(Google Chrome)至少十年来,Google Chrome一直是大多数 Windows PC 用户的首选浏览器,但它并非没有问题。特别是,Chrome中的内存使用通常是它最大的缺点,太多的标签会占用你 PC 的可用系统资源。
如果您在Chrome运行时查看(Chrome)Windows 任务管理器(Windows Task Manager)或Mac 活动监视器(Mac Activity Monitor),您会看到Google Chrome Helper进程占用了您的系统资源,但Google Chrome Helper是什么,是否可以禁用它?
为了帮助您,以下是您需要了解的有关Google Chrome Helper流程的所有信息。

什么是谷歌浏览器助手?(What is Google Chrome Helper?)
谷歌浏览器(Google Chrome)的核心是一个非常标准的网络浏览器。它允许您访问页面、保存书签、更改默认主页等等——您希望在浏览器中看到的所有功能。
如果您想要更多功能,则需要安装第三方 Chrome 扩展程序(install third-party Chrome extensions)。这些是由外部开发人员创建的附加功能,用于扩展Chrome浏览器的功能。有很多很棒的 Chrome 扩展(great Chrome extensions)可以尝试,但也有很多用处不大(并且有潜在风险)的扩展。
Chrome 的功能也有扩展,称为插件,某些网站将使用这些扩展来扩展功能。例如,一个网站可能有一个第三方插件来启用视频播放或访问某些硬件组件。

这就是 Chrome 浏览器的Google (Chrome)Chrome Helper(Google Chrome Helper)组件变得有用的地方。Google Chrome Helper进程(和Google Chrome Helper ( Renderer ) 进程)是加载到您的浏览器中的第三方内容的通用名称,无论是第三方扩展程序还是视频播放器等嵌入内容。
特别是,这些插件通常需要标准插件和扩展之外的额外系统访问权限。例如,通过Chrome浏览器安装新软件的网站将需要一个非沙盒插件,该插件有权访问Chrome本身之外的资源。
大多数用户不会注意到它甚至存在。但是,如果您的 PC 或Mac在使用(Mac)Chrome时显得迟钝,Google Chrome Helper可以帮助您追踪问题。使用第三方插件的不良扩展程序或资源密集型页面会导致Chrome Helper在某些情况下达到最大CPU或RAM使用率。(RAM)
这是Chrome 中的 Adobe Flash(Adobe Flash in Chrome)被证明存在问题的原因之一,导致谷歌(Google)默认阻止它。在Google禁用Flash支持之前,使用Flash的网站需要访问适当的Flash插件,这可能会导致Chrome 速度变慢或(Chrome to slow down or crash)完全崩溃。
是什么导致 Google Chrome 助手 CPU 和 RAM 使用率高(What Causes High Google Chrome Helper CPU and RAM Usage)
附加到Google Chrome Helper的(Google Chrome Helper)CPU或RAM使用率高的主要原因不是浏览器本身,而是使用它的插件或扩展程序。尽管Chrome仍因系统资源管理不善而闻名,但您可以采取一些措施来帮助限制Chrome的影响,包括完全禁用Chrome Helper进程。
但是,如果您首先使用Windows 任务管理器(Windows Task Manager)或Mac 活动管理器(Mac Activity Manager)进行调查,您将找不到很多答案。通用Google Chrome Helper或Google Chrome Helper ( Renderer ) 进程是第三方插件或扩展程序导致问题的唯一迹象。
要尝试诊断它,请在您使用Chrome时追溯您的步骤并监控您的资源使用情况。从新的Chrome(Chrome)浏览器页面开始(Start),并尝试加载使您的 PC 看起来缓慢的页面。如果这不会影响您的 PC,请尝试使用您启用的一些扩展程序,看看这些扩展程序是否会导致资源使用量激增。
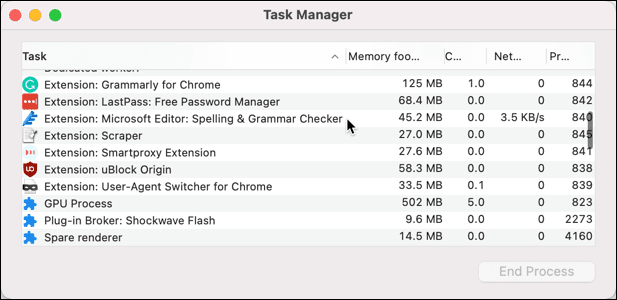
您还可以使用内置的Google Chrome 任务管理器(Google Chrome Task Manager)来监控每个单独的内部Chrome进程。这将允许您识别导致问题的Chrome中的特定组件,例如流氓插件。
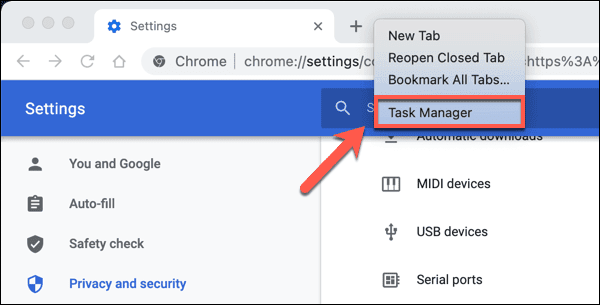
- 要打开Chrome 任务管理器(Chrome Task Manager),请右键单击标签栏并选择任务管理器(Task Manager )选项。
内存占用(Memory footprint )和CPU列将帮助您识别麻烦的插件或扩展。如果一个进程使用过多的CPU或RAM,您可以选择它,然后选择End Process按钮立即结束它。这将导致它在Chrome中崩溃,但Chrome将保持打开状态供您使用。
如何减少 Google Chrome 助手系统资源的使用(How to Reduce Google Chrome Helper System Resource Usage)
如果您想使用Google Chrome降低(Google Chrome)CPU或RAM的高使用率,您可以在禁用Google Chrome Helper并限制浏览器中的所有第三方插件之前采取一些步骤。
首先,考虑您在Chrome中使用的扩展程序和插件。如果某些页面导致速度变慢,请尝试阻止任何第三方插件加载。
- 您可以通过选择地址URL栏旁边的锁定图标,然后选择(lock icon )站点设置(Site settings )选项来对某些页面执行此操作。

