如果您使用的是Windows 10 PC,您可能希望获取有关您的用户帐户或 PC 上其他帐户的一些信息,例如全名、帐户类型等。因此,在本教程中,我们将向您展示如何获取所有信息有关您的用户帐户或 PC 上所有用户帐户的详细信息。如果您有太多的用户帐户,那么就不可能记住所有这些帐户的详细信息,而这正是本教程提供帮助的地方。
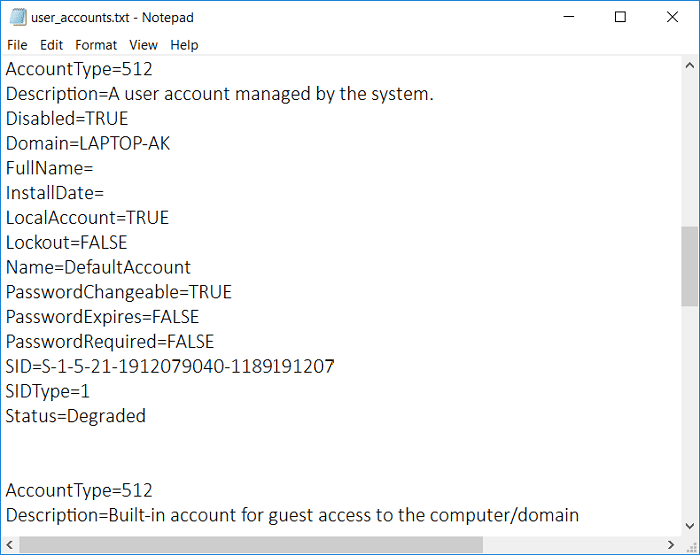
您还可以将包含每个帐户详细信息的整个用户帐户列表保存到记事本文件中,以便将来轻松访问。可以使用命令提示符通过一个简单的命令提取用户帐户的详细信息。因此,不要浪费任何时间,让我们看看如何在下面列出的指南的帮助下查看Windows 10中的用户帐户详细信息。(View User Account Details)
如何在Windows 10中(Windows 10)查看用户帐户详细信息(View User Account Details)
确保 创建一个还原点(create a restore point),以防万一出现问题。
方法 1:查看特定用户帐户的详细信息(Method 1: View Details of a particular User Account)
1.打开命令提示符(Command Prompt)。用户可以通过搜索“ cmd”然后按 Enter 来执行此步骤。
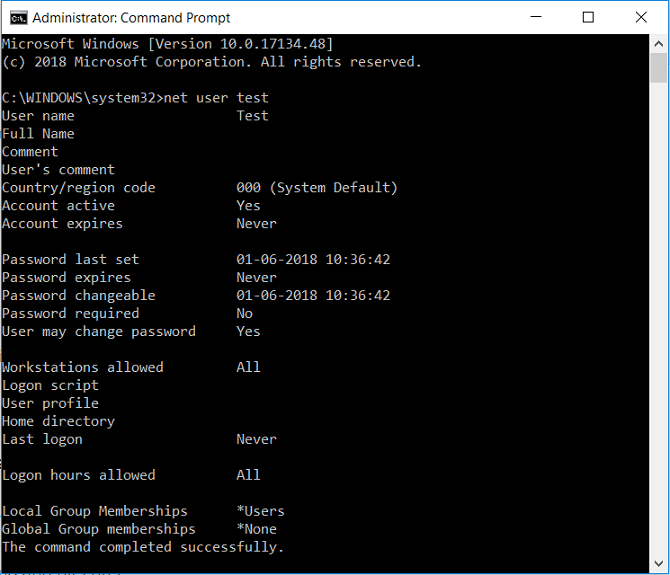
2.在 cmd 中键入以下命令并按Enter:
网络用户用户名(net user user_name)
注意:(Note:) 将(Replace)user_name 替换为您要提取详细信息的用户帐户的实际用户名。
3.有关哪个字段代表什么的详细信息,请滚动到本教程的末尾。
4.重新启动您的 PC 以保存更改,这是 如何在 Windows 10 中查看用户帐户详细信息。(How to View User Account Details in Windows 10.)
方法二:查看所有用户账号详情(Method 2: View Details of All User Accounts)
1.打开命令提示符(Command Prompt)。用户可以通过搜索“ cmd”然后按 Enter 来执行此步骤。
2.在 cmd 中键入以下命令并按Enter:
wmic 用户帐户列表已满(wmic useraccount list full)

