远程桌面协议 (RDP)(Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP))是 Microsoft开发的专有协议, 它为用户提供图形界面以通过网络连接连接到另一台计算机。用户为此目的使用RDP客户端软件,而另一台计算机必须运行(RDP)RDP服务器软件。在这篇文章中,我们将探讨如何解决 Windows 11/10 上的一般远程桌面连接问题(troubleshoot general Remote Desktop connection issues)。

修复远程桌面(Fix Remote Desktop)连接问题
当远程桌面客户端不工作(Remote Desktop client is not working)或无法连接到远程桌面(cannot connect to a remote desktop)但未提供有助于确定原因的消息或其他症状时,请尝试以下概述的故障排除步骤。
1]检查(Check)本地计算机上RDP协议的状态
您需要启用远程桌面(enable Remote Desktop)以检查和更改本地计算机上RDP协议的状态。(RDP)您还可以使用命令提示符或 PowerShell 启用远程桌面(enable Remote Desktop using Command Prompt or PowerShell)。
2]检查(Check)远程计算机上RDP协议的状态
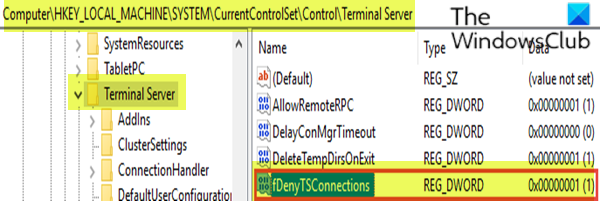
要检查和更改远程计算机上RDP协议的状态,请使用网络注册表连接。
由于这是注册表操作,建议您备份注册表(back up the registry) 或 创建系统还原点 作为必要的预防措施。完成后,您可以执行以下操作:
- 按Windows键 + R 调用“运行”(Run)对话框。
- 在“运行”对话框中,键入
regedit并按 Enter 以打开注册表编辑器(open Registry Editor)。 - 在注册表编辑器中,选择 File,然后选择 Connect Network Registry。
- 在“ 选择计算机(Select Computer)”对话框中,输入远程计算机的名称。
- 选择检查名称。(Check Names.)
- 选择确定(OK)。
- 接下来, 导航或跳转到下面的注册表项路径:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
- 在该位置的右侧窗格中,双击fDenyTSConnections键以编辑其属性。
- 要启用RDP,请将fDenyTSConnections的(fDenyTSConnections)值(Value)数据 从 1 设置为 0。
值 0 表示启用RDP,而值 1 表示禁用RDP 。
相关(Related):远程桌面选项(Remote Desktop option is greyed out)在 Windows 10 上显示为灰色,
3]检查(Check)组策略对象(Group Policy Object)( GPO )是否阻止本地计算机上的RDP
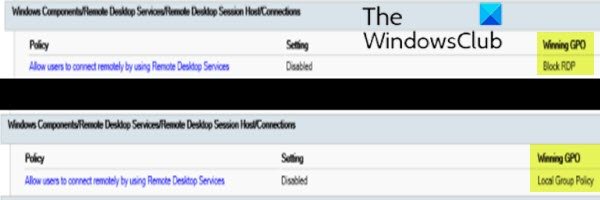
如果您无法在用户界面中 打开RDP ,或者(RDP)fDenyTSConnections的值 在您更改后 恢复为 1 ,则(1)GPO可能会覆盖计算机级别的设置(GPO)
要检查本地计算机上的组策略配置,请执行以下操作:
gpresult /H c:\gpresult.html
- 命令执行后,打开 gpresult.html。
- 在Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections连接中,找到允许用户使用远程桌面服务进行远程连接(Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services) 策略。
如果此策略的设置为 Enabled,则组策略(Group Policy)不会阻止RDP连接。如果此策略的设置为 Disabled,请选中 Winning GPO。这是阻止RDP连接的GPO 。
4]检查(Check)GPO是否阻止远程计算机上的RDP
要检查远程计算机上的组策略配置,请在提升的(Group Policy)CMD提示符下运行以下命令:
gpresult /S <computer name> /H c:\gpresult-<computer name>.html
