本指南将帮助您了解、分析、故障排除和修复(fix Windows Blue Screen of Death)Windows 11/10/8/7中的 Windows 蓝屏死机、停止错误(Stop Errors)、错误代码(Error Codes)、错误检查(Bug Check)错误、系统崩溃错误、系统故障、内核错误崩溃。当 Windows 遇到危及安全系统操作的情况(即“错误”)时,系统会停止。
(Blue Screen)Windows 11/10 11/10蓝屏死机(Death)_
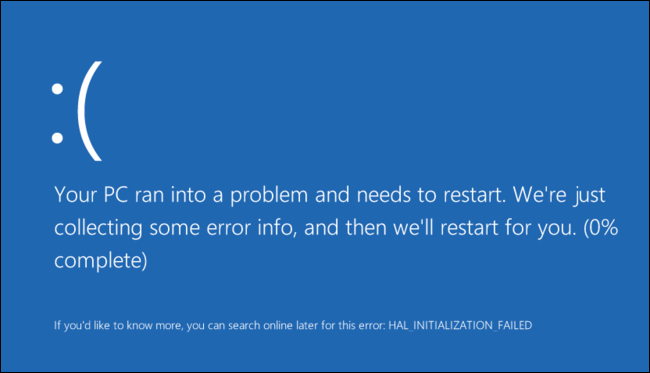
这种情况称为“错误检查(bug check)”。它通常也被称为系统崩溃、内核错误、系统故障或停止错误(Stop Error)。
在Windows XP中,Windows 错误报告(Windows Error Reporting)系统基本上是手动的,但现在在Windows 7和Windows Vista中得到了改进和简化。虽然情况可能如此,但蓝屏(Blue Screens)并没有消失。Windows 7/8上看到它们。
通常,当发生蓝屏(BSOD)时,它会在 PC 立即重新启动之前停留一秒钟。这样我们就无法阅读所写的内容。要解决这个问题,必须从“启动(StartUp)和系统恢复(System Recovery)”设置中禁用自动 PC 重启选项。了解错误代码有助于识别问题/解决方案。执行以下操作:
禁用UAC。Control Panel > System和Maintenance > System > Advanced System Settings > Advanced选项卡>在启动(Startup)和恢复下Recovery > Click Settings > Clear自动重新启动(Automatically Restart)复选框>单击确定。启用UAC。
在大多数情况下,Windows 会尝试自行修复问题,但如果无法自行恢复,则会导致蓝屏。
Windows 11/10 中的蓝屏错误

Windows系统的用户肯定在某一时刻经历过“致命异常”的恐怖,通常称为“蓝屏死机”或BSOD。尽管BSOD已在很大程度上被扔到软件渣堆中,但在Vista中,崩溃并没有完全消除。当Windows遇到危及安全系统操作的情况(即“错误”)时,系统会停止。这种情况称为“错误检查”。它通常也称为系统崩溃、内核错误、系统故障或停止(Stop)错误。当Windows遇到如此严重的错误迫使它停止运行时,它会显示一个死亡(BLUE SCREEN OF DEATH)的蓝屏或只是“亲切地”称为BSOD!
在Windows 11/10/8/7中,与 XP 系统基本上是手动的不同,Windows 错误报告在(Windows Error Reporting)Windows 7和Vista中得到了改进和简化。必须跟进以查看是否有可用的解决方案。这是一个相当痛苦的过程。在Windows 10/8/7/Vista中,整个报告和跟进过程是自动化的。
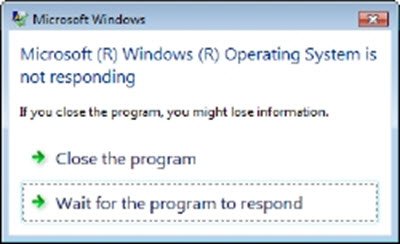
如今,Windows 11/10/8/7/Vista用户更常看到如下消息:“ Microsoft Windows 操作系统没有响应(Microsoft Windows Operating System is not responding)。” 并且给了用户两种可能。他们可以“关闭程序”或“等待(Wait)程序响应”。” 一个人(” One)等待问题得到解决,或者一个人只是关闭程序并准备丢失信息。至少,这些信息看起来不那么令人生畏。
