part of the 802.11ac Wave 1 were introduced to the market in 2013, while the ones in Wave 2 were introduced in 2016. Wave 2 is an improved version of the standard. The 802.11ac Wave 2 wireless routers have higher throughput and add support for MU-MIMO: while the Wave 1 routers can provide speeds of up to 1.3 Gbps, the ones in Wave 2 can deliver speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps. Therefore, if you buy a wireless router today, it is a good idea to check whether it offers support for 802.11ac Wave 2, to benefit from improved wireless speed and coverage.
What is 802.11ax?
802.11ax or IEEE802.11ax is a wireless networking standard that is still in the works and has not yet been approved. It is expected that it will be finalized and approved sometime during late 2019, as shared by ZDNet: Next-generation 802.11ax wi-fi: Dense, fast, delayed.
802.11ax is also referred to as Wi-Fi 6. It is also known as High-Efficiency Wireless (HEW) and is designed to work in the same 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands as the standards that we mentioned so far. It appears that it will also be capable of working with additional bands between 1 and 7 GHz, when they become available. The 802.11ax wireless networking standard aims to improve the average data transfer speeds by up to four times more than the 802.11ac standard. It should offer significantly improved speeds, especially in crowded places such as airports, train stations, restaurants, or coffee shops.

Wireless routers and mesh Wi-Fi systems with Wi-Fi 6 have already shown up on the market. However, they tend to have a premium price, and most people can't afford them. As soon as the standard is approved and finalized, expect more affordable Wi-Fi equipment to be launched.
What is 802.11ad?
IEEE 802.11ad is a wireless networking standard that is also known as WiGig or 60 GHz Wi-Fi. It is a form of Wi-Fi that, instead of using traditional wireless frequency bands such as 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, uses a microwave section of the radio spectrum, running at about 60 GHz. It allows for incredibly fast data transfer speeds of up to 7 Gbps. However, because it works on a microwave range frequency, it has the significant disadvantage of not being able to pass through walls and has a range of only 3 to 32 feet (1 to 10 meters). It is "lightning fast," but it is designed to cover only one room when no walls or obstacles stand in the way.

There are few wireless routers on the market with support for 802.11ad, and few network devices that have support for it. One of the routers that we tested with 802.11ad is Netgear Nighthawk X10.
What is Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 4, and so on?
On October 3, 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced that it added a new naming for the wireless networking standards, to make it easier for people to identify them. After all, 802.11ax, 802.11ad, 802.11ac, 802.11n, and all the other similar names are not easy to remember, and most people have no idea what they mean. Their thinking is that Wi-Fi, followed by a number, is easy to remember. The rule is that the higher the number, the newer and the better the standard. You already know by now what Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, and Wi-Fi 4 mean. However, to summarize, here is what they are:
- Wi-Fi 6 identifies devices that support the 802.11ax wireless networking standard
- Wi-Fi 5 identifies devices that support the 802.11ac wireless networking standard, including 802.11ac Wave 2
- Wi-Fi 4 identifies devices that support the 802.11n wireless networking standard
To help you understand what each of the modern Wi-Fi networking standards offers, we made a table which compares their frequency bands and maximum theoretical speed:

Wi-Fi 1, Wi-Fi 2, and Wi-Fi 3 are not branded. That is likely because the Wi-Fi Alliance did not consider older Wi-Fi standards to be used much. However, for the sake of completion, we believe that the correct branding would have been:
- Wi-Fi 1 should have been 802.11b. This standard was released in 1999, it uses the 2.4 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 11 Mbps.
- Wi-Fi 2 should have been 802.11a. It was released in 1999, it uses the 5 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 54 Mbps.
- Wi-Fi 3 should have been 802.11g. This standard was released in 2003, it uses the 2.4 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 54 Mbps.
802.11ax vs 802.11ac vs 802.11n or Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 5 vs Wi-Fi 5, and real-life speeds
If you read the specifications of each Wi-Fi standard, and the maximum theoretical speed that each can achieve, you are going to be impressed. However, in real life, the speeds you get are much lower. You can find out more about this subject, in this article: What does AC1200, AC1750, AC1900 or more, mean and what's the difference?
To give you a realistic perspective on the real-life speed you get from the different standards that are available, we took one of the most powerful wireless routers - ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AX11000 - and made some measurements with SpeedTest, on a laptop with an Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX200 network card. Our internet connection offers a download speed of 1 Gbps, and an upload speed of 500 Mbps.
We first connected to the Wi-Fi emitted by the router, on the 2.4 GHz band, using the 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) standard, and the maximum download speed we measured is of 221.28 Mbps.

We then switched to the first 5 GHz band of the two emitted by the router, using the 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) standard. The maximum download speed that we reached is 630.10 Mbps. The Wi-Fi 5 standard is 2.8 times faster than the Wi-Fi 4 standard when using this wireless router.

Lastly, we switched to the second 5 GHz band, which used the 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) standard. This time we reached a maximum download speed of 762.03 Mbps. That is 20% faster than Wi-Fi 5, which is a substantial improvement, but far from the maximum theoretical speeds that are promised by the Wi-Fi 6 standard.

Hopefully, this quick comparison has given you a more realistic perspective of the speeds you can achieve, in real life, when using different Wi-Fi standards.
Do wireless routers use one or more Wi-Fi standards?
Yes, most of them do! Manufacturers make wireless routers that can work on one, two, or even three bands simultaneously, while supporting different wireless standards on each band. Most wireless routers today are dual-band or tri-band routers because they offer more speed and compatibility with various devices. All the wireless routers sold today have support for the 802.11n standard (usually on the 2.4 GHz band), and also add support for the 802.11ac standard (on the 5 GHz band). High-end wireless routers do all that, but can also include a third band (5 GHz or even 60 GHz), that is used for newer standards such as 802.11ac Wave 2, 802.11ax or 802.11ad.

Whether you have a single-band, dual-band, or tri-band router, the good thing is that the firmware should let you choose what Wi-Fi standards and bands you want to enable and use. You can select whether to activate only the 2.4 GHz band and the wireless standards supported on it, or you can choose to activate only the 5 GHz band and the wireless standards supported on it. Furthermore, you can also enable all the bands and all the wireless standards available on your router, mixing everything to get the desired results for your network.
Do you plan on getting new devices that support newer Wi-Fi standards?
Are you using Wi-Fi 5 compatible devices? Do you believe that it is worth upgrading to the latest Wi-Fi 6 standard, or is it too soon to invest in it? Comment below and share your opinion about all the wireless networking standards, their naming conventions, and features.










