借助 GIMP 或G NU I mage M操作程序,创建具有史诗般外观的缩略图和(P)高质量徽标(high-quality logos)从未如此简单且经济实惠。GIMP是一个免费使用的开源答案,适用于寻找Adobe Photoshop 替代品(Adobe Photoshop alternative)的图像编辑器。它对初学者也很友好,并且拥有一个充满技巧和窍门的蓬勃发展的社区,可帮助生成您的图像所需的更改和修订。
GIMP提供了大量工具和资源来拍摄任何图像并添加您自己的专业风格。那些从事网页设计、图形艺术家和业余摄影师的人会发现GIMP是一个很棒的程序,可以轻松满足他们的图像增强需求。对于那些刚开始从事图像处理(image manipulation)领域的人来说也是如此。

对于初学者,尤其是在处理新界面时,使用GIMP的冒险似乎令人生畏。当您想要的编辑很少时,裁剪或调整图像(image shouldn)大小等操作不应该要求您跳过箍。通过花时间学习基础知识以及在哪里寻找特定的东西,很快就会意识到为什么GIMP是一项伟大的投资。

一旦我们下载并安装了GIMP 程序(GIMP program),我们将研究基本的编辑,同时帮助导航界面,并引导您完成如何创建与本文所用的缩略图类似的缩略图。我们还将提供一些资源,您可以使用这些资源为未来的GIMP项目找到高级帮助。
下载并安装 GIMP(Download and Install GIMP)

- 导航到开发人员的网站(developer’s website)并选择您的下载。该文件将开始下载。等待几秒钟,直到尝试安装。
- 运行最近下载的文件。安装程序打开后,单击安装(Install )按钮将 gimp 安装到默认文件夹(default folder)。
- 要更改安装设置和加载项,请改为单击自定义。(Customize )
- 按照提供的所有安装说明进行操作。完全安装GIMP可能需要几分钟时间。
- 安装完成后,您就可以开始使用GIMP了。
使用 GIMP:学习基础知识(Using GIMP: Learning The Basics)

通过启动GIMP(GIMP)并将其拉到空白画布窗口(canvas window)开始以下步骤。我们将在每个部分中使用相同的图像。
Image Scaling/Resizing
- 单击(Click)“文件”选项卡并通过选择“打开”导入您的图像...(Open…) (CTRL + O)

- 图像加载后,单击“图像”选项卡,然后从下拉菜单中选择缩放图像。(Scale Image)

- 将出现一个对话框(dialog box)以启用编辑。

- 使用提供的选项缩放/调整图像大小。
- 通过宽度和高度(width and height)或 X、Y 分辨率(Y resolution)调整图像。
- 可以通过像素、百分比、厘米等进行修改。
- 了解使图像变大会导致图像像素化程度更高。
- 调整好参数后,单击“缩放(Scale )”继续。
文件大小减少(File Size Reduction)
- 单击“文件”选项卡并选择导出为...(Export As… )(Shift + CTRL + E)

- 选择要保存文件的名称和位置。(name and location)

- 单击(Click)选择文件类型(Select File Type)(按扩展名)旁边的“+”以打开文件类型(file type)列表以将其另存为。首选有损文件类型(file type),例如jpg 或 png 。(jpg or png)

- 接下来,单击“导出(Export )”按钮以弹出一个新的选项窗口。

- 保存的东西越少,图像文件(image file)的大小就越小。
- 确保将压缩级别(Compression level)设置为“ 9 ”以获得最小尺寸。
- 确定要保存图像的哪些元素后,单击导出(Export)。
图像裁剪(Image Cropping)
- 导航到“工具”选项卡并选择“Transform Tools > Crop” (Shift + C)

- 您还可以通过单击界面左上角附近工具文档中的图标来选择(Tool Doc)裁剪工具。(Crop Tool)

- 接下来,按住鼠标左键,将光标拖过要作为最终图像制作的区域。
- 确定后,您选择的部分之外的图像的所有部分都会变暗,而设置为最终图像的部分将保持不变。

- 您可以使用框的角来调整区域,方法是通过拖动鼠标按钮(mouse button)来缩小或扩大它们。
- 获得所需的图像后,左键单击它,按Enter,或同时按Shift + C以裁剪到您的选择。