此命令生成的文件 ( gpresult-<computer name>.htmlgpresult.html )使用的相同信息格式。
5]修改阻塞GPO
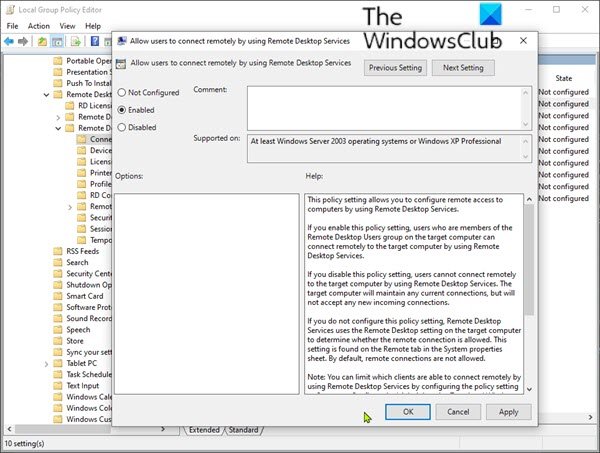
您可以在组策略对象编辑器(Group Policy Object Editor)( GPE ) 和组策略管理控制台 (GPMC)中修改这些设置。
要修改阻止策略,请使用以下方法之一:
使用 GPE,执行以下操作:
- 按Windows key + R调用“运行”对话框。
- 在 Run 对话框中键入
gpedit.msc并按 Enter打开 Group Policy Editor(open Group Policy Editor)。 - 在本地组策略编辑器(Local Group Policy Editor)中,使用左窗格导航到以下路径:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections
- 在该位置的右窗格中,双击允许用户使用远程桌面服务进行远程连接以(Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services)编辑其属性。
- 将策略设置为 Enabled 或 Not configured。
- 单击应用(Apply)>确定(OK)并退出。
- 在受影响的计算机上,以管理员身份打开命令提示符窗口,然后运行以下命令:
gpupdate /force
使用GPMC导航到将阻止策略应用于受影响计算机的组织单位 (OU),然后从 OU 中删除该策略。
6]检查(Check)RDP服务的状态
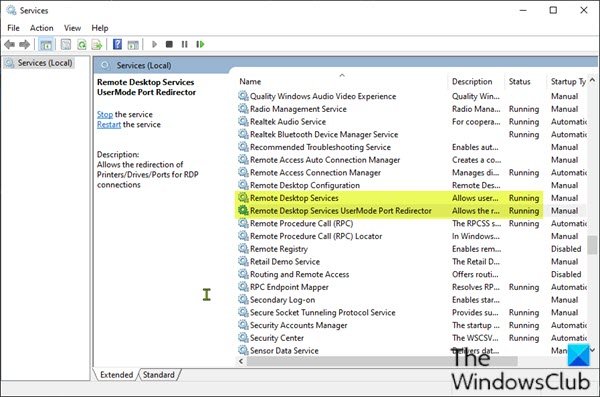
在本地(客户端)计算机和远程(目标)计算机上,应运行以下服务:
- 远程桌面服务(Remote Desktop Services)( TermService )
- 远程桌面服务用户模式端口重定向器(Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector)( UmRdpService )
在任一计算机上,如果一个或两个服务未运行,请启动它们。
请执行下列操作:
- 按Windows key + R调用“运行”对话框。
- 在 Run 对话框中,键入
services.msc并按 Enter打开 Services(open Services)。 - 在“服务(Services)”窗口中,滚动并找到上述两个服务。
- 双击(Double-click)条目以编辑其属性。
- 在属性窗口中,单击开始(Start)按钮。
- 单击确定(OK)。
您还可以使用PowerShell在本地或远程管理服务(如果远程计算机配置为接受远程PowerShell cmdlet)。
7]检查(Check)RDP监听器的状态
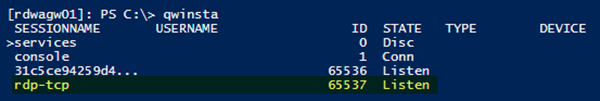
此过程使用PowerShell,因为相同的 cmdlet 在本地和远程工作。对于本地计算机,您还可以使用具有管理权限的命令提示符。
要连接到远程计算机,请执行以下操作:
- 按Windows key + X打开高级用户菜单(open Power User Menu)。
- 点击键盘上的A以在管理员/提升模式下启动 PowerShell 。
- 在PowerShell控制台中,键入以下命令并按Enter:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
如果列表包含 状态为 Listen的(Listen)rdp-tcp,如上图所示,则RDP侦听器正在工作。跳转(Jump)到下面的故障排除步骤 10](Troubleshooting step 10])。否则(Otherwise),您需要从工作计算机中导出RDP侦听器配置。(RDP)
请执行下列操作:
- 登录到与受影响计算机具有相同操作系统版本的计算机,然后访问该计算机的注册表。
- 导航(Navigate)或跳转到以下注册表项:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
- 将条目导出到 .reg 文件(Export the entry to a .reg file)。
