您知道Windows的(Windows)系统配置 (msconfig.exe)(System Configuration (msconfig.exe) )工具有多出色吗?尽管它是一个很小且有些隐蔽的工具,但它允许您更改有关Windows(Windows)工作方式的很多事情。除其他外,系统配置(System Configuration )工具可让您配置Windows的启动方式、更改启动过程(boot procedure)、选择启动服务和程序,以及启动一系列有用的管理程序。如果您想了解更多关于系统配置(System Configuration)可以做的事情,请阅读这篇文章:
注意:(NOTE:)本文涵盖Windows 10、Windows 7 和Windows 8.1。在阅读之前,您应该知道我们假设您已经知道如何启动系统配置(System Configuration)。如果您不这样做,请先阅读以下内容:在Windows中启动(Windows)系统配置(System Configuration)的 8 种方法(所有版本)。此外,如果您不知道您正在使用的Windows版本,本教程应该会有所帮助:我安装了哪个版本的Windows?
1.选择Windows启动(Windows startup)时加载哪些驱动程序和服务
系统配置(System Configuration)工具,也称为msconfig.exe,是一个带有设置和快捷方式的窗口。它们都分为几个选项卡,每个选项卡都可以让您访问不同的内容。“系统配置(System Configuration)”窗口中的第一个选项卡称为“常规(General)”,您可以在其中配置 Windows 的启动方式。

在“常规”选项卡的(General)“启动选择”("Startup selection")列表中,您可以选择让Windows执行以下操作:
-
“正常启动”:("Normal startup": )表示 Windows 按原样启动,所有(ALL )已安装的启动项、驱动程序和服务。大多数Windows(Windows)设备应默认选择此模式,除非您已经对启动时(boot time)加载的驱动程序、服务或应用程序进行了一些更改。
-
“诊断启动”("Diagnostic startup"):此模式类似于启动到安全模式(Mode)。安全模式(Safe Mode)仅运行Windows服务和驱动程序。除了它们之外,诊断启动(Diagnostic startup)还可能在它们之上运行网络服务或来自第三方应用程序的重要服务,例如您的防病毒软件、防火墙或安全套件(firewall or security suite)。如果您想排除Windows文件和服务是系统不稳定(system instability)问题的根源,此模式很有用。请注意,如果您选择“诊断启动”("Diagnostic startup" ),然后单击或点击应用(Apply),则“选择性启动”("Selective startup")是显示为选中的那个。但是,没有什么可担心的,因为这是很正常的。发生这种情况是因为“诊断启动”("Diagnostic startup")是具有预定义设置的“选择性启动” 。("Selective startup" )
-
“选择性启动”:("Selective startup":)使Windows仅使用其基本服务和驱动程序启动。此外,它还允许您从“服务”和“启动”选项卡中选择要运行的其他服务和启动项(Services and Startup)。
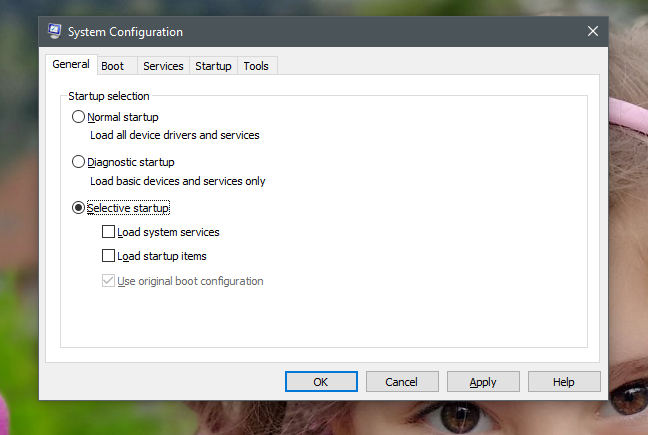
还需要注意的是,如果您在启动模式之间切换,进行一些故障排除,然后再次使用“正常启动”("Normal startup"),所有服务和启动项都将在启动时启用。
如果您想要阻止某些应用程序、驱动程序或服务随Windows自动启动,您需要查看服务和启动项列表并再次对其进行编辑。您可以在本指南后面看到如何做到这一点。不过现在,请注意,一旦您进行了更改,“选择性启动”("Selective startup")将被检查为活动启动选择(startup selection)。
2. 查看您的 PC 上安装了哪些操作系统并选择默认的操作系统
系统配置(System Configuration)工具还提供了一种图形方式来选择首先加载您 PC 上安装的操作系统。在系统配置(System Configuration)工具中,切换到启动(Boot)选项卡,您可以查看计算机上安装的所有操作系统,如果您有多重启动设置,请选择默认操作系统。(default one)要选择新的默认操作系统(default operating system),请单击或点击(click or tap)它,然后单击“设为默认值”。("Set as default.")

