在监控系统资源方面,Windows 10任务管理器为您提供了强大的功能。(Task Manager)Processes选项卡共享比以往更多的信息,允许您根据需要自定义其显示的数据。以下是如何调整Windows 10中(Windows 10)任务管理器的“(Task Manager's) 进程(Processes)”选项卡并提高效率,方法是确保以比默认视图(default view)更适合您需求的方式显示与您相关的数据(data relevant):
什么是进程选项卡(Processes tab)以及如何访问它?
“进程(Processes)”选项卡列出了在任何给定时间运行的所有应用程序、后台进程和Windows进程,并提供了有关每个进程的有用数据。它在任务管理器(Task Manager)的完整版中可用。有几个选项可以打开任务管理器(Task Manager),但我们认为最舒服的是键盘快捷键(keyboard shortcut) "Ctrl + Shift + Esc”。如果您跳过了Windows 8,并且这是您第一次访问该工具,它会以什么方式打开我们将其称为紧凑视图,向您显示当前在您的 Windows 10 设备上运行的所有应用程序的列表。要打开任务管理器(Task Manager)的完整版本,请单击或点击(More details)精简视图底部的更多详细信息。

任务管理器(Task Manager)的完整版本打开,进程(Processes)选项卡是默认选项卡。

提示:(TIP:)可以自定义任务管理器以在您想要的任何选项卡中打开。(Task Manager)要了解更多信息,请阅读如何设置Windows 10任务管理器(Task Manager)的default view/tab。
1.如何在任务管理器(Task Manager)的进程选项卡中添加或删除数据列(Processes tab)
在“进程(Processes)”选项卡中,您可以获得有关当前在您的计算机上运行的每个应用程序、后台进程(background process)和Windows 进程的信息。(Windows process)这些数据是结构化的并按列显示。单击(Click)或点击列的标题,然后拖动它以按您喜欢的顺序重新排列列。您可以通过添加和删除列来挑选和选择“进程”选项卡中显示的信息。(Processes)右键单击或按住现有列的标题,然后选择在(header and select)任务管理器的(Task Manager)进程(Processes)选项卡中显示的十四个可选列中的哪一个。请记住,名称(Name)column 是唯一不能隐藏的列。

为确保您选择的列为您提供相关数据,以下是他们必须提供的内容的简要说明:
-
类型(Type)- 显示进程是应用程序、后台进程还是 Windows 进程。如果选择“按类型分组”("Group by type"),则此列变得多余
-
状态(Status)- 显示进程是否暂停。当某些东西被挂起时,它在后台运行,但它无法访问 CPU 周期并且使用很少的内存。
- 发布者 - 显示流程发布者的名称。
-
PID - 显示每个正在运行的进程的唯一进程标识符。这些数字可用于将正在运行的进程与列出 PID 的错误或事件相匹配。
-
进程名称(Process name)- 显示进程的可执行文件的名称。例如,7zFM.exe用于7-Zip 文件管理器(7-Zip File Manager)。
-
命令行(Command line)- 显示为每个进程运行的命令行语法。这使您可以查看是否使用特殊的命令行参数启动了任何应用程序或进程,并为您提供每个进程的可执行文件的位置。
-
CPU - 显示每个进程的处理器使用情况。
-
内存 -(Memory -)显示每个进程的 RAM 使用情况。
-
磁盘(Disk)- 显示每个进程的硬盘使用情况。
-
网络(Network)- 显示每个进程的网络使用情况。
-
GPU - 显示每个进程对视频卡的使用情况。
-
GPU 引擎(GPU engine)- 共享每个进程使用哪个 GPU 引擎。根据微软的说法:GPU 引擎代表图形卡上的一个独立硅单元,可以调度并且可以与另一个并行运行。您可以在此处(here)找到有关此概念的更多信息。
-
电源使用(Power usage)- 显示每个进程使用的电源。
-
电源使用趋势(Power usage trend)- 显示每个进程的电源使用总体趋势。
2.如何在任务管理器(Task Manager)的进程选项卡中对正在运行的(Processes tab)应用程序和进程进行排序(apps and processes)
默认情况下,任务管理器的进程(Task Manager's Processes)列表按进程类型(process type)进行逻辑排序。这意味着所有应用程序、后台进程和 Windows 10 进程都分组在一起,并在选项卡的第一列中的组内排序,称为Name。虽然我们是该系统的忠实拥护者,但您可能希望改为按字母顺序对列表进行排序。如果您希望所有活动的应用程序和进程按字母顺序显示,请单击(Click)或点击查看(View)并取消选择“按类型分组” 。("Group by type")

