写(Write)保护是一项旨在防止用户意外删除或更改磁盘或其他存储设备上的数据的功能。不幸的是,有时Windows拒绝使用驱动器,因为它在不应该的情况下将其检测为写保护。
好消息是Windows中的“ (Windows)Media is Write Protected”错误有多种修复方法。让我们看一下,从最明显的修复开始。

检查您的媒体(Media)是否有写保护开关(Write Protection Switch)
如果您在格式化或写入USB闪存驱动器、SD 卡(SD card)或类似的外部存储设备时遇到问题,请检查写保护开关。这是一个可以打开和关闭的物理滑动开关,如上图所示。
如果它被意外推到写保护位置,您将无法格式化或写入驱动器,直到您将其切换回。在切换开关之前,请务必先弹出驱动器!

从文件(Files)和文件夹中删除写保护(Write Protection)
如果您的问题是特定文件而不是整个磁盘的写保护,则很容易修复:
- 打开文件资源管理器( File Explorer)。
- 导航到受写保护的文件和/或文件夹。
- 选择文件和/或文件夹。

- 右键单击您的选择并选择Properties。
- 在常规(General)选项卡下,确保未选中标记为只读(Read-Only)的框。
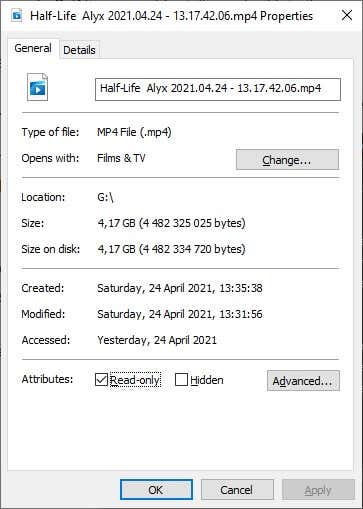
- 选择应用(Apply),然后选择确定(OK)。
如果您选择了包含其他文件和文件夹的文件夹,系统将要求您确认属性更改也应应用于主文件夹中的所有文件和文件夹。
运行磁盘扫描
在开始弄乱操作系统的内容之前,要做的一件好事是对有问题的驱动器进行物理扫描。如果磁盘损坏或损坏,可能会导致写保护错误。
在 Windows 中运行全盘扫描:
- 打开文件资源管理器(File Explorer)。
- 右键单击(Right-click)要扫描的驱动器,然后选择Properties。
- 转到工具(Tools)选项卡。
- 选择检查(Check)。
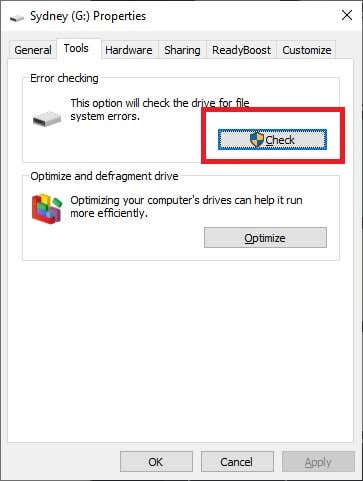
- 选择扫描和修复驱动器。(Scan and Repair Drive.)
如果扫描检测到并修复了驱动器上的任何问题,请尝试再次使用该驱动器。
运行完整的恶意软件扫描
某些(Certain)恶意软件可能会写保护驱动器以防止它们自己被删除。这不是您收到写保护错误的最可能原因,但由于恶意软件扫描(malware scan)快速且易于执行,因此无论如何都值得执行一次。
如果从系统或磁盘中删除恶意软件不能解决问题,请按照下面提到的步骤使驱动器恢复正常。
检查系统文件是否损坏
尝试使驱动器再次可写时,最后一项基本准备工作是运行系统文件检查器(System File Checker)( SFC )。这会将您所有的关键系统文件与黄金标准原件进行比较。如果任何文件已被更改或损坏,将下载并安装原始的新版本。
查看使用这些命令提示符命令来修复或修复损坏的文件(Use These Command Prompt Commands to Fix or Repair Corrupt Files)以获取有关如何使用SFC的说明。
使用高级格式化工具
如果您只想格式化驱动器,但被写保护阻止,那么答案可能是使用更强大的格式化实用程序。许多用户发誓要使用HP USB 格式化工具(HP USB Formatting Tool)来欺负受保护的外部磁盘进行合作。
它也是少数可让您将大型磁盘格式化为FAT32 格式(FAT32 format)的实用程序之一,这是不时需要的。请记住(Bear),您需要以管理员权限运行此应用程序才能运行。据报道,结果好坏参半,但以下解决方案稍微复杂一些,因此,如果您想先尝试使用格式化实用程序应用程序,这是一种选择。
(Remove Write Protection)使用DiskPart删除写保护
DiskPart是Windows中功能强大的命令行实用程序,可以从整个磁盘或特定分区中删除属性。
- 首先,插入写保护的USB驱动器(如果适用)。
- 打开开始菜单(Start Menu)并键入diskpart。
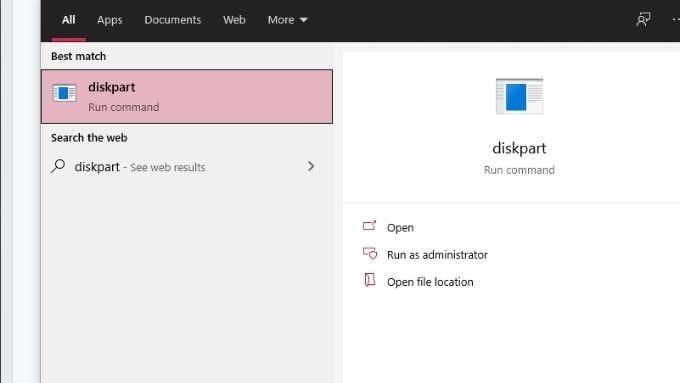
- 从结果中选择diskpart run 命令(diskpart run command)。
- 如果系统要求您提供管理员权限,请说yes。