3. 现在,如果您有很多用户帐户,那么这个列表会很长,因此最好将列表导出到记事本文件中。
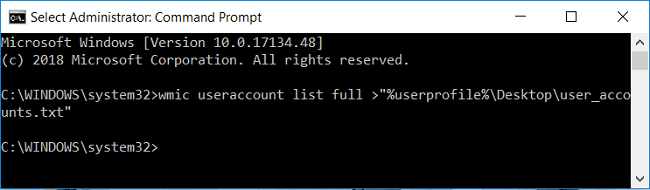
4. 在 cmd 中输入命令并按Enter:
wmic useraccount list full >”%userprofile%\Desktop\user_accounts.txt”
5. 上面的文件user_accounts.txt会保存在桌面,方便访问。
6. 就是这样,您已经成功学习了如何在 Windows 10 中查看用户帐户详细信息。(How to View User Account Details in Windows 10.)
输出文件的相关资料:(Information about Output File:)
| Properties |
Description |
| AccountType |
A flag that describes the characteristics of the user account.
-
256 = (UF_TEMP_DUPLICATE_ACCOUNT) Local user account for users who have a primary account in another domain. This account provides user access to this domain only—not to any domain that trusts this domain.
-
512 = (UF_NORMAL_ACCOUNT) Default account type that represents a typical user.
-
2048 = (UF_INTERDOMAIN_TRUST_ACCOUNT) Account for a system domain that trusts other domains.
-
4096 = (UF_WORKSTATION_TRUST_ACCOUNT) Computer account for a computer system running Windows that is a member of this domain.
-
8192 = (UF_SERVER_TRUST_ACCOUNT) Account for a system backup domain controller that is a member of this domain.
|
| Description |
Description of the account if available. |
| Disabled |
True or False if the user account is currently disabled. |
| Domain |
Name of the Windows domain (ex: computer name) the user account belongs. |
| FullName |
Full name of the local user account. |
| InstallDate |
The date the object is installed if available. This property does not need a value to indicate that the object is installed. |
| LocalAccount |
True or False if the user account is defined on the local computer. |
| Lockout |
True or False if the user account is currently locked out of Windows. |
| Name |
Name of the user account. This would be the same name as the “C:\Users\(user-name)” profile folder of the user account. |
| PasswordChangeable |
True or False if the password of the user account can be changed. |
| PasswordExpires |
True or False if the password of the user account expires. |
| PasswordRequired |
True or False if a password is required for the user account. |
| SID |
A security identifier (SID) for this account. A SID is a string value of variable length that is used to identify a trustee. Each account has a unique SID that authority, such as a Windows domain, issues. The SID is stored in the security database. When a user logs on, the system retrieves the user SID from the database, places the SID in the user access token, and then uses the SID in the user access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. Each SID is a unique identifier for a user or group, and a different user or group cannot have the same SID. |
| SIDType |
An enumerated value that specifies the type of SID.
-
1 = User
-
2 = Group
-
3 = Domain
-
4 = Alias
-
5 = Well Known group
-
6 = Deleted account
-
7 = Invalid
-
8 = Unknown
-
9 = Computer
|
| Status |
Current status of an object. Various operational and nonoperational statuses can be defined.
Operational statuses include: “OK”, “Degraded”, and “Pred Fail”, which is an element such as a SMART-enabled hard disk drive that may be functioning properly, but predicts a failure in the near future.
Nonoperational statuses include: “Error”, “Starting”, “Stopping”, and “Service”, which can apply during mirror resilvering of a disk, reloading a user permissions list, or other administrative work.
The values are:
- OK
- Error
- Degraded
- Unknown
- Pred Fail
- Starting
- Stopping
- Service
- Stressed
- NonRecover
- No Contact
- Lost Comm
|
受到推崇的:(Recommended:)
至此,您已经成功学习了如何在 Windows 10 中查看用户帐户详细信息,(How to View User Account Details in Windows 10)但如果您对本教程仍有任何疑问,请随时在评论区提问。
How to View User Account Details in Windows 10
If you are on a Windows 10 PC, you might want to get some information about your user аcсount or other accounts on your PC such as full name, accoυnt type etc. So in this tutоrial, we will show you how to get all the information about your user account or details of all the user accoυnt on your PC. Іf you have too many user accоunts, then it’s іmpossible to remember details all of them and thіs where this tutoriаl comes in to help.