- 在站点权限菜单中,您可以通过将Unsandboxed 插件访问权限(Unsandboxed plug-in access)设置为Block来阻止第三方插件。

如果Chrome扩展程序造成困难,那么您可以决定禁用这些扩展程序。
- 要禁用Chrome扩展程序,请选择右上角的三点菜单图标,然后选择(three-dot menu icon)More Tools > Extensions.

- 在Chrome扩展程序菜单中,选择扩展程序旁边的滑块以禁用它,将其置于关闭(off)位置。

也可以使用隐身模式解决(incognito mode)Chrome中的问题。默认情况下,Chrome会在隐身模式下阻止任何第三方插件和扩展程序。
- 要切换到隐身模式,请选择右上角的三点菜单图标,然后选择(three-dots menu icon)新建隐身窗口(New Incognito Window )选项。

如何在 Windows 和 Mac 上禁用 Google Chrome 助手(How to Disable Google Chrome Helper on Windows and Mac)
如果您仍在努力解决Chrome减速问题,并且您确定Google Chrome Helper进程是原因,那么您可以完全禁用它。
禁用Google Chrome Helper将阻止所有第三方插件在Chrome中运行。这可能会阻止某些网站资产(例如视频播放器)正常工作。如果您可能会使用此类资产,请务必在隐身模式下测试Google Chrome,以确保您的浏览器在之后能够继续正常工作。
- 首先,打开Chrome浏览器窗口并选择右上角的三点菜单图标。(three-dot menu icon )从那里,选择设置(Settings)选项。

- 在Chrome(Chrome)设置菜单的左侧选项面板中,选择隐私和安全(Privacy and security)。在右侧,选择站点设置(Site Settings)选项。

