浏览互联网时,您经常会遇到“cookies”一词。("cookies.")许多网站会告知您有关使用 cookie 的信息,并征求您的同意。Web 浏览器有许多用于管理 cookie 的设置,甚至浏览器插件也提到阻止各种 cookie。即使您知道这些“饼干”("cookies")并不完全是甜点,但您可能并不确切地知道它们是什么以及它们在互联网上的目的是什么。这就是为什么在本文中,我们将解释什么是 cookie、它们的作用和工作方式,以及互联网上最常使用的 cookie 类型。让我们开始吧:
什么是互联网上的 cookie?
Cookie 是保存有关您、您的网络浏览器和您在互联网上的行为的信息的文件。它们是存储在您的PC 或设备(PC or device)上的小文件,可供网站或 Web 应用程序使用,以定制您的在线体验。
饼干有什么作用?
Cookie 在发送者(通常是网站或网络应用程序)和接收者(您的设备)之间发送。cookie 由发送者创建和解释,而接收者只保留它并在发送者请求时将其发回。
浏览网页时,发送者是运行网站的服务器,接收者是访问该网站的用户的网络浏览器。他们的目的是识别用户,检查他或她过去在网站上的活动,并根据这些数据提供适当的内容。

用户第一次访问网站时,服务器会在该用户的网络浏览器(web browser)中存储一个特定的 cookie 。在随后访问该网站时,服务器会请求其 cookie,读取它并为该特定用户加载网站的特定配置。您可以将 cookie 视为 Web 服务器应用于每个用户的标签,Web 服务器读取该标签以识别用户。
这种识别对于实时用户数据至关重要的网站非常有用。例如,在使用在线商店(online shop)时,如果没有 cookie 的帮助,您将无法购买任何东西。没有它们,商店将无法识别您并构建您的购物车,因为每次您加载网页时,商店都会将您视为新用户并从头开始您的访问。
饼干里面是什么?
每个现代网络浏览器(web browser)都支持 cookie,它们的大小很小,大约 4 KB。为了帮助您了解 cookie 的结构,我们以我们网站 - Digital Citizen发送的(Digital Citizen)“cfduid” cookie 为例。我们使用Google Chrome对其进行了分析。
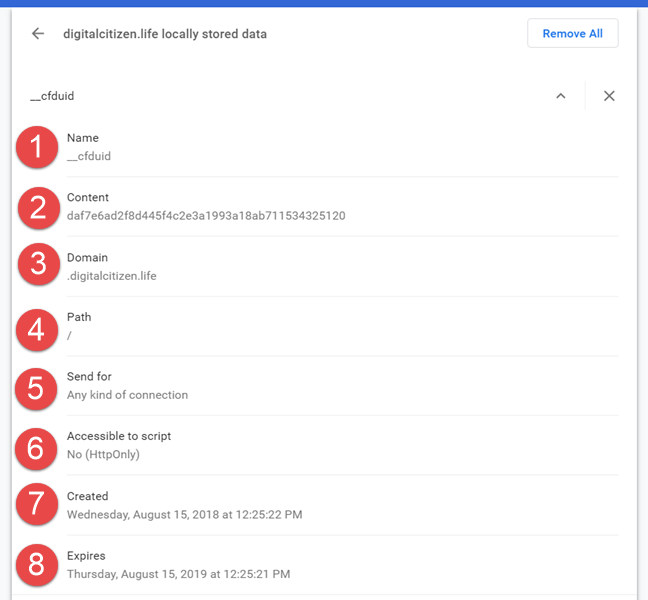
这是它的结构:
- 名称(Name)- cookie 的名称。
- 内容(Content)- cookie 包含的信息。
- 域(Domain)- 使用此 cookie 的域。
- 路径(Path)- 使用 cookie 的域的页面。如果路径是“/”,则表示整个网站都使用 cookie。
- 发送(Send for)- 连接使用 cookie 所需的安全级别。
- 可访问脚本(Accessible to script)- 它显示是否可以通过HTML以外的其他方式访问 cookie 。
- Created - 在用户的(Created)网络浏览器(web browser)上创建 cookie 的日期。
- 过期(Expires)- cookie 过期并且浏览器将其删除的时刻。
cookie 有多少种类型?
