Superfetch是一个多年来有多个名称的Windows系统进程。(Windows)在Windows XP上,它被称为Prefetch。Superfetch是在(Superfetch)Windows Vista中引入的,在最新版本的Windows 10中,它现在称为Sysmain。
最终,每一代Superfetch的目的都是相同的:通过在您需要使用它们之前将您经常使用的应用程序预加载到RAM中来提高Windows的性能。(Windows)但什么是Superfetch?

Superfetch (Sysmain) 是如何工作的?(How Does Superfetch (Sysmain) Work?)
在最新版本的Windows 10中,Superfetch服务现在以SysMain的名称显示。在Task Manager中,它显示为Service Host: SysMain。
如果您运行的是旧版本的Windows 10或任何版本的Windows 7或 8,这将在任务管理器(Task Manager)中显示为Service Host: Superfetch。

该服务在后台运行(使用很少的CPU资源)并分析您使用的RAM量以及您最常运行的应用程序。服务识别为“经常使用”的任何应用程序都会开始将应用程序预加载到RAM中。这样,下次您运行该应用程序时,它会更快地启动。
您可能会担心这意味着Superfetch正在耗尽您的所有RAM,但事实并非如此。该服务专注于将应用程序预加载到未使用的RAM中。这不会注册为消耗的内存。如果您将任务管理器(Task Manager)打开到进程(Processes)选项卡并查看您的内存(Memory)使用情况,您会看到这一点。

即使Superfetch使用预加载的应用程序消耗所有未使用的RAM ,消耗的(RAM)RAM使用率仍然没有显示 100%。这是因为Superfetch在后台运行,当您需要将该内存用于其他活动任务时,它会释放它正在使用的任何未使用的RAM 。
你应该杀死 Superfetch (Sysmain) 吗?(Should You Kill Superfetch (Sysmain)?)
一般来说,不需要停止Superfetch的运行。它使用非常少量的CPU,并且只使用未使用的RAM。所有这些对于普通用户来说是不明显的。
但是,在整个Microsoft(Microsoft)用户论坛中都有一些报告称,有时Superfetch ( Sysmain ) 进程实际上会导致性能问题。其中一些报告的问题包括:
- 恒定的 100% 磁盘利用率。
- 过热(Overheating)导致系统关闭。
- (Slow)启动计算机时启动时间很慢。
- 在弱硬件上,Superfetch可能会使用比您想要的更多的CPU和RAM 。
- 已知会在玩游戏时导致性能问题(performance issues while gaming)。
人们报告的最常见问题是 100% 磁盘利用率问题。如果是您,那么禁用Superfetch或Sysmain可能会解决问题。
由于Superfetch只是一项系统优化功能,因此您不会通过停止该服务来伤害Windows 。但是,您可能会注意到启动您喜欢的应用程序可能需要比平时更长的时间。
如何在 Windows 10 中禁用 Superfetch (Sysmain)(How To Disable Superfetch (Sysmain) In Windows 10)
禁用 Superfetch 是否安全?
如果您没有遇到性能问题或其他问题,最好让Superfetch ( Sysmain ) 运行。这是一个有用的过程,可以显着减少您启动经常使用的程序所花费的时间。
但是,如果您遇到高硬盘利用率、持续内存问题或整体性能不佳的问题,您可以尝试禁用Superfetch以查看它是否可以解决问题。如果是这样,则禁用该服务。否则(Otherwise),将其重新打开并继续进行故障排除。
要在 Windows 10 上禁用Superfetch ( Sysmain ):
- 选择“开始”菜单,键入services,然后选择“服务(Services)”应用。您也可以按Windows + R,键入services.msc并按 Enter。
- 在Services应用程序中,向下滚动到SysMain,右键单击该服务并选择Stop。如果您运行的是旧版本的Windows,请右键单击SuperFetch服务并选择Stop。

- 现在您需要在启动Windows时阻止服务重新启动。服务停止后,再次右键单击该服务并选择Properties。
- 在启动(Startup)类型下拉列表中,选择禁用(Disabled)。

