
您可能知道,有许多活动的后台进程和服务有助于Windows的顺利运行。这些后台进程/服务中的大多数使用最少的CPU 功率和 RAM(CPU power and RAM)。虽然,有时一个进程可能会出现故障或被破坏并最终使用比平时更多的资源,而为其他前台应用程序留下的资源很少。诊断策略服务(Policy Service)就是这样一个因在极少数情况下会占用系统资源而臭名昭著的过程。
诊断策略服务(Diagnostic Policy Service)是Svchost.exe(服务主机(Service Host))的共享进程之一,负责检测各种Windows组件的问题并对其进行故障排除。如果可能,该服务会尝试自动修复任何检测到的问题,如果没有,则记录诊断信息以进行分析。由于问题的诊断和自动故障排除是无缝体验的重要功能,因此诊断策略服务(Diagnostic Policy Service)已设置为在计算机启动时自动启动并在后台保持活动状态。消耗更多CPU 功率(CPU power)背后的确切原因超出预期的情况未知,但根据潜在的解决方案,罪魁祸首可能是服务的损坏实例、损坏的系统文件、病毒或恶意软件攻击(virus or malware attack)、大型事件日志(event log)文件等。
在本文中,我们解释了五种不同的方法,可帮助您将诊断策略服务的CPU消耗(Diagnostic Policy Service)恢复(CPU consumption)到正常水平。
修复服务主机(Fix Service Host):诊断策略服务高 CPU 使用率(Policy Service High CPU Usage)
诊断策略服务高 CPU 使用率的潜在修复(Potential fixes for Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU Usage)
大多数用户只需重新启动诊断策略服务即可解决异常高的(Diagnostic Policy Service)磁盘使用率(disk usage)问题。其他人可能需要执行一些扫描(SFC 和 DISM(SFC and DISM))来查找损坏的系统文件或运行内置的性能故障排除(performance troubleshooter)程序。更新到最新版本的 Windows(latest version of Windows)并清除事件查看器日志也可以解决此问题。最后,如果似乎没有任何效果,用户可以选择禁用该服务。但是,禁用诊断策略服务(Policy Service)意味着Windows将不再执行自动诊断和解决错误。
方法一:从任务管理器(Task Manager)结束进程
如果某件事提示了它的损坏实例,则一个进程可能会占用额外的系统资源。在这种情况下,您可以尝试手动终止进程(此处为诊断策略服务(Policy Service)),然后让它自动重新启动。所有这些都可以通过Windows 任务管理器(Windows Task Manager)(使用Windows 任务管理器(Windows Task Manager)杀死资源密集型进程(Kill Resource Intensive Processes))来实现。
1. 右键单击(Right-click )开始菜单( Start menu)按钮并选择任务管理器(Task Manager)。

2. 单击更多详细信息(More Details)以展开任务管理器(Task Manager)并查看所有当前活动的进程和服务。(currently active processes & services.)

3.找到服务主机:(Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service) Windows进程下的诊断策略服务。右键单击(Right-click )它并选择End task。(您也可以通过左键单击(left-click)选择服务,然后单击右下角的结束任务(End Task) 按钮(button)。)

诊断策略服务(Diagnostic Policy Service)将自动重新启动,但如果没有,只需重新启动计算机并检查问题是否仍然存在。
方法 2:运行 SFC 和 DISM 扫描
最近的Windows 系统(Windows system)更新甚至是防病毒攻击都可能损坏了某些系统文件,从而导致诊断策略服务(Diagnostic Policy Service)的CPU 使用率(CPU usage)很高。幸运的是,Windows具有内置实用程序来扫描和修复损坏/丢失的系统文件。第一个是系统文件检查器实用程序(System File Checker utility),顾名思义,它检查所有系统文件的完整性并用缓存副本替换损坏的文件。如果SFC扫描无法修复损坏的系统文件,用户可以使用部署映像服务和管理(Deployment Image Servicing and Management)( DISM )命令行工具(command-line tool)。
1.在Windows 搜索栏中(Windows search bar and click)键入命令提示符(Command Prompt),并在搜索结果到达时单击右侧面板中的以管理员身份运行。(Run as Administrator)

2.在命令提示符窗口中输入sfc /scannow并回车(Command Prompt window and press enter)执行。扫描可能需要一段时间,所以请坐下来,在验证过程(verification process)达到 100%之前不要关闭窗口。

3. 完成SFC 扫描(SFC scan)后,执行以下DISM 命令(DISM command)。同样(Again),请耐心等待扫描和恢复过程完成,然后再退出应用程序。完成后重新启动(Restart)计算机。
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

另请阅读:(Also Read:)如何通过系统空闲进程(System Idle Process)修复高 CPU 使用率(Fix High CPU Usage)
方法 3:更新 Windows 并运行性能(Run)疑难解答(Performance Troubleshooter)
如前所述,最近的Windows 更新也可能是(Windows update)诊断策略服务(Diagnostic Policy Service)异常行为的罪魁祸首。您可以尝试回滚到以前的更新或查找Microsoft推送的任何新更新以纠正错误。如果您在更新Windows时遇到任何问题,请运行内置更新疑难解答。
除了更新Windows之外,还可以运行系统性能疑难解答(System Performance troubleshooter)来扫描任何性能问题并自动修复它们。
1. 同时按Windows key + I 启动系统设置( System Settings ),然后单击更新和安全(Update & Security )设置。

