有故障的 Wi-Fi 连接不一定会毁了您的一天。有很多方法可以恢复丢失的互联网连接。遵循这些网络故障排除提示,您将立即启动并运行。
1. 检查您的设置
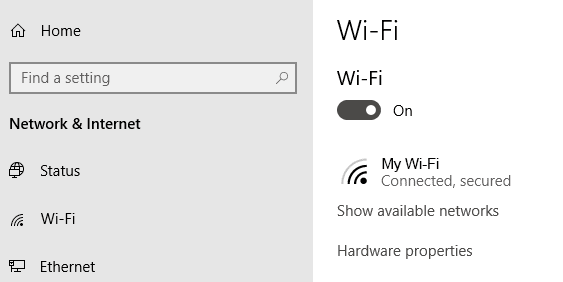
首先,检查您的 Wi-Fi 设置。转到设置(Settings)>网络和 Internet(Network & Internet) > Wi-Fi。将Wi-Fi(Wi-Fi)切换到开启(On)
位置。
手机和平板电脑也有开启和关闭 Wi-Fi 的设置。确保(Make)它已打开,以便您可以连接到网络。

您还想检查飞行模式(Airplane Mode)是否已打开。
2. 检查您的接入点
检查您的WAN
(广域网)和LAN(局域网)连接。用外行的话来说,这些是进出路由器的以太网(Ethernet)电缆。

如果您怀疑电缆是罪魁祸首,请尝试将它们换成新的。
3.绕过障碍
墙壁、家具和其他障碍物可能是您无法上网的原因。靠近路由器可以重新建立连接。如果靠近路由器不能解决问题,那么至少我们可以将其从嫌疑人列表中删除。
4.重启路由器
有时重新启动路由器可以帮助解决连接问题。这在路由器有一段时间没有关闭的情况下更是如此。快速重启可以让路由器恢复正常工作。
如果这不起作用,您还可以考虑重置路由器。但只有在您可以将其恢复为出厂设置时才这样做。您必须重新配置所有内容,包括SSID和密码。
5.检查Wi-Fi名称(Wi-Fi Name)和密码(Password)
检查网络连接的网络名称(也称为SSID)和密码。如果您习惯于在路由器范围内自动连接但现在无法连接,则可能是您不在时对网络进行了更改。

可能就像管理员更新密码一样简单,或者SSID可能已更改为其他密码。
6. 检查 DHCP 设置
路由器通常设置为DHCP服务器。此设置允许计算机自动加入网络。启用DHCP(DHCP)后,用户将不再需要手动设置IP 地址和DNS 服务器。(DNS Server)
要编辑 DHCP 设置,请转到Windows 设置(Windows Settings)
>网络和 Internet(Network & Internet) > Wi-Fi。在Wi-Fi下,单击管理已知网络(Manage Known
Networks)。选择一个网络并单击属性(Properties)。

在IP 设置(IP Settings)下,单击编辑(Edit)。从下拉菜单中,选择自动 (DHCP)(Automatic (DHCP))。

注意:(Note:)选择手动(Manual)将让您手动设置DNS 服务器地址(DNS Server Address)和IP 地址(IP Address)设置。
7. 更新视窗
您的网络问题可能是由您的系统引起的。如果是这种情况,Windows可能已经发布了修复程序。尝试将您的Windows计算机更新到最新版本。

转到Windows 设置(Windows Settings)>更新和安全(Update & Security)> Windows 更新(Windows Update)。单击检查更新(Check for Updates)。如果有可用更新,Windows将下载并安装它们。
8. 打开 Windows 网络诊断
Windows有一个名为Windows 网络(Windows Network) 诊断(Diagnostics)的工具,可让用户解决连接问题。
转到Windows 设置(Windows Settings)>网络和 Internet(Network & Internet) >状态(Status)。在更改您的网络设置(Change Your Network Settings)下,单击网络疑难解答(Network Troubleshooter)。

Windows 网络诊断将运行几个测试来查看可能导致您的 Wi-Fi 问题的原因。

如果没有发现任何问题,Windows 会通知您。否则,将为您提供解决问题的可能措施列表。
此工具或其版本应该在Windows 7到Windows 10中可用。
8 Easy-to-Do Ways to Troubleshoot Network Connection
Α faulty Wi-Fi
connection doesn’t have to ruin your day. There are plenty of ways you can
restorе а lost internet connection. Follow these network troubleshooting tips
and you’ll be up and running in no time.
1. Check Your Settings
First, check your
Wi-Fi settings. Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi. Switch Wi-Fi to the On
position.

Phones and
tablets also have settings that turn Wi-Fi on and off. Make sure that it is
turned on so you can connect to the network.

You also want to
check if Airplane Mode is turned on.
2. Check Your Access Points
Check your WAN
(wide area network) and LAN (local area network) connections. In layman’s
terms, these are the Ethernet cables that go to and from your router.

If you suspect
that the cables are the culprit, try swapping them out with new ones.
3. Go Around Obstacles
Walls, furniture,
and other obstructions can be the reason why you’re unable to go online. Moving
closer to the router can re-establish the connection. If moving closer to the
router does not solve the issue, then at least we can remove it from the list
of suspects.
4. Restart the Router
Sometimes
restarting the router can help fix connectivity issues. This is even truer in
cases where the router has not been turned off in a while. A quick restart can
jolt the router back into working like it used to.
If that doesn’t
work, you might also consider resetting the router. But only do so if you’re
okay with it being restored to its factory settings. You will have to
reconfigure everything including the SSID and password.
5. Check the Wi-Fi Name and Password
Check the network
name (otherwise known as SSID) and password of the network connection. If
you’re used to connecting automatically when in range of a router but are no
longer able to, changes may have been made to the network while you’re away.

It could be as
simple as administrators updating the password or the SSID could have been
changed to a different one.
6. Check DHCP Settings
Routers are
usually set up as DHCP servers. This setting lets computers join a network
automatically. With DHCP turned on, users will no longer have to mess with IP
Address and DNS Server settings manually.
To edit your DHCP
settings, go to Windows Settings
> Network & Internet > Wi-Fi. Under Wi-Fi, click Manage Known
Networks. Select a network and click Properties.

Under IP Settings, click Edit. From the drop-down menu, select Automatic (DHCP).

Note: Selecting Manual will let
you set your DNS Server Address and IP Address settings manually.
7.
Update Windows
Your network
problems could be caused by your system. If that is the case, Windows could
have possibly released a fix. Try updating your Windows machine to the latest
release.

Go to Windows Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update. Click Check for Updates. If there are updates
available, Windows will download and install them.
8.
Open Windows Network Diagnostics
Windows has a
tool called Windows Network Diagnostics that lets users troubleshoot connection
issues.
Go to Windows Settings > Network & Internet > Status. Under Change Your Network Settings, click Network Troubleshooter.

Windows Network
Diagnostics will run a couple of tests to see what’s possibly causing your
Wi-Fi issues.

Windows will let
you know if it does not find any issue. Otherwise, you will be given a list of
possible actions to take to resolve the problem.
This tool, or a
version of it, should be available in Windows 7 to Windows 10.