- 向下滚动,然后选择Additional permissions > Unsandboxed plugin access。

- 要禁用Google Chrome Helper,请将菜单顶部的滑块选择到关闭(off )位置。关闭此选项后,该选项将更新为不允许任何站点使用插件访问您的计算机(Do not allow any site to use a plugin to access your computer),而不是询问站点何时要使用插件访问您的计算机(推荐(Ask when a site wants to use a plug-in to access your computer (recommended))。

禁用后,您访问的页面将无法再运行第三方插件。这应该会阻止Google Chrome Helper进程出现在Windows 任务管理器(Windows Task Manager)或CPU或RAM使用率较高的Mac 活动监视器中。(Mac Activity Monitor)
在任何时候,您都可以回溯上述步骤并通过选择不允许任何站点使用插件访问您的计算机(Do not allow any site to use a plugin to access your computer )滑块重新启用Google Chrome Helper进程,将其返回到(Google Chrome Helper)打开(on)位置。
从谷歌浏览器切换(Switching from Google Chrome)
即使是上述方法也不能总是处理Google Chrome中(Google Chrome)异常的内存泄漏和(unusual memory leaks)CPU使用率过高的问题。如果您已禁用Google Chrome Helper并且Chrome运行速度仍然很慢,那么可能是时候考虑切换到替代浏览器(alternative browser)了,例如Windows上的Firefox或Mac上的Safari。
切换后,将书签(transfer your bookmarks)和其他个人数据从一个浏览器传输到另一个浏览器是一个简单的过程。如果您要切换到Firefox,您还可以安装一些顶级 Firefox 附加组件(top Firefox add-ons)来替换需要 RAM 的Chrome扩展。
What Is Google Chrome Helper and Can It Be Disabled?
Google Сhrome has been the browser of choice for most Windows PC uѕers fоr at least a decade, but it isn’t without its problems. In particular, memory usage in Chrome is often it’s biggest downfall, with tоo many tabs eаtіng up your PC’s availаble system resources.
If you take a look at Windows Task Manager or Mac Activity Monitor while Chrome runs, you can see the Google Chrome Helper process taking up your system resources, but what is Google Chrome Helper and is it possible to disable it?
To help you, here’s everything you need to know about the Google Chrome Helper process.

What is Google Chrome Helper?
At its core, Google Chrome is a pretty standard web browser. It allows you to visit pages, save bookmarks, change your default homepage, and more—all features you’d expect to see in a browser.
If you want more features, then you’ll need to install third-party Chrome extensions. These are add-on features, created by outside developers, that extend the functionality of the Chrome browser. There are plenty of great Chrome extensions to try, but there are also a lot of less useful (and potentially risky) extensions, too.
There are also extensions to Chrome’s functionality, named plugins, that certain websites will use to extend functionality. For instance, a website may have a third-party plugin to enable video playback or to access certain hardware components.

This is where the Google Chrome Helper component of the Chrome browser becomes useful. The Google Chrome Helper process (and the Google Chrome Helper (Renderer) process) is a generic name for third-party content loaded in your browser, whether it’s a third-party extension or embedded content like a video player.
In particular, these are plugins that typically require additional system access outside of standard plugins and extensions. For instance, a site that installs new software through the Chrome browser will require an unsandboxed plugin that has the authority to access resources outside of Chrome itself.
Most users won’t notice that it even exists. However, if your PC or Mac seems sluggish using Chrome, Google Chrome Helper could help you trace the problem. A bad extension or resource-heavy pages using third-party plugins will cause Chrome Helper to hit maximum CPU or RAM usage in certain circumstances.
This is one reason why Adobe Flash in Chrome proved problematic, leading to Google blocking it by default. Before Google disabled Flash support, websites using Flash would need to access the appropriate Flash plugin, potentially causing Chrome to slow down or crash entirely.
What Causes High Google Chrome Helper CPU and RAM Usage
The main cause of high CPU or RAM usage attached to the Google Chrome Helper isn’t the browser itself—it’s a plugin or extension using it. While Chrome still has a reputation for bad system resource management, there are things you can do to help limit Chrome’s impact, including disabling the Chrome Helper process entirely.
If you’re using the Windows Task Manager or Mac Activity Manager to investigate first, however, you won’t find many answers. The generic Google Chrome Helper or Google Chrome Helper (Renderer) process is the only indication that a third-party plugin or extension is causing the issue.
To try and diagnose it, retrace your steps and monitor your resource usage while you’re using Chrome. Start with a fresh Chrome browser page and try to load pages that make your PC seem sluggish. If that doesn’t impact your PC, try to use some of the extensions you’ve enabled to see if these cause a spike in resource usage.