- 将导出的 .reg 文件复制到受影响的计算机。
- 要导入RDP侦听器配置,请在受影响的计算机上打开一个具有管理权限的 PowerShell 窗口(或打开PowerShell窗口(PowerShell)并远程连接到受影响的计算机)。
要备份现有注册表项(To back up the existing registry entry),请输入以下 cmdlet:
cmd /c 'reg export "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp" C:\Rdp-tcp-backup.reg'
要删除现有注册表项(To remove the existing registry entry),请输入以下 cmdlet:
Remove-Item -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp' -Recurse -Force
要导入新的注册表项然后重新启动服务(To import the new registry entry and then restart the service),请运行以下 cmdlet。将<filename>占位符替换为导出的.reg文件的名称。
cmd /c 'regedit /s c:\<filename>.reg'
Restart-Service TermService -Force
执行完 cmdlet 后,您可以通过再次尝试远程桌面连接来测试配置。如果仍然无法连接,请重新启动受影响的计算机。
如果仍然无法连接,请继续执行下一个故障排除步骤,即检查 RDP 自签名证书的状态(check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate)。
8]检查(Check)RDP自签名证书的状态
如果仍然无法连接,请执行以下操作:
- 按Windows key + R调用“运行”对话框。
- 在“运行”对话框中,键入
mmc并按 Enter 以打开 Microsoft 管理控制台(open Microsoft Management Console)。 - 单击文件(File)菜单。
- 选择Add/Remove Snap-in。
- (Certificates)(Select Certificates)从管理单元列表中选择 证书。
- 单击添加(Add)。
- 当系统提示您选择要管理的证书存储时,选择 计算机帐户。(Computer account.)
- 单击下一步(Next)。
- 选择受影响的计算机。
- 单击完成(Finish)按钮。
- 单击确定(OK)。
- 现在,在Remote Desktop下的(Remote Desktop)Certificates 文件夹 中,删除RDP自签名证书。
- 在受影响的计算机上,重新启动远程桌面服务(Remote Desktop Services)服务。
- 刷新证书管理单元。
- 如果尚未重新创建RDP自签名证书,请检查(RDP)MachineKeys文件夹的权限。
9]检查(Check)MachineKeys文件夹的权限
在受影响的计算机上,执行以下操作:
- 按Windows key + E打开文件资源管理器(open File Explorer)。
- 导航到以下目录路径:
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\
- 在该位置,右键单击MachineKeys,选择 Properties,选择 Security,然后选择 Advanced。
确保(Make)配置了以下权限:
- BuiltinAdministrators:完全控制(Full control)
- 每个人:读,写(Read, Write)
10]检查RDP监听端口
在本地(客户端)计算机和远程(目标)计算机上,RDP侦听器应在端口 3389 上进行侦听。其他应用程序不应使用此端口。
要检查或更改RDP端口,请使用注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)。作为预防措施备份注册表或创建系统还原点,然后继续如下:
- 打开注册表编辑器,选择File,然后选择 Connect Network Registry。
- 在“ 选择计算机(Select Computer)”对话框中,输入远程计算机的名称。
- 选择检查名称。(Check Names.)