另一方面,至少可以说,蓝屏死机是/非常痛苦和令人沮丧的!(BSODs)
根据导致错误的原因,停止(Stop)错误的确切文本会有所不同。但格式是标准化的,由3 部分组成(3 parts):
- 第 1 部分(PART 1):符号错误名称:这是提供给操作系统的停止错误消息,对应于出现的(Stop Error)停止错误(Stop Error)编号。
- 第 2 部分(PART 2):故障排除建议:本文适用于该特定类型的所有停止(Stop)错误。
- 第 3 部分(PART 3):错误编号和参数:它的错误检查信息。单词STOP(STOP)后面的文本包括错误编号(以十六进制表示)和最多四个此错误类型的典型参数。
一般来说,任何类型的恢复都没有太多选择。通常,人们会尝试“重新启动”PC,希望由于某些驱动程序在编码和测试中被忽略的罕见情况而发生蓝屏死机。(BSOD)但是,如果BSOD持续存在,则可以采用一些策略来修复系统,有超过250 个记录在案的 BSOD 代码(250 documented BSOD codes)。
以最常见的 BSOD 为例:
错误代码0xA – IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL
这是一个相当常见的BSOD,当 NT 以特定IRQL运行时驱动程序非法访问内存位置时会发生这种情况。这是驱动程序编码错误,类似于尝试访问无效的内存位置。
参数:
1 – 引用的内存位置
2 – 引用时的 IRQL
3 – 0 == 读取,1 == 写入
4 – 引用内存的代码寻址
恢复/解决方法:
没有。这是一个致命错误,是驱动程序编码错误。
解决蓝屏(Blue Screen)死机(Death)错误的第一步是什么
Windows 10中的 BSOD 或停止错误似乎更好、更人性化且更易于使用。但他们没有提供很多细节。您必须强制您的操作系统在 Windows 10 中显示停止错误信息。
如何调试内存转储
要了解如何调试内存转储(Memory Dumps)以便找出蓝屏死机(BSOD)的原因,请下载并安装Microsoft 调试工具(Microsoft Debugging Tools)。确保您的页面文件仍然驻留在系统分区上。否则,Windows将无法保存调试文件。
您可以使用Crash Dump Analyzer 软件(Crash Dump Analyzer software)来分析故障转储报告。
TROUBLESHOOT WINDOWS STOP ERRORS/BSODs
- 首先(First),查看(Foremost)系统还原(System Restore)是否可以解决此问题。
- 否则,然后运行您的防病毒和反间谍软件以及您的 PC Junk/Registry Cleaner。
- 在此之后,运行Windows 检查磁盘实用程序(Windows Check Disk Utility)。
- 然后尝试确定您是否进行了任何软件或硬件更改或修改。
- 在大多数情况下,软件是受害者,而不是导致 BSOD 的原因。所以不排除硬件问题。可能是硬盘损坏、物理RAM有缺陷、 (RAM)CPU芯片过热或其他任何原因!
- 检查您是否可以在错误详细信息中看到驱动程序的名称。如果可以,那么只需禁用、删除该驱动程序或将其回滚到早期版本即可帮助解决该问题。网络(Network)接口卡、磁盘控制器和视频适配器(Video Adapters)通常是罪魁祸首。
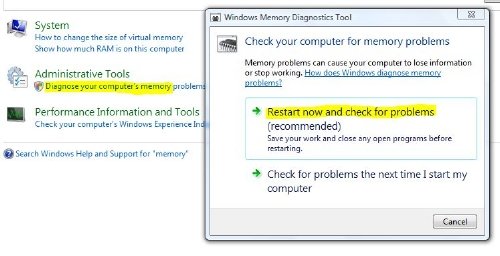