单击或点击列标题可让您根据该列中显示的值对正在运行的应用程序和进程进行排序。(running apps and processes)例如,单击内存(Memory)按进程使用的RAM量对列表进行排序。如果您想知道哪些进程在您的计算机上消耗的资源最多或最少,这可以派上用场。无论(Regardless)您使用哪种排序方法,如果您希望随时返回默认排序,请在“视图”菜单中选择(View)“按类型分组”("Group by type")选项。
3. 如何更改数据值在“进程”选项卡中的显示方式(Processes tab)
除了允许您自定义显示哪些信息之外,“进程(Processes)”选项卡还允许您决定如何显示某些数据。对于Memory、Disk和Network列,您可以选择是使用值(MB 内存、MB/s disk usage and Mbps network usage)显示数据,还是显示为总可用资源的百分比。在任务管理器(Task Manager)的进程(Processes)选项卡中右键单击或按住任何列的标题或进程(header or process),然后转到资源值(Resource values)。选择其中一项资源,然后选择百分比(Percents)或值(Values)根据您的需要和偏好显示数据。

4.如何在任务管理器中展开和折叠正在运行的进程(Task Manager)
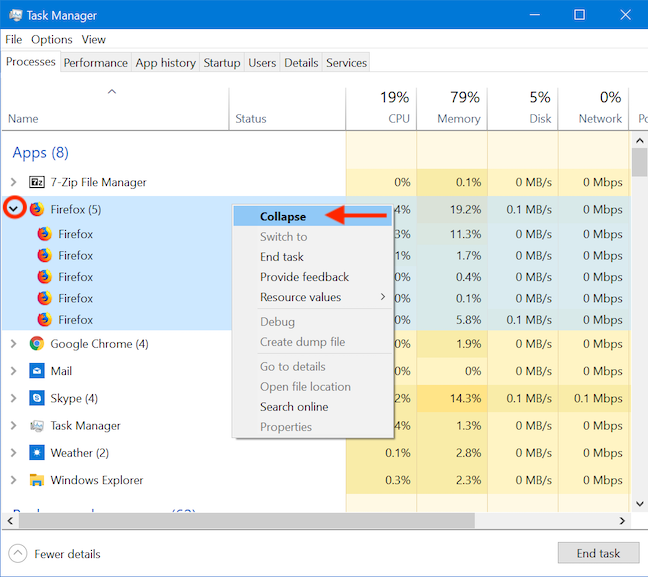
有些流程比其他流程更复杂,涉及的不仅仅是主要流程。任务管理器的(Task Manager's) 进程选项(Processes)卡允许您展开列出的进程并获取有关在它们下运行的子进程的更多详细信息。子流程的数量由每个流程后面的括号中的数字表示。要展开单个进程,请右键单击或按住它,然后单击或点击(click or tap) 展开(Expand)。更简单的方法是单击或点击进程左侧的箭头。

