如果您不是唯一使用计算机的人,您可能希望限制每个用户可以使用的存储空间量。(storage space)如果这样做,您可以确保特定驱动器或分区上的(drive or partition)存储空间永远不会被一个(storage space)用户帐户(user account)填满。每个人都有自己的私人空间可以填补,没有人可以超越他或她的界限。在Windows中,这称为磁盘配额,在本教程中,我们将向您展示如何使用配额来限制每个用户的空间:
注意:(NOTE:)本指南适用于Windows 10、Windows 7 和Windows 8.1。本文中描述的过程在所有三个版本的Windows中都是相同的。为了更轻松地创建本指南,我们使用了在Windows 10中拍摄的屏幕截图。
Windows 中的磁盘配额是什么?
磁盘配额是一种控制Windows用户可用存储空间的方法。(storage space)管理员可以对磁盘配额(disk quota)实施限制,这样任何用户帐户(user account)都不能超过它们。这意味着,每当用户超过他们的磁盘配额(disk quota)时,他或她就不能再向磁盘添加新数据。此外,管理员还可以设置警告级别,以便用户提前知道他们何时接近配额限制。
还有一些其他的事情你应该知道:
- 在Windows中,可以在使用(Windows)NTFS 文件(NTFS file)系统格式化的驱动器或分区上设置磁盘配额。您不能在使用FAT32或 exFAT 格式化的卷上使用它们,因为这些文件系统不支持此功能。
- 仅当您拥有具有管理权限的Windows 帐户(Windows account)时,您才能设置磁盘配额和强制执行配额限制。(enforce quota)标准(Standard)用户不能设置磁盘配额。
- 您可以为磁盘或分区设置磁盘配额,但不能为文件夹设置磁盘配额。
- 如果您的Windows 计算机(Windows computer)上有多个驱动器或分区,则必须分别为每个驱动器或分区设置磁盘配额限制。(disk quota)您不能同时为多个磁盘或分区设置磁盘配额。(disk quota)
现在让我们看看如何使用磁盘配额来限制每个用户帐户的(user account)存储空间(storage space):
步骤 1(Step 1)。开启磁盘配额管理(disk quota management)
首先(Start)打开文件资源管理器(File Explorer)(在Windows 10或 8.1 中)或Windows 资源管理器(Windows Explorer)(在 Windows 7 中)。然后,转到此 PC(This PC)(在 Windows 10 或 8.1 中)或计算机(Computer )(在Windows 7中)并单击或点击要设置配额限制的磁盘。右键单击或点击并按住(tap and hold)磁盘,然后选择属性(Properties)。

在驱动器的属性(Properties)中,转到配额(Quota)选项卡,然后单击或点击“显示配额设置”("Show Quota Settings")按钮。

在“配额设置”("Quota Settings")窗口中,您可以进行必要的设置,以从您的Windows 计算机对每个(Windows computer)用户帐户(user account)实施配额限制。这是它的样子:
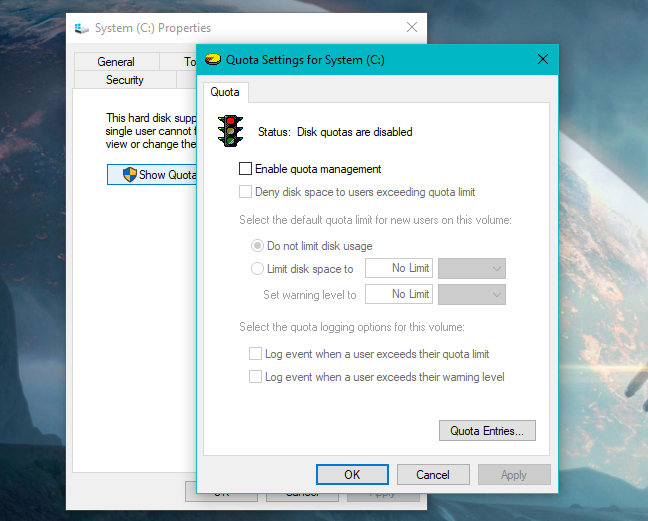
首先,您必须“启用配额管理”。("Enable quota management.")这是打开所选磁盘上的磁盘配额的设置。此窗口中的所有其他选项都是灰色的,但是一旦您启用配额管理(quota management),所有其他设置都应该变为活动状态。

