IP 地址(IP address)和子网掩码(subnet mask)是计算机网络的核心。它们不是易于整体理解的概念,尤其是在您没有技术背景的情况下。但是,只要稍加帮助,任何人都可以了解IP 地址(IP address)和子网掩码(subnet mask)的基础知识、它们的作用以及它们为何有用。如果您想知道IP 地址(IP address)是什么、互联网协议地址(internet protocol address)的用途是什么或子网掩码(subnet mask)是什么,请继续阅读。我们用简单的术语来解释这一切:
什么是IP 地址(IP address)?互联网协议地址(Internet Protocol address)的用途是什么?
为了帮助您理解 IP 地址是什么,简单来说,让我们使用现实生活中的类比:
你想给朋友写一封信。您已完成编写消息并想要发送它。为了让这封信到达目的地,您需要知道您朋友的地址——街道名称(street name)、号码和邮政编码(zip code)——并将其写在信上。否则,邮政服务不知道将您的信件投递到哪里。

将 IP 地址视为网络中计算机或设备的地址(Think of an IP address as the address of a computer or device inside a network)。IP 地址是网络设备的唯一标识符,用于与同一网络或 Internet 上的其他计算机或设备建立通信、发送和接收数据。
目前,IP(互联网协议(Internet Protocol))地址有两个相关标准:IP版本4(IPv4)(IP version 4 (IPv4))和IP版本6(IPv6)(IP version 6 (IPv6))。我们将在本指南的下两节中解释这些标准的含义,所以请耐心等待。🙂
您还应该知道IP 地址可以是静态的也可以是动态(an IP address can be either static or dynamic)的。静态IP 地址(IP address)是您需要通过Windows 网络(Windows network)设置自行配置的地址。动态地址由动态主机配置协议(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)( DHCP ) 分配,通常在有限的时间范围内(time frame)。DHCP是一种在网络中的专用服务器或专用网络硬件(network hardware)(例如无线路由器)上运行的服务。动态(Dynamic) IP地址(IP address)是最常用的,因为静态地址如果使用不慎会导致网络问题。静态IP 地址(IP address)es 也更难管理,因为它们需要人工干预来创建和管理,尤其是在更大的网络中,例如来自办公室或机构的网络。
因此,在典型的家庭网络(home network)或小型企业网络(business network)中,IP 地址由路由器通过DHCP自动分配和管理。
什么是Internet 协议版本 4(Internet Protocol Version 4) ( IPv4 ) 地址?
IP 版本 4 (IPv4)(IP version 4 (IPv4))是目前最常用的标准。IPv4使用 32 位地址,这将地址空间限制为 4.294.967.296 (2^32) 个可能的唯一地址。为了让大家容易理解,IPv4地址(IPv4 address)由四个用点分隔的十进制数字表示。这四个数字中的每一个都包含一到三位数字,每个数字的范围都可以从 0 到 255。例如,IPv4 地址(IPv4 address)可能如下所示:172.217.3.100。

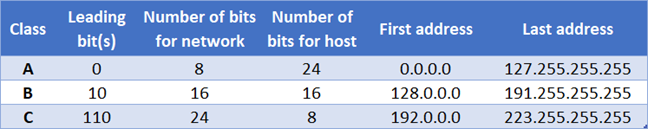
IPv4 地址(IPv4 address)分为三类,称为类。如下表所示,每个类之间的主要区别在于分配给网络和主机标识(network and host identification)的位数。此外,可以根据第一个整数的前导位的形式,从点十进制表示法来识别IPv4 地址来自的类别。(IPv4 address)比如上图中的IP地址就是(IP address)B类IP地址(B IP address),因为二进制形式的172(10101100)的前导位是1和0(10)(1 and 0 (10))。
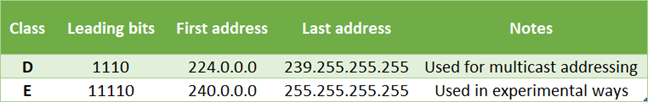
此外,还有用于特定操作的其他地址。如下表所示,D 类(class D)IPv4 地址用于多播寻址(multicast addressing)。在计算机网络中,多播(multicast)是指组通信(group communication),其中信息同时发送给一组目标计算机。例如,多播寻址(multicast addressing)用于互联网电视和多点视频会议(Internet television and multipoint video conferences)。E 类 IPv4(class E IPv4)地址不能在现实生活中使用,因为它们仅用于实验方式。
然而,由于世界上可能的 IP 地址组合已经用尽,IPv4目前正在逐步淘汰。因此,要添加更多网络设备,我们需要切换到IPv6,因为它允许我们使用更多的 IP 地址。
什么是Internet 协议版本 6(Internet Protocol Version 6) ( IPv6 ) 地址?
Internet 协议版本 6(Internet Protocol version 6)或IPv6于 1995 年创建,以取代IPv4地址。IP 版本 6 (IPv6)(IP version 6 (IPv6))是一个尚未广泛实施的标准,但一旦所有IPv4地址用完,就会实施。IPv6地址由用冒号分隔的八位数字组组成。与IPv4地址不同,这些地址还可以包含从a到f的字母,因此IPv6 地址(IPv6 address)可能看起来像这样:2a00:1450:400d:0802:0000:0000:0000:200e。作为与IPv4的比较(IPv4),这个标准可以管理2^128个地址。地址的最大数量是一个 39 位的大数字,这应该可以满足我们未来几十年对 IP 地址的需求。