2. 在Windows 更新选项卡(Windows Update tab)上,单击检查更新(Check For Updates)。该应用程序将开始寻找任何可用的更新并自动开始下载它们。安装新更新后重新启动计算机。(Restart)

3. 检查诊断策略服务(Diagnostic Policy Service)是否仍在占用您的系统资源,如果是,则运行更新疑难解答(Update troubleshooter)。再次打开更新和安全(Update & Security)设置并移至疑难解答(Troubleshoot )选项卡,然后单击其他疑难解答(Additional Troubleshooters)。

4. 在启动(Get)并运行部分下,单击Windows 更新(Windows Update)以查看可用选项,然后单击随后的运行疑难解答(Run the troubleshooter)按钮。按照屏幕上的说明完成故障排除过程(troubleshooting process)。
要运行系统性能疑难解答:(To run the System Performance troubleshooter:)
1.在开始搜索栏中键入(Search bar)控制面板(Control Panel),然后按Enter 键(Enter)打开它。

2. 单击故障排除(Troubleshooting)。
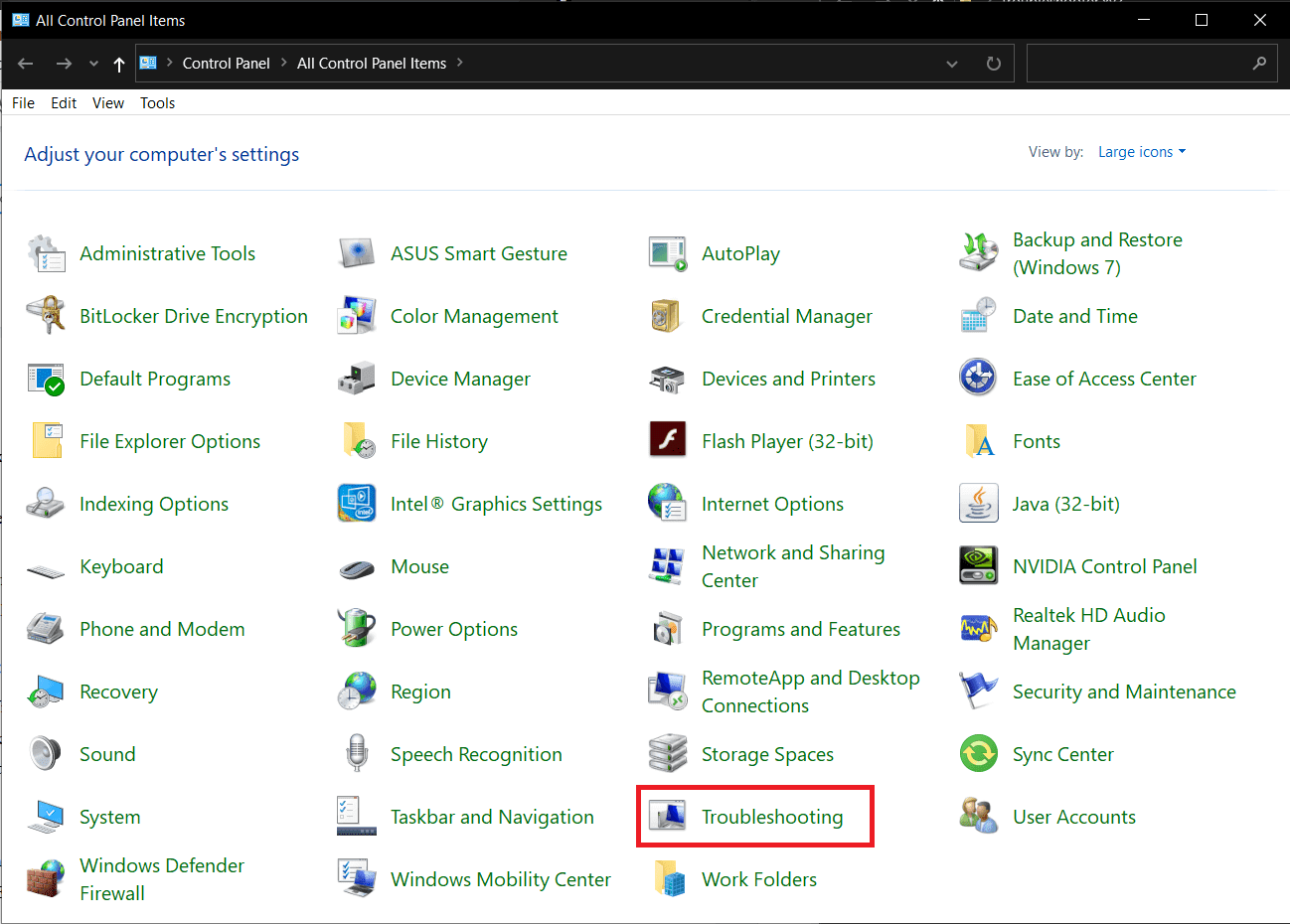
3. 在系统和安全(System and Security)下,单击运行维护任务(Run maintenance tasks)超链接。