现在SuperFetch ( SysMain ) 服务被永久禁用,下次启动计算机时不会重新启动。
使用注册表编辑器禁用 Superfetch (Sysmain)(Disable Superfetch (Sysmain) With Registry Editor)
在Windows 10上使用(Windows 10)任务管理器(Task Manager)禁用Superfetch的替代方法是使用注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)。
在您开始在注册表中执行任何操作之前,请确保先对注册表进行完整备份(take a full backup of the registry),以防万一出现任何问题。
当你准备好时:
- 选择开始菜单,键入regedit,然后选择注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)应用程序。
- 在注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)中,导航到HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > Session Manager > MemoryManagement > PrefetchParameters。
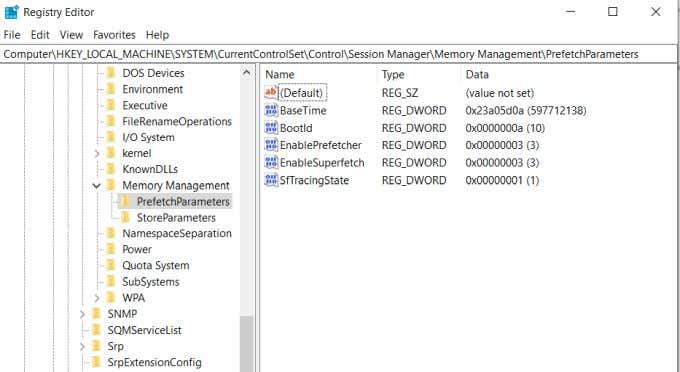
- 在本节中,您应该会看到一个名为EnableSuperfetch的键。右键单击该键并选择Modify。
- 在弹出的Edit DWORD窗口中,将(Edit DWORD)Value data字段更改为0并选择OK。

完成后,您可以关闭注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)。
此注册表项将禁用系统上的SuperFetch ( SysMain ) 服务。但是,在此注册表设置生效之前,您可能需要重新启动Windows计算机。(Windows)
使用命令提示符启用或禁用 SuperFetch (SysMain)(Enable Or Disable SuperFetch (SysMain) With Command Prompt)
如果您更喜欢使用命令提示符,可以使用一些简单的命令来启用或禁用SuperFetch服务。
首先以管理员模式(command prompt in administrator mode)打开命令提示符,然后使用以下命令:
- 启用(Enable):sc config “SysMain” start=auto & sc start “SysMain”
- 禁用(Disable):sc stop “SysMain” & sc config “SysMain” start=disabled
注意:如果您使用的是旧版本的Windows,请将上述命令中的“SysMain”替换为“SuperFetch”。
如果您更喜欢 PowerShell(prefer PowerShell),请使用管理员权限打开它并使用以下命令:
- 启用(Enable):Set-Service -Name “SysMain” -StartupType Automatic -Status Running
- 禁用(Disable):停止服务-强制-名称“SysMain”;设置服务-名称“SysMain”-StartupType
这种方法比在任务管理器(Task Manager)或Windows注册表中单击要快得多,也更简单。
如果这不能解决问题怎么办?(What If This Doesn’t Fix The Problem?)
如果禁用SuperFetch ( SysMain ) 不能解决您的问题,那么其他问题可能是问题的根源。
如果您仍然拥有 100% 的磁盘利用率,您可能需要升级到更大的硬盘驱动器,或者选择升级到SSD驱动器。SSD 驱动器(SSD drives)现在非常实惠,并且数据传输率远高于传统硬盘驱动器。
如果您遇到CPU利用率问题,请探索其他 CPU 故障排除技巧,以确定占用所有(other CPU troubleshooting tips)CPU资源的罪魁祸首。
What Is Superfetch (Sysmain) On Windows 10 And How To Disable It
Superfetch is a Windows sуstеm рroceѕs that has had multiple nаmes throughout the years. On Windowѕ XP іt was known as Prefetch. Superfetch was introduced in Windowѕ Vista, and on the latest versions of Windоws 10 it’s now known as Sysmain.
Ultimately, the purpose of every generation of Superfetch has been the same: to increase the performance of Windows by preloading apps you frequently use into RAM before you need to use them. But what is Superfetch?

How Does Superfetch (Sysmain) Work?
In the latest versions of Windows 10, the Superfetch service now shows up under the name SysMain. In the Task Manager, it shows up as Service Host: SysMain.
If you’re running an older version of Windows 10 or any version of Windows 7 or 8, this will show up in the Task Manager as Service Host: Superfetch.

This service runs in the background (using very little CPU power) and analyzes how much RAM you’re using and what apps you run most frequently. Any apps the service recognizes as “frequently used”, it’ll start preloading the app into RAM. This way, the next time you run the app, it’ll launch much more quickly.
You may be concerned that this means Superfetch is using up all of your RAM, but it isn’t. The service focuses on pre-loading apps into unused RAM. This doesn’t register as consumed memory. You’ll see this if you open Task Manager to the Processes tab and look at your Memory usage.