正如您在上图中所见,IPv6地址的管理非常具有挑战性。因此,有一些规则可以简化您编写这些地址的方式。如果一个或多个组为“0000”,则可以省略零并用两个冒号 (::) 替换,也可以省略组开头的零。此外,与IPv4相比,IPv6地址没有分类。
注意:(NOTE:)如果您想了解您的计算机或设备的(computer or device)IP 地址(IP address)或了解如何更改它,请阅读:
- 在Windows中查找(Windows)IP 地址(IP address)的8 种方法(所有版本)
- 在Windows 10中更改IP 地址的 3 种方法(IP address)
什么是子网掩码(subnet mask)?子网掩码(subnet mask)有什么用?
子网掩码(subnet mask)是一种划分IP网络(IP network)的方法。您可以将其视为您的电话号码的(phone number)区号(area code)。简单来说,网络中使用子网掩码(subnet mask)将它们分成两个或多个子网,使它们更易于管理。在家庭网络和小型企业网络中,您的所有网络计算机和设备通常都在同一个子网上,因此位于同一子网上的所有计算机或设备都具有相同的子网掩码(subnet mask)。
为了更专业一点,子网掩码(subnet mask)是一个 32 位数字,用于掩蔽IP 地址(IP address)并将IP 地址(IP address)分为网络地址和主机地址(network address and host address)。通过将网络位设置为全“1”并将主机位设置为全“0”来生成子网掩码。(subnet mask)
子网掩码(subnet mask)可以用两种方式表示:一种是通常的点十进制表示法,如IP地址(IP address),第二种是使用CIDR 表示法(CIDR notation)。

在CIDR 表示法(CIDR notation)中,子网掩码(subnet mask)被指定为网络的第一个IP 地址(IP address),后跟斜线字符 (/) 和子网前缀(subnet prefix)的位长度。例如,不要写像 192.168.1.0 这样的IP 地址和像 255.255.255.0 这样的(IP address)子网掩码(subnet mask),您可以只写地址,后跟一个斜线和前缀的位长,即位数“1 " 来自子网掩码(subnet mask)的二进制形式:192.168.1.0/24。不幸的是,计算子网前缀长度(subnet prefix length)并不容易,因此如果您想或必须这样做,我们建议您使用在线IP Subnet Calculator等工具。

子网掩码(subnet mask)用于子网划分过程(subnetting process),该过程涉及将网络划分为称为子网的较小部分。众所周知,一个IP地址(IP address)分为两部分,一是网络识别(network identification),一是主机识别(host identification)。使用子网掩码(subnet mask),将主网络划分为一个或多个较小的网络。这是通过IP 地址(IP address)和(子)网络掩码(network mask)之间的按位与运算(bitwise AND operation)来执行的。简单来说,这意味着主机号(host number)中的一部分位用于新的(子)网络标识(network identification)。