图像旋转(Image Rotation)
对于此修改,我们将导入另一个图像以叠加在当前图像之上。
- 在“文件”选项卡中,选择“打开为图层...”(Open As Layers…)(CTRL + ALT + O)

- 选择要添加到图像的图层,在本例中,我们将使用箭头,然后单击打开(Open)。
- 您会看到新图层放置在当前图像的顶部。要查看图层是如何堆叠的,图层窗口(layer window)位于右侧。

- 突出显示新图层后,返回“变换工具”(Transform Tools)并选择“旋转(Rotate)” 。您还可以在工具文档中找到(Tool Doc)旋转工具图标(Rotate Tool icon)。

- 这将拉出一个新的弹出窗口,同时将类似标线的纹理应用于您的图像。

- 如果您知道要应用的旋转角度,则可以在提供的框中输入值。如果没有,您可以选择使用标有“角度”框下方的滑动条,或者使用鼠标左键单击并拖动来自行旋转图像。(slide bar)
- 一旦结果符合您的喜好,请单击Rotate。
设计缩略图(Designing a Thumbnail)
在本节中,我们将向您展示我们如何使用GIMP(GIMP)为本文创建缩略图。本教程的部分内容将使用学习基础(Learning the Basics)中使用的一些工具。
在我们开始之前,最好收集您可能需要的任何图像。因为缩略图一直保持简单,所以它需要的唯一图像层是(image layer)GIMP 徽标(GIMP logo),通过Wikipedia获得。
下载并保存到您的计算机后,我们就可以开始了。
- 打开“文件”选项卡并选择新建...(New…) (CTRL + N)
- 这将打开一个“创建(Create)新图像”窗口,您可以在其中从预先创建的模板(Template)中选择或手动决定图像的大小。
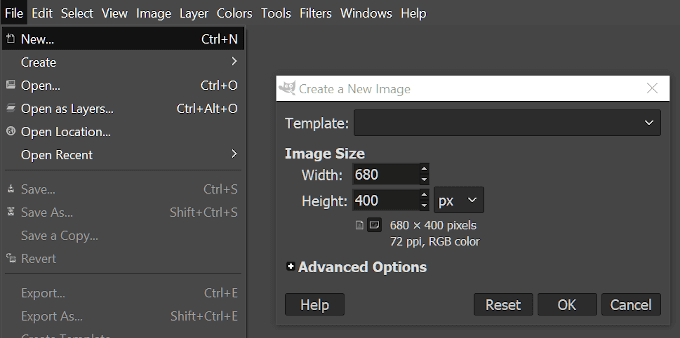
- 我们的缩略图永远不会大于 680px 宽度,因此我们将设置我们的图像大小(image size)。至于高度,我们将保持在 400px。
- 设置尺寸后,单击OK。
- 我们现在应该看一个空白(白色)的画布。您可以选择使用工具文档(Tool Doc)中的桶填充工具(Bucket Fill Tool)为背景着色,但现在我们将其保持为白色。
- 最好的办法是现在添加您的附加层,这样一旦我们开始添加文本,我们就可以对其进行调整,使其不会遮挡(t block)图像。因此,打开“文件”选项卡,这次选择“(time select) 作为图层打开”……(Open As Layers…)就像我们在图像旋转(Image Rotation)期间为箭头所做的那样。选择您之前下载的GIMP 徽标(GIMP logo),然后单击打开(Open)。
- 图层图像(layer image)是 1200 x 1200 ,对于680 x 400 的主图像来说太大了。我们需要将其缩小。如果您按照上述说明进行操作,请将图像宽度和高度(image width and height)调整为 200 像素。
- 然后我们可以将图像拖到一边,这样它就不会妨碍我们的文本,直到我们需要重新定位它。

- 接下来是正文。我们将使用快捷命令(shortcut command)并按下键盘上的“ T ”键来选择文本工具(Text Tool)。现在,左键单击图像漂亮的白色区域并开始输入您的标题。