- 检查你的记忆。使用 Windows内存诊断工具(Memory Diagnostic Tool)。转到控制面板并在(Control Panel)搜索(Search)框中键入“内存” 。在管理工具(Tools)下,单击诊断计算机的内存问题(Memory Problems)。在此处显示的Windows 内存诊断工具(Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool)中,选择其中一个选项。
- 仔细检查您的系统BIOS系统或主板的制造商是否提供更新?仔细检查BIOS文档;(BIOS)将所有BIOS(BIOS)选项重置为其默认值有时可以解决因过度调整而导致的问题。
- 检查系统资源是否不足?有时,磁盘空间(Disk Space)或RAM的严重短缺会导致蓝屏死机。
- 检查系统文件是否已损坏?在安全模式下(Safe Mode)工作,因为只有核心驱动程序和服务被激活。如果您的系统以安全模式(Safe Mode)启动但不正常,您很可能有问题的驱动程序。尝试在安全模式下运行(Safe Mode)设备管理器(Device Manager)并卸载最有可能的嫌疑人。或者在安全模式下运行(Safe Mode)系统还原(System Restore)。
- 运行Windows 10 蓝屏疑难解答。
MSDN print-link
BlueScreenView
如果您怀疑驱动程序(Driver)导致 BSOD ,该怎么办
如果您怀疑有错误的设备驱动程序导致 BSOD 出现故障,请调用一个鲜为人知但功能强大的故障排除工具,称为Driver Verifier Manager。在搜索栏中输入verifier并按回车键以调出(verifier)Verifier.exe。以管理员(Administrator)身份运行(Run)。此工具可帮助您实际识别有缺陷的驱动程序。
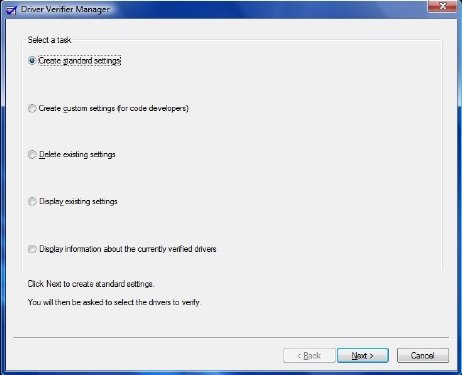
现在选择“创建标准设置”。接下来(Next),选择您要验证的驱动程序类型。未签名的驱动程序可能是导致问题的原因,因为它们是为旧版本的Windows创建的。点击 Next(Click Next),直到完成。
Driver Verifier Manager以下列方式工作。您可以随时让驱动程序验证程序(Driver Verifier)在启动时停止您的计算机,而不是您的机器向您抛出无法解读的BSOD ,而(BSOD)BSOD可以相当准确地解释实际问题!然后,您可以选择通过更新、回滚或卸载有问题的驱动程序来解决问题。
请注意,在极少数情况下,Driver Verifier Manager确实会发现不合格的驱动程序;有可能它可能不是违规的。所以要格外小心。将已识别的Driver/s视为可疑人员,并在这种情况下做出最佳判断。
缩小到有问题的驱动程序(Driver)后,您有三个选项:更新(Update)、回滚(Roll Back)或卸载设备驱动程序(Device Driver)。
为此,请打开设备管理器(Device Manager)。打开设备的属性对话框,然后使用驱动程序(Driver)选项卡上的以下按钮执行维护任务:
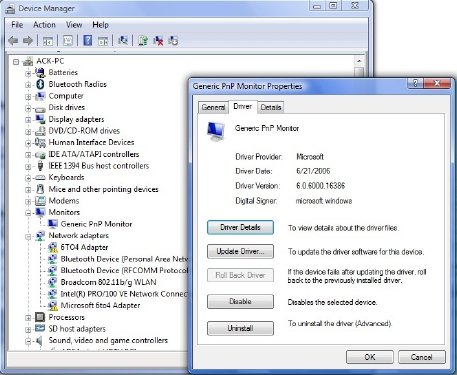
- 更新驱动程序(Update Driver):这将启动硬件更新向导(Hardware Update Wizard)。
- 回滚驱动程序(Roll Back Driver):这将卸载最近更新的驱动程序并将您的配置回滚到早期版本。
- 卸载驱动程序(Uninstall Driver):这将完全卸载所选硬件的驱动程序文件和注册表设置。
阅读(Read):如何找到导致 Windows 蓝屏的驱动程序?
