有时您可能需要查看最近安装在Ubuntu中的软件包列表以进行故障排除,或者可能只是为了查找您安装的未显示在菜单中的程序。有两种方法可以找出最近安装的内容。您可以使用Synaptic 包管理器(Synaptic Package Manager)按日期查看最近安装的包,也可以使用终端(Terminal)窗口从命令提示符查看。
使用 Synaptic 包管理器
要使用Synaptic Package Manager(Synaptic Package Manager)查看最近安装的软件包,请选择Administration | Synaptic Package Manager系统(System)菜单中的突触软件包管理器。
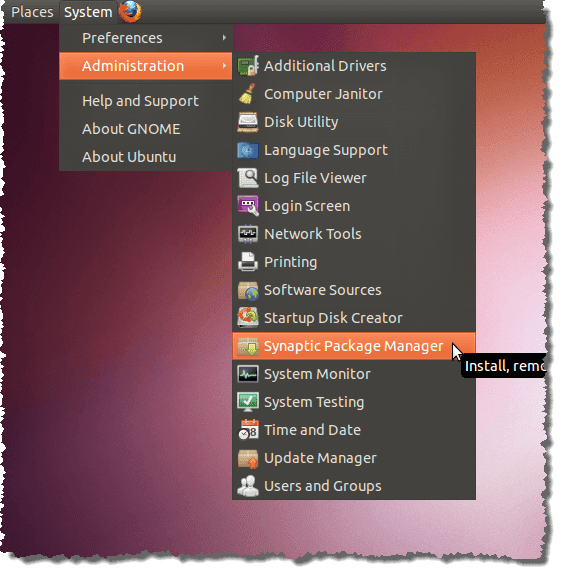
在Synaptic 包管理器(Synaptic Package Manager)对话框中,从文件(File)菜单中选择历史记录。(History)

显示历史(History)对话框。使用Synaptic 包管理(Synaptic Package Manager)器安装和删除的所有包都按月份和日期列出。单击(Click)左侧窗格中一个月左侧的箭头可显示该月内安装或删除软件包的日期。单击(Click)日期可在右侧窗格中查看在该日期安装或删除了哪些软件包。
注意:(NOTE:)只有使用Synaptic 软件包管理(Synaptic Package Manager)器安装的软件包才会显示在历史记录(History)对话框中。如果您使用其他方法安装了其他软件,例如Ubuntu 软件中心(Ubuntu Software Center),则此处未列出。

要关闭“历史记录”(History)对话框,请单击“关闭”(Close)按钮。

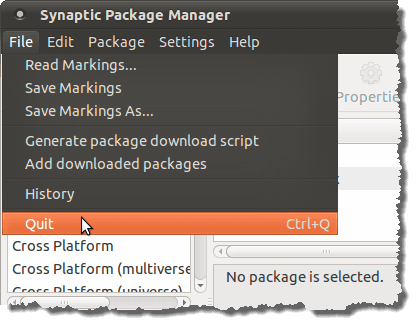
要关闭Synaptic 包管理器(Synaptic Package Manager),请从文件(File)菜单中选择退出。(Quit)
使用终端窗口
如果您更喜欢在终端(Terminal)窗口中工作,您可以使用命令行获取已安装软件包的列表。为此,请选择Accessories | Terminal应用程序(Applications)菜单中的终端。

在提示符处输入(Enter)以下命令,然后按Enter。
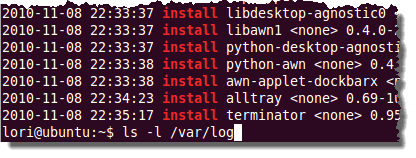
cat /var/log/dpkg.log | grep “\ install\ “
注意:(NOTE:)每个反斜杠后面都有一个空格。
此命令显示dpkg.log文件中与术语“ install ”匹配的条目,包括前后的空格。“ install ”条目表示已完全安装的软件包。

dpkg.log 文件中的所有“安装(install)”条目都显示在终端(Terminal)窗口中,最后列出的最新条目。

如果dpkg.log文件中的日期没有按照您的需要返回,则可能存在其他dpkg日志文件。dpkg.log文件每周轮换和归档。(dpkg.log)您可以通过列出/var/log目录的内容来找到可用的dpkg日志文件。(dpkg)
为此,请在提示符处输入以下命令,然后按Enter。
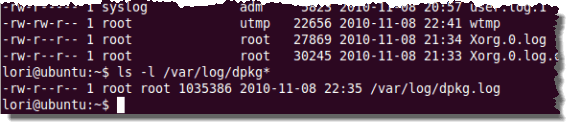
$ ls –l /var/log
注意:(NOTE:) “ ls ”之后是一个破折号和一个小写“ L ”,后跟另一个空格。
请注意(Notice),您将获得/var/log目录中所有日志的列表,而不仅仅是dpkg的日志。要仅显示dpkg的日志文件,请在提示符处输入以下命令并按Enter。
$ ls –l /var/log/dpkg*
注意:(NOTE:)同样,在“ ls ”之后是一个破折号和一个小写“ L ”,然后是另一个空格。
我们的系统中只显示一个dpkg.log文件,因为它是我们最近安装的一个新系统。要打开dpkg.log文件进行查看,请在提示符处输入以下命令并按Enter。
$ gedit /var/log/dpkg.log