- 全部输入后,突出显示文本(CTRL + A)并选择您要使用的字体。我们使用了Bauhaus 93字体,它不是标准字体。GIMP将获取位于Windows 字体文件夹(Windows Font folder)中的所有字体并将它们添加到其选择库中。您可以通过从DaFont和Google Fonts等网站下载其他字体并将它们移动到Windows Font 文件夹(Windows Font folder)来添加其他字体。
- 接下来,调整字体的大小,使其与图像完全吻合,但不会占用太多空间。我们选择了 100px。
- 进行文本调整后,您可以通过切换到移动工具来移动(Move Tool)文本框(text box)以适应您需要的位置。您可以通过单击不是文本的图像区域并单击“ (text and clicking ‘)M ”来轻松完成此操作。
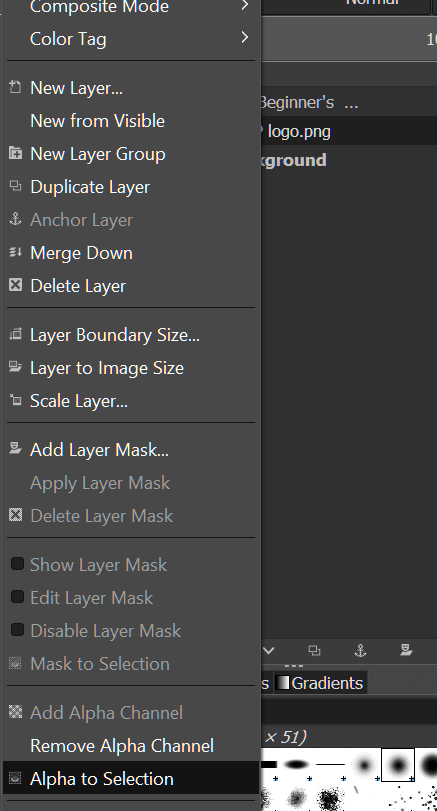
- 在右侧窗口中选择文本层(text layer),右键单击它,然后从列表中选择(list select) Alpha to Selection。这将为图像中的文本添加动画边框。
- 接下来,我们将需要添加一个附加层。为此,在同一个右侧窗口(side window)中,找到并单击创建新图层(Create a New Layer)按钮。这将打开创建新图层的窗口。不要担心这里的大部分内容,这是一个更高级的教程。现在,只需确保“填充:”部分(” section)在下拉列表中具有透明度,然后单击(Transparency )确定(OK)。

- 将创建一个新图层,镜像您已将Alpha(Alpha)应用于选择(Selection)的文本。默认情况下它应该是选定的图层。我们现在要在文本周围添加一个边框。
- 单击“选择”选项卡并选择“增长(Grow)” 。在弹出的选择框中,将值设置为“ (selection box)2 ”,然后单击“确定(OK)” 。

- 此时,为了方便您,请单击图层窗口中原始文本图层(text layer)旁边的眼睛图标。(Eye icon)单击后眼睛会消失,这将在您填充边框时隐藏文本的可见性。

- Click Shift + B选择桶填充工具(Bucket Fill Tool),然后单击主颜色方块(color square)以打开颜色选项。您可以从几个默认选项中进行选择或创建自己的选项。我们选择了带有HTML 符号(HTML notation)1b56ff的蓝色阴影。
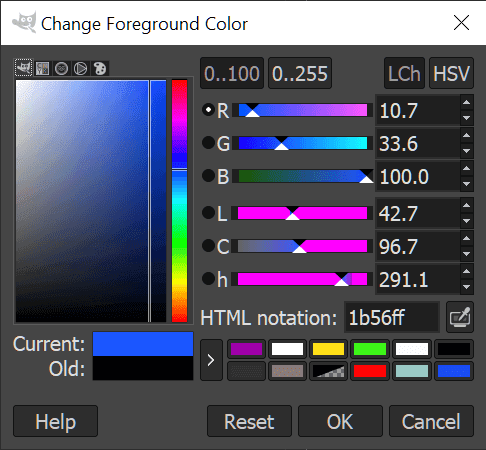
- 如果您碰巧对CSS(CSS)有所了解,则可以使用该框中的颜色代码。
- 将(Drag)光标拖到由动画边框标记的不可见文本区域上,然后左键单击以填充颜色。