4. 在以下窗口中,单击高级并选中(Advanced )自动应用修复(Apply repairs automatically)旁边的框。单击下一步(Next )以运行疑难解答。

另请阅读:(Also Read:) 修复桌面窗口管理器高 CPU(Fix Desktop Window Manager High CPU) ( DWM.exe )
方法 4:清除事件查看器日志(Event Viewer log)
事件查看器程序(Event Viewer program)维护所有应用程序和系统错误消息(application and system error messages)、警告等的记录。这些事件日志可以累积到相当大的大小,并为服务主机进程(Service Host process)提示问题。简单地(Simply)清除日志可以帮助解决诊断策略服务(Diagnostic Policy Service)的问题。我们建议您定期清除事件查看器(event viewer)日志以避免将来出现任何问题。
1.按Windows key + R运行命令(Run command)框,键入eventvwr.msc并单击确定(Ok )以打开事件查看器( Event Viewer)应用程序。

2. 在左侧窗格中,通过单击小箭头展开(arrow and select)Windows 日志(Windows Logs)文件夹,然后从随后的列表中选择应用程序。(Application )

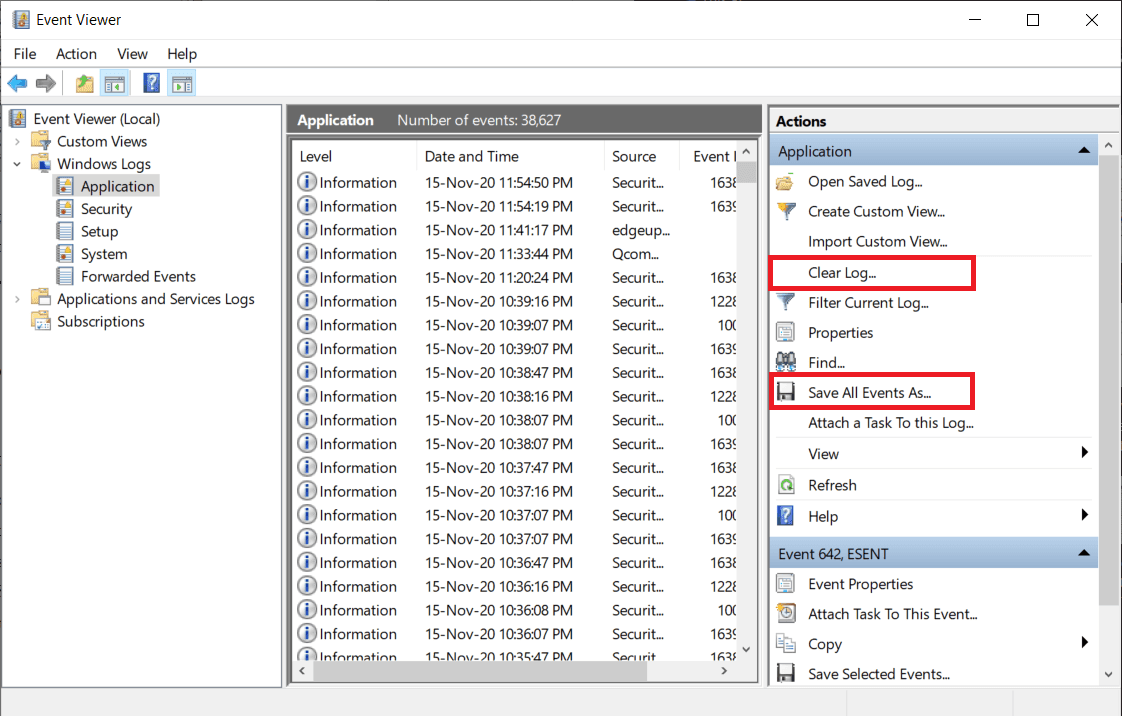
3.首先(First),通过单击右侧窗格中的Save All Events As... 保存(Save All Events As… )当前事件日志(event log)(默认情况下,文件将以.evtx 格式(.evtx format)保存,以 .text 或 .csv 格式保存另一个副本。)并保存后,单击清除日志...(Clear log…)选项。在随后的弹出窗口中,再次单击清除(Clear )。
4. 对安全(Security)、设置(Setup)和系统(System)重复上述步骤。清除所有事件日志后重新启动计算机。(Restart)
方法 5:禁用诊断策略服务(Policy Service)并删除SRUDB.dat 文件(SRUDB.dat file)
最终,如果以上方法都无法修复 Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU 使用率问题,那么您可以选择完全禁用它。(Ultimately, if none of the above methods were able to fix Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU usage issue, then you can choose to disable it altogether.)您可以通过四种不同的方式禁用该服务,最简单的一种是通过服务(Services)应用程序。除了禁用之外,我们还将删除SRUDB.dat 文件(SRUDB.dat file),该文件存储有关计算机的各种信息(应用程序电池使用情况(battery usage)、应用程序从硬盘驱动器写入和读取的字节数、诊断等)。诊断策略服务(policy service)每隔几秒就会创建和修改一次文件,这会导致磁盘使用率(disk usage)很高。
1.在运行命令框中键入(Run command box and click)services.msc ,然后单击确定(OK)打开服务(Services )应用程序。(有 8 种方法可以打开Windows服务(Services)管理器(Manager),因此请随意选择。)