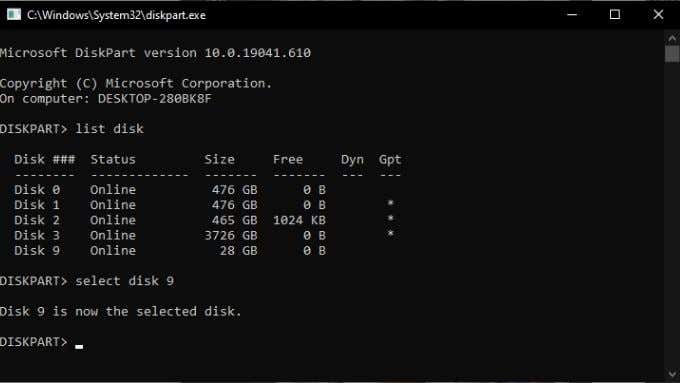
- 在DiskPart的命令行中,键入list disk并按Enter 键(Enter)。

- 在驱动器列表中查找您的USB磁盘,记下它的磁盘号(disk number)。你很快就会需要它!
- 现在,键入select disk #,但将 # 替换为正确的磁盘号。然后按Enter。
- 键入属性磁盘清除只读(attributes disk clear readonly),然后按Enter键。

- 收到确认消息后,键入Exit并按Enter。
(Remove Write Protection)使用Regedit删除写保护
有时,驱动器被标记为写保护,您会收到“ Media is Write Protected”错误,因为(Media)Windows注册表中的相应值不正确。如果可能,请避免在注册表中乱搞。如果这是您最后的手段,请考虑备份您的注册表(backing up your registry),以防出现问题。
话虽如此,以下是如何从 Windows 中的USB驱动器中删除写保护:
- (Insert)将要修改的驱动器插入USB端口。
- 打开开始菜单(Start Menu)并键入注册表编辑器(Registry Editor)。
- 从结果中选择注册表编辑器。(Registry Editor)