常见 Windows 蓝屏错误(Common Windows Blue Screen Errors)和解决方案列表
停止 0x000000D1 或DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_OR_EQUAL
可能是最常见的蓝屏死机!当 NT 以特定IRQL运行时,驱动程序非法访问内存位置时会发生这种情况。这是驱动程序编码错误,类似于尝试访问无效的内存位置。恢复/解决方法:通常没有。但这些可能对KB810093、KB316208和KB810980有所帮助。
停止 0x0000000A(STOP 0x0000000A)或IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL
内核模式进程或驱动程序试图在未经授权的情况下访问内存位置。此停止(Stop)错误通常是由故障或不兼容的硬件或软件引起的。有问题的设备驱动程序的名称经常出现在Stop错误中,可以为解决问题提供重要线索。如果错误消息指向特定设备或设备类别,请尝试移除或更换该类别中的设备。如果在安装过程中出现此(Setup)停止(Stop)错误,则怀疑驱动程序、系统服务、病毒扫描程序或备份程序不兼容。这个KB314063可能会告诉你方向。
硬件驱动程序或系统服务请求的数据不在内存中。原因可能是物理内存有缺陷或软件不兼容,尤其是远程控制和防病毒程序。如果安装设备驱动程序或应用程序后立即出现错误,请尝试使用安全模式(Mode)删除驱动程序或卸载程序。有关详细信息,请参阅KB894278和KB183169。
停止 0x000000C2 或BAD_POOL_CALLER
内核模式进程或驱动程序试图执行非法内存分配。问题通常可以追溯到驱动程序或软件中的错误。它也偶尔是由硬件设备的故障引起的。有关详细信息,请参阅KB265879。
停止 OX000000ED(STOP OX000000ED)或UNMOUNTABLE_BOOT_VOLUME
如果Windows无法访问包含引导文件的卷,则会出现这种情况。但是,如果您在更新至 Vista(TO Vista)时收到此消息,请检查您是否有兼容的磁盘控制器驱动程序,并重新检查驱动器电缆,并确保其配置正确。如果您要重复使用 ATA-66 或 ATA-100 驱动程序,请确保您使用的是 80 连接器电缆,而不是标准的 40 连接器IDE电缆。请参阅KB297185和KB315403。
停止 0x0000001E 或KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED
Windows内核检测到非法或未知的处理器指令,这通常是由错误的驱动程序或硬件设备导致的无效内存和访问冲突的结果。错误消息通常标识有问题的驱动程序或设备。如果在安装驱动程序或服务后立即发生错误,请尝试禁用或删除新添加的内容。
停止 0x00000024 或 NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM
NTFS文件系统驱动程序中出现问题。FAT32驱动器存在类似的停止(Stop)错误 0x23 。最可能的原因是磁盘或磁盘控制器中的硬件故障。检查系统中所有硬盘的所有物理连接并运行Check Disk。KB228888将为您提供帮助。
停止 0x0000002E 或 DATA_BUS_ERROR
出现故障或有缺陷的物理内存(包括视频适配器中使用的内存)是此Stop错误的最常见原因。该错误也可能是硬盘损坏或主板损坏的结果。
停止 0x0000003F(STOP 0x0000003F)或 NO_MORE_SYSTEM_PTES
您的系统用完了页表条目 ( PTE(PTEs) )。这种相对不常见的错误的原因可能是失控的备份程序或错误的设备驱动程序。有关详细信息,请参阅KB256004。
停止 0x00000077(STOP 0x00000077)或KERNEL_STACK_INPAGE_ERROR
系统试图从虚拟内存(页面文件)中读取内核数据,但未能在指定的内存地址找到数据。此停止(Stop)错误可能由多种问题引起,包括内存故障、硬盘故障、磁盘控制器或电缆配置不当、数据损坏或病毒感染。有关其他信息,请单击KB228753。
停止 0x0000007F(STOP 0x0000007F)或 UNEXPECTED_KERNEL_MODE_TRAP
最有可能是由于硬件(Hardware)故障,如内存芯片缺陷、内存模块不匹配、CPU故障或风扇或电源故障是此BSOD的可能原因。如果您对CPU进行了超频,也会发生这种情况。该消息提供了更多详细信息。如需更多帮助,请参阅KB137539。
停止 0x000000D8(STOP 0x000000D8)或 DRIVER_USED_EXCESSIVE_PTES
这表明编写不佳的驱动程序导致您的计算机请求大量内核内存。故障排除建议与STOP 0X3F(STOP 0X3F)消息中的建议相同。KB256004将帮助您
停止 0X000000EA(STOP 0X000000EA)或 THREAD_STUCK_IN_DEVICE_DRIVER
它可能在您安装新的视频适配器或更新(且编写不佳)的视频驱动程序后发生。更换视频适配器或使用不同的视频驱动程序可能会有所帮助。请参阅KB293078。
停止 0XC000021A(STOP 0XC000021A)或 STATUS_SYSTEM_PROCESS_TERMINATED
如果Windows存在严重的安全问题,则会发生这种情况。诸如Winlogon或CSRSS之类的子系统受到威胁;或由于系统文件不匹配;或者如果系统权限被错误地修改。此问题的常见原因是某些第 3 方程序。尝试识别您已安装的任何新程序并将其卸载。
停止 0XC00000221(STOP 0XC00000221)或STATUS_IMAGE_CHECKSUM_MISMATCH
这表示页面文件损坏;或磁盘或文件损坏;或硬件故障。该错误将指示损坏的系统文件的确切性质和名称。您可能必须使用Windows恢复环境(Environment)或系统还原(System Restore)或上次正确配置(Known Good Configuration)来解决此问题。
REGISTRY_ERROR
这种停止错误很少见,是由于未能从硬盘正确读取注册表造成的。最好尝试从备份中恢复注册表。
DIVIDE_BY_ZERO_ERROR