您可以再次单击箭头,也可以右键单击或按住该进程,如果要再次隐藏子进程,请转到折叠。(Collapse)
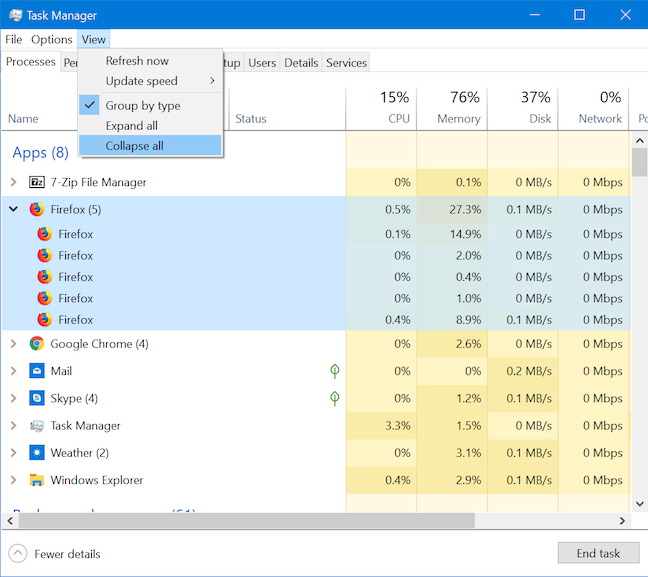
您还可以通过单击或点击查看(View)然后全部展开(Expand all)来展开任何折叠的条目。

要立即折叠所有展开的条目,请单击或点击(click or tap) 查看(View)菜单中的全部折叠。(Collapse all)
提示:(TIP:)对于多进程应用程序,右键单击或按住(right-clicking or pressing-and-holding)主(父)进程时,上下文菜单显示灰色选项。右键单击或按住每个子进程以与其交互。

5.如何使用任务管理器结束正在运行的进程(Task Manager)
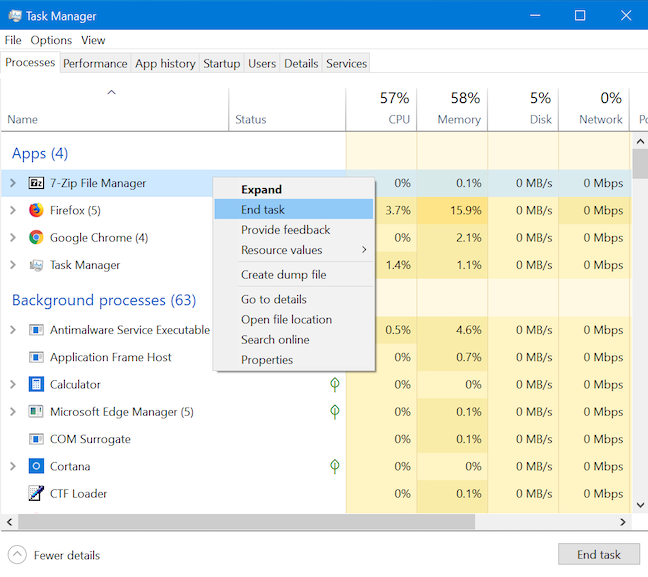
任务管理器(Task Manager)的主要用途是关闭不再响应的正在运行的进程。右键单击或按住任何进程并打开上下文菜单。单击(Click)或点击结束任务(End task)以关闭进程。
您还可以选择应用程序并单击(app and click)或点击“进程(Processes)”选项卡右下角的“结束任务(End task)”按钮以关闭进程。
6. 如何向微软提供关于正在运行的进程的反馈(Microsoft)
可以从任务管理器(Task Manager)轻松访问反馈中心(Feedback Hub),允许您对正在运行的进程提供反馈。右键单击或按住任何进程,然后选择提供反馈(Provide feedback)。

反馈中心(Feedback Hub)打开后,您可以使用您的Microsoft 帐户(Microsoft account)登录并使用它向 Microsoft 发送您的问题、批评或建议(Microsoft)。

7.如何使用任务管理器(Task Manager)为正在运行的进程创建转储文件(dump file)
转储文件(dump file)是一个使用 DMP 格式的大文件,并提供(DMP format)有关特定进程或应用程序在创建(process or application)转储文件(dump file)的确切时间正在执行的操作的详细信息。对于试图解决该过程的错误或问题的软件开发人员来说,这通常会派上用场。要创建转储文件(dump file),请右键单击或按住任何进程,然后单击(process and click)或点击“创建转储文件”。("Create dump file.")