3.选择PC等待您选择要启动的操作系统的时间(operating system)
如果您有多重引导设置,另一个重要设置是超时(Timeout )设置。您设置的秒数表示您的 PC 在引导时等待您选择可用操作系统之一的时间。如果在设定的时间内(set time)没有做出任何选择,则默认操作系统启动。

默认情况下,超时(Timeout)设置为 30 秒。如果您有多重引导设置,您可能希望将其设置为较小的值。例如,我们更喜欢将Timeout设置为仅 10 秒。这样,如果我们不选择其他操作系统(operating system),则默认(default one)操作系统的总启动时间(boot timing)不会受到太大影响。
4. 更改有关Windows启动方式的一些高级设置,例如可以使用多少个处理器内核或多少 RAM
对于计算机上安装的Windows 操作系统,(Windows operating)系统配置(System Configuration)工具还允许您配置有关其启动方式的复杂细节。
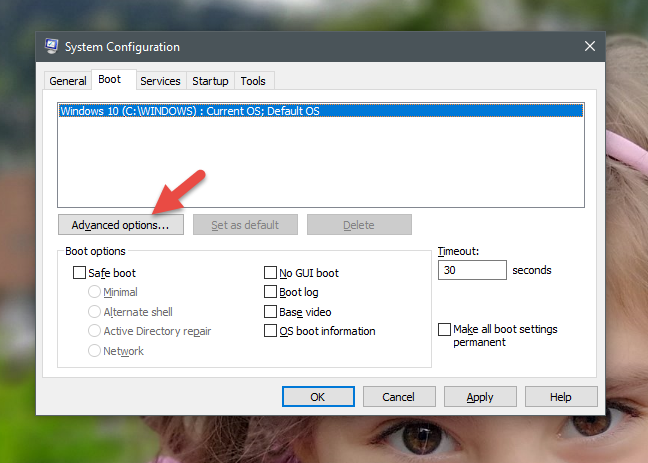
对于每个现有的操作系统,如果您单击或点击“高级选项”("Advanced options")按钮,您可以设置诸如在启动时分配给操作系统(operating system)的处理器(内核)的数量,或可用于的最大RAM量。它。
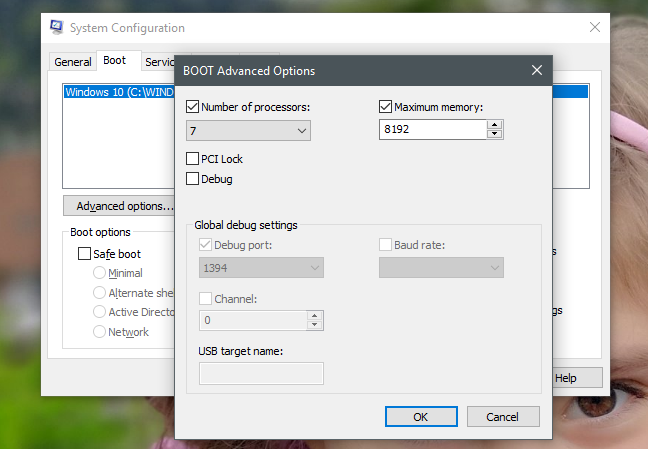
如果您设置了处理器内核和RAM(RAM)的最大数量,Windows将继续正确识别处理器拥有的实际内核数量和物理RAM的数量。但是,它只能使用有限数量的处理器内核和您设置的最大内存。
5. 使 Windows 启动进入安全模式
对于安装在您 PC 上的每个Windows 操作系统,(operating system)系统配置(System Configuration)工具还允许您选择是否要使其启动到安全模式(Safe Mode)。为此,在启动(Boot)选项卡中,您必须选中名为“安全启动”("Safe boot")的选项并选择其可用选项之一:
-
最小 -(Minimal - )正常的安全启动,具有用户界面且未启用网络服务。
-
备用外壳(Alternate shell)-在安全模式下(Safe Mode)打开命令提示符(Command Prompt)。网络服务和图形用户界面(user interface)被禁用。
-
Active Directory 修复(Active Directory repair)- 正常的安全启动,此外还运行Active Directory服务和功能。
-
网络(Network)- 启用网络服务的正常安全启动。