dpkg.log文件在gedit中(dpkg.log)打开。列出了所有软件包,不仅是具有“ install ”状态的软件包。这使得找到完全安装的软件包变得更加困难。
提示:(TIP:)使用cat /var/log/dpkg.log | grep “\ install\ “命令可能是查看已安装软件包列表的最佳方式,因为仅显示日志文件中的 “ install ” 条目。如果您需要查看比dpkg.log文件中可用的软件包更旧的已安装软件包,只需将cat命令中的(cat)dpkg.log文件名替换为您使用ls –l /var/log/dpkg*找到的其他dpkg日志文件名命令。

要关闭gedit ,请从文件(File)菜单中选择退出。(Quit)

您可能会注意到使用终端(Terminal)窗口生成的列表更加完整。列出了使用任何方法安装的程序(Programs),而不仅仅是使用Synaptic 包管理器(Synaptic Package Manager)安装的程序。
通过洛里考夫曼
Display a List of Recently Installed Software Packages in Ubuntu
There may be times when you need to view a list of the packages that were recently installed in Ubuntu for troubleshooting purposes or maybe just to find a program you installеd that does not display in the menυ. There are two ways to find oυt what was installed recently. You can view recentlу installed packages by date using the Synaptic Package Manager and from the command prompt using a Terminal window.
Use the Synaptic Package Manager
To view software packages installed recently using the Synaptic Package Manager, select Administration | Synaptic Package Manager from the System menu.

On the Synaptic Package Manager dialog box, select History from the File menu.

The History dialog box displays. All packages installed and removed using the Synaptic Package Manager are listed by month and date. Click the arrow to the left of a month in the left pane to display dates within that month on which software packages were installed or removed. Click a date to view what packages were installed or removed on that date in the right pane.
NOTE: Only software packages installed using the Synaptic Package Manager are displayed on the History dialog box. If you installed other software using other methods, such as the Ubuntu Software Center, they are not listed here.

To close the History dialog box, click the Close button.

To close the Synaptic Package Manager, select Quit from the File menu.

Use a Terminal window
If you prefer working in a Terminal window, you can get a list of installed software packages using the command line. To do this, select Accessories | Terminal from the Applications menu.

Enter the following command at the prompt and press Enter.
cat /var/log/dpkg.log | grep “\ install\ “
NOTE: There is a space after each of the backslashes.
This command displays entries from the dpkg.log file that match the term “ install “, including the spaces before and after. The “install” entries indicate packages that have been fully installed.

All the “install” entries in the dpkg.log file are displayed in the Terminal window, the most recent entries listed last.

If the dates in the dpkg.log file don’t go back as far as you need, there may be other dpkg log files. The dpkg.log file is rotated and archived weekly. You can find available dpkg log files by listing the contents of the /var/log directory.
To do this, enter the following command at the prompt and press Enter.
$ ls –l /var/log
NOTE: After “ls ” is one dash and a lowercase “L” followed by another space.

Notice that you get a listing of all the logs in the /var/log directory, not just the logs for dpkg. To display only the log files for dpkg, enter the following command at the prompt and press Enter.
$ ls –l /var/log/dpkg*
NOTE: Again, after the “ls ” is one dash and a lowercase “L” followed by another space.

Only one dpkg.log file displays in our system, because it is a new system we installed recently. To open the dpkg.log file for viewing, enter the following command at the prompt and press Enter.
$ gedit /var/log/dpkg.log

The dpkg.log file opens in gedit. All packages are listed, not only the ones with the “install” status. This makes it harder to find the fully installed packages.
TIP: Using the cat /var/log/dpkg.log | grep “\ install\ “ command is probably the best way of viewing a list of installed packages, because only “install” entries in the log file are displayed. If you need to view installed packages that are older than those available in the dpkg.log file, simply replace the dpkg.log filename in the cat command with other dpkg log filenames you find using the ls –l /var/log/dpkg* command.

To close gedit, select Quit from the File menu.

You may notice that the list generated using the Terminal window is more complete. Programs installed using any method are listed, not just programs installed using the Synaptic Package Manager.
by Lori Kaufman













