如果您想了解HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE是什么以及如何访问它,请阅读此简短指南,该指南将解释HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE的定义、位置和注册表子项。

什么是 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE?(What is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE?)
所有低级Windows 设置(Windows Settings)和应用程序(Application)设置都存储在称为Windows 注册表(Windows registry)的数据库中。它存储设备驱动程序、用户界面、内核、文件夹路径、开始(Start)菜单快捷方式、已安装应用程序的位置、DLL文件以及所有软件值和硬件信息的设置。但是,如果您打开Windows注册表,您可能会看到几个根键(root keys),每个都有助于特定的Windows功能。例如,HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE,缩写为HKLM,就是这样一种Windows根密钥。它包括以下配置详细信息:
- 视窗操作系统
- 安装的软件
- 设备驱动程序
- (Boot)Windows 7/8/10/Vista启动配置,
- Windows 服务,以及
- 硬件驱动程序。
必读:(Must Read:) 什么是 Windows 注册表及其工作原理?(What is the Windows Registry & How it Works?)
如何通过注册表编辑器访问 HKLM
(How to Access HKLM via Registry Editor
)
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE或HKLM通常称为注册表配置单元(registry hive),可以使用注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)进行访问。此工具可帮助您创建、重命名、删除或操作根注册表项、子项、值和值数据。它可用于修复系统中的多个问题。但是,在使用注册表编辑器工具时必须始终小心,因为即使是一个错误的条目也可能使机器无法使用。
注意:(Note:)因此,建议您在使用注册表编辑器进行任何操作之前备份密钥。(back up the key)例如,如果您想删除残留或垃圾文件,除非您确定条目,否则您不应该自己动手。否则,您可以使用第三方注册表清理工具,帮助您自动删除所有不需要的注册表项。
您可以通过注册表(Registry)编辑器打开HKLM,如下所示:
1. 同时 按下Windows + R键启动运行对话框。(Run dialog box)
2. 输入regedit(regedit) 如下,点击 OK。

3. 在左侧边栏中双击计算机(Computer)将其展开并选择HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE文件夹选项,如图所示。
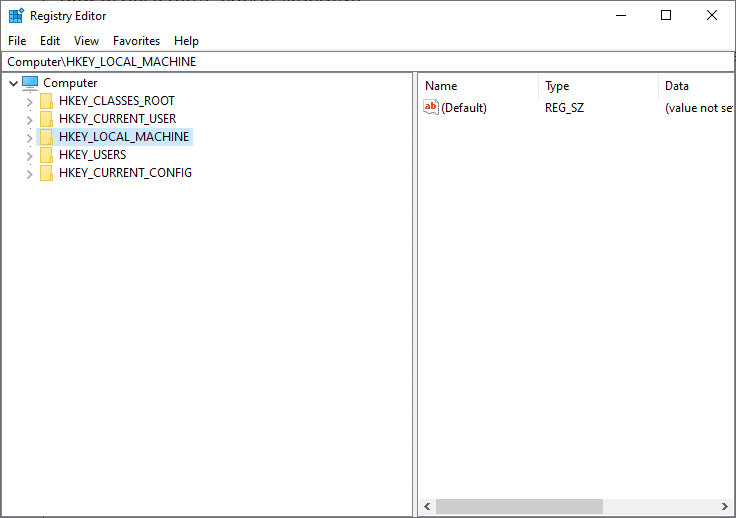
4. 现在,再次双击HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE选项以展开它。
注意(Note):如果您之前已经使用过注册表编辑器,它将处于展开状态。

HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE 中的键列表
(List of Keys in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
)
在HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE(HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE)键文件夹内有许多注册表键文件夹,定义如下:
注意:(Note:)上述注册表项可能会根据您使用的Windows 版本(Windows version)而有所不同。
-
BCD00000000 子项– 启动(BCD00000000 Subkey)Windows操作系统所必需的启动配置数据存储在此处。
-
COMPONENTS 子项(COMPONENTS Subkey)——Windows 操作系统(Windows Operating System)中所有组件的配置设置都存储在此子项中。
-
DRIVERS 子项(DRIVERS Subkey)——有关驱动程序的详细信息,包括系统中安装的软件和硬件,都存储在Drivers子项中。它为您提供有关安装日期、更新日期、驱动程序工作状态等的信息。
-
SOFTWARE 子项(SOFTWARE Subkey)– Software项是注册表编辑器最常用的子项之一。您打开的应用程序(Applications)的所有设置和操作系统的用户界面详细信息都存储在这里。(User Interface)
-
SCHEMA 子项– 它是在(SCHEMA Subkey)Windows 更新(Windows Update)或其他一些安装程序期间创建的临时注册表项。一旦您完成Windows(Windows)更新或安装过程,这些将自动删除。
-
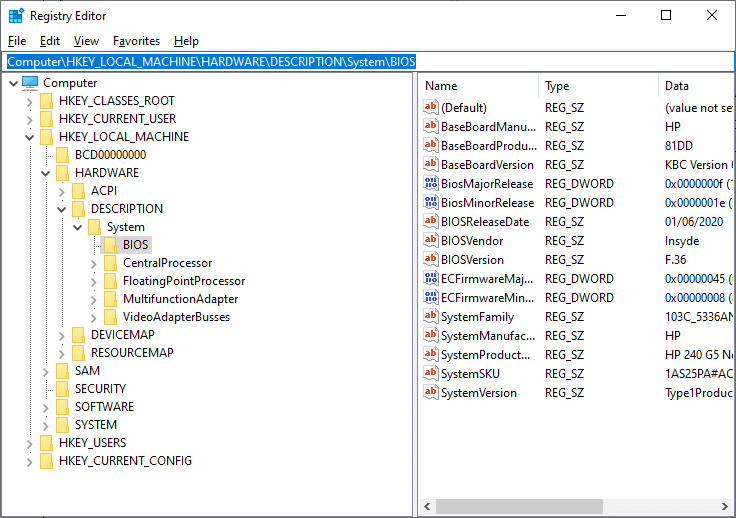
HARDWARE 子项(HARDWARE subkey)– Hardware子项存储与BIOS(基本输入(Basic Input)和输出系统(Output System))、硬件和处理器相关的所有数据。
例如,考虑导航路径Computer\ HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\ HARDWARE\ DESCRIPTION\ System\ BIOS。在这里,存储了当前BIOS和系统的所有数据。
另请阅读:(Also read:) 如何在 Windows 上备份和还原注册表(How to Backup and Restore the Registry on Windows)
HKLM 中的隐藏子键(Hidden Subkeys in HKLM)
注册表(Registry)编辑器中的几个子项默认是隐藏的,无法查看。当您打开这些键时,它们及其关联的子键可能看起来是空的或空白的。以下是HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE中的隐藏子键:
-
SAM 子项(SAM subkey)– 此子项保存域的安全帐户管理器(Security Accounts Manager)( SAM ) 的数据。每个数据库都包含组别(Group Aliases)名、用户(User)帐户、访客(Guest)帐户、管理员(Administrator)帐户、域的登录(Login)名等。
-
SECURITY 子键(SECURITY subkey)——用户的所有安全策略都存储在这里。此数据链接到域的安全数据库或系统中的相应注册表。
如果您想查看SAM或SECURITY子项,您必须使用System Account登录(System Account)注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)。系统帐户是比任何其他帐户(包括管理员(Administrator)帐户)具有更高权限的帐户。
注意:(Note:)您还可以使用一些第三方软件实用程序(例如PsExec)来查看系统中的这些隐藏子项。(不建议)
受到推崇的(Recommended)
我们希望本指南对您有所帮助,并且您已经了解了HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE、它的定义、如何访问它以及 HKLM 中的注册表子项列表(HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, its definition, how to access it, and a list of registry subkeys in HKLM)。此外,如果您对本文有任何疑问或建议,请随时将它们放在评论部分。
What is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE?
If you are looking to learn what HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE іs, and how to access it, read this short guide that wіll explain the definition, location, and registry subkeys of HKΕY_LOCAL_MACHІNE.