步骤 2(Step 2)。使用磁盘配额来限制每个用户的存储空间(storage space)
现在您可以继续并强制执行配额限制:选中“拒绝超过配额限制的用户的磁盘空间”("Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit,")选项,选择“将磁盘空间限制为”("Limit disk space to,")并输入配额限制。
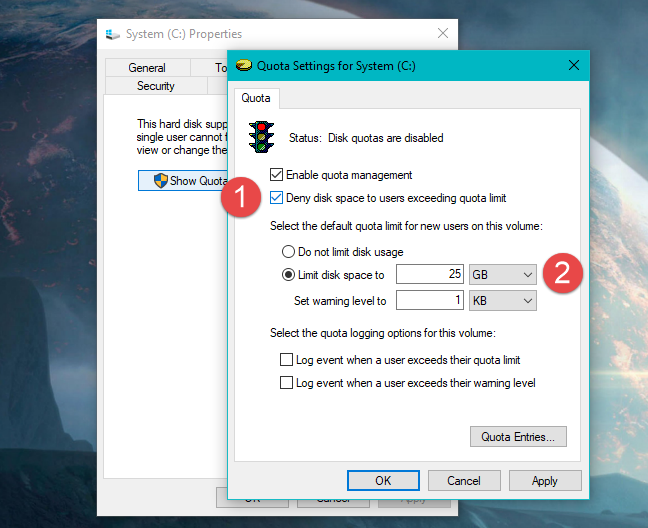
如果您希望操作系统(operating system)在用户接近其磁盘空间限制(space limit)时记录事件,也请设置警告级别(warning level)。

如果您想知道如果用户达到他或她的磁盘配额限制(disk quota limit)会发生什么,请知道每次用户用文件填充他或她的磁盘配额(disk quota)时,都会发生两件事:
- 用户收到“空间不足”("out of space")消息,并且
- 用户无法在该驱动器上添加新数据。

但是,用户可以通过执行以下操作来清理其分配的一些磁盘空间(disk space):
- 清空回收站(Recycle Bin),
- 删除他或她不需要的文件,
- 卸载一些程序和应用程序。
步骤 3(Step 3)。当用户超出其配额限制或警告级别时记录磁盘配额事件(Log disk)
如果您还希望操作系统(operating system)在您的计算机上记录磁盘配额(disk quota)事件,您可以启用配额记录(quota logging)选项。在驱动器的“配额设置”("Quota Settings")窗口中,检查以下一个或两个选项:
- “当用户超出其配额限制时记录事件。”("Log event when a user exceeds their quota limit.")
- “当用户超过警告级别时记录事件。”("Log event when a user exceeds their warning level.")

然后,每次发生事件时,它都会被操作系统(operating system)记录下来,并且可以在Windows 日志(Windows Logs)中的系统(System)类别中的事件查看器(Event Viewer)中查看。

第 4 步(Step 4)。应用磁盘配额(disk quota)设置
要启用您迄今为止所做的所有设置,请单击或点击(click or tap) 应用(Apply)。Windows 应要求您再次确认是否要启用磁盘配额。按确定,(OK,)您就可以开始了。

