无法安装 Windows 11 并出现此 PC 无法运行 Windows 11 错误?以下是如何启用 TPM 2.0 和 SecureBoot,以修复 PC 健康检查应用程序中的“此 PC 无法运行 Windows 11”错误。(Unable to install Windows 11 and getting This PC can’t run Windows 11 error? Here’s how to enable TPM 2.0 and SecureBoot, in order to fix the “This PC Can’t Run Windows 11” error in the PC Health Check application.)
微软(Microsoft)终于在几周前(2021 年 6 月(June 2021))宣布了对全球最常用的计算机操作系统Windows 10的期待已久的更新。正如预期的那样,Windows 11将引入许多新功能、原生应用程序和通用用户界面,将进行视觉设计大修、游戏改进、对Android应用程序的支持、小部件等。(Android)开始(Start)菜单、操作中心等元素, 并且Microsoft Store也已针对最新版本的Windows进行了全面改造。当前的(Current)Windows 10用户将被允许升级到 Windows 11在 2021 年底向公众提供最终版本时无需任何额外费用。

修复此 PC 无法运行 Windows 11 错误(Fix This PC can’t run Windows 11 Error)
如果您的 PC 无法运行 Windows 11(Run Windows 11)错误的修复步骤
Windows 11 的系统要求(System Requirements for Windows 11)
除了详细说明 Windows 11 将带来的所有变化外,微软(Microsoft)还透露了运行新操作系统的最低硬件要求。它们如下:
- 具有 1 Gigahertz(Gigahertz) ( GHz ) 或更高时钟速度和 2 个或更多内核的现代 64 位处理器(这里是能够运行Windows 11的(Windows 11)Intel、AMD和Qualcomm 处理器(Qualcomm processors)的完整列表。)
- 至少 4 GB 的 RAM
- 64 GB 或更大的存储设备(HDD或SSD,它们都可以工作)
- 最小分辨率为 1280 x 720 且大于 9 英寸(对角线)的显示器
- 系统固件必须支持UEFI和Secure Boot
- 可信平台模块(Platform Module)( TPM ) 2.0 版
- 显卡应(Card)与DirectX 12或更高版本的WDDM 2.0驱动程序兼容。
为了让事情变得更容易,并允许用户通过单击检查他们当前的系统是否与Windows 11兼容,(Windows 11)微软(Microsoft)还发布了PC 健康检查应用程序(PC Health Check application)。但是,该应用程序的下载链接不再在线,用户可以改为安装开源的WhyNotWin11工具。
许多能够使用Health Check应用程序的用户报告说在运行检查时收到“此 PC 无法运行 Windows 11”弹出消息。弹出消息还提供了有关 Windows 11 无法在系统上运行的更多信息,原因包括 - 不支持处理器、存储空间小于 64GB、不支持/禁用TPM和安全启动。(Secure Boot)虽然解决前两个问题需要更改硬件组件,但TPM和安全启动(Secure Boot)问题可以很容易地解决。

方法 1:如何从BIOS启用(BIOS)TPM 2.0
受信任的平台模块(Trusted Platform Module)或TPM是一种安全芯片(加密处理器),它通过安全地存储加密密钥为现代Windows计算机提供基于硬件的安全相关功能。TPM芯片包含多种物理安全机制,使黑客、恶意应用程序和病毒难以更改它们。Microsoft强制要求在 2016 年后生产的所有系统中使用TPM 2.0(TPM芯片的最新版本。之前的称为TPM 1.2)。因此,如果您的计算机不是过时的,则安全芯片很可能已预先焊接到您的主板上,但只是被禁用了。
此外,为了运行Windows 11需要(Windows 11)TPM 2.0让大多数用户感到意外。早些时候,微软(Microsoft)将 TPM 1.2 列为最低硬件要求,但后来将其更改为TPM 2.0。
TPM安全技术可以从BIOS菜单进行管理,但在启动之前,让我们确保您的系统配备了与Windows 11兼容的TPM。去做这个 -
1. 右键单击开始菜单(Start menu)按钮并从高级用户菜单中选择运行。(Run )