8.如何在任务管理器(Task Manager)中查看正在运行的进程的详细信息
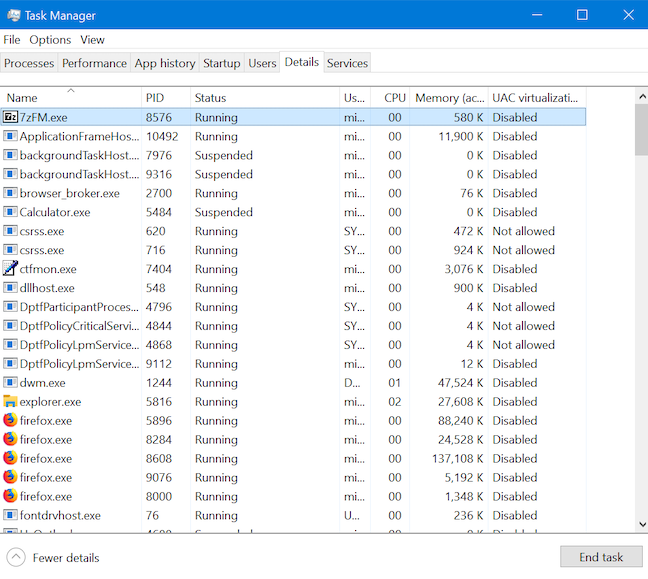
毫无疑问,任务管理器(Task Manager)的“详细信息(Details)”选项卡提供了有关正在运行的进程的精确详细信息。但是,此选项卡的排序选项是有限的,因此查找有关某个进程的更多信息可能会变成寻宝游戏(treasure hunt),尤其是当您的计算机上运行许多进程时。幸运的是,“进程”选项卡通过在“(Processes)详细信息(Details)”选项卡中提供突出显示相应进程的选项来弥补这一点。右键单击或按住任何进程,然后单击或点击“转到详细信息("Go to details)”。

焦点移至详细信息(Details)选项卡,其中突出显示了相应的可执行文件。
9.如何在任务管理器中找到正在运行的进程的位置(Task Manager)
使用任务管理器(Task Manager)还可以更轻松地在硬盘上查找与应用程序或进程对应的可执行文件的确切位置。右键单击或按住(Right-click or press-and-hold)“进程”选项卡中的进程(Processes),然后单击或点击“打开文件位置”。("Open file location.")

文件资源管理器(File Explorer)在存储应用程序可执行文件的文件夹中打开。文件夹打开时会选择相应的文件。

10.如何使用任务管理器(Task Manager)研究未知进程或应用程序(process or app)
任务管理器的进程(Task Manager's Processes) 选项卡(tab show)不仅显示当前打开的应用程序,而且还显示后台进程,这主要是高级用户感兴趣的。要研究未知应用程序或进程,请在(app or process)进程(Processes)选项卡中右键单击或按住它,然后单击或点击在线搜索(Search online)。
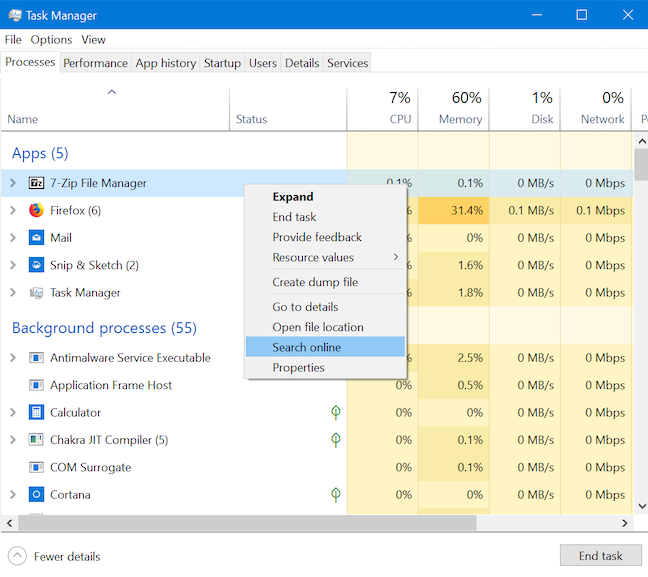
在新选项卡中,您的默认 Web 浏览器使用Bing上进程或应用程序的可执行文件的名称运行 Web 搜索(无论您的默认搜索引擎(default search engine)如何),帮助您获取更多信息。