此停止错误是由试图除以零的应用程序引起的。如果您收到此错误并且不知道是哪个应用程序导致的,您可能需要尝试检查内存转储。
KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED
错误配置的设备驱动程序通常会导致此类错误。难以隔离和排除故障。
INVALID_PROCESS_ATTACH_ATTEMPT
此错误代码 0x5(Bugcode 0x5)表示内核进程正在尝试附加到另一个进程。为了帮助进行诊断,用户应该记下发生故障时正在执行的所有应用程序。没有恢复或解决方法。
HARDWARE_INTERRUPT_STORM
此类错误通常是由编写不当的驱动程序或固件引起的。难以排除故障,但设备管理器(Device Manager)或系统信息(System Information)工具可以帮助您。
INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE
当Windows从硬盘读取时出现此停止错误。此错误可能是由错误的设备驱动程序引起的。您也可以尝试运行您的防病毒软件。
PFN_LIST_CORRUPT
此错误代码 0x4E(Bugcode 0x4E)错误通常是由错误的RAM引起的。您可能需要检查或更换RAM 。如果这不起作用,则没有其他已知的恢复或解决方法
MACHINE_CHECK_EXCEPTION
如果您对CPU进行了超频,则可能会出现这种情况。还要检查你的电源。
MULTIPLE_IRP_COMPLETE_REQUESTS
此错误代码 0x44(Bugcode 0x44)表示驱动程序逻辑错误。已经看到这发生在负载很重的系统上。没有恢复或解决方法。
NMI_HARDWARE_FAILURE
通常是由坏SIMMS引起的。最好致电您的硬件供应商。
您可能还想借助BlueScreenView。它是一个实用程序,可以存储在“蓝屏死机”崩溃期间创建的所有小型转储文件,并在一个表中显示有关所有崩溃的信息。对于每次崩溃,BlueScreenView会显示 minidump 文件名、崩溃的日期/时间、蓝屏显示的基本崩溃信息(Bug Check Code和 4 个参数)以及可能导致崩溃的驱动程序或模块的详细信息(文件名、产品名称、文件描述和文件版本)。对于上窗格中显示的每个崩溃,您可以在下窗格中查看崩溃期间加载的设备驱动程序的详细信息。蓝屏视图(BlueScreenView)还会标记其地址在崩溃堆栈中找到的驱动程序,因此您可以轻松找到可能导致崩溃的可疑驱动程序。
其他资源:(Additional Resources:)
- 使用 WhoCrashed 分析您的故障转储(Analyze your crash dumps with WhoCrashed)
- Windows 错误检查或停止错误代码列表。
阅读(Read):紫色,棕色,黄色,红色,绿色死亡屏幕解释。
Troubleshoot Windows Blue Screen of Death or Stop Errors
This guide will help you understand, analyze, troubleshoot and fix Windows Blue Screen of Death, Stop Errors, Error Codes, Bug Check errors, system crash errors, system fault, kernel error crashes in Windows 11/10/8/7. When Windows encounters a condition that compromises safe system operation (i.e., a “bug”), the system halts.
Blue Screen of Death in Windows 11/10

This condition is called a ‘bug check‘. It is also commonly referred to as a system crash, a kernel error, a system fault, or a Stop Error.
In Windows XP, the Windows Error Reporting system was essentially manual but has now been improved & streamlined in Windows 7 & Windows Vista. While this may be the case, Blue Screens haven’t just vanished. You may still get to see them on Windows 7/8 too.
Usually, when a BSOD occurs, it stays for a second before the PC immediately restarts. This way we are unable to read what is written. To get around it, one has to disable the auto PC restart option from the StartUp & System Recovery settings. Knowing the error code can help identify the problem/solution. Do it as follows:
Disable UAC. Control Panel > System And Maintenance > System > Advanced System Settings > Advanced tab > Under Startup And Recovery > Click Settings > Clear the Automatically Restart check box > click OK. Enable UAC.
Windows will attempt to fix the problem on its own in most cases, but if it cannot recover on its own, it will cause a blue screen.