You could also save the entire list of user accounts with details of every account to a notepad file where it can be easily accessed in future. Details of user accounts can be extracted via a simple command using the command prompt. So without wasting any time, let’s see How to View User Account Details in Windows 10 with the help of the below-listed guide.
How to View User Account Details in Windows 10
Make sure to create a restore point just in case something goes wrong.
Method 1: View Details of a particular User Account
1. Open Command Prompt. The user can perform this step by searching for ‘cmd’ and then press Enter.

2.Type the following command into cmd and hit Enter:
net user user_name

Note: Replace user_name with actual username of the user account for which you want to extract the details.
3.For detail information about which field represents what, please scroll to the end of this tutorial.
4.Reboot your PC to save changes and this is How to View User Account Details in Windows 10.
Method 2: View Details of All User Accounts
1. Open Command Prompt. The user can perform this step by searching for ‘cmd’ and then press Enter.
2.Type the following command into cmd and hit Enter:
wmic useraccount list full

3. Now if you have many user accounts, then this list will be long so it will be a better idea to export the list into a notepad file.
4. Type the command into cmd and hit Enter:
wmic useraccount list full >”%userprofile%\Desktop\user_accounts.txt”

5. The above file user_accounts.txt will be saved on the desktop where it can be easily accessed.
6. That’s it, and you have successfully learned How to View User Account Details in Windows 10.
Information about Output File:
| Properties |
Description |
| AccountType |
A flag that describes the characteristics of the user account.
-
256 = (UF_TEMP_DUPLICATE_ACCOUNT) Local user account for users who have a primary account in another domain. This account provides user access to this domain only—not to any domain that trusts this domain.
-
512 = (UF_NORMAL_ACCOUNT) Default account type that represents a typical user.
-
2048 = (UF_INTERDOMAIN_TRUST_ACCOUNT) Account for a system domain that trusts other domains.
-
4096 = (UF_WORKSTATION_TRUST_ACCOUNT) Computer account for a computer system running Windows that is a member of this domain.
-
8192 = (UF_SERVER_TRUST_ACCOUNT) Account for a system backup domain controller that is a member of this domain.
|
| Description |
Description of the account if available. |
| Disabled |
True or False if the user account is currently disabled. |
| Domain |
Name of the Windows domain (ex: computer name) the user account belongs. |
| FullName |
Full name of the local user account. |
| InstallDate |
The date the object is installed if available. This property does not need a value to indicate that the object is installed. |
| LocalAccount |
True or False if the user account is defined on the local computer. |
| Lockout |
True or False if the user account is currently locked out of Windows. |
| Name |
Name of the user account. This would be the same name as the “C:\Users\(user-name)” profile folder of the user account. |
| PasswordChangeable |
True or False if the password of the user account can be changed. |
| PasswordExpires |
True or False if the password of the user account expires. |
| PasswordRequired |
True or False if a password is required for the user account. |
| SID |
A security identifier (SID) for this account. A SID is a string value of variable length that is used to identify a trustee. Each account has a unique SID that authority, such as a Windows domain, issues. The SID is stored in the security database. When a user logs on, the system retrieves the user SID from the database, places the SID in the user access token, and then uses the SID in the user access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. Each SID is a unique identifier for a user or group, and a different user or group cannot have the same SID. |
| SIDType |
An enumerated value that specifies the type of SID.
-
1 = User
-
2 = Group
-
3 = Domain
-
4 = Alias
-
5 = Well Known group
-
6 = Deleted account
-
7 = Invalid
-
8 = Unknown
-
9 = Computer
|
| Status |
Current status of an object. Various operational and nonoperational statuses can be defined.
Operational statuses include: “OK”, “Degraded”, and “Pred Fail”, which is an element such as a SMART-enabled hard disk drive that may be functioning properly, but predicts a failure in the near future.
Nonoperational statuses include: “Error”, “Starting”, “Stopping”, and “Service”, which can apply during mirror resilvering of a disk, reloading a user permissions list, or other administrative work.
The values are:
- OK
- Error
- Degraded
- Unknown
- Pred Fail
- Starting
- Stopping
- Service
- Stressed
- NonRecover
- No Contact
- Lost Comm
|
Recommended:
That’s it you have successfully learned How to View User Account Details in Windows 10 but if you still have any queries regarding this tutorial please feel free to ask them in the comment’s section.





