您的计算机硬件和 Windows 7 限制了您的计算机可以使用的内存量。对于 32 位操作系统,该限制为 4GB RAM。64 位操作系统可以使用更多。但是,如果您的 Windows 7 64 位 PC 无法识别计算机中的所有RAM,则有一个快速修复可能会起作用。了解如何修复Windows 7 64 位可以使用的最大RAM量。(RAM Windows 7)
Windows 7 和最大内存
许多 32 位版本的Windows 7用户感到失望的是,并非所有 4GB(或更多)的RAM都可以被操作系统实际使用。许多人选择了 64 位版本的Windows 7,但仍然无法让操作系统识别和使用 PC 中安装的所有内存。
通常,您的计算机硬件和 Windows 7 一起工作以识别您的 PC 中的硬件。这包括您已安装的内存或RAM 。有时,您的计算机不知道您拥有什么,并且可能会报告您的RAM比实际少。假设这不是硬件错误或故障,您可以尝试一个技巧。
修复Windows 7 64 位可以寻址的(Can Address)最大内存(Maximum Memory Windows 7)
您在 PC 中安装的内存量不一定是 Windows 7 64 位可以处理的量。地址(Address)只是意味着使用。幸运的是,您可以指定 Windows 7 64 位在启动时应该寻址多少内存。
(Log)使用具有管理权限的帐户登录到Windows 7 64 位。(Windows 7)单击(Click)开始,然后右键单击我(Start)的电脑(My Computer)。从菜单中选择属性。(Properties)
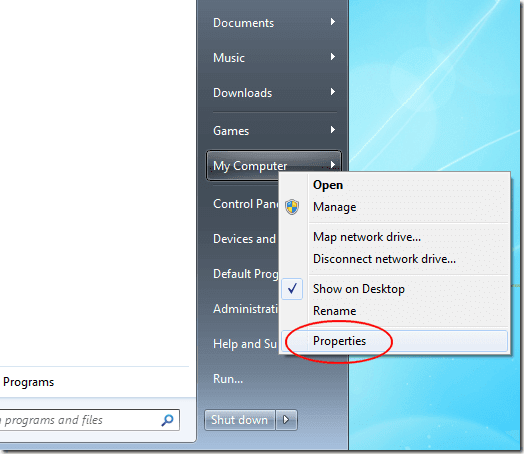
这将为您的计算机打开“属性(Properties)”窗口。在标有System的部分中,记下Installed Memory (RAM)的数量。然后,关闭“属性(Properties)”窗口。

单击开始(Start),然后单击运行(Run)。如果您的开始(Start)菜单上没有运行(Run)命令,您可以按住键盘上的Windows键并按R键。打开“运行”(Run)对话框,输入MSCONFIG并单击“确定(OK)”按钮。
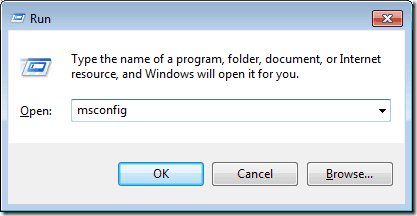
这将打开“系统配置(System Configuration)”窗口。单击启动(Boot)选项卡,然后单击高级选项(Advanced Options)按钮。

这将打开BOOT 高级选项(BOOT Advanced Options)窗口。单击“最大内存”(Maximum Memory)选项并输入您之前在“我的电脑属性”(My Computer Properties)窗口中记下的最大内存量。完成后,单击“确定(OK)”按钮,关闭已打开的所有剩余窗口,然后重新启动计算机。

Windows 7 64 位并不总是能正确识别您在 PC 中安装的内存量。您可以通过更改BOOT Advanced Options(BOOT Advanced Options)窗口中的值手动指定 Windows 7 64 位应使用多少内存来解决此问题。
假设您没有硬件或软件错误,Windows 7 应该能够正确识别您安装了多少内存以及启动时使用的最大内存量。
Fix the Maximum Amount of Memory Usable by Windows 7 64-bit
Your computer’s hardware and Windows 7 limit the amount of mеmory that yoυr computer can usе. In the case of 32-bit operating systems, that limit is 4GB of RAM. 64-bit operating systems can use much more. However, if your Windows 7 64-bit PC is having trouble recognizing all of the RAM in your computer, thеre is а quick fix that may work. Learn how to fix the mаximum amount of RAM Windows 7 64-bit can use.
Windows 7 and Maximum Memory
Many users of the 32-bit version of Windows 7 were disappointed that not all of their 4GB of RAM (or more) could actually be used by the operating system. Many opted for the 64-bit version of Windows 7 but still had trouble getting the operating system to recognize and use all of the memory installed in the PC.
Typically, your computer’s hardware and Windows 7 works together to identify the hardware you have in your PC. This includes the memory or RAM you have installed. Occasionally, your computer is not aware of what you have and may report that you have less RAM than you actually do. Assuming this is not a hardware error or failure, there is one trick you can try.
Fix the Maximum Memory Windows 7 64-bit Can Address
The amount of memory you have installed in your PC is not necessarily the amount that Windows 7 64-bit can address. Address simply means use. Luckily, you can specify how much memory Windows 7 64-bit should address on boot up.
Log in to Windows 7 64-bit with an account that has administrative privileges. Click on Start and then right click on My Computer. Choose Properties from the menu.

This opens the Properties window for your computer. In the section labeled System, note the amount of Installed Memory (RAM). Then, close the Properties window.

Click on Start and then on Run. If you don’t have the Run command on your Start menu, you can hold down the Windows key on your keyboard and press the R key. With the Run dialog box open, type in MSCONFIG and click the OK button.

This opens the System Configuration window. Click on the Boot tab and then click on the Advanced Options button.

This opens the BOOT Advanced Options window. Click on the Maximum Memory option and type in the maximum amount of memory you noted earlier in the My Computer Properties window. When finished, click the OK button, close all remaining windows that you have opened, and restart your computer.

Windows 7 64-bit does not always correctly identify the amount of memory you have installed in your PC. You can fix this problem by manually specifying how much memory Windows 7 64-bit should use by changing a value in the BOOT Advanced Options window.
Assuming you have no hardware or software errors, Windows 7 should then be able to correctly identify how much memory you have installed and the maximum amount of memory to use at boot up.