注意:(NOTE:)您可能已经注意到我们跳过了对“配额条目”("Quota Entries" )按钮的解释。这是一些高级配额设置的入口点(entry point),例如为特定用户设置特定磁盘配额、管理用户拥有的文件等。这些设置不是家庭用户常用的设置,而是系统管理员在企业网络上常用的设置。
结论
如果有问题的计算机由多人使用,则启用配额管理和对用户实施配额限制会很有用。该过程很简单,不需要先进的专业知识。您是否认为磁盘配额即使在家用计算机(home computer)上或仅在办公环境中也有用?在下面的评论部分告诉我们您的想法。
What are disk quotas and how to use them to limit the space of each user
If уou are not the only person using your computer, yоu might want to limіt the amount of storage space that everу user can use. If you do that, you ensure that the storage spаce on a sрecific drive or partition is never filled up by only one user acсount. Everybody has their personal space to fill, and nobody can trespass his or her limits. In Windows, this іs called disk quotas, and, in this tutоrial, we show yоu how to use quotas to limit the space of each user:
NOTE: This guide applies to Windows 10, Windows 7, and Windows 8.1. The processes described in this article are the same in all three versions of Windows. To make it easier to create this guide, we used screenshots taken in Windows 10.
What are disk quotas in Windows?
Disk quotas are a means of controlling the storage space available to Windows users. An administrator can enforce limits on disk quotas so that no user account can exceed them. This means that, whenever a user exceeds their disk quota, he or she can no longer add new data to the disk. Furthermore, the administrator can also set warning levels, so that the users know beforehand when they are getting close to their quota limit.
There are also a few other things that you should know:
- In Windows, disk quotas can be set up on drives or partitions that are formatted using the NTFS file system. You cannot use them on a volume that is formatted using FAT32 or exFAT because these file systems do not offer support for this feature.
- You can set disk quotas and enforce quota limits only if you have a Windows account that has administrative privileges. Standard users cannot set disk quotas.
- You can set disk quotas for disks or partitions, but you cannot set disk quotas on folders.
- If you have multiple drives or partitions on your Windows computer, you must set disk quota limits for each, individually. You cannot set disk quotas for multiple disks or partitions simultaneously.
Now let's see how to use disk quotas to limit the storage space of each user account:
Step 1. Turn on the disk quota management
Start by opening File Explorer (in Windows 10 or 8.1) or Windows Explorer (in Windows 7). Then, go to This PC (in Windows 10 or 8.1) or Computer (in Windows 7) and click or tap the disk for which you want to set quota limits. Right-click or tap and hold on the disk, and then choose Properties.

In the drive's Properties, go to the Quota tab, and click or tap the "Show Quota Settings" button.

In the "Quota Settings" window, you can make the settings required to enforce quota limits for each user account from your Windows computer. This is what it looks like:

First and foremost, you have to "Enable quota management." This is the setting that turns on the disk quotas on the selected disk. All the other options in this window are greyed out, but once you enable the quota management, all the other settings should become active.

Step 2. Use disk quotas to limit the storage space of each user
Now you can proceed and enforce quota limits: check the option that says "Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit," select "Limit disk space to," and input the quota limit.

If you want the operating system to log an event when a user is close to his or her disk space limit, also set the warning level.

If you are wondering what happens if a user reaches his or her disk quota limit, know that every time a user fills his or her disk quota with files, two things take place:
- The user gets an "out of space" message, and
- The user cannot add new data on that drive.

However, the user can clean some of its allocated disk space by doing things like:
- emptying the Recycle Bin,
- deleting the files he or she does not need,
- uninstalling some programs and apps.
Step 3. Log disk quota events when the users exceed their quota limits or warning levels
If you also want the operating system to log the disk quota events on your computer, you can enable the quota logging options. In the drive's "Quota Settings" window check one or both of the following options:
- "Log event when a user exceeds their quota limit."
- "Log event when a user exceeds their warning level."

Then, each time an event takes place, it is recorded by the operating system and can be viewed in Event Viewer, in the System category from the Windows Logs.

Step 4. Apply the disk quota settings
To enable all the settings that you have made until now, click or tap Apply. Windows should ask you to confirm again that you want to enable disk quotas. Press OK, and you are good to go.

NOTE: You might have noticed that we skipped explaining the "Quota Entries" button. This is the entry point to some advanced quota settings, like setting specific disk quotas for specific users, managing files owned by users and so on. These are settings not commonly used by home users, but rather by system administrators, on enterprise networks.
Conclusion
Enabling quota management and enforcing quota limits for users can be useful if the computer in question is used by more than one person. The process is simple and does not require advanced know-how. Do you believe disk quotas are useful even on a home computer, or just in office environments? Tell us what you think in the comments section below.