- 单击(Click)眼睛图标(Eye icon)曾经所在的区域以重新显示原始文本。然后,将原始文本拖到图层窗口(layer window)中的彩色图层上方。
- 右键单击最顶层并选择Merge Down。图像现在应该如下所示:

- 现在我们将为文本添加一些阴影。单击(Click)“滤镜”选项卡,选择Light and Shadow > Drop Shadow (Legacy)…
- 在弹出窗口(pop-up window)中,选择阴影的 x,y 访问、半径和不透明度。

- 对于缩略图,我们在 X 和 Y 中选择了“ 8 ”,在模糊半径中选择了“ (blur radius)20 ” ,并将不透明度调至“ 100 ”。
- 您可以更改阴影的颜色以使其在背景上更明显,例如,如果您的背景是黑色的,最好选择更亮的颜色(brighter color)。然而,由于我们的背景是白色的,黑色就很好了。
- 为避免图像发生偏移,请在按OK之前取消选中标记为(OK)Allow resizing的框。
- 合并(Merge Down)文本图层(text layer)顶部的阴影图层(Drop Shadow layer)。
- “选择”选项卡 >无(None)(Shift + CTRL + A)
- 这不是必需的,但我们决定为GIMP 徽标(GIMP logo)添加阴影。如果您选择这样做,方向是相同的。除此之外,选择GIMP 徽标(GIMP logo)图层并将其移动到缩略图中所需的位置。
- 最后,如果您觉得白色背景不够,可以突出显示背景图层(Background layer),选择桶填充工具(Bucket Fill Tool),然后继续添加一些颜色。我们选择了一种微妙的灰色,以免淹没阴影。成品应如下所示:

- 现在,所需要做的就是导出为(Export As)并将其保存到您的首选位置。
使用 GIMP:附加帮助(Using GIMP: Additional Help)

一旦您开始使用GIMP(GIMP)不久,您就会觉得自己已经掌握了基础知识并开始寻求更复杂和专业的风格编辑。有无数的教程可以帮助您扩展您对GIMP 软件(GIMP software)的工作知识。
您可以从官方 GIMP 教程部分开始,但我更喜欢使用(official GIMP tutorials section)YouTube准确搜索我正在寻找的内容。
GIMP还拥有遍布互联网的大型用户社区,其中包括(user community)subreddit、非官方讨论平台(如GIMP 论坛(GIMP Forums)和GIMP 聊天(GIMP Chat))、StackExchange的图形设计部分(Graphic Design section)中的标记问题以及(tagged questions)Google Plus GIMP 用户(GIMP users)组等社交媒体渠道。
The Beginner’s Guide To Using GIMP
Τhanks to GIMP, or the GNU Image Manipulation Program, it’s never been easier and more affordable to create epic looking thumbnails and high-quality logos. GIMP is a free to use, open-source answer to image editors looking for an Adobe Photoshop alternative. It’s also quite beginner friendly and has a thriving community filled with tips and tricks to help produce the alterations and revisions that your image requires.
GIMP provides plenty of tools and resources to take any image and add your own professional touch. Those in web design, graphic artists, and amateur photographers will find that GIMP is a great program that can easily accommodate their image enhancing needs. The same can also be said for those just starting out in image manipulation fields.

For beginners, especially when it comes to dealing with new interfaces, your adventure into using GIMP can seem daunting. When the edits you want are minimal, something along the lines of cropping or resizing an image shouldn’t require that you jump through hoops. By taking the time to learn the foundations and where to look for specific things, it won’t take long to realize why GIMP is a great investment.