如果您想了解如何更改Windows 10(Windows 10)电脑以及本地家庭网络中的所有计算机和设备的(home network)子网掩码(subnet mask),请阅读本指南:在Windows 10中更改子网掩码(Subnet Mask)的 4 种方法。
什么是 DNS、网关、WINS?
我们确实意识到这个主题有点技术性,尽管我们试图尽可能地使用简单的术语,所以这里有一个简短而友好的版本来说明所有这些互补概念的含义。如果您知道它们的含义会更好,因为要了解IP 地址(IP address)的工作原理,您还需要了解这些额外的主题,这些主题共同作用以实现我们的网络计算机和设备之间的通信。
因此,事不宜迟,以下是对它们的简短描述:
- 网关(Gateway)- 网关通常是位于网络上的路由器,充当另一个网络和互联网的接入点。(access point)例如,您的Internet 服务提供商(Internet Service Provider)有一个或多个网关服务器,您的计算机使用这些网关服务器连接到 Internet。在大型商业环境中,网关还用于连接公司拥有的不同子网/网络。
- DNS 服务器(DNS Server)- 它代表域名系统(Domain Name System),它是用于将易于记忆的地址(例如 www.digitalcitizen.life)与其IP 地址(IP address)相匹配的互联网连接设备和计算机的命名系统。如果您的DNS 服务器(DNS server)不工作,那么您将无法使用传统的网站地址浏览网页。DNS 服务器(DNS Server)通常由您的Internet服务提供商提供(Internet Service Provider)。您可以在此处找到更详细的说明:什么是DNS?有(How)什么用?。但是(How),您也可以自行更改DNS 服务器(DNS server)。通过 3 种更改DNS(DNS)的方式了解更多信息Windows 10中的设置和什么是第三方DNS 服务器(DNS server)?使用公共DNS 服务器(DNS server)的8 个理由
- WINS 服务器(WINS Server)- 它代表Windows Internet 名称服务(Windows Internet Name Service),它是一种过时的命名系统类型,用于旧计算机和Microsoft操作系统,如Windows 98或Windows 2000。它用于将 IP 地址动态映射到计算机名称。但是,DNS服务器现在用于此任务,因为它们性能更好。
您对 IP 地址或子网掩码有任何疑问吗?
现在您对 IP 地址和子网掩码有了基本的了解,您应该能够非常轻松地正确配置Windows设备的网络设置。您对 IP 地址或子网掩码还有其他问题吗?在下面的评论中提问(Ask),我们将尽力提供帮助。
What is an IP address and a subnet mask, in simple terms?
IP addresses and subnet masks stand at the core of computer networking. They are not сoncepts that are easy to understand in their entiretу, especially if you do not have a technical bаckground. However, with a bit of help, anybody can understand the basics of IP addreѕses and ѕubnet masks, what they do, and why they are useful. If you want to know what аn IP address is, what's the purpose of an internet protocоl аddresѕ, or what's a subnet mask, read on. We're explaining it all in simple terms:
What is an IP address? What is the purpose of an Internet Protocol address?
To help you understand what IP addresses are, in simple terms, let's use an analogy from real life:
You want to send a written letter to a friend. You are done writing the message and want to send it. For the letter to reach its destination, you need to know your friend's address - street name, number, and zip code - and write it on the letter. Otherwise, the postal service doesn't know where to deliver your letter.

Think of an IP address as the address of a computer or device inside a network. The IP addresses are the unique identifiers of network devices used to establish communication, send, and receive data to or from other computers or devices in the same network or on the internet.
At present, there are two relevant standards for IP (Internet Protocol) addresses: IP version 4 (IPv4) and IP version 6 (IPv6). We are going to explain what these standards mean in the next two sections of this guide, so bear with us for a little longer. 🙂
You should also know that an IP address can be either static or dynamic. A static IP address is one that you need to configure yourself through the Windows network settings. A dynamic address is assigned by the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), usually for a limited time frame. DHCP is a service that runs on dedicated servers in your network or on specialized network hardware, such as wireless routers. Dynamic IP addresses are the most used since static addresses can cause network problems if used carelessly. Static IP addresses are also harder to manage, as they require manual intervention to create and manage, especially in larger networks such as those from offices or institutions.
Thus, in a typical home network or a small business network, IP addresses are assigned and managed automatically by the router via DHCP.
What is an Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) address?
IP version 4 (IPv4) is the most used standard right now. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, which limits the address space to 4.294.967.296 (2^32) possible unique addresses. So that everyone can easily understand them, IPv4 addresses are represented by four decimal numbers separated by dots. Each of these four numbers contains one to three digits, and each of them can range from 0 to 255. For example, an IPv4 address could look like this: 172.217.3.100.

IPv4 addresses are divided into three categories, called classes. As you can see in the table below, the main difference between each class is the number of bits allocated for network and host identification. Also, the class from which an IPv4 address comes can be identified according to the form of the leading bits of the first integer, from dot-decimal notation. For example, the IP address in the picture above is a class B IP address because the leading bits of the binary form of 172 (10101100) are 1 and 0 (10).

Also, there are other addresses used for particular actions. As you can see in the table below, the class D IPv4 addresses are used for multicast addressing. In computer networking, multicast refers to group communication where information is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. For example, multicast addressing is used in Internet television and multipoint video conferences. The class E IPv4 addresses cannot be used in real life because they are only used in experimental ways.