2.在文本字段中输入tpm.msc并单击 OK 按钮。

3. 耐心等待(Wait)本地计算机(Local Computer)上的TPM管理(TPM Management)应用程序启动,检查状态(Status )和规范版本( Specification version)。如果“状态”(Status)部分反映“ TPM已准备好使用”且版本为 2.0,则Windows 11运行状况(Windows 11)检查(Health Check)应用程序可能是此处出现问题的应用程序。微软(Microsoft)自己已经解决了这个问题并删除了该应用程序。稍后将发布健康检查(Health Check)应用程序的改进版本。

另请阅读:(Also Read:) 在 Windows 10 中启用或禁用安全登录(Enable or Disable Secure Login in Windows 10)
但是,如果状态(Status)指示TPM已关闭或无法找到,请按照以下步骤启用它:
1. 如前所述,TPM只能从BIOS/UEFI菜单启用,因此首先关闭所有活动的应用程序窗口,然后在桌面上按Alt + F4 从选择菜单中选择关闭(Shut Down ),然后单击确定。
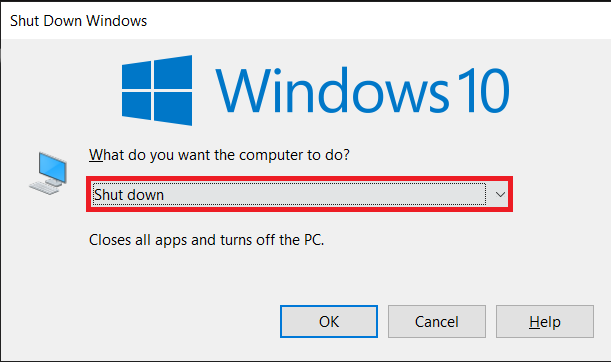
2. 现在,重新启动计算机并按BIOS键进入菜单。每个制造商的BIOS 密钥( BIOS key)都是唯一的,可以通过执行快速Google搜索或阅读用户手册来找到。最常见的BIOS键是 F1、F2、F10、F11或Del。
3. 进入BIOS菜单后,找到安全(Security )选项卡/页面并使用键盘箭头键切换到它。对于某些用户,可以在高级设置下找到(Advanced Settings)安全(Security)选项。
4. 接下来,找到TPM 设置(TPM settings)。确切的标签可能会有所不同;例如,在某些配备 Intel 的系统上,它可能是“ PTT ”、“Intel Trusted Platform Technology”,或者只是AMD机器上的“TPM Security”和“fTPM”。
5. 将TPM 设备( TPM Device)状态设置为可用(Available ),将TPM 状态(TPM State)设置为已启用(Enabled)。(确保(Make)你没有弄乱任何其他与 TPM 相关的设置。)

6.保存(Save )新的TPM设置并重新启动计算机。再次运行Windows 11检查以确认您是否能够修复此 PC 无法运行Windows 11错误。
方法 2:启用安全启动(Method 2: Enable Secure Boot)
顾名思义,安全启动(Secure Boot)是一种安全功能,只允许受信任的软件和操作系统启动。传统的BIOS(traditional BIOS)或传统引导将加载引导加载程序而不执行任何检查,而现代UEFI引导技术存储官方Microsoft证书并在加载前交叉检查所有内容。这可以防止恶意软件干扰启动过程,从而提高总体安全性。(已知安全启动会在启动某些Linux发行版和其他不兼容的软件时引起问题。)
要检查您的计算机是否支持安全启动(Secure Boot)技术,请在“运行命令(Run Command)”框中键入msinfo32 ( Windows徽标键 + R),然后按 Enter。