如果您想详细了解Windows中的(Windows)安全模式(Safe Mode ),您可能会对这些指南感兴趣:
- 在Windows 10中启动进入安全模式的 7 种方法(Mode)
- 在Windows 10中通过网络(Networking)启动进入安全模式的 6 种方法(Mode)
- 在Windows 7中启动进入安全模式的 3 种方法(Mode)
- 在Windows 8.1中启动进入安全模式的(Boot Into Safe Mode)5种方法(Ways)
6.禁用Windows启动(Windows boot)加载屏幕,记录启动过程(startup process),使用标准视频驱动程序等
同样在其引导(Boot)选项卡中,系统配置(System Configuration)工具为您提供了一组高级选项,可应用于标准和安全模式(Safe Mode )引导过程:
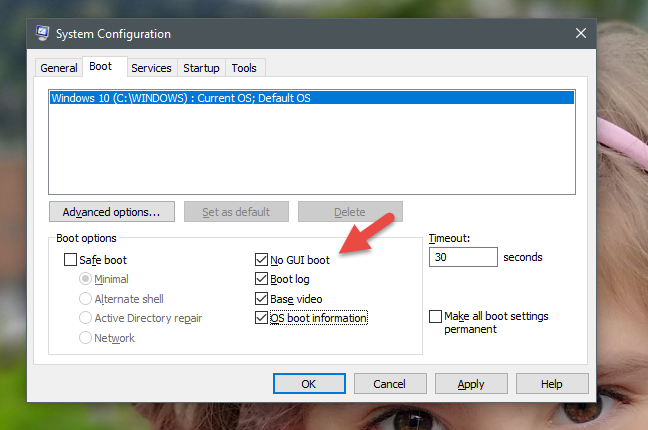
-
“无 GUI 启动”("No GUI boot") - 在启动过程中,您不会看到通常的加载屏幕(loading screen),只有没有信息的黑屏。
-
“启动日志”("Boot log") - 在启动过程中,Windows会写入包含有关启动过程(startup process)信息的完整日志。通常,可以在以下位置找到它:“C: WindowsNtbtlog.txt ”。
-
“基本视频”("Base video") - 如果您刚刚安装了糟糕的视频驱动程序,此选项很方便。它是标准的Windows 启动(Windows startup),不同之处在于它只加载Windows附带的标准视频驱动程序,而不是特定于您的视频卡(video card)的驱动程序。
-
“OS 启动信息”("OS boot information") - 此选项应与“No GUI Boot”一起使用。("No GUI Boot.")通常的Windows加载屏幕将被黑屏取代,显示有关在启动过程(startup process)中加载的驱动程序的完整信息。如果您的Windows在启动期间崩溃,此可视化模式(visualization mode)可用于识别导致崩溃的驱动程序。
7.选择Windows启动哪些服务
系统配置(System Configuration)工具中的服务(Services)选项卡显示Windows启动时启动的所有服务的列表。对于每项服务,您会看到其名称、制造商、当前状态以及禁用日期(如果已禁用)。
您可以选中要在启动时运行的服务并取消选中您不想运行的服务。如果您希望仅查看由您的应用程序安装的第三方服务,请选中“隐藏所有 Microsoft 服务”框。("Hide all Microsoft services.")