Blue Screen Errors in Windows 11/10

Users of the Windows system are sure to have experienced, at one point or another, the terrors of “The Fatal Exception”, commonly called the “Blue Screen Of Death”, or BSOD. Although the BSOD has largely been thrown onto the software slag heap, in Vista, crashes haven’t been totally banished. When Windows encounters a condition that compromises safe system operation (i.e., a “bug”), the system halts. This condition is called a ‘bug check’. It is also commonly referred to as a system crash, a kernel error, a system fault, or a Stop error. When Windows encounters such a serious error that forces it to stop running, it displays a BLUE SCREEN OF DEATH or just ‘lovingly’ called BSOD!
In Windows 11/10/8/7, unlike XP, where the system was essentially manual, the Windows Error Reporting has been improved & streamlined in Windows 7 & Vista. One had to follow-up to see if a solution had become available. This was a rather painful process. In Windows 10/8/7/Vista, this entire reporting and follow-up process is automated.
These days a Windows 11/10/8/7/Vista user is more often likely to see a message as follows: “Microsoft Windows Operating System is not responding.” And users are given two possibilities. They can either “Close the program” or “Wait for the program to respond.” One waits in the hope that the issue will be resolved, or else then one just closes the program and gets prepared to lose information. At least, these messages look less daunting.

The BSODs on the other hand were/are quite traumatic and frustrating, to say the least!
The exact text of a Stop error varies, according to what caused the error. But the format is standardized and is made up of 3 parts:
- PART 1: Symbolic error name: This is the Stop Error message that is given to the OS and corresponds to the Stop Error number that appears.
- PART 2: Troubleshooting recommendations: This text applies to all Stop Errors of that particular type.
- PART 3: Error number and parameters: Its the bug check information. The text following the word STOP includes the error number, in hexadecimal notation, and up to four parameters that are typical of this error type.
In general, there are not too many options for any type of recovery. Normally, one tries to just “reboot” the PC in the hope that the BSOD occurred because of a rare condition of some driver which was overlooked in coding and testing. But if the BSOD persists, there are some tactics that may be employed to repair the system there are over 250 documented BSOD codes.
Take, for example, the most common BSOD:
Bugcode 0xA – IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL
This is a fairly common BSOD that occurs when a driver has illegally accessed a memory location while NT is operating at a specific IRQL. This is a driver coding error, akin to trying to access an invalid memory location.
Parameters:
1 – memory location that was referenced
2 – IRQL at time of reference
3 – 0 == read, 1 == write
4 – code addressed which referenced memory
Recovery/Workaround:
There is none. This is a fatal error and is a driver coding error.
What is the first step to take to resolve a Blue Screen of Death error
The BSODs or Stop Errors in Windows 10 appear to be better and more user-friendly and easier on the eyes. But they don’t give many details. You have to force your OS to display Stop Error information in Windows 10.
How to Debug Memory Dumps
To know how to debug Memory Dumps so that you can find out the cause for your BSOD, download and install the Microsoft Debugging Tools. Make certain that your page file still resides on the system partition. Otherwise, Windows will not be able to save the debug files.
You can use Crash Dump Analyzer software to analyze crash dump reports.
TROUBLESHOOT WINDOWS STOP ERRORS/BSODs

- First & Foremost, see if a System Restore can resolve this issue.
- Else, then run your anti-virus and anti-spyware and your PC Junk/Registry Cleaner.
- After this, Run the Windows Check Disk Utility.
- Then try to identify if you’ve made any software or hardware change or modification.
- In most cases, the software is the victim and not the cause of BSOD’s. So don’t rule out hardware problems. It could be damaged hard disks, defective physical RAM, overheated CPU chips or anything else!
- Check if you can see a driver’s name in the error details. If you can, then simply disabling, removing, or rolling back that driver to an earlier version can help solve that problem. Network interface cards, disk controllers, and Video Adapters are the culprits, most often.
- Check your memory. Use the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool. Go to Control Panel and type “memory” in the Search box. Under Administrative Tools, click Diagnose Your Computer’s Memory Problems. In the Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool, shown here, select one of the options.
- Check your system BIOS carefully Is an update available from the manufacturer of the system or motherboard? Check the BIOS documentation carefully; resetting all BIOS options to their defaults can sometimes resolve an issue caused by over tweaking.
- Check if you are low on system resources? Sometimes a critical shortage of Disk Space or RAM can cause BSOD’s.
- Check if a system file has been damaged? Work in Safe Mode, as only the core drivers and services are activated. If your system starts in Safe Mode but not normally, you very likely have a problem driver. Try running Device Manager in Safe Mode and uninstalling the most likely suspect. Or run System Restore in Safe Mode.
