如果您经常使用互联网,那么您很有可能没有遇到过对等或 P2P 一词(term peer-to-peer or P2P)。无论是在新闻文章中(news article),在电视上,还是在与朋友的谈话中,他告诉你他刚刚通过P2P下载了最新版本的(P2P)Linux,你都可能偶然发现了这个词。如果你想知道什么是点对点网络,P2P是做什么用的,还想看一些点对点网络的例子,你应该阅读这篇文章:
什么是对等网络?
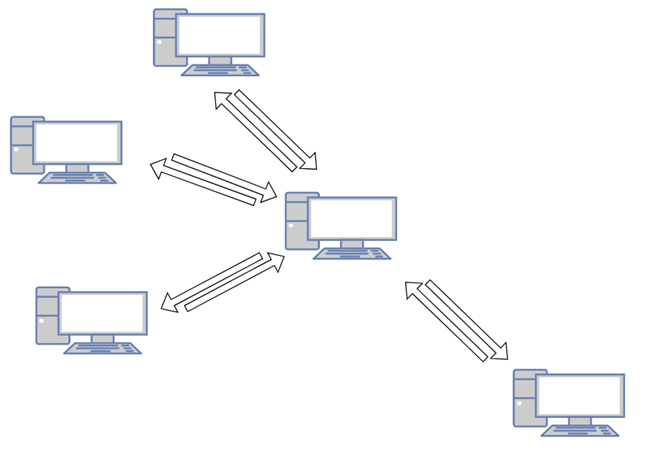
对等(Peer-to-peer),或缩写形式的P2P,是指使用分布式架构的计算机网络。在P2P网络中,属于其中的所有计算机和设备都称为对等点,它们共享和交换工作负载(share and exchange workloads)。对等网络(peer-to-peer network)中的每个对等点都与其他对等点相等。没有特权对等点,也没有网络中心的主要管理员设备(administrator device)。

在某种程度上,对等网络是计算机世界(computer world)中最平等的网络。每个对等点与其他对等点是平等的,每个对等点具有与其他对等点相同的权利和义务。对等点既是客户端又是服务器。
事实上,点对点网络(peer-to-peer network)中可用的每个资源和每个资产都在对等点之间共享,而不涉及任何中央服务器。P2P 网络(P2P network)中的共享资源可以是处理器使用率(processor usage)、磁盘存储容量(disk storage capacity)或网络带宽(network bandwidth)等。
P2P(点对点)用于什么?
对等网络的主要目标是共享资源并帮助计算机和设备协同工作、提供特定服务或执行特定任务。如前所述,P2P用于共享各种计算资源,例如处理能力、网络带宽(network bandwidth)或磁盘存储空间(disk storage space)。但是,对等网络最常见的用例是在 Internet 上共享文件。(use case)对等网络非常适合文件共享(file sharing),因为它们允许连接到它们的计算机同时接收文件和发送文件。
想象一下这种情况:您打开Web 浏览器(web browser)并访问您下载文件的网站。在这种情况下,网站充当服务器,您的计算机充当接收文件的客户端。您可以将其比作单向道路:您下载的文件是一辆从 A 点(网站)到 B 点(您的计算机)的汽车。

当您从对等网络(peer-to-peer network)下载相同文件时,使用 BitTorrent 平台作为起点(starting point),下载的执行方式会有所不同。该文件以来自许多其他计算机的位和部分下载到您的计算机,这些计算机也连接到相同的P2P 网络(P2P network)并且已经具有该文件或至少其中的一部分。同时,文件也会从您的计算机发送(上传)到其他需要它的设备。这种情况类似于一条双向的道路:文件就像多辆小型汽车来到您的 PC 上,同时在请求时也留给其他人。
为什么点对点网络有用?
P2P网络具有一些使其有用的特性:
- 很难把它们拿下来。即使其中一个节点关闭,其他节点仍在运行和通信。要使P2P(点对点)网络停止工作,您必须关闭其所有对等点。
- 对等网络具有令人难以置信的可扩展性。添加新的对等点很容易,因为您不需要在中央服务器上进行任何中央配置。
- 在文件共享方面,对等网络(peer-to-peer network)越大,速度越快。将相同的文件存储在P2P 网络(P2P network)中的许多对等点上意味着当有人需要下载它时,该文件会同时从多个位置下载。
P2P(点对点)网络示例
我们都使用点对点网络来连接计算机和设备,而无需配置服务器。必须为一切创建服务器既昂贵又难以管理,因此在某些情况下,使用P2P网络更容易且更实惠。以下是点对点网络的一些常见用例示例:

-
Windows 10 更新通过Microsoft的服务器和P2P提供。此处有关于此功能的更多信息:优化 Windows 10 更新交付(Optimize Windows 10 update delivery)。
- 在 Internet 上共享大文件通常使用P2P(点对点)网络架构(network architecture)来完成。例如,一些在线游戏平台使用P2P在用户之间下载游戏。暴雪娱乐(Blizzard Entertainment)使用P2P分发暗黑破坏神 III(Diablo III)、星际争霸 II(StarCraft II)和魔兽(World)世界(Warcraft)。另一家大型出版商Wargaming 也在(Wargaming)他们的《坦克(Tanks)世界(World)》 、《战舰(Warships)世界(World)》和《战机(Warplanes)世界(World)》游戏中做同样的事情。其他的,比如Steam 或 GOG(Steam or GOG),选择不使用P2P并更喜欢在世界各地维护专用下载服务器。
- 许多Linux操作系统是通过使用P2P传输的BitTorrent下载分发的。此类示例包括Ubuntu、Linux Mint和Manjaro。
- 在Windows 7和Windows 8.1中,当您在两台计算机之间创建临时网络时,您将在它们之间创建一个对等网络。
- 如果您使用的是Windows 7、Windows 8.1 或版本 1803(Version 1803)之前的 Windows 10 版本,您可以将家中的计算机连接到家庭组(Homegroup),从而在它们之间创建对等网络(peer-to-peer network)。家庭组(Homegroup)是一小组计算机,它们相互连接以共享存储和打印机(share storage and printers)。这是对等技术(peer-to-peer technology)最常见的用途之一。有人可能会说家庭组(Homegroups)不能点对点,因为网络中的计算机连接到路由器。但是,请记住,路由器与管理家庭组中的计算机共享(Homegroup share)的内容没有任何共同之处在他们中间。路由器不作为服务器工作,而只是作为本地网络和互联网之间的接口或网关。(interface or gate)如果您愿意,可以在以下文章中找到有关Microsoft选择实施P2P 技术的方式的更多信息: (P2P technology)Win 7 中基于点对点的功能(Peer-To-Peer based Features in Win 7)、[MS-HGRP]:家庭组协议([MS-HGRP]: HomeGroup Protocol)和家庭组:实用指南拥有 Windows 7 的家庭幸福(HomeGroup: A practical guide to domestic bliss with Windows 7)。
- 不幸的是,点对点网络也常用于非法活动(peer-to-peer networks are also commonly used for illicit activities)。P2P是一项有争议的技术,因为它被广泛用于盗版。由于这项技术的优势,网络上有许多网站可以通过P2P网络访问受版权保护的内容,例如电影、音乐、软件或游戏。(P2P)虽然该技术本身并不违法,并且它有许多不涉及盗版的合法用途,但有些人使用P2P的方式是非法的。使用P2P时,请确保不要从事盗版或其他受法律制裁的活动。