您在此选项卡中所做的选择仅适用于常规选项卡中的当前启动(General)选择(startup selection)。如果您使用的是“正常启动”("Normal startup,"),然后禁用了某些服务,则启动选择(startup selection)会自动更改为“选择性启动”。("Selective startup.")
如果您在决定哪些服务在启动时停止运行时需要帮助,请阅读本指南:哪些Windows服务可以安全禁用以及何时禁用?。
8.管理启动程序(仅限Windows 7)
如果您使用的是Windows 10或Windows 8.1,“启动(Startup)”选项卡只会为您提供“打开任务管理器”的链接。("Open Task Manager.")这是因为您的计算机启动应用程序(startup apps)的管理是使用任务管理器(Task Manager)完成的。

但是,如果您使用的是Windows 7,则“启动”选项卡会显示(Startup)Windows启动时启动的所有程序和文件的列表。对于每个项目,您会看到它的名称、制造商、用于启动它的命令(通常是程序的路径和其他参数(如果使用),以及存储它的注册表启动位置(registry startup location)和禁用日期)它被禁用了。

关于注册表位置(registry location)要记住的一件事是,如果您看到一个以HKLM开头的,这意味着启动项是“全局的”——应用于活动操作系统上定义的所有(operating system)用户帐户(user account)。从一个用户帐户(user account)禁用它们意味着它们将被所有用户帐户(user account)禁用。
以HKCU(HKCU)开头的位置用于仅对当前用户帐户(user account)有效的启动项。他们可能没有为其他用户帐户(user account)启动。此外,如果您想阻止它们完全启动,则需要为每个用户帐户(user account)单独禁用它们。
就像“服务(Services)”选项卡一样,您所做的选择将应用于“常规”选项卡中的当前启动(General)选择(startup selection)。
9.启动管理程序和面板
很少有人知道系统配置中的(System Configuration)工具(Tools)选项卡及其作用。如果单击它,您将获得Windows管理工具列表,例如系统信息(System Information)、注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)、事件查看器(Event Viewer)、性能监视器(Performance Monitor)等。
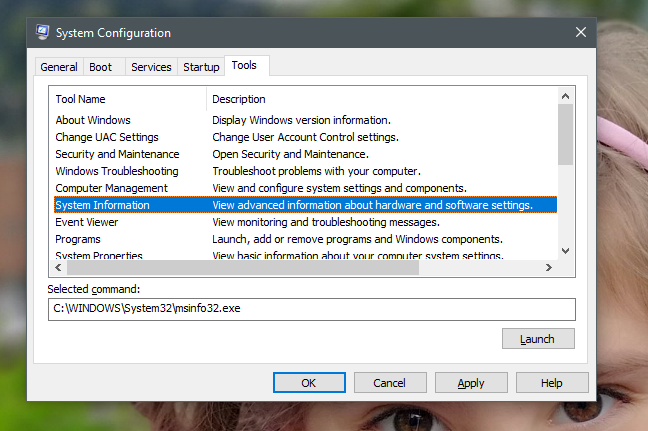
对于每个工具,系统配置(System Configuration)都会显示其名称和描述(name and description)。如果单击或点击它,您可以在Selected command字段中看到用于启动它的命令。要运行任何可用工具,请选择您想要的工具,然后单击或点击Launch。

如您所见,系统配置中的(System Configuration)工具(Tools)选项卡很方便,因为它列出了在解决系统稳定性或性能问题(system stability or performance problems)时通常使用的管理工具。
保存您在系统配置(System Configuration)中所做的更改
完成所需的所有更改后,不要忘记按Apply或OK,以便应用它们。此外,如果您是第一次使用该工具,当您关闭它时,可能会提示您需要重新启动 PC 才能使新设置生效。
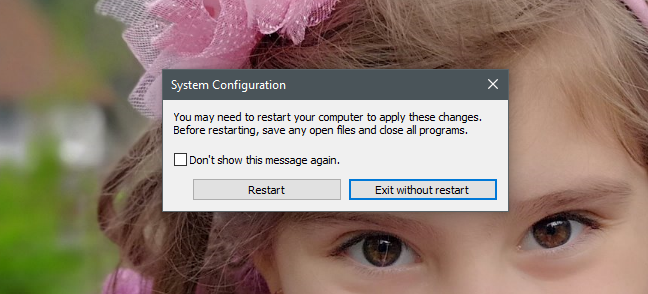
如果您不想再次看到此消息,请选中“不再显示此消息”("Don't show this message again")框,然后选择您喜欢的重新启动选项。(restart option)
您是否正在(Are)使用系统配置工具(System Configuration tool)来改变Windows的工作方式?
如您所见,系统配置 (msconfig.exe)实用程序是一种多功能工具,可为想要更改(System Configuration (msconfig.exe) )Windows启动和工作方式的人们提供有用的功能。它可以是管理Windows 计算机(Windows computer)启动过程(startup process)的绝佳工具,也可以用于解决稳定性和性能问题(stability and performance problems)。你用它来配置Windows吗?你有什么问题吗?让我们(Let)在下面的评论部分讨论。
9 things you can do with System Configuration, in Windows
Do you know how excellent the System Configuration (msconfig.exe) tool from Windows is? Although it is a small and somewhat hidden tool, it allows you to change quite a few things about the way Windows works. Among other things, the System Configuration tool lets you configure how Windows starts, change the boot procedure, select startup services, and programs, and also start a series of useful administrative programs. If you want to know more about the things you can do with System Configuration, read this article:
NOTE: This article covers Windows 10, Windows 7 and Windows 8.1. Before reading it, you should know that we assume you already know how to start System Configuration. If you do not, read this first: 8 ways to start System Configuration in Windows (all versions). Also, if you do not know the version of Windows that you are using, this tutorial should help: What version of Windows do I have installed?
1. Choose what drivers and services are loaded at Windows startup
The System Configuration tool, also known as msconfig.exe, is a window with settings and shortcuts. They are all split into several tabs, and each tab gives you access to different things. The first tab in the System Configuration window is called General, and it is the place where you can configure how Windows starts.