Once we’ve downloaded and installed the GIMP program, we’ll look into basic editing, while helping navigating the interface, and walk you through how to create a thumbnail like the one used for this article. We’ll also provide a few resources you can use to find advanced help for future GIMP projects.
Download and Install GIMP

- Navigate to the developer’s website and select your download. The file will begin downloading. Allow a few seconds to pass until attempting to install.
- Run the recently downloaded file. Once the installer opens, click the Install button to have gimp installed to the default folder.
- To change installation settings and add-ons, click Customize instead.
- Follow all installation instructions as they’re presented. It may take several minutes for GIMP to be fully installed.
- After installation is complete, you can begin using GIMP.
Using GIMP: Learning The Basics

Begin the steps below by having GIMP launched and pulled up to a blank canvas window. We’ll use the same image throughout each section.
Image Scaling/Resizing
- Click the “File” tab and import your image by selecting Open… (CTRL + O)

- After the image loads in, click the “Image” tab and select Scale Image from the drop-down menu.

- A dialog box will appear to enable edits.

- Scale/Resize your image using the options provided.
- Adjust the image by width and height or the X, Y resolution.
- Modifications can be made by pixels, percent, centimeters, etc.
- Understand that making the image larger can result in a more pixelated image.
- Once parameters have been adjusted, click Scale to proceed.
File Size Reduction
- Click the “File” tab and select Export As… (Shift + CTRL + E)

- Choose a name and location for where you’d like to save the file.

- Click the ‘+’ next to Select File Type (By Extension) to open a list of file types to save it as. A lossy file type such as jpg or png is preferred.

- Next, click the Export button to have a new window of options pop-up.

- The less things saved, the smaller the size of the image file.
- Ensure that the Compression level is set to ‘9’ for the smallest size.
- Once you’ve decided which elements of the image you’d like saved, click Export.
Image Cropping
- Navigate to the “Tools” tab and select Transform Tools > Crop (Shift + C)

- You can also select the Crop Tool by clicking on its icon in the Tool Doc near the top-left of the interface.

- Next, holding down the left-mouse button, drag your cursor across the area you want to make as your final image.
- Once settled, all parts of the image outside of the part you selected, will darken while the part set as your final image will remain intact.

- You can adjust the area using the corners of the box by either shrinking or expanding them by dragging your mouse button.
- Once you have the image as you’d like it, either left-click it, press Enter, or press Shift + C simultaneously to crop to your selection.

Image Rotation
For this modification, we’re going to import another image to layer atop our current image.
- In the “File” tab, select Open As Layers… (CTRL + ALT + O)

- Select the layer you’d like to add to the image, in this case we’ll be using an arrow, and click Open.
- You’ll see the new layer placed on top of the current image. To see how the layers are stacked, the layer window is located on the right.

- With the new layer highlighted, head back into Transform Tools and choose Rotate. You can also find the Rotate Tool icon in the Tool Doc.

- This will pull up a new pop-up window while applying a reticle-like texture to your image.

- If you know the angle of rotation you want to apply, you can enter the values into the provided boxes. If not, you can choose to use the slide bar just below the box labeled ‘Angle’ or rotate the image yourself using your mouse’s left-click and drag.
- Using the exact values provides more precise results, quicker.
- Once the results are to your liking, click Rotate.
Designing a Thumbnail

In this section, we’re going to show you how we created the thumbnail for this article using GIMP. Portions of this tutorial will use some of the tools used in Learning the Basics.
Before we begin, it’s best to gather up any images you may need. Because the thumbnail has been kept simple, the only image layer it will require is the GIMP logo, acquired via Wikipedia.
Once downloaded and saved to your computer, we can get started.
- Open the “File” tab and select New… (CTRL + N)
- This will pull up a “Create a New Image” window where you can select from a pre-created Template or decide on the size of the image manually.

- Our thumbnails are never any larger than 680px width, so we’ll set our image size as such. As for the height, we’ll keep it at 400px.
- Once the dimensions are set, click OK.
- We should now be looking at a blank (white) canvas. You can choose to color the background however you like using the Bucket Fill Tool in the Tool Doc, but for now, we’ll keep it white.
- The best thing to do is add your additional layer now, that way once we begin adding the text, we’ll be able to adjust it so that it doesn’t block out the image. So, open the “File” tab and this time select Open As Layers… just as we did for the arrow during Image Rotation. Select the GIMP logo you downloaded earlier and click Open.
- The layer image is a 1200 x 1200 which is much too large for our primary image at 680 x 400. We’ll need to scale it down. If you follow the instructions illustrated above, adjust the image width and height to 200px.
- We can then drag the image off to the side so that it’s out of the way for our text until we need to reposition it.