- 选择确定(OK)。
- 接下来, 导航或跳转到下面的注册表项路径:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
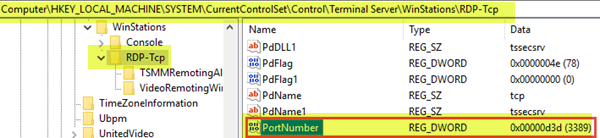
- 在该位置的右窗格中,双击PortNumber条目以编辑其属性。
- 在属性窗口中,如果数值(Value)数据字段的值不是3389,请将其更改为 3389。
- 单击确定(OK)以保存更改。
- 重新启动远程桌面服务(Remote Desktop Services)服务。
11]检查(Check)另一个应用程序没有使用相同的端口
请执行下列操作:
- 以提升模式打开 PowerShell。
- 要连接到远程计算机,请运行以下命令:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
接下来,运行以下命令:
cmd /c 'netstat -ano | find "3389"'
- 查找状态为(Look)Listening的(Listening)TCP端口 3389(或分配的RDP端口) 的条目。
注意(Note):使用该端口的进程或服务的进程标识符 ( PID ) 显示在PID列下。
- 要确定哪个应用程序正在使用端口 3389(或分配的RDP端口),请输入以下命令:
cmd /c 'tasklist /svc | find "<pid listening on 3389>"'
- 查找(Look)与端口关联 的PID编号条目(从
netstat 输出中)。与该PID关联的服务或进程显示在右列中。 - 如果远程桌面服务(Remote Desktop Services)( TermServ.exe )以外的应用程序或服务正在使用该端口,您可以使用以下方法之一解决冲突:
将其他应用程序或服务配置为使用不同的端口(推荐)。
卸载其他应用程序或服务。
将RDP(RDP)配置为使用不同的端口,然后重新启动远程桌面服务(Remote Desktop Services)服务(不推荐)。
12]检查(Check)防火墙是否阻塞了RDP端口
您可以使用psping 工具测试您是否可以通过端口 3389 访问受影响的计算机。
请执行下列操作:
- 转到不受影响的另一台计算机并下载(download) psping 。
- 以管理员身份打开命令提示符窗口,切换到安装 psping的目录,然后输入以下命令:
psping -accepteula <computer IP>:3389
Connecting to <computer IP>:远程计算机是可访问的。
(0% loss):所有连接尝试都成功。
远程计算机拒绝网络连接(The remote computer refused the network connection):远程计算机不可访问。
(100% loss):所有连接尝试均失败。
- 在多台计算机上运行 psping 以测试它们连接到受影响计算机的能力。
- 请注意受影响的计算机是否阻止来自所有其他计算机、其他一些计算机或仅另一台计算机的连接。
您可以采取的其他步骤包括:
- 让您的网络管理员验证网络是否允许RDP流量流向受影响的计算机。
- 调查源计算机和受影响计算机之间的任何防火墙的配置(包括受影响计算机上的Windows 防火墙(Windows Firewall)),以确定防火墙是否阻止了RDP端口。
希望这篇文章可以帮助您成功解决您可能遇到的RDP连接问题!(RDP)
Fix Remote Desktop connection issues & errors on Windows 11/10
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft which provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection. The user employs RDP client software for this purpose, while the other computer must run RDP server software. In this post, we will explore how to troubleshoot general Remote Desktop connection issues on Windows 11/10.

Fix Remote Desktop connection issues
Try the outlined troubleshooting steps below when a Remote Desktop client is not working or cannot connect to a remote desktop but doesn’t provide messages or other symptoms that would help identify the cause.
1] Check the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer
You’ll need to enable Remote Desktop to check and change the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer. You can also enable Remote Desktop using Command Prompt or PowerShell.
2] Check the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer

To check and change the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer, use a network registry connection.
Since this is a registry operation, it is recommended that you back up the registry or create a system restore point as necessary precautionary measures. Once done, you can proceed as follows:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
regedit and hit Enter to open Registry Editor. - In the Registry Editor, select File, then select Connect Network Registry.