尽管cookie(term cookie)一词相当笼统,但 cookie 的使用方式有很多种。这就是为什么互联网上有不同类型的 cookie。最常见的类型如下:
- 会话 cookie(Session cookies) - 最常见的一种。它们存在于临时内存中,直到Web 浏览器(web browser)关闭。它们无害,因为当您的浏览会话(browsing session)结束时,它们的所有信息都会被删除。
- 持久性 cookie(Persistent cookies) - 也称为跟踪 cookie。它们会在用户的设备上持续存在,直到它们被删除或到期(expiry date)。它们用于收集有关用户的信息,记录他或她在特定网站上一段时间内的行为。
- 安全 cookie(Secure cookies) - 仅在使用安全HTTPS 连接(HTTPS connection)时才有效的加密 cookie 。这些 cookie 用于确保其信息不会被与用户连接到同一网络的潜在黑客窃取。它们保留有关用户的基本信息,主要用于用户进行金融交易的网站。因为它们是加密的,所以它们比其他类型的 cookie 安全得多。
- HttpOnly cookie(HttpOnly cookies) - 它们不能被HTTP以外的任何协议使用。此类 cookie 确保只有创建它们的网站才能使用它们。只有会话 cookie 可以是 HttpOnly,它们通常不会对用户造成任何隐私或安全风险(privacy or security risks)。
- 第三方 cookie(Third-party cookies) - 这些 cookie 属于不同的域,而不是发送它们的域。它们通常由广告发送,可以存储用户在使用同一广告网络(advertising network)的多个网站上的浏览历史记录。这些 cookie 可能会损害您的隐私,因为一些广告网络使用它们来跟踪太多关于您的数据,以显示有针对性的广告。
- Zombie cookie - 删除后重新创建的 cookie。它们通常由 Web 分析服务使用并存储在浏览器之外,因为它们可以跨安装在同一台计算机上的浏览器使用。他们重新创建自己的原因是为了防止用户删除 cookie 后数据变得碎片化。它们也可能被用于恶意目的,因为Web 浏览器(web browser)无法控制它们的存在。只有安全产品才能识别僵尸 cookie 并将其删除。
饼干是什么时候发明的(简明的历史(concise history))?
1994年7 月, (July 1994)Netscape Communications的一名员工不得不开发一个电子商务应用程序。他必须找到一种简单的方法来为每个用户保留购物车(shopping cart),而不会使服务器超载,因此他决定最好的方法是将这些信息存储在每个用户的Web 浏览器中。(web browser)由于 cookie 已经在IT 行业(IT industry)的不同领域中使用,他认为它们也可以用于网页浏览。
第一个使用和支持 cookie 的浏览器是1994年10 月的(October 1994)Mosaic Netscape。一年后,Internet Explorer 2也支持 cookie。从那时起,所有网络浏览器都提供了对 cookie 的支持。尽管创建它们的原因是积极的,但现在 cookie 被用于各种目的,其中一些是不道德或不合法的。
为什么我会在每个网站上看到有关 cookie 的消息?
如果您居住在欧洲(Europe),或者您正在使用欧洲(Europe)IP 地址(IP address)浏览网页,您会在您访问的许多网站上看到有关使用 cookie 的提示。显示这些提示是因为通用数据保护条例 (GDPR)(General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR))立法适用于所有组成欧盟(European union)的国家,以及所有拥有欧洲用户的网站和在线服务(website and online services)。
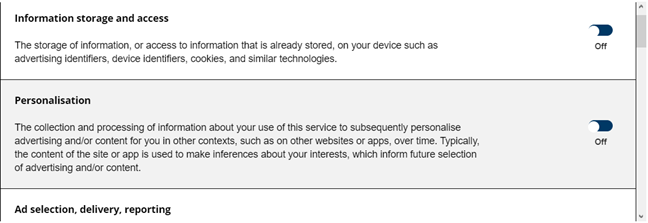
这些提示的目的是告知所有欧洲用户关于 cookie、它们的使用方式和原因,并征求他们的明确同意。我们建议您阅读这些提示并仅允许您可以使用的用途。
如何查看和管理网站存储在您的网络浏览器中的 cookie
如果您想知道如何查看和管理您的网络浏览器存储在您设备上的 cookie,我们提供了涵盖所有主要网络浏览器的指南。他们来了:
- 查看(和删除)存储在Google Chrome中的 cookie 的 2 种方法(Google Chrome)
- 如何查看和删除存储在Mozilla Firefox中的 cookie(Mozilla Firefox)
- 如何查看和删除存储在Microsoft Edge中的 cookie(Microsoft Edge)
- 查看和删除 Opera 中存储的 cookie 的 2 种方法
- 在Chrome(Chrome)、Firefox、Edge、Opera 和 Internet Explorer(Opera and Internet Explorer)中禁用第三方 cookie
结论
Cookies 在互联网上被广泛使用,因为它们通过向每个用户提供最有用的内容来让网站变得更加强大。在某些情况下,如果不使用 cookie,网站将无法运行。它们还允许网站了解他们的用户和他们正在访问的页面。但是,就像任何其他技术一样,它们也可以用于不道德的目的。这就是为什么了解 cookie 如何工作以及如何使用它们对于任何浏览网络的数字公民来说都是一项有用的技能。如果您对 cookie 有任何疑问,请随时在下方发表评论。
Simple questions: What are cookies and what do they do?
When browsing the internet, you often encounter the term "cookies." Many websites inform you about using cookies, and ask for your approval. Web browsers have many settings for managing cookies and even browser add-ons mention blocking cookies of all kinds. Even though you know that these "cookies" are not exactly a sweet dessert, you may not know precisely what they are and what their purpose is on the internet. This is why, in this article, we explain what cookies are, what they do and how they work, and what kind of cookies are most frequently used on the internet. Let's get started:
What are cookies on the internet?