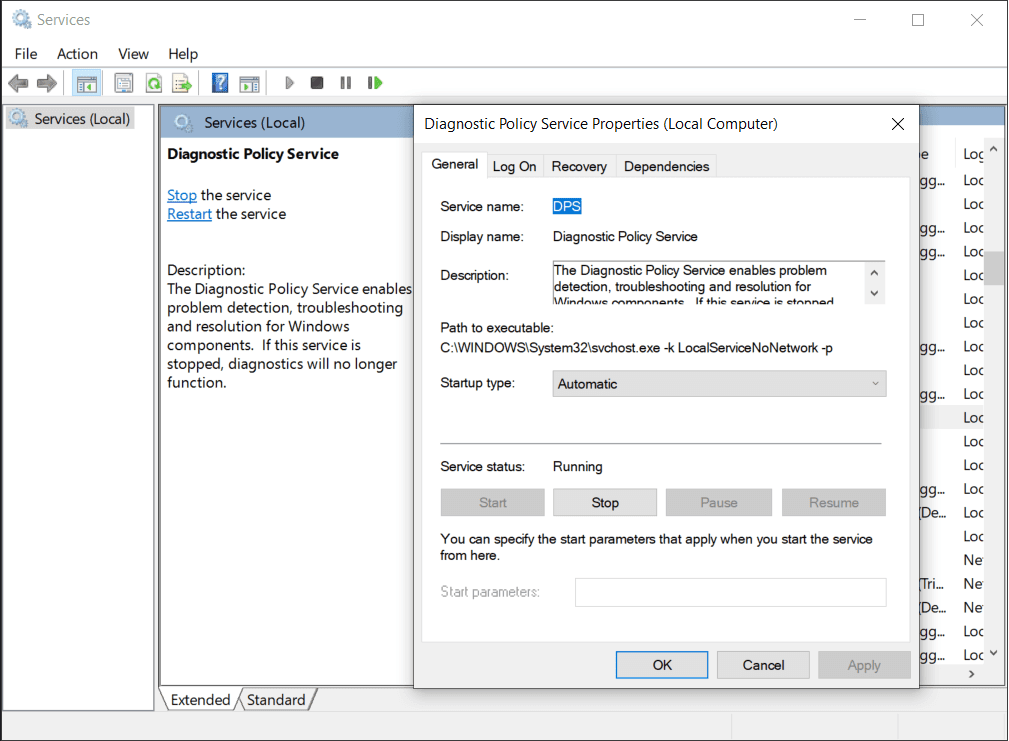
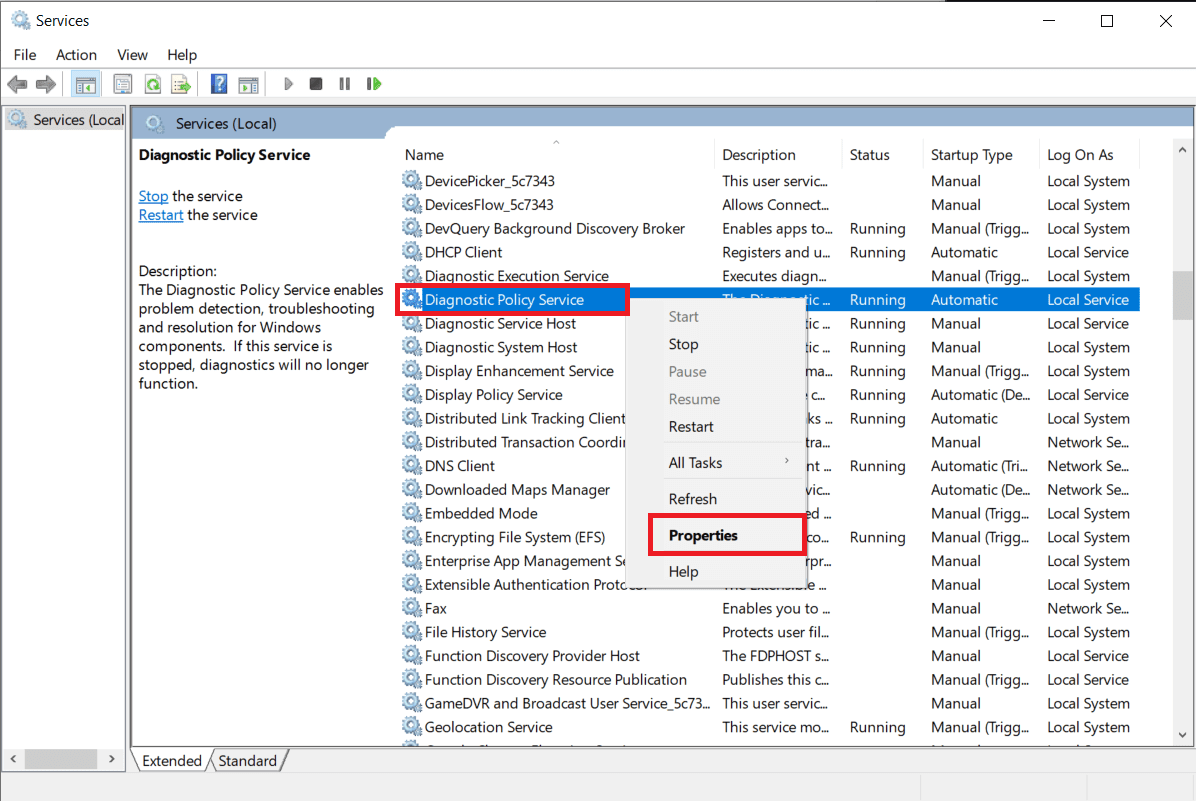
2. 确保所有服务都按字母顺序排序(单击名称列(Name column )标题这样做)并查找诊断策略服务(Diagnostic Policy Service),然后 右键单击(right-click )并选择属性(Properties)。
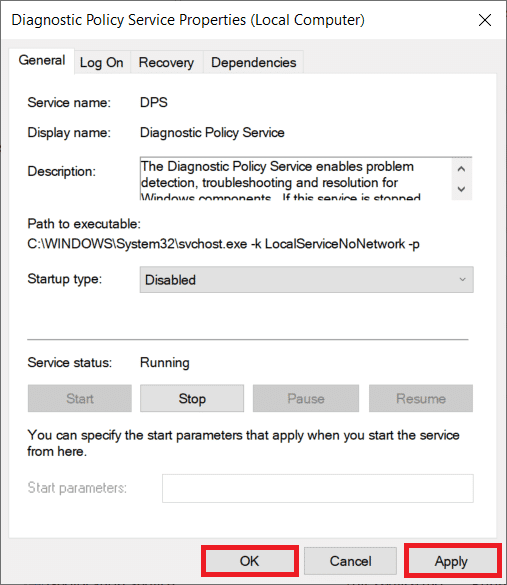
3. 在常规(General)选项卡下,单击停止(Stop )按钮终止服务。
4. 现在,展开启动类型(Startup type)下拉菜单并选择禁用(Disabled)。