11.如何从任务管理器查看正在运行的应用程序的属性(Task Manager)
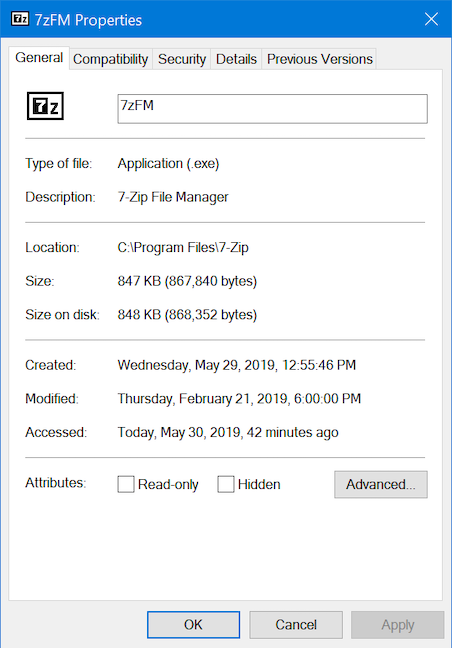
进程或应用程序的属性提供了大量有关运行它的可执行文件的信息。它们显示文件的大小、位置、访问日期和安全设置,并让您解决兼容性问题。右键单击或按住任务管理器(Task Manager)的进程(Processes)列表中的应用程序或进程(app or process),然后选择属性(Properties)。
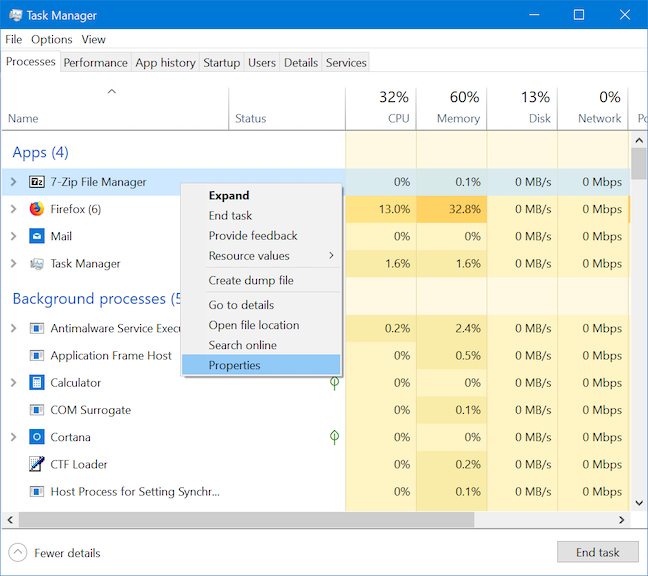
“属性(Properties)”窗口打开,您可以访问有关该应用程序的有用信息。
您的任务管理器(Task Manager)的进程选项卡(Processes tab)有多拥挤?
由于我们介绍了您可以自定义此选项卡的不同方式,因此请告诉我们您选择在任务管理器(Task Manager)中查看的内容。您是像大多数用户一样保持基本还是更喜欢更详细的视图?在下面发表评论(Comment),让我们讨论。
11 ways to manage running processes with the Task Manager in Windows 10
The Windows 10 Task Manager gives you a lot of power when it comes to monitoring system resources. The Processes tab shares more information than ever before, allowing you to customize the data it shows according to your needs. Here is how to tweak the Task Manager's Processes tab in Windows 10 and become more efficient, by ensuring the data relevant to you is displayed in a way that suits your needs better than the default view:
What is the Processes tab and how to access it?
The Processes tab lists all the apps, background processes, and Windows processes running at any given time, providing useful data about each of them. It is available in the full version of the Task Manager. There are several options available to open the Task Manager, but we think the most comfortable is the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Shift + Esc." If you skipped Windows 8, and if this is your first time accessing the tool, it opens in what we call the compact view, showing you a list of all the apps currently running on your Windows 10 device. To open the full version of the Task Manager, click or tap More details at the bottom of the compact view.