Cookies are files that hold information about you, your web browser and your behavior on the internet. They are tiny files stored on your PC or device, which can be used by websites or web apps to tailor your online experience.
What do cookies do?
Cookies are sent between a sender (usually a website or a web app) and a receiver (your device). A cookie is created and interpreted by the sender, while the receiver only holds it and sends it back if the sender asks for it.
When browsing the web, the sender is the server on which a website runs, and the receiver is the web browser of the user who visits that website. Their purpose is to identify the user, check for his or her past activity on the website and provide appropriate content based on this data.

The first time a user visits a website, the server stores a particular cookie in the web browser of that user. On subsequent visits to the website, the server asks for its cookie, reads it and loads a particular configuration of the website for that specific user. You can think of cookies like a tag applied by web servers to every user, which is read by web servers to identify users.
This identification is beneficial on websites where real-time user data is critical. For example, when using an online shop, you cannot buy anything without the help of cookies. Shops would not be able to identify you and build your shopping cart without them because each time you load a web page, the shop would see you as a new user and start your visit from scratch.
What is inside of a cookie?
Every modern web browser supports cookies, and they have a small size, of roughly 4 KB. To help you understand the structure of a cookie, let's use as an example the "cfduid" cookie sent by our website - Digital Citizen. We analyzed it using Google Chrome.

Here is its structure:
- Name - the name of the cookie.
- Content - the information the cookie contains.
- Domain - the domain using this cookie.
- Path - the page of the domain where the cookie is used. If the path is "/" it means that the cookie is used across the whole website.
- Send for - the level of security the connection needs to have to use the cookie.
- Accessible to script - it shows whether or not the cookie can be accessed through other ways than HTML.
- Created - the date the cookie was created on the user's web browser.
- Expires - the moment when the cookie expires and the browser deletes it.
How many types of cookies are there?
Even though the term cookie is rather general, there are many ways a cookie can be used. This is why there are different types of cookies on the internet. The most common types are the following:
- Session cookies - one of the most common. They exist in temporary memory until the web browser is closed. They are not harmful because all their information is deleted when your browsing session is over.
- Persistent cookies - also called tracking cookies. They last on the user's device until they are deleted or reach their expiry date. They are used to gather information about the user, recording his or her behavior on a specific website over a period of time.
- Secure cookies - an encrypted cookie that works only when using a secure HTTPS connection. These cookies are used to ensure that their information cannot be stolen by potential hackers connected to the same network as the user. They keep essential information about the user and are used mostly on websites where users perform financial transactions. Because they are encrypted, they are a lot more secure than other types of cookies.
- HttpOnly cookies - they cannot be used by any protocol other than HTTP. Such cookies ensure that only the website that created them can use them. Only session cookies can be HttpOnly, and they generally do not imply any privacy or security risks for users.
- Third-party cookies - these cookies belong to a different domain, other than the one that sent them. They are usually sent by ads and can store the browsing history of a user across multiple websites that use the same advertising network. These cookies may hurt your privacy because some ad networks use them to track way too much data about you, to display targeted ads.
- Zombie cookie - cookies that recreate themselves after they are deleted. They are generally used by web analytics services and stored outside of the browser because they are available across browsers installed on the same computer. The reason they recreate themselves is to prevent data from becoming fragmented after the user deletes the cookies. They can also be used for malicious purposes because the web browser cannot control their existence. Only security products can identify zombie cookies and remove them.
When were cookies invented (a concise history)?
In July 1994, an employee at Netscape Communications had to develop an e-commerce application. He had to find an easy way to keep the shopping cart for every user, without overloading the server, so he decided that the best way to do this was to store this information in the web browser of every user. Because cookies were already used in different fields of the IT industry, he decided they could also be used for web browsing.
The first browser to use and support cookies was Mosaic Netscape, in October 1994. One year later, Internet Explorer 2 also supported cookies. Since then, all web browsers have offered support for cookies. Even though the reason why they were created is a positive one, cookies are now used for all kinds of purposes, some of which are not ethical or legal.
Why am I seeing messages about cookies on every website?
If you live in Europe, or you are browsing the web using a European IP address, you see prompts about the use of cookies on many websites that you visit. These prompts are shown because of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) legislation that is applied in all the countries that form the European union, and to all the website and online services that have European users.

The purpose of these prompts is to inform all European users about cookies, how they are used and why, and ask for their explicit consent. We recommend that you read these prompts and permit only the uses that you are OK with.
How to see and manage the cookies stored in your web browser by websites
If you want to know how to see and manage the cookies your web browser stores on your device, we have guides that cover all the major web browsers. Here they are:
Conclusion
Cookies are widely used on the internet because they allow websites to be more powerful by providing the most useful content to every user. In some cases, websites cannot function without using cookies. They also allow websites to learn about their users and the pages they are visiting. However, just like any other technology, they can also be used for unethical purposes. That is why knowing how cookies work and how they are used is a useful skill for any digital citizen browsing the web. If you have any questions about cookies, do not hesitate to leave a comment below.