In the "Startup selection" list from the General tab, you can choose to make Windows do a:
-
"Normal startup": meaning that Windows starts as is, with ALL the installed startup items, drivers, and services. This mode should be selected by default on most Windows devices, except when you have already made some changes to what drivers, services or apps are loaded at boot time.
-
"Diagnostic startup": this mode is similar to booting into Safe Mode. Safe Mode runs only Windows services and drivers. Besides them, the Diagnostic startup might also run, on top of them, networking services or important services from third-party applications such as your antivirus, firewall or security suite. This mode is useful if you want to rule out Windows files and services as being the source of system instability problems. Note that if you select the "Diagnostic startup" and then click or tap Apply, the "Selective startup" is the one shown as selected. However, there is nothing to worry about, as this is quite normal. It happens because the "Diagnostic startup" is a "Selective startup" with a predefined set of settings.
-
"Selective startup": makes Windows start only with its essential services and drivers. Furthermore, it also allows you to select other services and startup items that you want to run, from the Services and Startup tabs.

It is also important to note that if you switch between startup modes, do some troubleshooting and then go back to using the "Normal startup" again, all the services and startup items are going to be enabled at startup.
If what you want is to stop some apps, drivers or services from starting automatically with Windows, you need to go through the list of services and startup items and edit them again. You can see how to do that, later in this guide. For now though, note that once you make changes, the "Selective startup" is going to be checked as the active startup selection.
2. See what operating systems are installed on your PC and choose which one is the default
The System Configuration tool also offers a graphical way of choosing which of the operating systems installed on your PC loads first. In the System Configuration tool, switch to the Boot tab, and you can view all the operating systems installed on your computer and select the default one if you have a multi-boot setup. To select a new default operating system, click or tap on it and then on "Set as default."

3. Choose how long the PC waits for you to select the operating system to be booted
If you have a multi-boot setup, another important setting is the Timeout setting. The number of seconds you set represents how long your PC waits for you to select one of the available operating systems when booting. If no choice is made during the set time, the default operating system starts.

By default, the Timeout is set to 30 seconds. If you have a multi-boot setup, you might want to set it to a smaller value. We, for instance, prefer to set the Timeout to only 10 seconds. This way, if we do not select another operating system, the total boot timing of the default one is not affected that much.
4. Change some advanced settings about how Windows boots, like how many processor cores or how much RAM it can use
For the Windows operating system installed on your computer, the System Configuration tool also lets you configure complicated details about the way it boots.

For each of the existing operating systems, if you click or tap on the "Advanced options" button, you can set things such as the number of processors (cores) allocated to the operating system at boot, or the maximum amount of RAM available to it.