P2P网络是分发内容最经济的方法之一,因为它们使用对等方的带宽,而不是内容创建者的带宽。
P2P(点对点)网络的历史
对等网络的前身似乎是USENET,它是在 1979 年开发的。它是一个允许用户阅读和发布消息/新闻的系统。它是一个类似于今天的在线论坛的网络系统,但不同之处在于(network system)USENET不依赖中央服务器或管理员(server or administrator)。USENET将相同的消息/新闻复制到网络中的所有服务器。同样,对等网络分发和使用所有可用的资源。
P2P历史上的下一件大事是1999 年(year 1999)Napster诞生(Napster)的那一年。Napster是人们用来分发和下载音乐的文件共享软件。在Napster(Napster)上分享的音乐通常是受版权保护的,因此分发是非法的。然而,这并没有阻止人们得到它。尽管Napster是让P2P成为主流的公司,但Napster最终失败并被当局关闭,因为上面的所有内容都是非法共享的。如今(Nowadays),P2P仍然是合法和非法地通过 Internet 共享文件的最受欢迎的技术之一。

图片来源:(Image source:) 维基百科(Wikipedia)
您对点对点网络还有其他问题吗?
正如您在本指南中所见,点对点是一项复杂的技术,它诞生并基于一个简单的原则:去中心化。你现在知道它的目的是诚实的,尽管它并不总是出于正确的原因使用。有些人争论是否应该禁止它,因为P2P仍然是非法分发受版权保护的内容的最重要手段。但是,是否应该因为作家的手艺很差而禁止使用钢笔?
What are P2P (peer-to-peer) networks and what are they used for?
If уou are using the internet regularly, it is highly unlikеly that you have not encountered the term peer-to-peer or P2P. Whether it was mentioned іn a news article, on TV, or in a conversation with a friend, who told you that he just downloaded the latest vеrsion of Linux through P2Р, you may haνe stumblеd υpon this term. If you want to know what peer-to-peer networks are, what P2P is usеd for, аnd also see some peer-to-peer network examples, you should rеad this article:
What is a peer-to-peer network?
Peer-to-peer, or P2P in its abbreviated form, refers to computer networks using a distributed architecture. In P2P networks, all the computers and devices that are part of them are referred to as peers, and they share and exchange workloads. Each peer in a peer-to-peer network is equal to the other peers. There are no privileged peers, and there is no primary administrator device in the center of the network.

In a way, peer-to-peer networks are the most egalitarian networks in the computer world. Each peer is equal to the others, and each peer has the same rights and duties as the others. Peers are both clients and servers at the same time.
In fact, every resource and each asset that's available in a peer-to-peer network is shared among peers, without any central server being involved. The shared resources in a P2P network can be things such as processor usage, disk storage capacity, or network bandwidth.
What is P2P (peer-to-peer) used for?
The primary goal of peer-to-peer networks is to share resources and help computers and devices work collaboratively, provide specific services, or execute specific tasks. As mentioned earlier, P2P is used to share all kinds of computing resources such as processing power, network bandwidth, or disk storage space. However, the most common use case for peer-to-peer networks is the sharing of files on the internet. Peer-to-peer networks are ideal for file sharing because they allow the computers connected to them to receive files and send files simultaneously.
Imagine this situation: you open your web browser and visit a website where you download a file. In this case, the website works as a server, and your computer acts as a client receiving the file. You can compare it to a one-way road: the file that you download is a car that goes from point A (the website) to point B (your computer).

When you download the same file from a peer-to-peer network, using a BitTorrent platform as a starting point, the download is performed differently. The file is downloaded to your computer in bits and parts that come from many other computers that also connected to the same P2P network and already have that file or at least parts of it. At the same time, the file is also sent (uploaded) from your computer to other devices that are asking for it. This situation is similar to a two-way road: the file is like multiple small cars coming to your PC, while also leaving to others when it is requested.