5. 单击应用(Apply )按钮保存更改,然后单击确定(OK )关闭属性窗口。
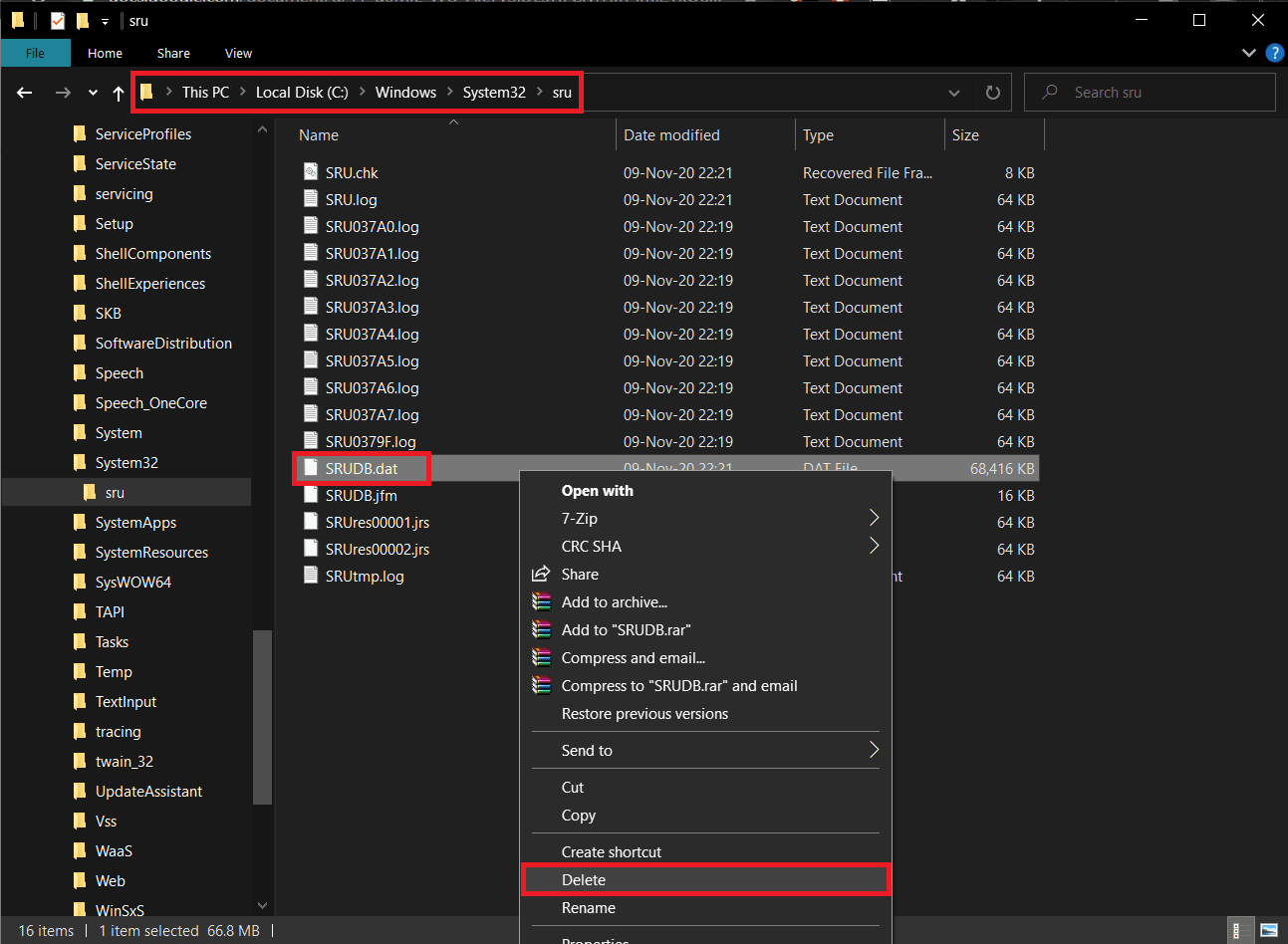
6.接下来,双击桌面上的文件资源管理器( File Explorer)快捷方式图标打开相同的,然后前往以下地址:
C:\WINDOWS\System32\sru
7. 找到SRUDB.dat文件,右键单击(right-click )它,然后选择Delete。确认可能出现的任何弹出窗口。
如果您未能成功从服务管理器应用程序禁用诊断策略服务(If you weren’t successful in disabling the Diagnostic Policy Service from the Services Manager application),请尝试其他三种方法之一。(try one of the other three methods.)
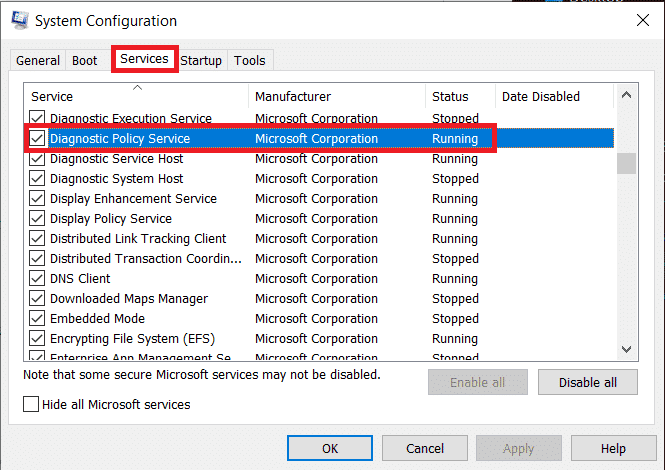
1.从系统配置: ( From System Configuration: )打开System Configuration > 服务(Services) tab > Uncheck/untick诊断策略服务。
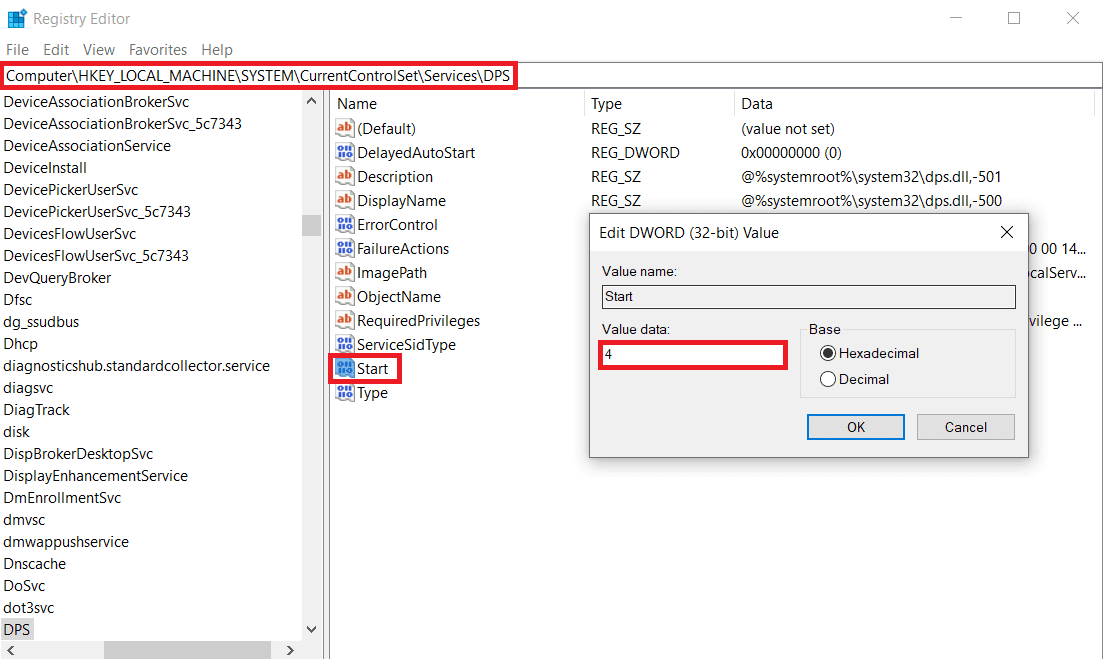
2.从注册表编辑器:( From Registry Editor:)打开注册表编辑器并(Registry Editor and Head)前往:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DPS
3. 双击右窗格中的开始,然后将( Start)数值数据更改(Change Value Data)为4。
4. 重新启动计算机(Restart the computer),Windows将自动重新创建SRDUB.dat 文件(SRDUB.dat file)。诊断策略服务(Policy Service)不应再处于活动状态,因此会导致任何性能问题。
推荐的:(Recommended:)
- 修复服务主机(Fix Service Host):本地系统(System)(svchost.exe)高 CPU 和磁盘使用率(High CPU and Disk Usage)
- (Fix High CPU Usage)修复服务主机(Service Host)的高 CPU 使用率:本地系统
- 如何使用 CMD 修复或修复损坏的硬盘(Fix Corrupted Hard Drive Using CMD)?
- 修复 Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation(Fix Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation)高CPU 使用率(CPU usage)
我们希望本指南对您有所帮助,并且您能够修复Windows 10计算机 上的服务主机:诊断策略服务 CPU 使用率高的问题。(fix Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU usage)您可以尝试防止该问题在未来再次发生的几件事是更新所有计算机驱动程序并执行定期防病毒扫描。您还应该卸载已达到其目的且不再需要的第三方应用程序。如需有关诊断(Diagnostic)政策服务(Policy Service)的任何帮助,请在下面的评论部分与我们联系。
Fix Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU Usage
As you mіght be aware, there аre a number of active background processes and services that сontribute to the smooth functioning of Windows. Most of thesе bаckgroυnd processes/services utilize a minimal amount of CPU power and RAM. Although, sometimes a proceѕs may malfunction or be rendered corrupt and end up utilizing way more resources than usual, leaving little for other foreground applicatіons. The Diagnоstic Policy Servіce is one such рrocess nоtorious for hogging up the system resources on rare occasions.
The Diagnostic Policy Service is one of the shared processes of Svchost.exe (Service Host) and is responsible for detecting problems with various Windows components and also troubleshooting them. The service tries to automatically fix any detected issues if possible and if not, log the diagnostic information for analysis. Since diagnosis and automatic troubleshooting of problems is an important feature for a seamless experience, the Diagnostic Policy Service has been set to automatically start when the computer boots on and stay active in the background. The exact reason behind it consuming more CPU power than intended isn’t known but based on the potential solutions, the culprits may be a corrupt instance of the service, corrupt system files, a virus or malware attack, large event log files, etc.
In this article, we have explained five different methods that will help you bring down the CPU consumption of the Diagnostic Policy Service back to normal.