- 在注册表编辑器中,导航到HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > StorageDevicePolicies。
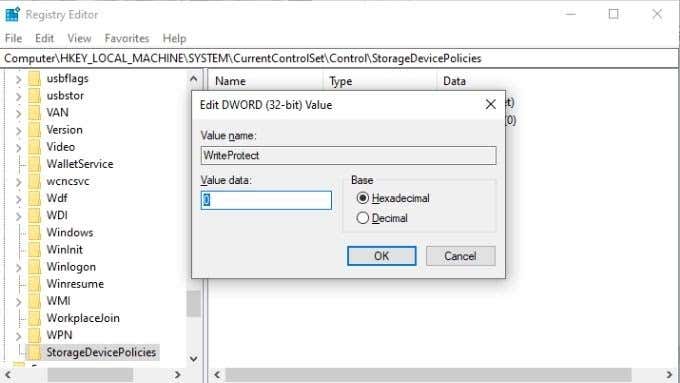
- 双击WriteProtect。这将打开编辑 DWORD(Edit DWORD)窗口。
- 查找数值数据框(Value data box),然后输入0作为新值。

- 选择确定(OK)并关闭注册表编辑器。
- 重新启动计算机并再次检查磁盘。
如果没有要更改的StorageDevicePolicies值怎么办?(StorageDevicePolicies)
创建 StorageDevicePolicies
如果您很不幸没有更改正确的注册表值,那么您将不得不自己进行更改。别担心,你有这个。
- 如上所述打开注册表编辑器。(Registry Editor)
- 导航到HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control。
- 右键单击右侧窗格的空白区域(empty area of the right-hand pane)并选择New > Key。
- 将新密钥命名为StorageDevicePolicies,然后按Enter确认。

- 选择StorageDevicePolicies。
- 再次,右键单击右侧窗格的空白区域并选择New > DWORD(32-bit) Value。
- 将新的 DWORD 值命名为WriteProtect,然后按Enter确认。

- 双击WriteProtect。这将打开编辑 DWORD(Edit DWORD)窗口。
- 查找数值数据框(Value data box),然后输入0作为新值。
- 选择确定(OK)并关闭注册表编辑器。
- 重新启动计算机并再次检查磁盘。
呸!希望(Hopefully)这最后的手段能为您解决Windows中的“(Windows)媒体(Media)被写保护”问题!
How to Fix “Media Is Write Protected” in Windows
Write protection іs a fеature that intеnds to prevent users from acсidentally deleting or altering data on a disk or other storage devices. Unfortunately, sometimеs Windоws refuses to work with a drive because it detects it as write protected when it shouldn’t be.
The good news is that there are various fixes for the “Media is Write Protected” error in Windows. Let’s have a look, starting with the most obvious fixes.

Check Your Media for a Write Protection Switch
If you’re having trouble formatting or writing to a USB flash drive, SD card or similar external storage device, check for a write protection switch. This is a physical sliding switch that can be toggled on and off, as shown in the picture above.
If it was accidentally pushed into the write protection position, you won’t be able to format or write to the drive till you toggle it back. Be sure to eject the drive first before toggling the switch!

Removing Write Protection from Files and Folders
If your problem is write protection of specific files and not the entire disk, it’s easy to fix:
- Open File Explorer.
- Navigate to the files and/or folders that are write protected.
- Select the files and/or folders.

- Right-click on your selection and select Properties.
- Under the General tab, make sure the box labeled Read-Only is unchecked.

