任何操作系统都可能崩溃,包括Ubuntu。如果您在运行Linux并遇到问题,这里有一些原因和解决方案可以帮助您摆脱崩溃。
如果Ubuntu挂起,首先要尝试的是重新启动系统(reboot your system)。有时您可能需要进行冷启动。关闭计算机电源,然后将其重新启动。重新启动计算机可以解决许多问题,例如内存不足、应用程序崩溃和浏览器挂起。
(Make)记下您在计算机崩溃之前所做的事情。如果在使用特定应用程序时总是发生这种情况,请研究以了解是否有任何更新或已知问题。众所周知,某些应用程序有时会崩溃,例如Audacity和 OpenShot Video Editor。

要解决应用程序问题,请重新启动、修复或重新加载软件。或者,通知创建它的人。
Firefox更新也导致Linux死机。在他们解决问题之前,您可能必须避免使用Firefox 。
如果应用程序没有导致您的问题,则您的硬盘驱动器可能空间不足或存在硬件问题。
本文介绍了以下诊断崩溃并从崩溃中恢复的方法:
- 释放硬盘空间
- 测试你的记忆力
- 硬件故障
- 间歇性硬件问题
- 从 X 服务器崩溃中恢复
- 从另一个来源启动 Linux
如何释放硬盘空间(How To Free Up Hard Drive Space)
- 要了解硬盘驱动器上有多少可用空间,请单击“开始(Start)”按钮,然后单击“附件(Accessories)”,然后单击“磁盘(Disks)” 。

Ubuntu没有像 Windows 一样的磁盘清理工具和内置碎片整理(built-in defrag like Windows)工具。那么,你能做些什么来释放一些磁盘空间呢?
- 清空你的垃圾
- 删除 .ISO 下载
- 删除(Remove)不再需要的旧内核
- 卸载不使用的游戏和应用
- 使用系统清洁剂
- 定期清理 APT 缓存
- 保持系统更新
上面的最后一个要点似乎违反直觉。与占用更多空间的Windows更新相比, (Windows)Linux更新释放空间。
记忆不足(Low Memory)

如果您正在运行Ubuntu并且系统随机崩溃,则可能是内存不足。内存不足可能是由于打开的应用程序或数据文件多于您已安装的内存容量。
如果这是问题所在,请不要一次打开这么多或在计算机上升级到更多内存。
内存不足的另一个原因是RAM出现故障。运行内存测试以确定您的RAM内存是否损坏。
如何执行内存测试(How To Perform a Memory Test)
- 首先打开或重新启动系统。
- 按住键盘上的(Bring)Shift 键(Shift)调出GRUB菜单。
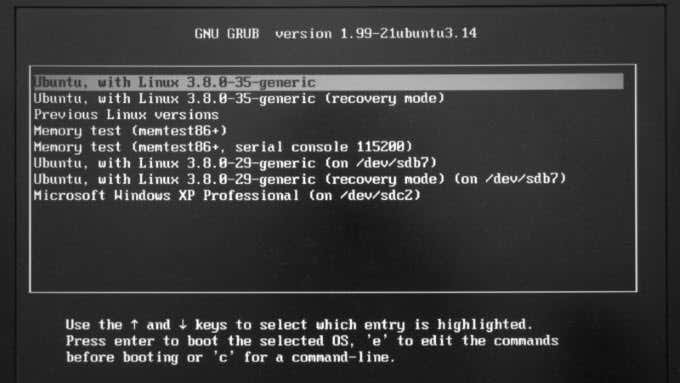
- 使用箭头键,找到Ubuntu memtest86+标签。

- 按下回车键后,内存测试将自动运行。测试运行时,您将看到蓝屏。
- 在您按下退出键之前,测试不会结束。让测试运行至少一次完整的通过。如果您的问题是间歇性的,请让测试运行更长时间。
如果测试发现任何错误,您需要更换一张RAM存储卡。
其他硬件故障(Other Hardware Failures)
如果您的计算机关机并且根本无法开机(没有灯也没有声音),请首先检查以确保插座有电。如果您的插座有电,最可能的原因是电源故障。
如果它尝试通电然后在 30 秒内重新断电,则可能是风扇速度缓慢或不转动。或者检测风扇速度的传感器可能出现故障。
其他可能导致您的计算机崩溃的组件包括:
- (Overheating)由于风扇速度缓慢或根本不转动而导致过热
- 硬盘崩溃
- 电源不好
- 主板或CPU故障
- 显卡问题
- 传感器
您还可以自己测试硬盘驱动器的故障。一定数量的错误是可以接受的。即使是新的硬盘驱动器也已经有一些错误。