- Run the Windows 10 Blue Screen Troubleshooter.
MSDN print-link
BlueScreenView
What to do if you suspect that a Driver is causing BSOD’s
If you suspect that a buggy device driver is at fault for the BSOD’s, call upon a lesser-known but powerful troubleshooting tool called the Driver Verifier Manager. Enter verifier in the search bar and hit enter to bring up Verifier.exe. Run As Administrator. This tool helps you to actually identify the flawed driver.

Now select “Create Standard Settings”. Next, select the type of drivers you want to verify. Unsigned drivers are a likely cause of problems, as they are created for older versions of Windows. Click Next, till completion.
Driver Verifier Manager works in the following manner. Instead of your machine throwing up an undecipherable BSOD at you, at any time, you can make Driver Verifier stop your computer at startup, with a BSOD which will explain the actual problem, rather accurately! You can then choose to resolve the problem by either updating, rolling back or uninstalling the offending driver.
Please do note that in the rare eventuality the Driver Verifier Manager does find a non-conforming driver; there could be a possibility that it may not be the offending one. So do exercise extreme caution. Regard the identified Driver/s with suspicious and exercise your best judgment in such a case.
Having narrowed down to the problematic Driver, you have three options: Update, Roll Back or Uninstall the Device Driver.
To do that, open Device Manager. Open the properties dialog box for the device, and use the following buttons on the Driver tab to perform maintenance tasks:

- Update Driver: This will start the Hardware Update Wizard.
- Roll Back Driver: This will uninstall the most recently updated driver and will roll back your configuration, to the earlier version.
- Uninstall Driver: This will uninstall completely the driver’s files and registry settings for the selected hardware.
Read: How to find which Driver is causing the Blue Screen on Windows?
List of Common Windows Blue Screen Errors & solutions
STOP 0x000000D1 or DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_OR_EQUAL
Probably the most common BSOD! This occurs when a driver has illegally accessed a memory location while NT is operating at a specific IRQL. This is a driver coding error, akin to trying to access an invalid memory location. Recovery/Workaround: Usually none. But these may help KB810093 , KB316208 & KB810980.
STOP 0x0000000A or IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL
A kernel-mode process or driver attempted to access a memory location without authorization. This Stop error is typically caused by faulty or incompatible hardware or software. The name of the offending device driver often appears in the Stop error and can provide an important clue to solving the problem. If the error message points to a specific device or category of devices, try removing or replacing devices in that category. If this Stop error appears during Setup, suspect an incompatible driver, system service, virus scanner, or backup program. This KB314063 may show you the direction.
A hardware driver or system service requested data that was not in memory. The cause may be defective physical memory or incompatible software, especially remote control, and antivirus programs. If the error occurs immediately after installing a device driver or application, try to use Safe Mode to remove the driver or uninstall the program. For more information, see KB894278 & KB183169.
STOP 0x000000C2 or BAD_POOL_CALLER
A kernel-mode process or driver attempted to perform an illegal memory allocation. The problem can often be traced to a bug in a driver or software. It is also occasionally caused by a failure in a hardware device. For more information, see KB265879.
STOP OX000000ED or UNMOUNTABLE_BOOT_VOLUME
This occurs if Windows if unable to access the volume containing the boot files. But if you get this message while updating TO Vista, check that you have compatible drivers for the disk controller and also re-check the drive cabling, and ensure that it is configured properly. If you’re reusing ATA-66 or ATA-100 drivers, make sure you have an 80-connector cable, and not the standard 40-connector IDE cable. See KB297185 and KB315403.
STOP 0x0000001E or KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED
The Windows kernel detected an illegal or unknown processor instruction, often the result of invalid memory and access violations caused by faulty drivers or hardware devices. The error message often identifies the offending driver or device. If the error occurred immediately after installing a driver or service, try disabling or removing the new addition.
STOP 0x00000024 or NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM
A problem occurred within the NTFS file-system driver. A similar Stop error, 0x23, exists for FAT32 drives. The most likely cause is a hardware failure in a disk or disk controller. Check all physical connections to all hard disks in the system and run Check Disk. KB228888 will help you.
STOP 0x0000002E or DATA_BUS_ERROR
Failed or defective physical memory (including memory used in video adapters) is the most common cause of this Stop error. The error may also be the result of a corrupted hard disk or a damaged motherboard.