The full version of the Task Manager opens, and the Processes tab is the default tab.

TIP: The Task Manager can be customized to open in any tab you want. To find out more, read How to set the default view/tab for the Windows 10 Task Manager.
1. How to add or remove data columns in Task Manager's Processes tab
In the Processes tab, you get information on every app, background process, and Windows process currently running on your computer. This data is structured and displayed in columns. Click or tap on a column's header, and drag it to reorder the columns in the order you prefer. You can pick and choose the information shown in the Processes tab by adding and removing columns. Right-click or press-and-hold on an existing column's header and select which of the fourteen optional columns are displayed in the Processes tab of the Task Manager. Keep in mind that the Name column is the only column that you cannot hide.

To ensure that the columns you select provide you with relevant data, here is a run-down of what they have to offer:
-
Type - Displays whether the process is an app, a background process, or a Windows process. If "Group by type" is selected, this column becomes redundant
-
Status - Displays whether or not a process is suspended. When something is suspended, it is running in the background, but it has no access to CPU cycles and uses little memory.
- Publisher - Displays the name of the process's publisher.
-
PID - Displays a unique Process Identifier for each running process. These numbers can be used to match a running process with an error or event that lists the PID.
-
Process name - Displays the name of the process's executable. E.g., 7zFM.exe for 7-Zip File Manager.
-
Command line - Displays the command-line syntax run for each process. This lets you see if any apps or processes have been launched with special command-line parameters and also gives you the location of each process's executable file.
-
CPU - Shows each process's processor usage.
-
Memory - Shows each process's RAM usage.
-
Disk - Shows each process's hard disk usage.
-
Network - Shows each process's network usage.
-
GPU - Shows each process's usage of the video card.
-
GPU engine - Shares which GPU engine is utilized by each process. According to Microsoft: a GPU engine represents an independent unit of silicon on the graphics card, that can be scheduled and can operate in parallel with another. You can find our more about this concept, here.
-
Power usage - Displays the power used by each process.
-
Power usage trend - Shows the overall trend in power usage for each process.
2. How to sort running apps and processes in Task Manager's Processes tab
By default, the Task Manager's Processes list is sorted logically by process type. This means that all apps, background processes, and Windows 10 processes are grouped together and sorted within their group in this first column of the tab, called Name. While we are big fans of this system, you may wish to sort the list alphabetically instead. Click or tap View and deselect "Group by type" if you want all the active apps and processes to be displayed in an alphabetical list.

Clicking or tapping on a column's header allows you to sort the running apps and processes based on the values displayed in that column. E.g., clicking on Memory sorts the list by how much RAM the processes are using. This can come in handy if you are wondering what processes consume the most or the least resources on your computer. Regardless of the sorting method you are using, select the "Group by type" option in the View menu if you wish to return to the default sorting at any point.
3. How to change the way data values are displayed in the Processes tab
On top of allowing you to customize which information is shown, the Processes tab also lets you decide how some of that data is displayed. For the Memory, Disk and Network columns you can choose whether to display the data using values - MB of memory, MB/s disk usage and Mbps network usage - or as a percentage of the total available resource. Right-click or press-and-hold on any column's header or process in the Processes tab of theTask Manager, and go to Resource values. Choose one of the resources and then select either Percents or Values to have the data displayed according to your needs and preferences.