However, because the world is running out of possible combinations for IP addresses, IPv4 is currently being phased out. Therefore, to add more network devices, we need to switch to IPv6 because it allows us to use a lot more IP addresses.
What is an Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) address?
Internet Protocol version 6 or IPv6 was created in 1995 to replace IPv4 addresses. IP version 6 (IPv6) is a standard that is not yet widely implemented but will be once all the IPv4 addresses run out. IPv6 addresses are made up of eight-digit groups separated by colons. Unlike the IPv4 addresses, these can also contain letters from a to f, so an IPv6 address could well look like this: 2a00:1450:400d:0802:0000:0000:0000:200e. As a comparison to IPv4, this standard can manage 2^128 addresses. The maximum number of addresses is a massive number with 39 digits, and that should satisfy our needs for IP addresses for the next couple of decades.

As you can see in the picture above, the IPv6 addresses are quite challenging to manage. So, there are some rules that simplify the way you write these addresses. If one or more groups are "0000", the zeros may be omitted and replaced with two colons (::) and the zeros from the beginning of a group can also be omitted. Also, in contrast to IPv4, the IPv6 addresses are not divided into classes.
NOTE: If you want to find out the IP address of your computer or device or learn how to change it, read:
What is a subnet mask? What is a subnet mask used for?
A subnet mask is a way to divide an IP network. You can think of it as the area code of your phone number. In simple terms, subnet masks are used in networks to split them into two or more subnetworks, making them easier to manage. On home networks and small business networks, all your network computers and devices are usually on the same subnet, so all the computers or devices located on the same subnet have the same subnet mask.
To get a little more technical, a subnet mask is a 32-bit number that masks an IP address and divides the IP address into a network address and host address. The subnet mask is made by setting network bits to all "1" and setting host bits to all "0".
The subnet mask can be represented in two ways: one is the usual dot-decimal notation like an IP address, and the second is using the CIDR notation.

In CIDR notation, a subnet mask is specified as the first IP address of a network, followed by a slash character (/) and the bit-length of the subnet prefix. For example, instead of writing the IP address like 192.168.1.0 and the subnet mask like 255.255.255.0, you could write only the address, followed by a slash and the bit-length of the prefix, which is the number of bits "1" from the binary form of the subnet mask: 192.168.1.0/24. Unfortunately, it is not easy to calculate the subnet prefix length, so if you want or have to do it, we recommend you to use tools such as this online IP Subnet Calculator.

The subnet mask is used in the subnetting process, which involves dividing the network into smaller portions called subnets. As you know, an IP address is divided into two parts, one for network identification and one for host identification. Using the subnet mask, the main network is divided into one or more smaller networks. This is performed by a bitwise AND operation between the IP address and the (sub)network mask. In simple terms, this means that a part of the bits from the host number is used for the new (sub)network identification.

If you want to learn how to change the subnet mask on your Windows 10 PCs, as well as for all the computers and devices in your local home network, read this guide: 4 ways to change the Subnet Mask in Windows 10.
What are DNS, Gateway, WINS?
We do realize this topic is a bit more technical, although we're trying to use simple terms as much as possible, so here is a short and friendly version of what all of these complementary notions mean. It is better if you know what they mean because, to understand how an IP address works, you also need to understand these additional topics that work together to enable the communication between our network computers and devices.
So, without further ado, here is a short description of them:
- Gateway - a gateway is usually a router located on the network that acts as an access point to another network and the internet. For example, your Internet Service Provider has one or multiple gateway servers that your computer uses to connect to the internet. In large business environments, gateways are also used to connect the different subnets/networks that are owned by the company.
- DNS Server - it stands for Domain Name System, and it is a naming system for internet-connected devices and computers that matches easily-memorizable addresses, such as www.digitalcitizen.life to their IP address. If your DNS server is not working, then you are not able to browse the web using traditional website addresses. The DNS Server is usually provided by your Internet Service Provider. You can find a more detailed explanation here: What is DNS? How is it useful?. However, you can also change the DNS servers on your own. Find out more about it in 3 ways to change the DNS settings in Windows 10 and What is a third party DNS server? 8 reasons to use public DNS servers.
- WINS Server - it stands for Windows Internet Name Service, and it is an outdated type of naming system that was used on older computers and Microsoft operating systems, like Windows 98 or Windows 2000. It was used to map IP addresses to computer names dynamically. However, DNS servers are now used for this task as they perform better.
Do you have any questions regarding IP addresses or subnet masks?
Now that you have a basic understanding of what IP addresses and subnet masks are, you should be able to correctly configure the network settings of your Windows devices quite easily. Do you have any other questions about IP addresses or subnet masks? Ask away in the comments below, and we will do our best to help.