Why are peer-to-peer networks useful?
P2P networks have some characteristics that make them useful:
- It's hard to take them down. Even if one of the peers is shut down, the others are still operating and communicating. For a P2P (peer-to-peer) network to stop working, you have to close down all its peers.
- Peer-to-peer networks are incredibly scalable. Adding new peers is easy as you don't need to do any central configuration on a central server.
- When it comes to file-sharing, the larger a peer-to-peer network is, the faster it is. Having the same file stored on many of the peers in a P2P network means that when someone needs to download it, the file is downloaded from multiple locations simultaneously.
P2P (peer-to-peer) network examples
We all use peer-to-peer networks to connect computers and devices without the need to configure a server. Having to create a server for everything is expensive and difficult to manage, so in some situations, it's easier and more affordable to use P2P networks. Here are some examples of common use cases for peer-to-peer networks:

-
Windows 10 updates are delivered both from Microsoft's servers and through P2P. There is more information about this feature here: Optimize Windows 10 update delivery.
- Sharing large files over the internet is often done using a P2P (peer-to-peer) network architecture. For example, some online gaming platforms use P2P for downloading games between users. Blizzard Entertainment distributes Diablo III, StarCraft II, and World of Warcraft using P2P. Another large publisher, Wargaming, does the same with their World of Tanks, World of Warships, and World of Warplanes games. Others, like Steam or GOG, choose not to use P2P and prefer maintaining dedicated download servers around the world.
- Many Linux operating systems are distributed via BitTorrent downloads using P2P transfers. Such examples are Ubuntu, Linux Mint, and Manjaro.
- In Windows 7 and Windows 8.1, when you create an ad-hoc network between two computers, you create a peer-to-peer network between them.
- If you're using Windows 7, Windows 8.1, or a Windows 10 version before Version 1803, you can connect the computers in your home to a Homegroup, thus creating a peer-to-peer network between them. The Homegroup is a small group of computers that are connected between themselves to share storage and printers. This is one of the most common uses for peer-to-peer technology. Some people might say that Homegroups can't be peer-to-peer because the computers in the network are connected to a router. However, keep in mind that the router has nothing in common with managing what the computers from the Homegroup share among themselves. The router does not work as a server but merely as an interface or gate between the local network and the internet. If you want, you can find more information about the way Microsoft chose to implement the P2P technology, in these articles: Peer-To-Peer based Features in Win 7, [MS-HGRP]: HomeGroup Protocol, and HomeGroup: A practical guide to domestic bliss with Windows 7.
- Unfortunately, peer-to-peer networks are also commonly used for illicit activities. P2P is a controversial technology because it is widely used for piracy. There are many websites on the web that offer access to copyrighted content like movies, music, software, or games, through P2P networks, due to the advantages of this technology. While the technology itself is not illegal and it has many legitimate uses that don't involve piracy, the way some people use P2P is illegal. When using P2P, make sure not to engage yourself in piracy or other activities that are punished by law.

P2P networks are one of the most affordable methods of distributing content because they use the bandwidth of peers, not the bandwidth of the content's creator.
The history of P2P (peer-to-peer) networks
The precursor of peer-to-peer networks appears to be USENET, which was developed in 1979. It was a system that allowed users to read and post messages/news. It was a network system similar to the online forums today, but with the difference that USENET did not rely on a central server or administrator. USENET copied the same message/news to all the servers found in the network. Similarly, peer-to-peer networks distribute and use all the resources available to them.
The next big thing in the history of P2P was the year 1999 when Napster came to life. Napster was file-sharing software that was used by people to distribute and download music. The music shared on Napster was usually copyrighted and thus illegal to distribute. However, that did not stop people from getting it. Although Napster was the one that got P2P into the mainstream, Napster ultimately failed and was shut down by authorities because of all the content that was shared illegally on it. Nowadays, P2P remains one of the most popular technologies for sharing files over the internet, both lawfully and unlawfully.

Image source: Wikipedia
Do you have any other questions regarding peer-to-peer networks?
As you have seen in this guide, peer-to-peer is a sophisticated technology that was born and based on a simple principle: decentralization. You know now that its purpose is honest, although it's not always used for the right reasons. Some people argue whether it should be prohibited or not because P2P remains the most important means of distributing copyrighted content unlawfully. However, should a pen be forbidden from use because the writer is terrible at his or her craft?