- Next comes the text. We’ll use the shortcut command and hit the ‘T’ key on your keyboard to have the Text Tool selected. Now, left-click in the nice white area of the image and begin typing your title.

- Once it’s all typed out, highlight the text (CTRL + A) and select the font you’d like to use. We used the Bauhaus 93 font, which isn’t a standard font. GIMP will take all fonts located in the Windows Font folder and add them to its library of choices. You can add additional fonts by downloading them from sites like DaFont and Google Fonts and moving them over to the Windows Font folder.
- Next, adjust the size of the lettering so that it fits well within the image but doesn’t take up too much room. We settled on 100px.
- Once the text adjustments have been made, you can move the text box around to fit where you need it by swapping to the Move Tool. You can do this easily by clicking on an area of the image that isn’t the text and clicking ‘M’.

- Select the text layer in the window to the right, right-click it, and from the list select Alpha to Selection. This will add an animated border to the text in the image.

- Next, we’re going to need to add an additional layer. To do this, in the same right side window, locate and click the Create a New Layer button. This will open up the window to create a new layer. Don’t worry about most of what is on here, that’s for a more advanced tutorial. For now, just ensure that the “Fill with:” section has Transparency in the drop-down and click OK.

- A new layer mirroring the text that you had applied Alpha to Selection is created. It should be the selected layer by default. We’re now going to add a border around the text.
- Click the “Select” tab and choose Grow. In the selection box that pops up, set the value to ‘2’ and click OK.

- At this point, to make it easier for you, click the Eye icon next to the original text layer in the layers window. The eye will disappear once clicked, and this will hide the text’s visibility while you bucket fill in the border.

- Click Shift + B to select the Bucket Fill Tool and then click on the main color square to open up color options. You can select from a few default options or create your own. We settled on a shade of blue with the HTML notation of 1b56ff.

- If you happen to know a little about CSS, you can use the color codes in that box.
- Drag your cursor over the invisible text area marked by the animated border, and left-click to fill it with color.

- Click the area where the Eye icon used to be to re-reveal the original text. Then, drag the original text above the colored layer in the layer window.
- Right-click the top most layer and select Merge Down. The image should now look like this:

- Now we’ll add a bit of shadow to the text. Click the “Filters” tab, select Light and Shadow > Drop Shadow (Legacy)…
- In the pop-up window, select the x,y access of the shadow, the radius, and the opacity.

- For the thumbnail we selected ‘8’ in both X and Y, ‘20’ in blur radius, and cranked the opacity to ‘100’.
- You could change the color of the shadow to make it more visible on the backdrop, say for instance if your background was black it would be better to choose a brighter color. However, since our background is white, black is perfectly fine.
- To avoid a shift in the image, uncheck the box marked Allow resizing before pressing OK.
- Merge Down the Drop Shadow layer on top of your text layer.
- “Select” tab > None (Shift + CTRL + A)
- It’s not necessary but we decided to add a shadow to the GIMP logo. If you choose to do so, the directions are the same. Other than that, select the GIMP logo layer and move it into the position you want in the thumbnail.
- At the end, should you feel the white background to not be adequate, you can highlight the Background layer, select the Bucket Fill Tool, and proceed to add a bit of color. We’ve chosen a subtle gray so as not to drown out the shadowing. The finished product should look like this:

- Now, all that’s needed is to Export As and save it to your preferred location.
Using GIMP: Additional Help

It won’t be long once you start using GIMP before you’ll feel like you’ve mastered the basics and look toward more complicated and professional style editing. There are countless tutorials out there to sink your teeth into that can help with expanding your working knowledge of GIMP software.
You can begin in the official GIMP tutorials section but I prefer to search exactly what I’m looking for using YouTube.
GIMP also has a large user community spread across the internet that includes a subreddit, unofficial discussion platforms like GIMP Forums and GIMP Chat, tagged questions in the Graphic Design section of StackExchange, and social media channels like the Google Plus GIMP users group.


