检查安全启动状态( Secure Boot State)标签。
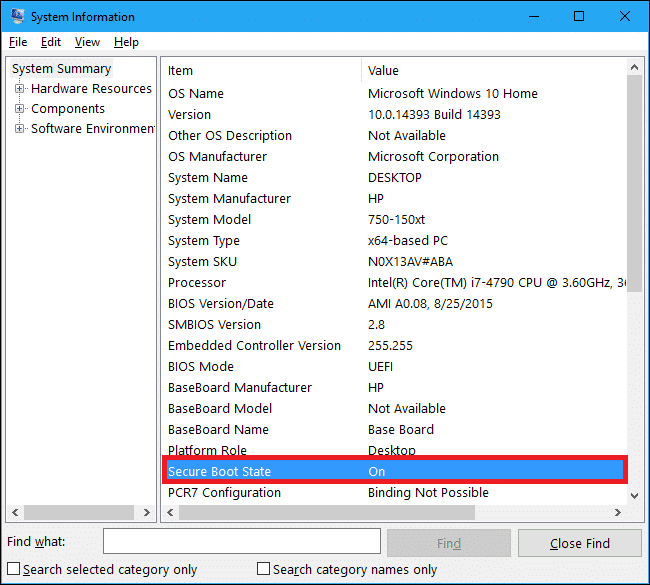
如果它显示“不支持”,您将无法安装Windows 11(没有任何技巧);另一方面,如果显示为“关闭”,请按照以下步骤操作。
1. 与TPM类似,可以从BIOS/UEFI菜单中启用安全启动。(Secure Boot)按照(Follow)之前方法的步骤1和2进入BIOS菜单(enter the BIOS menu)。
2. 切换到Boot选项卡并使用箭头键启用 Secure Boot 。(enable Secure Boot )
对于某些人来说,可以在“高级(Advanced)”或“安全(Security)”菜单中找到启用安全启动的选项。(Secure Boot)启用Secure Boot后,将出现要求确认的消息。选择接受(Choose Accept)或是继续。

注意:(Note:)如果Secure Boot选项灰显,请确保Boot Mode设置为UEFI而不是Legacy。
3.保存(Save )修改并退出。您不应再收到“此 PC 无法运行 Windows 11”错误消息。
受到推崇的:(Recommended:)
(Microsoft)为了运行Windows 11 ,微软理所当然地通过TPM 2.0和安全启动(Secure Boot)的要求来提高安全性。无论如何(Anyway),如果您当前的计算机不满足Windows 11的最低系统要求,请不要担心,因为一旦操作系统的最终版本发布,肯定会找到解决不兼容问题的方法。您可以放心,只要这些变通办法可用,我们就会与其他几个Windows 11指南一起介绍这些变通办法。
Fix This PC can't run Windows 11 Error
Unable to install Windows 11 and getting This PC can’t run Windows 11 error? Here’s how to enable TPM 2.0 and SecureBoot, in order to fix the “This PC Can’t Run Windows 11” error in the PC Health Check application.
The long-awaited update to Windows 10, the most used computer operating system across the world, was finally announced by Microsoft a couple of weeks ago (June 2021). As expected, Windows 11 will introduce a host of new features, the native applications, and the general user interface will receive a visual design overhaul, gaming improvements, support for Android applications, widgets, etc. Elements such as the Start menu, action center, and the Microsoft Store have also been completely revamped for the latest version of Windows. Current Windows 10 users will be allowed to upgrade to Windows 11 without any additional cost at the end of 2021, when the final version is made available to the public.

Fix This PC can’t run Windows 11 Error
Steps to Fix if Your PC Can’t Run Windows 11 error
System Requirements for Windows 11
Along with detailing all the changes that Windows 11 will bring forth, Microsoft also revealed the minimum hardware requirements to run the new OS. They are as follows:
- A modern 64-bit processor with a clock speed of 1 Gigahertz (GHz) or higher and 2 or more cores (Here is a complete list of Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm processors that will be able to run Windows 11.)
- At least 4 gigabytes (GB) of RAM
- 64 GB or larger storage device (HDD or SSD, either of them will work)
- A display with a minimum resolution of 1280 x 720 and larger than 9-inch (diagonally)
- The system firmware must support UEFI and Secure Boot
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0
- Graphics Card should be compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.0 driver.
To make things easier and allow users to check whether their current systems are compatible with Windows 11 by the press of a single click, Microsoft also released the PC Health Check application. However, the download link for the application is no longer online, and users can instead install the open-source WhyNotWin11 tool.
Many users who were able to get their hands on the Health Check app have reported receiving a “This PC can’t run Windows 11” pop-up message upon running the check. The pop-up message also provides more information on why Windows 11 can’t be run on a system, and the reasons include – processor is not supported, storage space is lesser than 64GB, TPM and Secure Boot are not supported/disabled. While resolving the first two issues will require changing hardware components, the TPM and Secure Boot issues can be resolved quite easily.