- In the Select Computer dialog box, enter the name of the remote computer.
- Select Check Names.
- Select OK.
- Next, navigate or jump to the registry key path below:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
- At the location, on the right pane, double-click the fDenyTSConnections key to edit its properties.
- To enable RDP, set the Value data of fDenyTSConnections from 1 to 0.
The value of 0 indicates RDP is enabled, while the value of 1 indicates RDP is disabled.
Related: Remote Desktop option is greyed out on Windows 10,
3] Check whether a Group Policy Object (GPO) is blocking RDP on a local computer

A GPO may be overriding the computer-level settings, if you can’t turn on RDP in the user interface or the value of fDenyTSConnections reverts to 1 after you’ve changed it
To check the group policy configuration on a local computer, do the following:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
cmd and then press CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER to open Command Prompt in admin/elevated mode. - In the command prompt window, type the command below and hit Enter.
gpresult /H c:\gpresult.html
- Once the command executes, open gpresult.html.
- In Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections, find the Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services policy.
If the setting for this policy is Enabled, Group Policy is not blocking RDP connections. If the setting for this policy is Disabled, check Winning GPO. This is the GPO that is blocking RDP connections.
4] Check whether a GPO is blocking RDP on a remote computer
To check the Group Policy configuration on a remote computer, run the command below in elevated CMD prompt:
gpresult /S <computer name> /H c:\gpresult-<computer name>.html
The file that this command produces (gpresult-<computer name>.html) uses the same information format as the local computer version (gpresult.html) uses.
5] Modify a blocking GPO

You can modify these settings in the Group Policy Object Editor (GPE) and Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
To modify the blocking policy, use one of the following methods:
Using GPE, do the following:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box type
gpedit.msc and press Enter to open Group Policy Editor. - Inside the Local Group Policy Editor, use the left pane to navigate to the path below:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections
- At the location, on the right pane, double click the Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services.to edit its properties.
- Set the policy to either Enabled or Not configured.
- Click Apply > OK and exit.
- On the affected computers, open a command prompt window as an administrator, and run the command below:
gpupdate /force
Using GPMC, navigate to the organizational unit (OU) in which the blocking policy is applied to the affected computers and delete the policy from the OU.
6] Check the status of the RDP services

On both the local (client) computer and the remote (target) computer, the following services should be running:
- Remote Desktop Services (TermService)
- Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector (UmRdpService)
On either computer, if one or both services are not running, start them.
Do the following:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
services.msc and hit Enter to open Services. - In the Services window, scroll and locate both aforementioned service.
- Double-click on the entry to edit its properties.
- In the properties window, click the Start button.
- Click OK.
You can also use PowerShell to manage the services locally or remotely (if the remote computer is configured to accept remote PowerShell cmdlets).
7] Check the status of the RDP listener

This procedure uses PowerShell because the same cmdlets work both locally and remotely. For a local computer, you can also use a command prompt that has administrative permissions.
To connect to a remote computer, do the following:
- Press Windows key + X to open Power User Menu.
- Tap A on the keyboard to launch PowerShell in admin/elevated mode.
- In the PowerShell console, type in the command below and hit Enter:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
If the list includes rdp-tcp with a status of Listen, as shown in the image above, the RDP listener is working. Jump to the Troubleshooting step 10] below. Otherwise, you’ll need to export the RDP listener configuration from a working computer.
Do the following:
- Sign in to a computer that has the same operating system version as the affected computer has, and access that computer’s registry.
- Navigate or jump to the following registry entry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
- Export the entry to a .reg file.
- Copy the exported .reg file to the affected computer.
- To import the RDP listener configuration, open a PowerShell window that has administrative permissions on the affected computer (or open the PowerShell window and connect to the affected computer remotely).