如果您知道如何自行维修,请更换故障组件。否则,请让您的计算机技术人员修理您的机器。
间歇性硬件问题(Intermittent Hardware Problems)
偶发问题的最常见原因是内存过热故障和硬盘驱动器错误。
如果测试无法识别出故障组件,您可能必须一次更换一个,直到发现问题为止。
从 X 服务器崩溃中恢复(Recovering From an X Server Crash)
Linux系统提供了多种从崩溃中恢复的方法。最简单的方法是重新启动。但是还有其他方法:
- 使用键盘快捷键重新启动 X 服务器。
- 切换虚拟控制台。
- (Kill)使用SSH通过网络(SSH)终止X 服务器。
- 使用 Magic SysRq 键。
从另一个来源启动 Linux(Boot Linux From Another Source)
如果您的计算机开机但拒绝加载Linux怎么办?您的硬盘驱动器可能损坏,或者操作系统文件可能已损坏。
如果您制作了Ubuntu Live CD 或USB,您可以从其他操作系统启动。
您需要提前完成此操作。或者,您在另一台计算机上进行实时启动。
有关详细说明,请参阅创建可引导 Linux USB 驱动器的工具或如何构建自己的可引导 Linux Live CD(How to Build Your Own Bootable Linux Live CD)。
许多因素都可能导致您的系统崩溃。没有一种解决方案。在最坏的情况下,如果上述建议都不起作用,您可能需要一台新计算机或一位优秀的计算机技术人员。
Common Reasons for Ubuntu Crashes and How to Recover
Any operаting system can crash, including Ubuntu. If you are running Linux and have a problem, here are a few reasons and solutions to help you get out of your crash.
If Ubuntu hangs, the first thing to try is to reboot your system. Sometimes you might have to do a cold boot. Power your computer off and then bring it back up. Restarting your computer resolves many problems such as low memory, application crashes, and the browser hangs.
Make note of what you did just before the computer crashed. If it always happens while using a specific application, research to find out if there are any updates or known issues. Some applications are known to crash at times, such as Audacity and OpenShot Video Editor.

To resolve application issues, restart, repair or reload the software. Or, notify the people who created it.
Firefox updates have also caused Linux to freeze. You may have to avoid using Firefox until they fix the issues.
If an application is not causing your problem, you may be out of room on your hard drive or have a hardware issue.
This article covers the following ways to diagnose and recover from a crash:
- Freeing up hard drive space
- Testing your memory
- Hardware failures
- Intermittent hardware problems
- Recovering from an X Server crash
- Boot Linux from another source
How To Free Up Hard Drive Space
- To find out how much free space you have on your hard drive, click the Start Button, then Accessories, and then Disks.

Ubuntu doesn’t have the same disk clean-up tools and built-in defrag like Windows. So, what can you do to free up some disk space?
- Empty your trash
- Delete .ISO downloads
- Remove old kernels you no longer need
- Uninstall games and apps you don’t use
- Use a system cleaner
- Regularly clean APT Cache
- Keep your system updated
The last bullet point above might seem counterintuitive. Linux updates free up space as opposed to Windows updates that take up more space.
Low Memory

If you are running Ubuntu and your system randomly crashes, you may be running out of memory. Low memory could be caused by opening more applications or data files than will fit in the memory you have installed.
If that is the problem, do not open so much at one time or upgrade to more memory on your computer.
Another cause of low memory is a failing RAM. Run a memory test to determine whether your RAM memory is bad.
How To Perform a Memory Test
- Start by turning on or restarting your system.
- Bring up the GRUB menu by holding down Shift on your keyboard.

- Using the arrow keys, find the Ubuntu memtest86+ label.

- After you press the enter key, the memory test will automatically run. You will see a blue screen while the test is running.
- The test won’t end until you press the escape key. Let the test run for at least one full pass. If your problem is very intermittent, let the test run much longer.
Should the test find any errors, you need to replace one of your RAM memory cards.
Other Hardware Failures
If your computer powers off and will not power on at all (has no lights and no sounds), first check to make sure there is power at the outlet. The most likely cause if you have power at the outlet is a bad power supply.
If it tries to power up and then powers back down within 30 seconds, you may have a slow or non-moving fan. Or the sensor that detects fan speed may be failing.
Other components that can cause your computer to crash are:
- Overheating due to fans being slow or not turning at all
- Hard drive crash
- Bad power supply
- Failing motherboard or CPU
- Graphics card problems
- Sensors
You can also test your hard drive for failures yourself. A certain number of errors are acceptable. Even new hard drives already have some errors.

If you know how to do your own repairs, replace the failing component. Otherwise, have your computer technician repair your machine.
Intermittent Hardware Problems
The most common causes of sporadic problems are overheating memory failures and hard drive errors.
If testing doesn’t identify the failing component, you may have to replace them one at a time until you find the problem.
Recovering From an X Server Crash
Linux systems provide multiple ways to recover from a crash. The easiest way is a reboot. But there are other methods:
- Use a keyboard shortcut to restart the X server.
- Switch virtual consoles.
- Kill the X server over the network using SSH.
- Use the Magic SysRq key.
Boot Linux From Another Source
What if your computer powers on but refuse to load Linux? You could have a bad hard drive, or the operating system files could be corrupted.
If you have made an Ubuntu Live CD or USB, you can boot from that other operating system.
You need to have done this in advance. Or, you make a Live boot on a different computer.
See Tools To Create A Bootable Linux USB Drive or How to Build Your Own Bootable Linux Live CD for detailed instructions.
Many factors can cause your system to crash. There isn’t one solution. In the worst-case scenario, if none of the above suggestions work, you may need a new computer or a good computer technician.