Method 1: How to Enable TPM 2.0 from BIOS
A Trusted Platform Module or TPM is a security chip (cryptoprocessor) that provides hardware-based, security-related functions to modern Windows computers by securely storing encryption keys. TPM chips include multiple physical security mechanisms making it difficult for hackers, malicious applications, and viruses to alter them. Microsoft mandated the use of TPM 2.0 (the latest version of TPM chips. The previous one was called TPM 1.2) for all systems manufactured post-2016. So if your computer isn’t archaic, it is likely that the security chip is pre-soldered onto your motherboard but is simply disabled.
Also, the requirement of a TPM 2.0 in order to run Windows 11 caught most users by surprise. Earlier, Microsoft had listed TPM 1.2 as the minimum hardware requirement but later changed it to TPM 2.0.
The TPM security technology can be managed from the BIOS menu but before booting into it, let’s ensure your system is equipped with a Windows 11 compatible TPM. To do this –
1. Right-click on the Start menu button and select Run from the power user menu.

2. Type tpm.msc in the text field and click on the OK button.

3. Wait patiently for the TPM Management on Local Computer application to launch, check Status and the Specification version. If the Status section reflects ‘The TPM is ready for use’ and the version is 2.0, the Windows 11 Health Check app might be the one at fault here. Microsoft themselves have addressed this issue and have taken down the application. An improved version of the Health Check app will be released later.

Also Read: Enable or Disable Secure Login in Windows 10
However, if the Status indicates that the TPM is off or cannot be found, follow the below steps to enable it:
1. As mentioned earlier, TPM can only be enabled from the BIOS/UEFI menu, so start by closing down all the active application windows and press Alt + F4 once you are on the desktop. Choose Shut Down from the selection menu and click on OK.

2. Now, restart your computer and press the BIOS key to enter the menu. The BIOS key is unique for each manufacturer and can be found by performing a quick Google search or by reading the user manual. The most common BIOS keys are F1, F2, F10, F11, or Del.
3. Once you have entered the BIOS menu, find the Security tab/page and switch to it using the keyboard arrow keys. For some users, the Security option will be found under Advanced Settings.
4. Next, locate the TPM settings. The exact label may vary; for example, on some Intel-equipped systems, it might be “PTT,” “Intel Trusted Platform Technology,” or simply “TPM Security” and “fTPM” on AMD machines.
5. Set the TPM Device status to Available and TPM State to Enabled. (Make sure you do not mess with any other TPM-related setting.)

6. Save the new TPM settings and reboot your computer. Run the Windows 11 check again to confirm if you’re able to fix This PC can’t run Windows 11 error.
Method 2: Enable Secure Boot
Secure Boot, as the name suggests, is a security feature that only allows trusted software and operating systems to boot. The traditional BIOS or the legacy boot would load the bootloader without performing any checks, while the modern UEFI boot technology stores official Microsoft certificates and cross-checks everything before loading. This prevents malware from messing with the boot process and, thus, results in improved general security. (Secure boot is known to cause issues when booting certain Linux distributions and other incompatible software.)
To check whether your computer supports the Secure Boot technology, type msinfo32 in the Run Command box (Windows logo key + R) and hit enter.

Check the Secure Boot State label.

If it reads ‘Unsupported,’ you won’t be able to install Windows 11 (without any trickery); on the other hand, if it reads ‘Off,’ follow the below steps.
1. Similar to TPM, Secure Boot can be enabled from within the BIOS/UEFI menu. Follow steps 1 and 2 of the previous method to enter the BIOS menu.
2. Switch to the Boot tab and enable Secure Boot using the arrow keys.
For some, the option to enable Secure Boot will be found inside the Advanced or Security menu. Once you enable Secure Boot, a message requesting confirmation will appear. Choose Accept or Yes to continue.

Note: If the Secure Boot option is greyed out, ensure the Boot Mode is set to UEFI and not Legacy.
3. Save the modification and exit. You should no longer receive the “This PC can’t run Windows 11” error message.
Recommended:
Microsoft is rightfully doubling down on security with the requirement of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot in order to run Windows 11. Anyway, fret not if your current computer does not meet the minimum system requirements for Windows 11, as workarounds to incompatibility issues are sure to be figured out once the final build for the OS is released. You can rest assured that we will be covering those workarounds whenever they are available, along with several other Windows 11 guides.