Fix Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU Usage
Potential fixes for Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU Usage
Most users will be able to solve the unusually high disk usage of the Diagnostic Policy Service by simply restarting it. Others might need to perform a few scans (SFC and DISM) to look for corrupt system files or run the built-in performance troubleshooter. Updating to the latest version of Windows and clearing event viewer logs can also resolve the issue. Finally, if nothing seems to work, users have the option to disable the service. However, disabling the Diagnostic Policy Service implies that Windows will no longer carry out auto-diagnosis and resolve errors.
Method 1: End the Process from Task Manager
A process may hog up additional system resources if something prompted a corrupt instance of it. In that case, you can try manually terminating the process (Diagnostic Policy Service here) and then allowing it to automatically restart. All of this can be achieved from the Windows Task Manager (Kill Resource Intensive Processes with Windows Task Manager).
1. Right-click on the Start menu button and select Task Manager.

2. Click on More Details to expand Task Manager and have a look at all the currently active processes & services.

3. Locate the Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service under Windows processes. Right-click on it and select End task. (You can also select the service by left-click and then click on the End Task button at the bottom right.)

The Diagnostic Policy Service will restart automatically, although if it doesn’t, simply restart your computer and check if the issue persists.
Method 2: Run SFC and DISM scan
A recent Windows system update or even an antivirus attack may have corrupted certain system files resulting in high CPU usage of the Diagnostic Policy Service. Fortunately, Windows has built-in utilities to scan for and repair corrupted/missing system files. The first one is the System File Checker utility and as the name suggests, it checks the integrity of all system files and replaces the broken ones with a cached copy. If an SFC scan fails to fix corrupted system files, users can employ the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) command-line tool.
1. Type Command Prompt in the Windows search bar and click on Run as Administrator in the right panel when search results arrive.