- Select Apply and then OK.
If you’ve selected a folder that contains other files and folders, you’ll be asked to confirm that the attribute change should also be applied to all files and folders inside the primary folder.
Run a Disk Scan
One good bit of housekeeping to do before you start messing around with the guts of your operating system is to do a physical scan of the drive in question. If the disk is damaged or corrupted, that may cause a write protection error.
To run a full disk scan in Windows:
- Open File Explorer.
- Right-click on the drive you want to scan and select Properties.
- Go to the Tools tab.
- Select Check.

- Select Scan and Repair Drive.
If the scan detects and repairs any problems on the drive, try to use the drive again.
Run a Full Malware Scan
Certain malware may write protect drives to prevent their own deletion. It’s not the most likely reason you’re getting the write protection error, but since a malware scan is quick and easy to do, it’s worth performing one anyway.
If removing the malware from the system or disk doesn’t fix the issue follow the steps mentioned below to return the drive to normal.
Check System Files for Corruption
The final piece of essential prep work when trying to make a drive writable again is to run the System File Checker (SFC). This will compare all of your crucial system files to the gold standard originals. If any files have been altered or corrupted, pristine new versions will be downloaded and installed.
Check out Use These Command Prompt Commands to Fix or Repair Corrupt Files for instructions on how to use SFC.
Use Advanced Formatting Tools
If all you want to do is format a drive, but you’re being blocked by write protection, then the answer may be to use a formatting utility with a little more muscle. Many users swear by the HP USB Formatting Tool to bully write protected external disks into cooperating.
It’s also one of the few utilities that lets you format large disks into FAT32 format, something that’s necessary from time to time. Bear in mind that you need to run this app with administrator privileges for it to work. Results are reportedly mixed, but the following solutions are a little more complex, so if you want to take a chance with a formatting utility app first this is one option.
Remove Write Protection With DiskPart
DiskPart is a powerful command line utility in Windows that can remove attributes from entire disks or specific partitions.
- First, insert the USB drive that is write protected, if applicable.
- Open the Start Menu and type diskpart.

- Select the diskpart run command from the results.
- If you’re asked for administrator permissions, say yes.

- At the command line for DiskPart, type list disk and press Enter.

- Look for your USB disk in the list of drives, make a note of its disk number. You’ll need it shortly!
- Now, type select disk #, but replace the # with the correct disk number. Then press Enter.

- Type attributes disk clear readonly and then press the Enter key.

- After receiving the confirmation message, type Exit and press Enter.
Remove Write Protection with Regedit
Sometimes a drive is marked as write protected and you’ll get the “Media is Write Protected” error because the corresponding value in the Windows registry is incorrect. If possible, avoid messing around in your registry. If this is your last resort, please consider backing up your registry in case something goes wrong.
With that being said, here’s how to remove write protection from a USB drive in Windows:
- Insert the drive you want to modify into a USB port.
- Open the Start Menu and type Registry Editor.

- Select Registry Editor from the results.

- In the registry editor, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > StorageDevicePolicies.
- Double-click WriteProtect. This will open the Edit DWORD window.
- Look for the Value data box, then enter 0 as the new value.

- Select OK and close the registry editor.
- Restart your computer and check the disk again.
What if there is no StorageDevicePolicies value to change?
Creating StorageDevicePolicies
If you’re unlucky enough not to have the right registry value to change, you’re just going to have to make it yourself. Don’t worry, you’ve got this.
- Open the Registry Editor as detailed above.
- Navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control.
- Right-click in an empty area of the right-hand pane and select New > Key.
- Name the new key StorageDevicePolicies and press Enter to confirm.

- Select StorageDevicePolicies.
- Again, right-click in the empty space of the right hand pane and select New > DWORD(32-bit) Value.
- Name the new DWORD value WriteProtect and press Enter to confirm.

- Double-click WriteProtect. This will open the Edit DWORD window.
- Look for the Value data box, then enter 0 as the new value.

- Select OK and close the registry editor.
- Restart your computer and check the disk again.
Phew! Hopefully this last resort will solved the “Media is Write Protected” issue in Windows for you!
