To back up the existing registry entry, enter the following cmdlet:
cmd /c 'reg export "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp" C:\Rdp-tcp-backup.reg'
To remove the existing registry entry, enter the following cmdlets:
Remove-Item -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp' -Recurse -Force
To import the new registry entry and then restart the service, run the cmdlets below. Replace the <filename> placeholder with the name of the exported .reg file.
cmd /c 'regedit /s c:\<filename>.reg'
Restart-Service TermService -Force
Once done executing the cmdlets, you can test the configuration by trying the remote desktop connection again. If you still can’t connect, restart the affected computer.
If you still can’t connect, proceed with the next troubleshooting step which is to check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate.
8] Check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate

If you still can’t connect, do the following:
- Press the Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
mmc and hit Enter to open Microsoft Management Console. - Click the File menu.
- Select Add/Remove Snap-in.
- Select Certificates from the list of snap-ins.
- Click Add.
- When you are prompted to select the certificate store to manage, select Computer account.
- Click Next.
- Select the affected computer.
- Click the Finish button.
- Click OK.
- Now, in the Certificates folder under Remote Desktop, delete the RDP self-signed certificate.
- On the affected computer, restart the Remote Desktop Services service.
- Refresh the Certificates snap-in.
- If the RDP self-signed certificate has not been recreated, check the permissions of the MachineKeys folder.
9] Check the permissions of the MachineKeys folder
On the affected computer, do the following:
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\
- At the location, right-click MachineKeys, select Properties, select Security, and then select Advanced.
Make sure that the following permissions are configured:
- Builtin\Administrators: Full control
- Everyone: Read, Write
10] Check the RDP listener port

On both the local (client) computer and the remote (target) computer, the RDP listener should be listening on port 3389. No other applications should be using this port.
To check or change the RDP port, use the Registry Editor. As a precautionary measure back up the registry or create a system restore point, then continue as follows:
- Open Registry Editor, select File, then select Connect Network Registry.
- In the Select Computer dialog box, enter the name of the remote computer.
- Select Check Names.
- Select OK.
- Next, navigate or jump to the registry key path below:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
- At the location, on the right pane, double-click the PortNumber entry to edit its properties.
- In the properties window, if the Value data field has a value other than 3389, change it to 3389.
- Click OK to save changes.
- Restart the Remote Desktop Services service.
11] Check that another application isn’t using the same port
Do the following:
- Open a PowerShell in elevated mode.
- To connect to a remote computer, run the command below:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
Next, run the following command:
cmd /c 'netstat -ano | find "3389"'
- Look for an entry for TCP port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port) with a status of Listening.
Note: The process identifier (PID) for the process or service using that port appears under the PID column.
- To determine which application is using port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port), enter the following command:
cmd /c 'tasklist /svc | find "<pid listening on 3389>"'
- Look for an entry for the PID number that is associated with the port (from the
netstat output). The services or processes that are associated with that PID appear on the right column. - If an application or service other than Remote Desktop Services (TermServ.exe) is using the port, you can resolve the conflict by using one of the following methods:
Configure the other application or service to use a different port (recommended).
Uninstall the other application or service.
Configure RDP to use a different port, and then restart the Remote Desktop Services service (not recommended).
12] Check whether a firewall is blocking the RDP port
You can use the psping tool to test whether you can reach the affected computer by using port 3389.
Do the following:
- Go to a different computer that isn’t affected and download psping.
- Open a command prompt window as an administrator, change to the directory in which you installed psping, and then enter the following command:
psping -accepteula <computer IP>:3389
- Check the output of the psping command for results such as the following:
Connecting to <computer IP>: The remote computer is reachable.
(0% loss): All attempts to connect succeeded.
The remote computer refused the network connection: The remote computer is not reachable.
(100% loss): All attempts to connect failed.
- Run psping on multiple computers to test their ability to connect to the affected computer.
- Note whether the affected computer blocks connections from all other computers, some other computers, or only one other computer.
Additional steps you can take includes;
- Engage your network administrators to verify that the network allows RDP traffic to the affected computer.
- Investigate the configurations of any firewalls between the source computers and the affected computer (including Windows Firewall on the affected computer) to determine whether a firewall is blocking the RDP port.
Hope this post can help you successfully troubleshoot RDP connection issues you might be having!