What is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE?
All the low-level Windows Settings and Application settings are stored in a database called Windows registry. It stores settings of device drivers, user interface, kernel, paths to folders, Start menu shortcuts, location of installed applications, DLL files, and all the software values & hardware information. However, if you open the Windows registry, you may see several root keys, each contributing to a specific Windows function. For example, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, abbreviated as HKLM, is one such Windows root key. It includes the configuration details of:
- Windows OS
- Installed software
- Device Drivers
- Boot configurations of Windows 7/8/10/Vista,
- Windows services, and
- Hardware drivers.
Must Read: What is the Windows Registry & How it Works?
How to Access HKLM via Registry Editor
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE or HKLM is often called a registry hive and can be accessed using the Registry Editor. This tool helps you to create, rename, delete or manipulate the root registry keys, subkeys, values, and value data. It can be used to fix several problems in your system. However, you have to be always careful while using the registry editor tool because even a single wrong entry might make the machine unusable.
Note: Therefore, you are advised to back up the key before performing any operation with the registry editor. For instance, if you wish to delete the residual or junk files, you should not do it yourself unless you are certain about the entries. Otherwise, you can use a third-party registry cleaner that will help you remove all the unwanted registry entries automatically.
You can open HKLM through Registry editor as follows:
1. Launch the Run dialog box by pressing Windows + R keys together.
2. Type regedit as follows and click OK.

3. In the left sidebar double click on Computer to expand it and select the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE folder option, as depicted.

4. Now, again double-click on the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE option to expand it.
Note: If you have already used the registry editor before, it will be in an expanded state already.

List of Keys in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE
There are many registry key folders like inside the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE key folder, as defined below:
Note: The mentioned registry keys may differ according to the Windows version you use.
-
BCD00000000 Subkey – The boot configuration data that is essential to boot the Windows operating system is stored here.
-
COMPONENTS Subkey – The configuration settings of all the components in the Windows Operating System are stored in this subkey.
-
DRIVERS Subkey – The details regarding the drivers, both software and hardware installed in your system are stored in the Drivers subkey. It gives you information regarding the date of installation, update date, working state of drivers, etc.
-
SOFTWARE Subkey – The Software key is one of the most commonly used subkeys of the registry editor. All the settings of the Applications you open and the User Interface details of the Operating System are stored here.
-
SCHEMA Subkey – It is a temporary registry key created during the Windows Update or some other installation programs. These are deleted automatically, once you complete the Windows update or installation process.
-
HARDWARE subkey – The Hardware subkey stores all the data relevant to the BIOS (Basic Input and Output System), hardware, and processors.
For instance, consider the navigation path, Computer\ HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\ HARDWARE\ DESCRIPTION\ System\ BIOS. Here, all the data of the current BIOS and system are stored.

Also read: How to Backup and Restore the Registry on Windows
Hidden Subkeys in HKLM
Few subkeys in the Registry editor are hidden by default and cannot be viewed. When you open these keys, they may seem empty or blank, along with their associated subkeys. The following are the hidden subkeys in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE:
-
SAM subkey – This subkey holds the data of the Security Accounts Manager (SAM) for domains. Every database holds Group Aliases, User accounts, Guest accounts, Administrator accounts, Login names of domain, and so on.
-
SECURITY subkey – All the security policies of the user are stored here. This data is linked to the security database of the domain or the corresponding registry in your system.
If you want to view the SAM or SECURITY subkey, you have to log in to the Registry Editor using System Account. A system account is an account that has higher permissions than any other account, including an Administrator account.
Note: You can also use some third-party software utilities like PsExec to view these hidden subkeys in your system. (Not Recommended)
Recommended
We hope that this guide was helpful and you have learned about HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, its definition, how to access it, and a list of registry subkeys in HKLM. Also, if you have any queries, or suggestions regarding this article, then feel free to drop them in the comments section.