2. Type sfc /scannow in the Command Prompt window and press enter to execute. The scan may take a while so sit back and do not close the window until the verification process reaches 100%.

3. After completing the SFC scan, execute the following DISM command. Again, wait patiently for the scan and restoring process to finish before exiting the application. Restart the computer when done.
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

Also Read: How to Fix High CPU Usage by System Idle Process
Method 3: Update Windows and Run the Performance Troubleshooter
As mentioned earlier, a recent Windows update can also be the culprit behind the abnormal behaviour of the Diagnostic Policy Service. You can try rolling back to the previous update or look for any new updates pushed by Microsoft rectifying the mistake. If you are facing any issues while updating Windows, run the built-in update troubleshooter.
Apart from updating Windows, also run the System Performance troubleshooter to scan for any performance issues and have them fixed automatically.
1. Press the Windows key + I simultaneously to launch the System Settings then click on Update & Security settings.

2. On the Windows Update tab, click on Check For Updates. The application will start looking for any available updates and automatically start downloading them. Restart your computer once the new update has been installed.

3. Check if the Diagnostic Policy Service is still hogging up your system resources and if it is, then run the Update troubleshooter. Open Update & Security settings again and move to the Troubleshoot tab then Click on Additional Troubleshooters.

4. Under the Get up and running section, click on Windows Update to view the available options and then click on the ensuing Run the troubleshooter button. Follow the on-screen instructions and go through the troubleshooting process.
To run the System Performance troubleshooter:
1. Type Control Panel in the Start Search bar and press Enter to open the same.

2. Click on Troubleshooting.

3. Under System and Security, click on the Run maintenance tasks hyperlink.

4. On the following window, click on Advanced and check the box next to Apply repairs automatically. Click on Next to run the troubleshooter.

Also Read: Fix Desktop Window Manager High CPU (DWM.exe)
Method 4: Clear the Event Viewer log
The Event Viewer program maintains a record of all the application and system error messages, warnings, etc. These event logs can build up to a considerable size and prompt issues for the Service Host process. Simply clearing the logs can help resolve issues with the Diagnostic Policy Service. We recommend you clear the event viewer logs regularly to avoid any future issues.
1. Launch the Run command box by pressing Windows key + R, type eventvwr.msc and click on Ok to open the Event Viewer application.

2. On the left pane, expand the Windows Logs folder by clicking on the tiny arrow and select Application from the ensuing list.

3. First, save the current event log by clicking on Save All Events As… on the right pane (by default the file will be saved in .evtx format, save another copy in either .text or .csv format.) and once saved, click on the Clear log… option. In the ensuing pop-up, click on Clear again.

4. Repeat the above steps for Security, Setup, and System. Restart the computer after clearing all the event logs.
Method 5: Disable the Diagnostic Policy Service and delete SRUDB.dat file
Ultimately, if none of the above methods were able to fix Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU usage issue, then you can choose to disable it altogether. There are four different ways via which you can disable the service, the simplest one being from the Services application. Along with disabling, we will also be deleting the SRUDB.dat file which stores all kinds of information regarding the computer (application battery usage, bytes written and read from the hard drive by applications, diagnosis, etc.). The file is created and modified by the diagnostic policy service every few seconds which leads to high disk usage.
1. Type services.msc in the Run command box and click on OK to open the Services application. (There are 8 Ways to Open Windows Services Manager so feel free to make your own choice.)

2. Make sure all the services are sorted alphabetically (click on the Name column header to do so) and look for the Diagnostic Policy Service then right-click and select Properties.

3. Under the General Tab, click on the Stop button to terminate the service.
4. Now, expand the Startup type drop-down menu and select Disabled.

5. Click on the Apply button to save the changes and then on OK to close the Properties window.

6. Next, double-click on the File Explorer shortcut icon on your desktop to open the same and head down the following address:
C:\WINDOWS\System32\sru
7. Find the SRUDB.dat file, right-click on it, and select Delete. Confirm any pop-ups that may appear.

If you weren’t successful in disabling the Diagnostic Policy Service from the Services Manager application, try one of the other three methods.
1. From System Configuration: Open System Configuration > Services tab > Uncheck/untick the Diagnostic Policy Service.

2. From Registry Editor: Open Registry Editor and Head down to:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DPS
3. Double-click on Start in the right pane then Change Value Data to 4.

4. Restart the computer and Windows will automatically recreate the SRDUB.dat file. The Diagnostic Policy Service should no longer be active and therefore, causing any performance issues.
Recommended:
We hope this guide was helpful and you were able to fix Service Host: Diagnostic Policy Service High CPU usage on Windows 10 computer. A few things you can try to prevent the issue from occurring again in the future are updating all computer drivers and performing regular antivirus scans. You should also uninstall third-party applications that have served their purpose and aren’t required anymore. For any assistance regarding the Diagnostic Policy Service, connect with us in the comments section below.

