STOP 0x0000003F or NO_MORE_SYSTEM_PTES
Your system ran out of page table entries (PTEs). The cause of this relatively uncommon error may be an out-of-control backup program or a buggy device driver. For more information, see KB256004.
STOP 0x00000077 or KERNEL_STACK_INPAGE_ERROR
The system has attempted to read kernel data from virtual memory (the page file) and failed to find the data at the specified memory address. This Stop Error can be caused by a variety of problems, including defective memory, a malfunctioning hard disk, an improperly configured disk controller or cable, corrupted data, or a virus infection. For additional information, click KB228753.
STOP 0x0000007F or UNEXPECTED_KERNEL_MODE_TRAP
Most likely due to a Hardware failure, like defective memory chips, mismatched memory modules, a malfunctioning CPU, or a failure in your fan or power supply are the probable reasons for this BSOD. It can also occur if you have overclocked your CPU. The message gives more details. For more help see KB137539.
STOP 0x000000D8 or DRIVER_USED_EXCESSIVE_PTES
This indicated that a poorly written driver is causing your computer to request large amounts of kernel memory. Troubleshooting suggestions are identical to those found in the STOP 0X3F message. KB256004 will help you
STOP 0X000000EA or THREAD_STUCK_IN_DEVICE_DRIVER
It could occur after you install a new video adapter or an updated (and poorly written) video driver. Replacing the video adapter or using a different video driver could help. See KB293078.
STOP 0XC000021A or STATUS_SYSTEM_PROCESS_TERMINATED
This occurs if there is a serious security problem with Windows. A subsystem, such as Winlogon or the CSRSS is compromised; or due to a mismatch in system files; or if system permissions have been incorrectly modified. A common cause of this problem is some 3rd-party programs. Try to identify any new program which you have installed and uninstall it.
STOP 0XC00000221 or STATUS_IMAGE_CHECKSUM_MISMATCH
This indicates a damaged page file; or disk or file corruption; or faulty hardware. The error will indicate the exact nature and the name of the damaged system file. You may have to use the Windows recovery Environment or a System Restore or Last Known Good Configuration to resolve this issue.
REGISTRY_ERROR
This stop error is rare and is caused due to failure to read the registry properly from the hard disk. Best to try and restore the registry from your backup.
DIVIDE_BY_ZERO_ERROR
This stop error is caused by an application trying to divide by zero. If you receive this error & don’t know which application caused it, you might want to try & examine memory dump.
KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED
An incorrectly configured device driver usually causes this type of error. Difficult to isolate and troubleshoot.
INVALID_PROCESS_ATTACH_ATTEMPT
This Bugcode 0x5 indicates that a kernel process was making an attempt to attach to another process. To aid in the diagnosis, the user should note all applications that were executing at the time of the failure. There is no recovery or workaround.
HARDWARE_INTERRUPT_STORM
Such an error is usually caused by a poorly written driver or firmware. Difficult to troubleshoot, but Device Manager or System Information tool can help you.
INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE
This stop error occurs when Windows has trouble reading from the hard disk. This error can be caused by a faulty device driver. You may also try running your antivirus.
PFN_LIST_CORRUPT
This Bugcode 0x4E error is usually caused by faulty RAM. You may want to get your RAM checked or replaced. If that doesn’t work, there is no other known recovery or workaround
MACHINE_CHECK_EXCEPTION
If you have overclocked your CPU, this could result. Also check your power supply.
MULTIPLE_IRP_COMPLETE_REQUESTS
This Bugcode 0x44 indicates a fault in driver logic. This has been seen to occur on a heavily loaded system. There is no recovery or workaround.
NMI_HARDWARE_FAILURE
Usually caused by bad SIMMS. Best to call your hardware vendor.
You may also want to take the help of BlueScreenView. It is a utility that cans all your minidump files created during ‘blue screen of death’ crashes and displays the information about all crashes in one table. For each crash, BlueScreenView displays the minidump filename, the date/time of the crash, the basic crash information displayed in the blue screen (Bug Check Code and 4 parameters), and the details of the driver or module that possibly caused the crash (filename, product name, file description, and file version). For each crash displayed in the upper pane, you can view the details of the device drivers loaded during the crash in the lower pane. BlueScreenView also marks the drivers that their addresses found in the crash stack, so you can easily locate the suspected drivers that possibly caused the crash.
Additional Resources:
- Analyze your crash dumps with WhoCrashed
- List of Windows Bug Check or Stop Error Codes.
Read: Purple, Brown, Yellow, Red, Green Screen of Death explained.