Even though Superfetch is consuming all unused RAM with preloaded apps, consumed RAM usage still doesn’t show 100%. This is because Superfetch is running in the background, and it’ll release any unused RAM it’s using whenever you need to use that memory for other active tasks.
Should You Kill Superfetch (Sysmain)?
Generally, there’s no need to stop Superfetch from running. It uses a very miniscule amount of CPU, and only uses unused RAM. All of this is unnoticeable to the general user.
However, there have been some reports throughout Microsoft user forums that sometimes the Superfetch (Sysmain) process actually causes performance issues. Some of these reported issues include:
- Constant 100% disk utilization.
- Overheating leading to system shutdown.
- Slow bootup time when you start your computer.
- On weak hardware, Superfetch could use more CPU and RAM than you might like.
- Has been known to cause performance issues while gaming.
The most common problem people report is the 100% disk utilization issue. If this is you, then disabling Superfetch or Sysmain may resolve the problem.
Since Superfetch is only a system optimization feature, you won’t hurt Windows by stopping the service. However, you may notice that launching your favorite apps may take a little longer than usual.
How To Disable Superfetch (Sysmain) In Windows 10
Is it safe to disable Superfetch?
If you aren’t experiencing performance issues or other problems, it’s a good idea to leave Superfetch (Sysmain) running. It is a useful process that significantly cuts down on the time it takes you to launch programs that you use frequently.
However, if you are experiencing high hard drive utilization, constant memory issues, or overall poor performance, you can try disabling Superfetch to see if it resolves the problem. If it does, then leave the service disabled. Otherwise, turn it back on and continue troubleshooting.
To disable Superfetch (Sysmain) on Windows 10:
- Select the Start menu, type services, and select the Services app. You could also press Windows + R, type services.msc and press Enter.
- In the Services app, scroll down to SysMain, right-click on the service and select Stop. If you’re running an older version of Windows, right-click on the SuperFetch service and select Stop.

- Now you need to prevent the service from restarting when you start Windows. Once the service is stopped, right-click on the service again and select Properties.
- In the Startup type dropdown, select Disabled.

Now the SuperFetch (SysMain) service is permanently disabled and will not restart the next time you start your computer.
Disable Superfetch (Sysmain) With Registry Editor
An alternative to using Task Manager to disable Superfetch on Windows 10 is using the Registry Editor.
Before you start doing anything inside the registry, make sure you take a full backup of the registry first, just in case anything goes wrong.
When you’re ready:
- Select the Start menu, type regedit, and select the Registry Editor app.
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > Session Manager > MemoryManagement > PrefetchParameters.

- In this section, you should see a key called EnableSuperfetch. Right-click this key and select Modify.
- In the Edit DWORD window that pops up, change the Value data field to 0 and select OK.

You can close the Registry Editor when you’re finished.
This registry entry will disable the SuperFetch (SysMain) service on your system. However, you may need to restart your Windows machine before this registry setting takes effect.
Enable Or Disable SuperFetch (SysMain) With Command Prompt
If you prefer working with the command prompt, there are some simple commands you can use to enable or disable the SuperFetch service.
Open the command prompt in administrator mode first, and then use the following commands:
- Enable: sc config “SysMain” start=auto & sc start “SysMain”
- Disable: sc stop “SysMain” & sc config “SysMain” start=disabled
Note: If you’re using an older version of Windows, replace “SysMain” with “SuperFetch” in the commands above.
If you prefer PowerShell, open it with administrator rights and use the following commands:
- Enable: Set-Service -Name “SysMain” -StartupType Automatic -Status Running
- Disable: Stop-Service -Force -Name “SysMain”; Set-Service -Name “SysMain” -StartupType
This approach can be much faster and simpler than clicking around in the Task Manager or the Windows registry.
What If This Doesn’t Fix The Problem?
If disabling SuperFetch (SysMain) doesn’t resolve your issue, then something else may be the source of the problem.
If you’re still having 100% disk utilization, you may need to upgrade to a larger hard drive, or opt to upgrade to an SSD drive. SSD drives are very affordable now, and have data-transfer rates far above that of traditional hard drives.
If you’re having CPU utilization issues, then explore other CPU troubleshooting tips to nail down the culprit that’s chewing up all of your CPU resources.