4. How to expand and collapse running processes in the Task Manager
Some processes are more complex than others, involving more than just the main process. The Task Manager's Processes tab allows you to expand listed processes and get more details about the subprocesses running under them. The number of subprocesses is indicated by a number in brackets following each process. To expand a single process, right-click or press-and-hold on it, and click or tap Expand. An easier way to do this is by clicking or tapping the arrow to the left of the process.

You can click the arrow again, or you can right-click or press-and-hold on that process, and go to Collapse if you want to hide the subprocesses again.

You can also expand any collapsed entries by clicking or tapping View and then Expand all.

To instantly collapse all expanded entries, click or tap Collapse all from the View menu.

TIP: For multi-process applications, the contextual menu displays greyed out options when right-clicking or pressing-and-holding the main (parent) process. Right-click or press-and-hold on each subprocess to interact with it.

5. How to end running processes using the Task Manager
The primary use of the Task Manager is to close running processes that are no longer responding. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process and a contextual menu opens. Click or tap End task to close the process.
You can also select the app and click or tap the End task button on the bottom-right corner of the Processes tab to close the process.

6. How to provide feedback on a running process to Microsoft
The Feedback Hub is easily accessible from the Task Manager, allowing you to offer feedback on a running process. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process, and then choose to Provide feedback.

When the Feedback Hub opens, you can sign in with your Microsoft account and use it to send your issue, criticism, or suggestion to Microsoft.

7. How to create a dump file for a running process using the Task Manager
A dump file is a large file that uses the DMP format and provides details on what a particular process or application is doing at the exact time the dump file is created. This usually comes in handy to software developers trying to solve a bug or a problem with that process. To create a dump file, right-click or press-and-hold on any process and click or tap "Create dump file."

8. How to see details for a running process in the Task Manager
The Details tab of the Task Manager unsurprisingly provides precise details about running processes. However, this tab's sorting options are limited, so finding more about a certain process can turn into a bit of a treasure hunt, especially if you have many processes running on your computer. Luckily, the Processes tab makes up for that by providing an option to highlight the corresponding process in the Details tab. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process, and then click or tap "Go to details."

The focus moves to the Details tab, where the corresponding executable file is highlighted.

9. How to find the location of a running process in the Task Manager
Finding the exact location on your hard drive of the executable file corresponding to an app or a process is also made easier with the Task Manager. Right-click or press-and-hold on the process in the Processes tab and click or tap on "Open file location."

The File Explorer opens at the folder where your application's executable file is stored. The corresponding file is selected when the folder opens.

10. How to research an unknown process or app using the Task Manager
Not only does the Task Manager's Processes tab show apps that are currently open, but it also displays background processes, which are mostly of interest to more advanced users. To research an unknown app or process, right-click or press-and-hold on it in the Processes tab, and then click or tap Search online.

In a new tab, your default web browser runs a web search with the name of the process's or app's executable file on Bing (regardless of your default search engine), helping you get more information.

11. How to view the properties of a running app from the Task Manager
The properties of a process or an application offer a lot of information about the executable that runs it. They show the file's size, location, access dates, and security settings, and let you troubleshoot compatibility issues. Right-click or press-and-hold on an app or process from the Processes list of the Task Manager and choose Properties.

The Properties window opens, providing you access to useful information about the app.

How crowded is your Task Manager's Processes tab?
Since we went over the different ways you can customize this tab, let us know what you choose to see in your Task Manager. Do you keep it basic like the majority of users or prefer a more detailed view? Comment below and let's discuss.






