If you set a maximum number of processor cores and RAM, Windows continues to correctly identify the real number of cores that the processor has and the amount of physical RAM. However, it can only use the limited number of processor cores and the maximum memory that you have set.
5. Make Windows boot into Safe Mode
For each Windows operating system installed on your PC, the System Configuration tool also lets you select if you want to make it boot into Safe Mode. To do that, in the Boot tab, you must check the option called "Safe boot" and select one of its available options:
-
Minimal - the normal safe boot, with a user interface and no networking services enabled.
-
Alternate shell - opens the Command Prompt in Safe Mode. The networking services and the graphical user interface are disabled.
-
Active Directory repair - a normal safe boot which runs, additionally, the Active Directory services and features.
-
Network - the normal safe boot with networking services enabled.

If you want to read more about the Safe Mode in Windows, these guides might interest you:
6. Disable the Windows boot loading screen, log the startup process, use standard video drivers and others
Also in its Boot tab, the System Configuration tool gives you a set of advanced options which can be applied to both standard and Safe Mode boot procedures:

-
"No GUI boot" - during boot, you are not shown the usual loading screen, only a black screen with no information.
-
"Boot log" - during boot Windows writes a complete log with information about the startup process. Usually, it can be found at this location: "C:WindowsNtbtlog.txt."
-
"Base video" - this option is handy if you just installed lousy video drivers. It makes a standard Windows startup, with the difference that it loads only the standard video drivers that come with Windows, instead of the ones specific to your video card.
-
"OS boot information" - this option should be used together with "No GUI Boot." The usual Windows loading screen will get replaced with a black screen, displaying complete information about the drivers that are loaded during the startup process. If your Windows crashes during boot, this visualization mode can be useful to identify the driver that causes the crash.
7. Select what services are started with Windows
The Services tab from the System Configuration tool shows a list of all the services that start when Windows starts. For each service, you see its name, the manufacturer, the current status and the date when it was disabled if it was disabled.
You can check the services you want to run at startup and uncheck the ones you do not. If you desire to see only third-party services, installed by your applications, check the box that says "Hide all Microsoft services."

The selections you make in this tab are applied only to your current startup selection, from the General tab. If you were using a "Normal startup," and then you disabled some services, the startup selection gets changed automatically to "Selective startup."
If you need help in deciding which services to stop from running at startup, read this guide: Which Windows services are safe to disable and when?.
8. Manage the startup programs (only in Windows 7)
If you are using Windows 10 or Windows 8.1, the Startup tab gives you just a link to "Open Task Manager." This is because the management of your computer's startup apps is done using the Task Manager.

However, if you are using Windows 7, the Startup tab shows a list of all the programs and files that start when Windows starts. For each item, you see its name, the manufacturer, the command used to start it, which is usually the path towards the program and additional parameters if used, and the registry startup location where it is stored and the date when it was disabled if it was disabled.

One thing to remember about the registry location is that, if you see one starting with HKLM, it means that the startup item is "global" - applied to all user accounts defined on the active operating system. Disabling them from one user account means that they get disabled for all user accounts.
The locations starting with HKCU are for startup items active only for the current user account. They might not be starting up for other user accounts. Also, they need to be disabled individually, for each user account, if you want to prevent them from starting altogether.
Just like the Services tab, the selections you make are applied to your current startup selection, from the General tab.
9. Launch administrative programs and panels
Few people know about the Tools tab in System Configuration and what it does. If you click on it, you get a list of Windows administrative tools such as System Information, the Registry Editor, Event Viewer, Performance Monitor and so on.

For each tool, System Configuration shows its name and description. If you click or tap on it, you can see the command used to start it, in the Selected command field. To run any of the available tools, select the one you want and click or tap Launch.

As you can see, the Tools tab from System Configuration is handy as it lists administrative tools generally used during troubleshooting system stability or performance problems.
Save the changes you have made in System Configuration
After you are done making all the changes you wanted, do not forget to press Apply or OK, so that they are applied. Also, if you are using the tool for the first time, when you close it, you might be informed that you need to restart your PC for the new settings to take effect.

If you do not want to see this message again, check the box that says "Don't show this message again" and choose the restart option you prefer.
Are you using the System Configuration tool to change the way Windows works?
As you can see, the System Configuration (msconfig.exe) utility is a versatile tool that offers useful features for people who want to change the way Windows starts and works. It can be an excellent tool for managing the startup process of your Windows computer but also for troubleshooting stability and performance problems. Are you using it to configure Windows? Have you had any issues with it? Let's discuss in the comments section below.