You can also use the built-in Google Chrome Task Manager to monitor each individual internal Chrome process. This will allow you to identify the specific component in Chrome, such as a rogue plugin, that’s causing issues.
- To open Chrome Task Manager, right-click the tab bar and select the Task Manager option.

The Memory footprint and CPU columns will help you to identify troublesome plugins or extensions. If a process is using too much CPU or RAM, you can select it, then select the End Process button to end it immediately. This will cause it to crash in Chrome, but Chrome will remain open for you to use.
How to Reduce Google Chrome Helper System Resource Usage
If you want to reduce high CPU or RAM usage using Google Chrome, there are a few steps you can take before you disable the Google Chrome Helper and limit all third-party plugins in your browser.
First, consider the extensions and plugins you’re using in Chrome. If certain pages cause a slowdown, try and block any third-party plugins from loading.
- You can do this for certain pages by selecting the lock icon next to the address URL bar, then selecting the Site settings option.

- In the site permissions menu, you can block third-party plugins by setting Unsandboxed plug-in access to Block.

If Chrome extensions are causing difficulty, then you may decide to disable these instead.
- To disable Chrome extensions, select the three-dot menu icon in the top-right, then select More Tools > Extensions.

- In the Chrome extensions menu, select the slider next to an extension to disable it, placing it in the off position.

It may also be possible to troubleshoot issues in Chrome by using incognito mode. By default, Chrome will block any third-party plugins and extensions in incognito mode.
- To switch to incognito mode, select the three-dots menu icon in the top-right, then select the New Incognito Window option.

How to Disable Google Chrome Helper on Windows and Mac
If you’re still struggling to troubleshoot a Chrome slowdown, and you’re sure that the Google Chrome Helper process is the cause, then you can disable it entirely.
Disabling Google Chrome Helper will stop all third-party plugins from running in Chrome. This could block some site assets, such as video players, from working correctly. If you’re likely to use assets like these, be sure to test Google Chrome in incognito mode to be sure your browser will continue to work correctly afterwards.
- To begin, open a Chrome browser window and select the three-dot menu icon in the top-right. From there, select the Settings option.

- In the left-hand options panel in the Chrome settings menu, select Privacy and security. On the right, select the Site Settings option.

- Scroll down, then select Additional permissions > Unsandboxed plugin access.

- To disable the Google Chrome Helper, select the slider at the top of the menu to the off position. When this is turned off, the option will update to Do not allow any site to use a plugin to access your computer, rather than Ask when a site wants to use a plug-in to access your computer (recommended).

Once disabled, pages you access will no longer be able to run third-party plugins. This should stop the Google Chrome Helper process from appearing in Windows Task Manager or in Mac Activity Monitor with high CPU or RAM usage.
At any point, you can retrace the steps above and re-enable the Google Chrome Helper process by selecting the Do not allow any site to use a plugin to access your computer slider, returning it to the on position.
Switching from Google Chrome
Even the methods above can’t always deal with unusual memory leaks and excessive CPU usage in Google Chrome. If you’ve disabled the Google Chrome Helper and Chrome is still slow to run, it may be time to consider switching to an alternative browser like Firefox on Windows or Safari on Mac.
Once you’ve switched, it’s an easy process to transfer your bookmarks and other personal data from one browser to another. If you’re switching to Firefox, you can also install some top Firefox add-ons to replace RAM-hungry Chrome extensions.













